BIO 225: Arthropods
1/137
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
138 Terms
4 General characteristics of arthropods
Defining Characteristic
Diverse?
Symmetry?
Protostomes or Deuterostomes
Jointed foot
Great diversity
Bilateral symmetry
Protostomes
What 4 main factors make arthropods so diverse and abundant?
Versatile exoskeleton
Efficient locomotion
Open circulatory system
Great sensory system
What is the Arthropods way of distributing blood throughout their body?
Diffusion
Phylum Arthropoda: General outline of Phylum, subphyla, classes, and orders
Phylum Arthropoda
Subphylum Trilobita
Subphylum Chelicerata
Class Arachidna
Orders: Spiders, harvestmen, ticks and mites
Subphylum Myriapoda
Class Chilopoda
Class Diplopoda
Subphylum Crustacea
Subphylum Hexapoda
Class Insecta
Orders: Lepidoptera, Hemiptera, Odoanata, Ceoeloptera, Hymenoptera, Orthoptera, Diptera
Phylum Arthropoda 5 subphyla
Trilobita, Chelicerata, Myriapoda, Crustacea, Hexapoda
Subphylum Trilobita 3 general characteristics:
Extinct
Found in ocean as fossils
Chiton-like
What (externally) separates Trilobites from Polyplacophorans?
Trilobites have antennae, more than 8 plaques, and legs
Subphylum Chelicerata general characteristics
Antennae?
Appendages?
Organism covered?
No antennae
6 pairs of appendages
1st pair chelicerae (fangs)
2nd pair Pedipalps (grasping and sensing)
8 walking legs
Horseshoe crab
Do Chelicerata have antennae?
No
What types of appendages do Chelicerata have? How many pairs?
They have 6 pairs of appendages. The 1st pair are the Chelicerae (fangs), the 2nd pair are the Pedipalps (mating), and the rest are their 8 walking legs.
What subphylum would the Horseshow crab be found in?
Subphylum Chelicerae
What medically beneficial thing do Horseshoe crabs offer?
Their blood
What does Horseshoe crab blood do? What is it used for?
Contains endotoxins from bacteria, allowing it to kill bacteria, and serves sterilizes small pieces of bacteria; Used to sterilize medical equipment and products.
Subphylum Chelicerata, Class Arachnida organism covered
Spiders
What is the subphylum for spiders? What is the class?
Subphylum Chelicerata, Class Arachnida
Spider internal structure
Cephalothorax (1st segment)
Abdomen (2nd segment)
Simple eyes (detect motion)
Compound eyes (detects shape)
Pumping stomach (feeds on liquids)
Silk gland (silk)
What are the two major body segments in spiders?
Cephalothorax
Abdomen
2 kinds of Spider eyes and what they detect
Simple eyes (motion)
Compound eyes (shape)
What kind of stomach do spiders have? What does it do
A pumping stomach; it pumps liquified food through the gut for digestion
Spider silk is used for what?
Used to coat surgical instruments, implants, and catheters.
Spiders use their silk for:
Webbing, egg sacs, and drag lines
What structure in spiders is important for reproduction?
Pedipalps
Reproduction in spiders
Male spiders transfer sperm packets (spermatophores) to the female using clubbed pedipalps
What organism has Sexual dimorphism? What does this mean?
Spiders; You cannot externally differentiate the male and female
Venomous spiders in US
Black widow
Brown Recluse
Black widow pattern
Hourglass
Black widow venom contains what and causes what when they bite you?
A neurotoxin that releases a lot of Ach; causes uncontrollable muscle contractions
Brown recluse pattern
Violin-shaped pattern
The Brown Recluse causes what when they bite you? What happens?
Hemolytic necrosis; death of the tissue in the area where one is bitten
If spiders are big enough, they can eat what?
Small animals
Harvestman are also called what?
Daddy-long-legs
Harvestmen have how many body segments? What are they?
They have one body segment; their legs
Ticks and mites 2 general characteristics
Cephalothorax and abdomen are fused
Mouth parts are projected forward (anteriorly)
In ticks and mites the _________ and _________ are fused.
Cephalothorax, Abdomen
What segment are legs usually found in on ticks and mites?
The cephalothorax
Demodex are also called what?
The follicle mite
Where do Demodex (follicle mites) live and what do they eat?
They live on eyelashes or hair follicles; they eat dead skin cells
Chiggers (larva)
What do the larva cause?
Where can you find them?
How do they feet and what do they eat?
What happens when the larva mature?
What do the adults eat? What do adults NOT eat?
Causes itching;
usually find them in areas where clothing is tight.
Inserts tube into skin and eats skin cells.
They fall off and the tube remains.
Adults eat small arthropods, they DO NOT feed on humans like the larvae.
What disease passed by ticks causes rashes and high fevers?
Rocky Mountain Spotted Disease
Rocky Mountain spotted disease
Vector: ticks
Causes: rashes and high fevers
What disease passed by ticks causes a Bull’s eye-patterned rash on the skin?
Lyme Disease
What is the characteristic rash pattern caused by Lyme Disease?
Bull’s eye pattern
What bacteria causes Lyme Disease?
Borrelia burgdorferi
Main vector of Lyme Disease
Deer tick
How do deer ticks transfer bacteria to the host?
Borrelia reproduce inside the ticks body and then is transferred to the host through its saliva.
Deer ticks are also called what?
Blacklegged ticks
For deer ticks, both the ______ and _____ stages can infect the host
Nymphal, Adult
Main host of deer tick
White-footed mouse
What common diseases do ticks cause?
Rocky Mountain Spotted Disease
Lyme Disease
Lone star tick pattern; which gender is it found on?
White spot on the female’s body
The lone star tick can trigger what?
It can trigger an allergic reaction to red meat
Subphylum Myriapoda general characteristic?
Many legs
Subphylum Myriapoda 2 classes
Chilipoda
Diplopoda
Class Ciliopoda 5 general characteristics
Organisms?
Carnivorous or herbivorous?
Fast or slow moving?
First body segment contains
How many legs per segment?
Centipedes
Generally carnivorous
Fast-moving
1st body segment contains venomous claws/fangs
1 pair of legs per body segment
Class Diplopoda 5 general characteristics
Millipedes
Generally Herbivores
Slow-moving
Defense involves curling up into ball and contains poisonous repellent fluid
2 Pairs of legs per body segment
Subphylum Crustacea 4 general characteristics
Two pairs of antennae (sensory structures)
At least 10 walking legs
Molting
Diversity
Crustaceans generally have ___ body segments: the _________ and __________.
two; Cephalothorax, abdomen
5 Internal structures of the crayfish
Antenna
Antennule
Antennal gland
Cephalothorax
Abdomen
Antennae function as _______ structures
sensory
Antennae tend to have what kind of receptors? What are the responsible for?
Olfactory; responsible for smell and taste
What are antennal glands (green glands)?
Functions like a kidney; filters blood and excretes urine out of their face
Crayfish have an _____ circulatory system
open
Ecdysis
Parts of old cuticle are shed
Apolysis
Parts of old cuticle are broken down
A large portion of the crayfish exoskeleton is _______ and ______; what does this help with?
Membranous and flexible; this helps with its reabsorption when they molt
Molting sequence in lobster
Rupture of membrane and abdomen between the carapace
Part of the exoskeleton resorbed while the hardened bit on the outside is shed
Crayfish begins to wriggle free and absorb water, causing them to stretch and grow
New cuticle will begin to harden
When is an arthropod most vulnerable?
After molting
Terrestrial crustaceans
Isopods (pill bugs, bathynomous giganteus)
Brachiopoda
Large Isopod talked about in class
Bathynomous giganteus
Subphylum Hexapoda 3 general characteristics
6 walking legs
Incredibly diverse and abundant
Very adaptable
Class Insecta general characteristics
3 major body segments
Class Insecta 3 major body segments
Head, thorax, and abdomen
In Class Insecta, what are each of the segments responsible for?
Head - sensory
Thorax - locomotion
Abdomen - reproduction, digestion, respiration
Insect major sensory structures
Antennae (olfactory sensors)
Eyes (ocelli and compound eyes)
Mouth (chemoreception)
Hairs (mechanoreception)
Thorax structures
6 legs
Wings
Abdomen structures (3 main ones)
Fat body (storage of nutrients)
Ovipositor (egg laying)
Spiracles (respiration)
Parasitic insects (parasitoids) are _______-specific
species
Benefits of parasitoids
Biocontrol method (will target specific invasive species)
What insects have muscles attached directly to their wings?
Dragonflies and Locusts
Muscles in Dragonflies and Locust wings are attached to the muscles _______.
directly
Structure of the Locust and Dragonfly wings
Direct flight muscles
Sternotergal muscles
Where are the Sternotergal, longitudinal, and direct muscles?
Where are they?
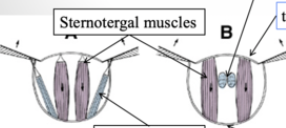
When sternotergal muscles contract, the wings are ___; when direct muscles contract, the wings are ____
up; down
When direct muscles contract, stergnotergal muscles ______
relax
What insects have muscles indirectly moving their wings?
Flies and midges
Wings in flies and midges are moved by muscles ________
indirectly
Structure of fly and midge wings (what kinds of muscles?)
Longitudinal muscles
Sternotergal muscles
When longitudinal muscles are _______ the wings are up; when the longitudinal muscles ______, the wings are down.
Relaxed; contract
In insects with indirect muscles in their wings, movement of the __________ causes their wings to move
exoskeleton
_______ muscles have faster flight in insects
indirect
Synchronous flight; what kind of musculature?
nerve impulses stimulates the flight; direct flight muscles
Asynchronous flight; what kind of musculature?
nerve impulses are periodic and trigger antagonistic muscles to contract and stimulate other muscles; usually indirect flight muscles
Insect nutrition: 3 main parts of the digestive system
Foregut
mouth to crop/gizzard); preliminary digestion
Midgut
Stomach and gastric cecae; main site for digestion and absorption of nutrients
Hindgut
Intestine (colon) and rectum; water absorption and feces formation
Most insects are:
Carnivores, omnivores, or herbivores?
Herbivores
Gas exchange in insects happens in the ________ system.
Tracheal
Tracheal system structure
Spiracles - openings to outside of body
Trachea
a. Taenidia
Tracheoles
Gas exchange process in insects
Air enters through the spiracles
Air flows through the trachea and into the tracheoles, where O2 diffuses into the blood/muscles
In insects, blood plays a major role in transporting ________.
nutrients
What are two ways different aquatic insects can respire?
Gills; trachea run through the gill flaps and diffuse O2 from the water into the body
Some insects have spiracles/breathing tube, meaning they have to surface to get air (i.e. Diving beetles)
Insect compound eyes detect ____
motion