histology: epithelium & glands
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
lecture 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
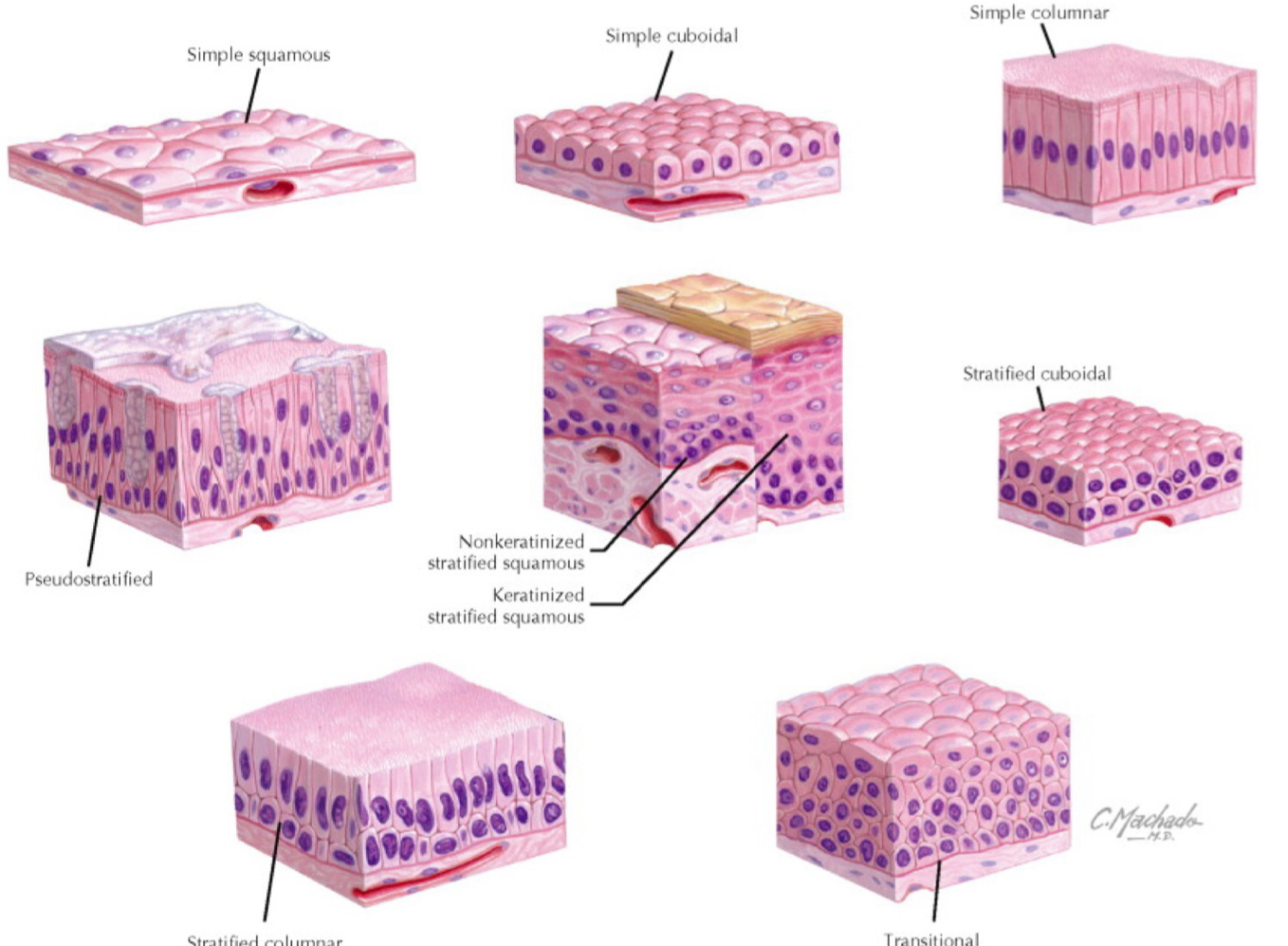
three types of epithelia:
simple
stratified
pseudostratified
and they can be:
squamous
cuboidal
columnar
cuboidal
transitional
pseudostraified
keratinized
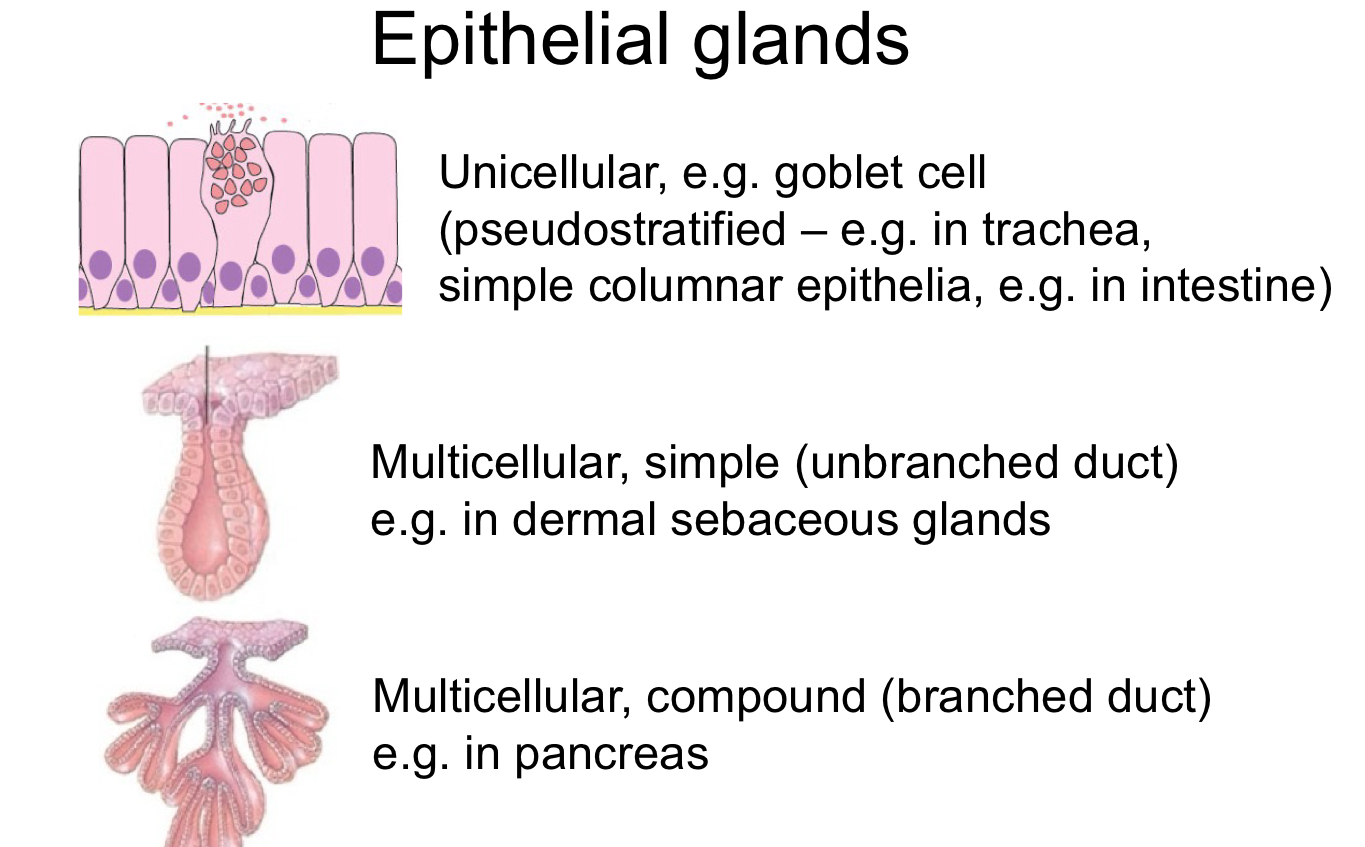
types of glands
unicellular
multicellular
simple
compound
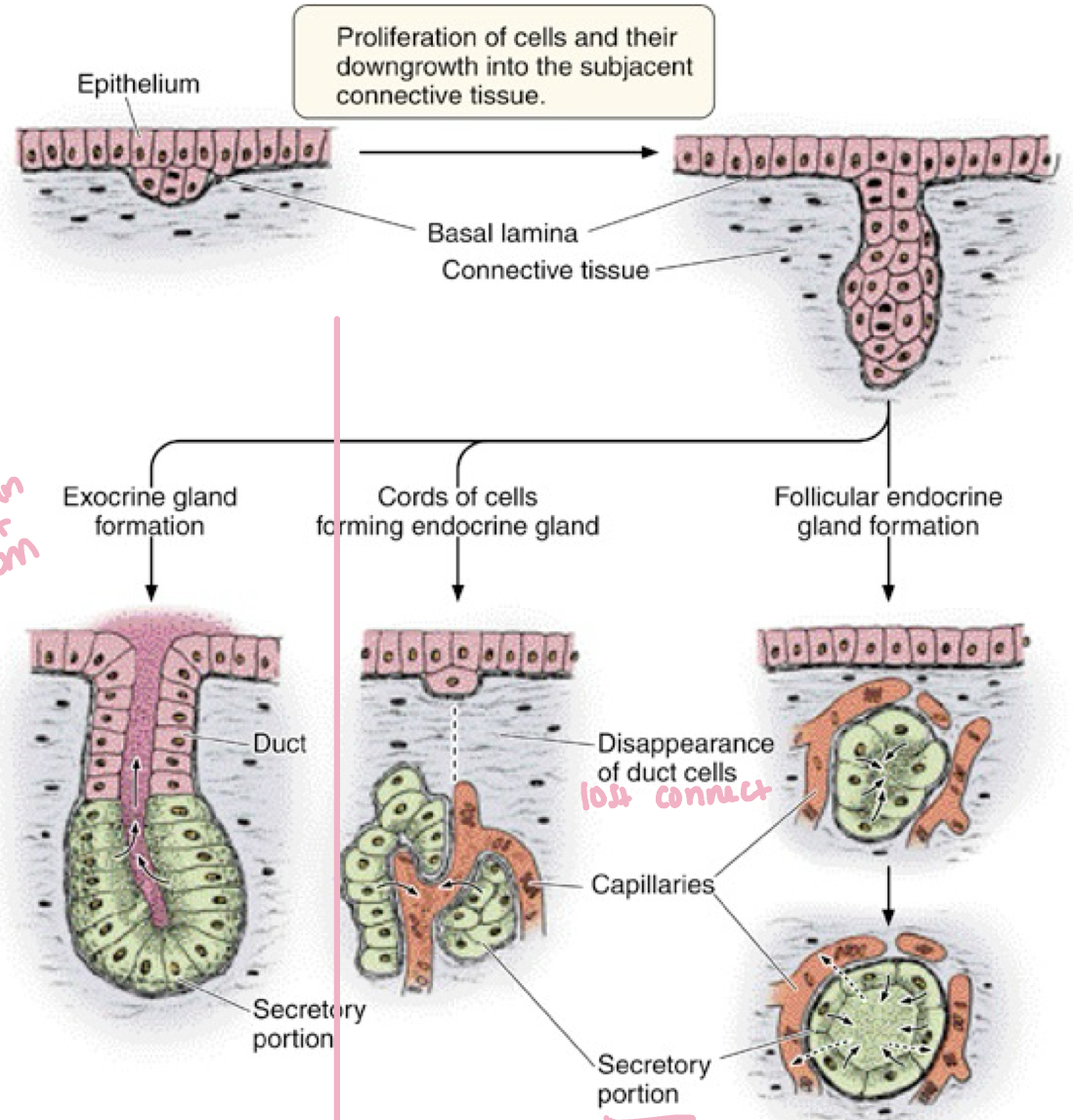
exocrine
endocrine
types of secretions
serous and mucous
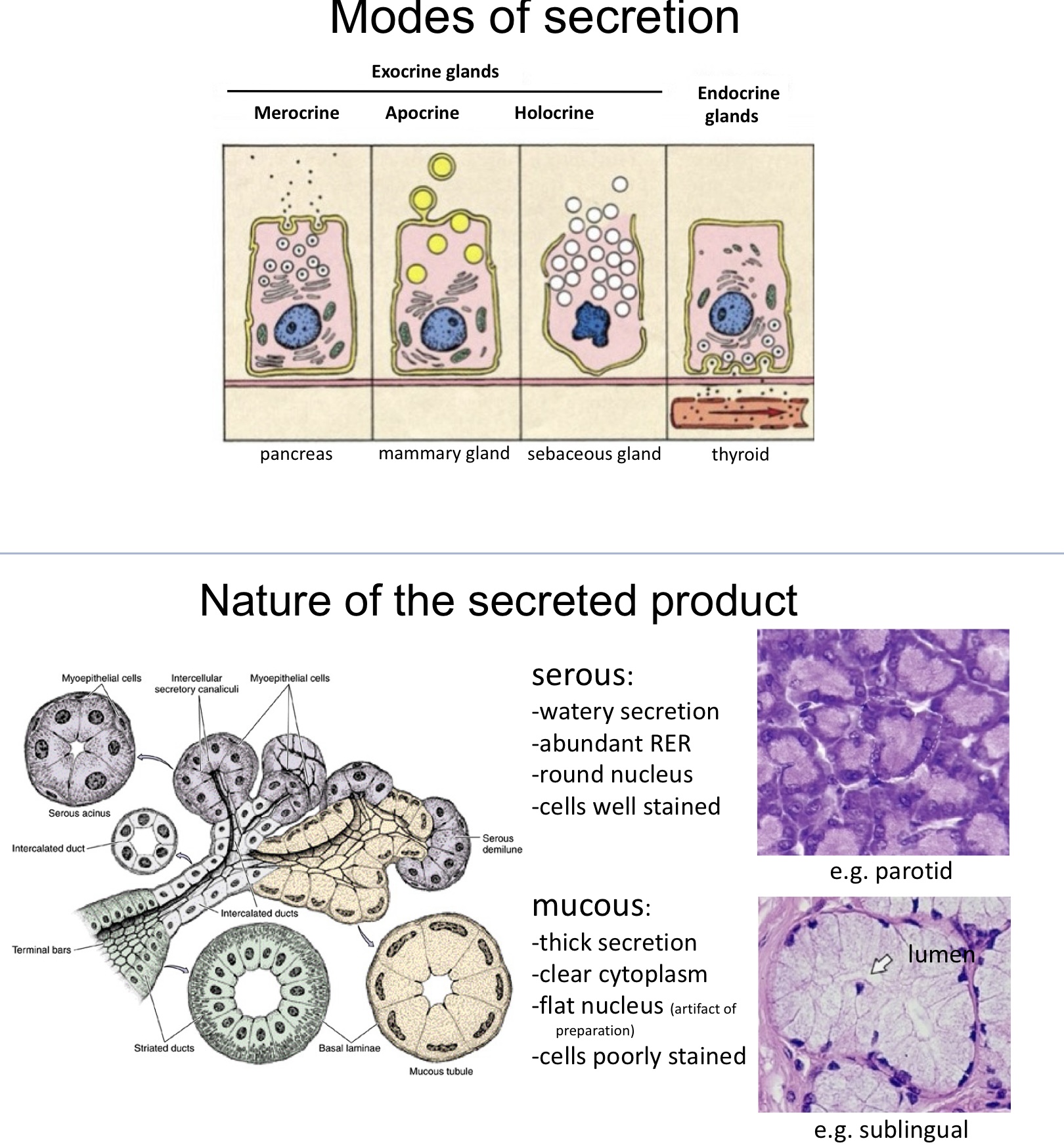
mechanisms of secretion
merocrine
apocrine
holocrine
characteristics of epithelia
form continuous sheet lining all free surfaces
one cell thick of multilayered
polarized: free apical surface vs basal surface attached to basal lamina
express keratin intermediate filaments
avascular
lining or glandular
external surface is
ectoderm-derived eg: epidermis
internal surface is
endoderm derived eg: GI, respiratory tract
internal surface is
mesoderm derived (mesothelium) eg: pericardial cavity
epithelial functions
protection: water proofing, insulation, stomach lining)
surface transport (cilia movement respiratory up; oviduct cilia move the ovum)
absorption (intestinal epithelium in microvilli and kidney tubules absorb nutrients)
secretion (unicellular and multicellular glands)
trans-epithelial transport
apical to basal: kidney tubules transport nutrients rom lumen to basal connective
basal to apical: lymph resorption into lymphatics
reproductive (seminiferous tubule generates sperm)
special sensory (taste buds, hair cells in cochlea)
contraction (myoepithelium)
keratinization
stratum corneum dead layer of skin
underneath is the granulosum which is dark because keratohyaline granules (- proteins)
no nuclei
VS
para-keratinization: no stratum granulosum and the surface cells are living
developed with eating harder foods
*all epithelial are avascular: blood is below the basement membrane
basal lamina
physical support
development: morphogenesis and differentiation
cell migration after injury
may be discontinuous
composed mainly of type IV collagen and laminin
external lamina
the equivalent of basal lamina bit these cells are non-polarized so they don’t have basal lamina
glands
epithelial gland types
modes of secretion
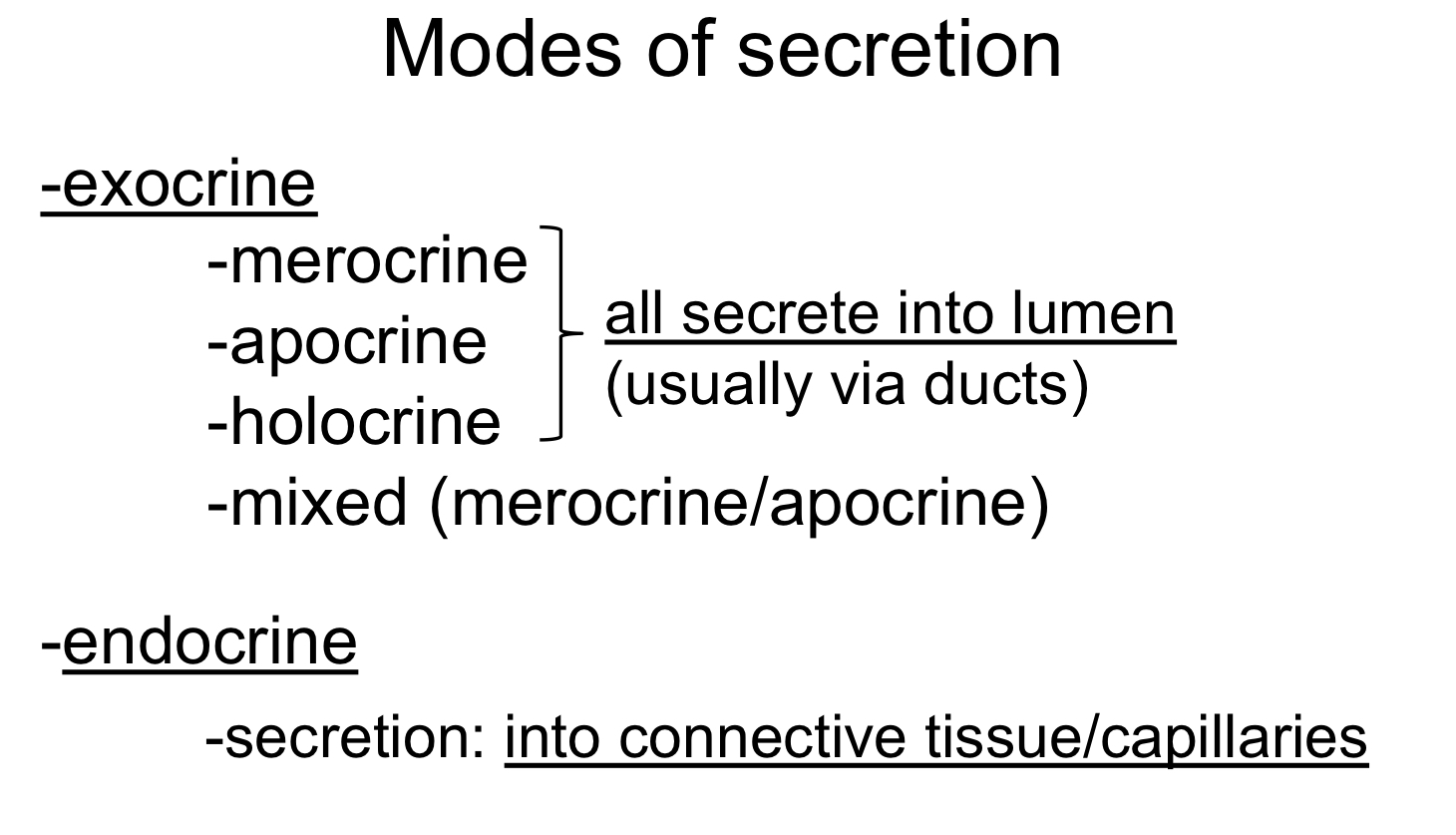
merocrine
secretion by exocytosis only product is released
apocrine
aka decapitation
portion of apical membrane and cytoplasm is released along with the product
holocrine
entire cell and its contents (sebum) become the secretory product
ex: fordyce spots secrete this way
entire sebaceous gland cell ruptures and disintegrates to release its contents. The cell's cytoplasm is filled with sebum (a mixture of lipids), and when the cell reaches maturity, it bursts, releasing sebum into the gland's duct. Fordyce spots result from sebaceous glands that are misplaced or "ectopic," meaning they are located on mucosal surfaces (like the lips and inside of the cheeks) where sebaceous glands are not typically found.
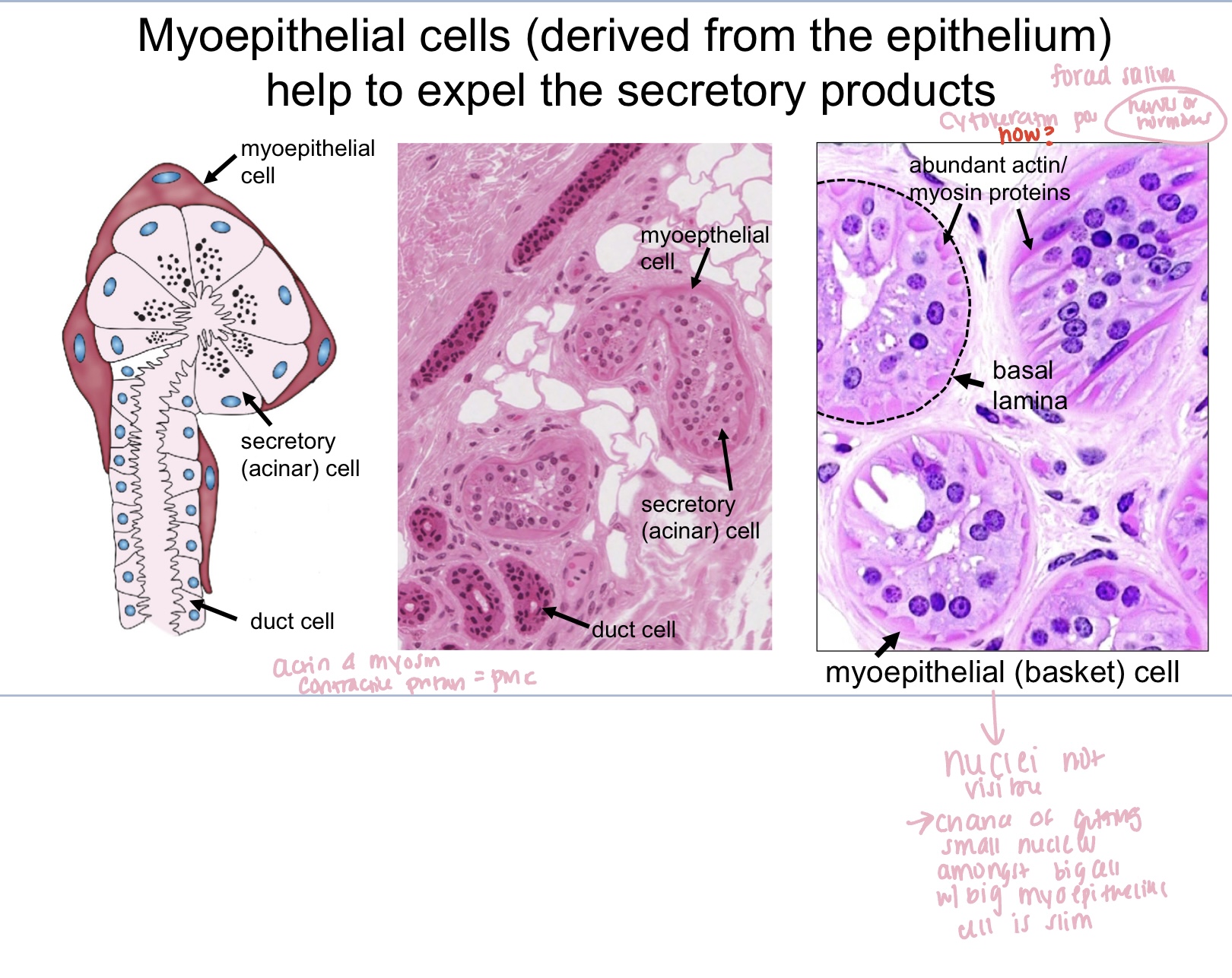
the extra