NRES 251 1/22-2/16
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Soil Composition
Microbes
Nutrients
Organic Matter
Soil Definition
Natural - livnig being
Complex - varies on depth, time, altitude, and place
Vital - needed for agriculture, plants give us oxygen
Dynamic - changing constantly
Interface - hydrosphere, biosphere, atmosphere, lithosphere
Fragile - easy to damage, just walking over and compacting soil can hurt all plants around the soil (100s of years to fix)
Talented - performs functions that have value
Soil Functions
Water storage and cleaning
Habitat for soil organisms
Engineering medium
infrastructure
Waste recycling
soil stores waste in organic compounds
biogeochemical recycling
Atmospheric Modification
Plant Medium
Plant Medium
Temperature
insulates plants
Water
Air
soil has an atmosphere in the spaces between the soil
Support
provides an anchor for the roots
Nutrients
required by plants
Macros
cations: Ca2+, Mg2+, K+, H4+
anions: SO42-, PO42-
Micros
cations: Cu2+, Zn2+, Mn2+, Ni2+, Fe2+
anions: B-, Cl-, Mo-
Toxins
soil can be a buffer (led)
Mineral (Soil Composition)
Sand 2-0.05 mm
Silt 0.05 - 0.002 mm
Clay <0.002 mm
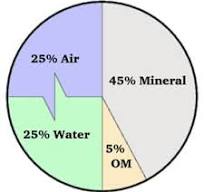
Ideal Soil
45% mineral
50% pores (25% air 25% water)
5% organic matter
Soil Horizons
O - organic matter (>20%)
A - organic matter (<20%)
E - elluviation (leaching and near surface)
B - illuviation (accumulation)
C- parent material (unconsolidated)
R - parent material (bedrock or consolidated)
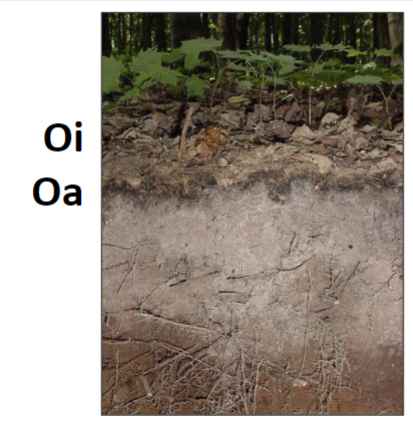
O Horizon
very dark in color
feels greasy or fibery
is not gritty (sand) or sticky (clay)
often wet
Oa - sapric material, highly decomposed
Oe - hemic material, intermediately decomposed
Oi - fibric material, least decomposed

A Horizon
highest quality for plants
darker in color, high biological activity
Ap - plow later (abupt boundary)
Ab - buried horizion

E Horizon
near surface horizon of leaching or elluviation
light in color
could have platy soil structure

B horizon
subsurface horizon of accumulation or illuviation
properties are derived from the materials that are accumulating in the horizion
Bt - clay accumulation
Bh - organic matter
Bs - Fe and AI accumulation
Bw- weakly developed

C Horizon
subsurface horizon of parent material
absent of pedogenic processes such as the formation soil structural aggregates

R Horizon
Subsurface horizon of consolidated, hard, continuous bedrock

Soil Forming Factors (CLORPT)
CLimate
precipitation
temperature
Organism
plants, animals, and people can have differential effects on weathering and soil disturbances
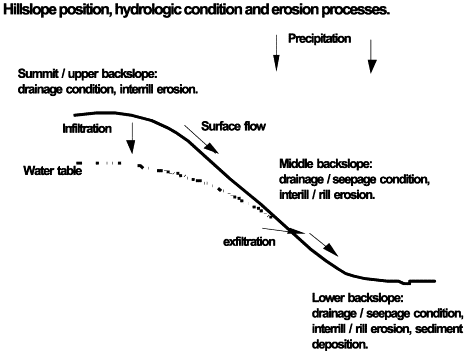
Relief (topography)
hillslope position
shoulder is most erodible
slope angle getting steeper (convex)
backslope is transportations
constant slope angle
footslope is depositoinal
decreasing slope angle (concave)
toeslope is most depositional
no slope
altitude and aspect
higher altitude regions are cooler regions
in the northern hemisphere, south and west aspects are warmer locations
Parent Material
primary rocks and minerals
igneous (basalt, gabbro, granite, rhyolite)
formed from hot, molten lava
sedimentary (sandstone, limestone)
formed from accumulation, deposition, cementation
Metamorphic (marble, quartzite, schist, gneiss)
changed with heat or pressure
Time