A&P - Test 2 review
1/788
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
789 Terms
Which of the following is true of synovial joints?
1) Functionally classified as synarthrosis
2) Bones are connected by hyaline cartilage
3) Functionally classified as amphiarthrosis
4) Bones are connected by fluid-filled cavity
4) Bones are connected by fluid-filled cavity
A meniscus is….
1) A fibrocartilage pad that provides padding between bones
2) A fluid filled space that prevents friction between muscle tendon and underlying bone
3) the articular cartilage that covers the ends of a bone at a synovial joint
4) The lubricating fluid within a synovial joint
1) A fibrocartilage pad that provides padding between bones
What do ribs do? Where does each set cover?
1) Protect your important stuff, Help you breathe, Give shape and support
2) 1–7: “True ribs”
Each rib connects directly to your breastbone (the bone in the middle of your chest).
They protect the heart and lungs.
8–10: “False ribs”
They don’t connect directly to the breastbone — they’re kind of “indirectly” attached.
They still help protect the lower lungs and upper belly stuff (like part of the liver and diaphragm).
11–12: “Floating ribs”
These last 2 pairs are called “floating” because they don’t connect to the front at all — only to the spine.
They hang out near the bottom of your ribcage and help protect the kidneys and some of the lower organs.
What are ribs attatched to on each end? What do those structures do?
1) The ribs connect to the spine and sternum/cartilage (all besides the “floating” 11th and 12th)
2) The spine supports your body and helps the ribs move. The sternum hold the ribs together, protects organs, and helps with breathing
Where does each rib type fall in the “Mobility vs stability” balance
1) True ribs (1-7) - High stability low mobility
2) False ribs (8-10) - mid point of stability and mobility
3) Floating ribs (11-12) - low stability high mobility
The epidermis is primarily what type of cell?
Keratinocytes
Which of the following epidermal layers is only found in thick skin ?
1) Stratum basale
2) Stratum spinosum
3) Stratum lucidum
4) Stratum corneum
Stratum Luciderm
Earwax is produced by which gland?
Ceruminous gland
Resp failure can lead to a change in the color of the skin, which is more evident in light-skinned individuals. Which pigmentation factor is affecting this change?
Hemoglobin
Squamous cell carcinomas are the 2nd most common of the skin cancers and are capable of metastasizing if not treated. This cancer affects which cells?
1) Basal cells of the stratum basale
2) Keratinocytes of the stratum spinosum
3) Melanocytes of the stratum basale
d) Langerhans cells of the stratum lucidum
2) Keratinocytes of the stratum spinosum
Label each level of structural organization below with examples from the skin
1) Cell →
2) Tissue →
3) Organ →
4) Organ system →
1) Cell → Keratinocytes
2) Tissue → epithelial
3) Organ → Epidermis
4) Organ system → Integumentary
your body has multiple requirements for life. Which one is your skin directly involved in regulating? Explain the basic mechanisms of how it does this
Regulating your temp: Sweating (evaporation) cools you down. Glands produce swear, as it evaporated it cools you down.
Blood vessels constriction happens when you are cold. This constricts your blood vessels and reduces blood flow to the skin which conserves your body temp
What ways (other than regulating your temp) does skin contribute to homeostasis
1) Protection
2) Kepping you hydrated
3) Vit. D synthesis
4) Responsiveness
How is pH important to the skin?
the acid mantle creates a low pH which reduces bacterial growth
which important trait of lipids does the skin rely on? What function does this contribute to?
Lemellar bodies contain glycolipids which make the skin waterproof
What are the 2 specific proteins that are present in the skin in large amounts? What are their function
Keratin - creating a dry layer on top of the dermis
Collagen - attracts and binds water, keeping the skin hydrated and firm
What kind of cell junctions are important in the epidermis? Describe the basic structure of those junctions and their functions
1) Desmesomes - made of cadherin proteins. These anchor and provide strength
2) Tight junctions - Made of claudins and occlaudins. These act as a tight seal
3) Gap junctions - made of channel proteins. These allow for cell-cell communication
Match each of the following skin layers with their main function:
1) Stratum basale
2) Stratum spinosum
3) Stratum corneum
a) Actively dividing stem cells
b) Waterproof barrier of dead cells
c) Strong desmosomal junctions between cells
1) Stratum basale - a) Actively dividing stem cells
2) Stratum spinosum - c) Strong desmosomal junctions between cells
3) Stratum corneum - b) Waterproof barrier of dead cells
Keratinocytes in the stratum granulosum produce and release lemellar bodies containing glycolipids. What roles do you think specific organelles have in producing them? (hint: What kind of macromolecule is a glycolipid? Where are materials packaged in cells?)
Glycolipids are a type of lipid (macromolecules). Materals are packaged via the smooth ER (prod of glycolipids). Production requires synthesis, modification, and packaging for exocytosis. So the organelles that are needed for production are….
1) Smooth ER - Production of glycolipids
2) Golgi - shipping and handeling
3) Lemellar bodies - use exocytosis to release contents
Where in the skin do you find each kind of tissue? What tissue subtypes?
a) Epithelial
b) Connective
c) Muscle:
d) Nervous
a) Epithelial: Found in the epidermis (Subtype - Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium)
b) Connective: Found in the dermis and hypodermis (Subtype - Areolar connective, dense irregular, and adipose)
c) Muscle: Found in hair follicles and blood vessels (Muscle → errector pilli) (Smooth muscle → involuntary)
d) Nervous: Found in the dermis and sensory structures (Nervous → never endings, corpuscles)
A major function of the integumentary system is thermoregulation. What are 2 major thermoregulatory mechanisms of the skin? (explain in a simple and concise way)
Two major thermoregulatory mechanisms of the skin are:
Sweating: When the body gets too hot, sweat glands release sweat onto the skin’s surface. As the sweat evaporates, it cools the body down.
Vasodilation: Blood vessels in the skin widen (dilate) to increase blood flow near the surface. This helps release excess heat from the blood into the air, cooling the body.
These processes help maintain a stable internal body temperature.
Which description of skeletal cartilage is INCORRECT?
Elastic cartilages are able to tolerate repeated bending.
Fibrocartilages are able to withstand both pressure and stretch.
Costal cartilages reinforce airways and support the external nose.
Articular cartilages cover the ends of most bones at moveable joints.
Costal cartilages reinforce airways and support the external nose.
Respiratory cartilages form the basic structure of the larynx (voice box) and reinforce other respiratory passageways. ______ cartilages connect the ribs to the sternum.
Costal
When chondrocytes in lacunae divide and form new matrix, it leads to an expansion of the cartilage tissue from within. This process is called __________.
interstitial growth
The pubic symphysis connects the two hip bones anteriorly and provides a little movement during childbirth. Choose the most appropriate tissue for this structure that is subjected to both pressure and stretch.
hyaline cartilage
bone
fibrocartilage
elastic cartilage
fibrocartilage
Bones do NOT have a role in __________.
glycogen production
movement
fat storage
blood cell formation
support
glycogen production
Which of the following pairs of terms is mismatched?
femur: long bone
cranial bones: flat bones
tarsals: short bones
sternum: long bone
sternum: long bone
Which of the following bones are NOT a part of the axial skeleton?
skull
vertebrae
upper limb
rib
upper limb
Which of the following statements regarding the skeleton is INCORRECT?
The axial skeleton includes the bones of the limbs.
The appendicular skeleton includes the shoulder and hip girdles.
The axial skeleton supports and protects internal organs.
The appendicular skeleton allows us to move around.
The axial skeleton includes the bones of the limbs.
________ growth occurs when chondrocytes divide and form new matrix, thereby expanding the cartilage tissue from within
Interstitial
The sternum is a ______ bone.
The sternum is a flat bone.
The bones of the limbs make up the _______ skeleton.
appendicular
Which of the following is a bone marking described as a round or oval opening through a
bone?
fossa
epicondyle
foramen
ramus
meatus
foramen
The _______ _______ is a remnant of the epiphyseal plate; it's the line of bone that marks where bone growth occurred in childhood.
epiphyseal line
___________ Cartilage is a smooth, white cartilage that covers the ends of bones at joints; it reduces friction and absorbs shock.
articular
___________ are concentric rings of bone matrix found in compact bone, surrounding the central (Haversian) canal.
lamellae
__________ are tiny channels that connect osteocytes in bone, allowing for nutrient and waste exchange
canaliculi
What is the structural unit of compact bone?
canaliculus
osteoid
Haversian canal
osteon
osteon
The structural unit of compact bone is the _______, an elongated cylinder oriented parallel to the long axis of the bone.
osteon
___________ is the unmineralized, organic portion of the bone matrix, primarily composed of collagen, that later hardens into bone
Osteoid
A homeostatic imbalance that activates these bone cells would lead to a loss of bone density.
osteoclasts
osteocytes
chondroblasts
osteoblasts
osteoclasts
__________ are mature bone cells that maintain the bone matrix and monitor mechanical stress.
osteocytes
__________ are the bone cells that break down bone. If they were activated more than normal, you should expect to see bone loss.
Osteoclasts
__________ are immature cartilage cells that produce the cartilage matrix
chondroblasts
________ are the bone-forming cells that secrete osteoid, which later mineralizes to become bone.
osteoblasts
Spongy bone contains ________.
osseous lamellae
osteons
trabeculae
lamellar bone
trabeculae
The cell responsible for secreting the matrix of bone is the ________.
osteocyte
chondrocyte
osteoclast
osteoblast
osteoblast
What is the bone matrix?
The bone matrix is the intercellular substance of bone tissue, made of:
Organic part (mainly osteoid): collagen fibers for flexibility and strength
Inorganic part: mineral salts (mainly calcium phosphate) that harden the bone and give it rigidity
What is intramembranous ossification?
the formation of bone from preexisting hyaline cartilage models
the formation of bone from preexisting elastic cartilage models
the formation of bone from within fibrous membranes
the formation of bone from preexisting fibrocartilage models
the formation of bone from within fibrous membranes
What would be the physical sign that a bone cannot continue longitudinal growth?
the presence of hyaline cartilage on the ends of the bone
the presence of osteoblasts
an epiphyseal line
the presence of osteons
an epiphyseal line
The epiphyseal plate is a zone of hyaline cartilage between the epiphysis and diaphysis of a long bone. When the cartilage is replaced with bone and the plate closes, the bone has reached its maximum ______. This ossified remnant of the "growth plate" is called the epiphyseal line
Length
Horizontal (width) growth occurs by _________ growth at the periosteum (bone surface)
appositional
The _________ is a tough, dense membrane covering the outer surface of bones (except at joints), containing blood vessels, nerves, and cells important for bone growth and repair.
periosteum
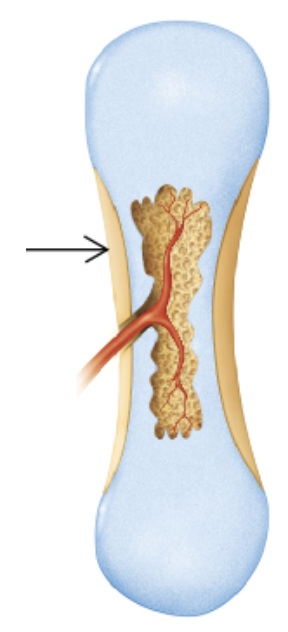
Which bone-forming process is shown in the figure?
endochondral ossification
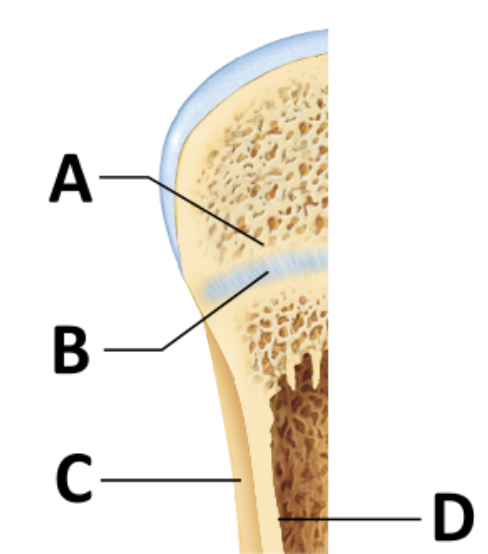
During bone growth, which significant event occurs at the surface indicated by the letter D?
bone resorption
As the bone widens, the matrix at the endosteal surface is _______ to maintain the proper thickness of the walls surrounding the medullary cavity.
resorbed
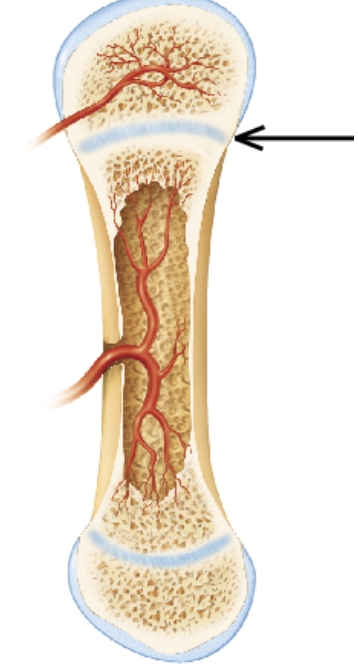
The arrow in the figure is pointing to which of the following structures?
the articular cartilage
a primary ossification center
a secondary ossification center
the epiphyseal plate
the epiphyseal plate
Which of the following statements is true?
Endochondral ossification leads to the formation of the clavicles and cranial bones.
Endochondral ossification occurs within fibrous connective tissue membranes.
During endochondral ossification, hyaline cartilage is broken down and replaced with bone.
Most bones in the body are formed by intramembranous ossification.
During endochondral ossification, hyaline cartilage is broken down and replaced with bone.
Endochondral ossification is the formation of bone within ________ cartilage
hyaline
Most bones below the base of the skull form by ______ ossification.
endochondral
____________ _________ is more complex than intramembranous ossification because the hyaline cartilage must be broken down as ossification proceeds
Endochondral ossification
What controls bone remodeling?
hormones and diet
the nervous system and hormones
mechanical stress and hormones
mechanical stress and diet
mechanical stress and hormones
Remodeling goes on continuously in the skeleton, regulated by genetic factors and two control loops that serve different homeostatic conditions. What are these two?
One is a negative feedback hormonal loop that maintains Ca2+ homeostasis in the blood; the other involves responses to mechanical and gravitational forces acting on the skeleton.
________ _________ _________ is a negative feedback hormonal loop mainly involving parathyroid hormone (PTH) and calcitonin to maintain blood Ca²⁺ levels.
Calcium homeostasis regulation
______ ____ states that bone remodeling in response to mechanical and gravitational forces acting on the skeleton.
Wolffs Law
Which of the following is UNLIKELY to affect bone remodeling?
mechanical stress
parathyroid hormone
glucagon
low blood Ca2+concentration
glucagon
Wolff's law is concerned with ________.
the diameter of the bone being dependent on the ratio of osteoblasts to osteoclasts
vertical growth of bones being dependent on age
the thickness and shape of a bone being dependent on stresses placed upon it
the function of bone being dependent on shape
the thickness and shape of a bone being dependent on stresses placed upon it
Which hormone increases osteoclast activity to release more calcium ions into the bloodstream?
parathyroid hormone
The correct order (from start to finish) of fracture repair is __________.
bone remodeling, hematoma formation, soft callus formation, and hard callus formation
hematoma formation, hard callus formation, bone remodeling, and fibrocartilaginous callus formation
bony callus formation, hematoma formation, fibrocartilaginous callus formation, and bone remodeling
hematoma formation, soft callus formation, bony callus formation, and bone remodeling
hematoma formation, soft callus formation, bony callus formation, and bone remodeling
Which of the following are correctly matched?
open (compound) fracture; the fractured bone ends penetrate the skin
nondisplaced fracture; the fractured bone ends are misaligned
incomplete fracture; the bone is broken through
linear fracture; the break is perpendicular to the bone's long axis
open (compound) fracture; the fractured bone ends penetrate the skin
a_________ fracture is a fracture where the break is parallel to the long axis of the bone.
linear
a ___________ fracture is a fracture where the bone cracks but does not break all the way through
incomplete
A _________ fracture is a fracture where the bone cracks but the ends remain aligned in their normal position
nondisplaced
Which type of fractures carry a high risk of infection?
Open (compound) fracture
a __________ fracture is Common a sports fracture resulting from a twisting force.
Spiral
A ______ is when a bone is crushed
Compression
A ______ is an incomplete fracture or cracking of the bone without actual separation of the parts. Common in children.
Greenstick
Your patient is returning for follow-up 6 weeks after sustaining a nondisplaced fracture of his radius. He tells you that his forearm is no longer painful, but he is concerned that he can palpate a "lump" in the bone at the site of the healing fracture. What is your response?
"I'm concerned that your bone is not healing properly. Let's ask the doctor about doing some X-rays."
"That lump may be a sign of infection. We need to obtain cultures from the site."
"That bump is a normal part of bone healing at this stage. As your body completes the process, the cells in your bone will gradually remodel it to its previous shape."
"The lump means that the fracture was not set properly. I'm concerned that the ends of the fracture aren't properly aligned."
"That bump is a normal part of bone healing at this stage. As your body completes the process, the cells in your bone will gradually remodel it to its previous shape."
Which of the following pairings is correct?
osteoporosis; increased bone density
rickets; deficiency of vitamin A
osteomalacia; excessive mineralization of the bone
Paget's disease; excessive and haphazard bone deposition and resorption
Paget's disease; excessive and haphazard bone deposition and resorption
Decreased bone density due to loss of bone mass. This is what?
Osteoporosis
Deficiency of vitamin D, leading to soft, weak bones in children. What is this?
Rickets disease
Softening of bones caused by defective bone mineralization (due to vitamin D deficiency in adults). What is this called?
osteomalacia
You are counseling a patient with osteoporosis about strategies for avoiding fractures. Which of the following comments would NOT be appropriate?
"Be sure to consistently take any calcium and vitamin D supplements prescribed by your provider."
"Adequate protein in your diet will help to keep your bones strong."
"You should avoid weight-bearing exercise and strength training because these types of exercise will further weaken your bones."
"Weight-bearing exercises like walking and strength training for your muscles will help to strengthen your bones."
"You should avoid weight-bearing exercise and strength training because these types of exercise will further weaken your bones."
The ________ bone is a tiny bone found in the medial portion of the orbit. It is a facial bone, not part of the cranium.
lacrimal
Which bone is NOT considered to be part of the cranium?
Occipital bone
Lacrimal bone
Sphenoid bone
Ethmoid bone
Lacrimal bone
Identify the suture found between the 2 parietal bones.
Lamdoidal suture
Sagittal suture
Coronal suture
Squamosal suture
Sagittal suture
Which of the following bones is unpaired?
Parietal
Zygomatic
Frontal
Temporal
Frontal bone: Unpaired — forms the forehead and part of the eye sockets.
Parietal bones: Paired — left and right sides of the skull.
Zygomatic bones: Paired — cheekbones.
Temporal bones: Paired — sides and base of the skull.
Which cranial bone spans the width of the cranial floor?
Occipital
Ethmoid
Temporal
Sphenoid
Sphenoid
The sphenoid bone is the large bat shaped bone that spans the floor of the skull.
sphenoid
Which of the following bones do not contain a sinus?
Maxillary
Sphenoid
Frontal
Nasal
Nasal
The sinuses found in the skull are collectively known as the paranasal sinuses because they encircle the nasal cavity. The _______ bones are small tombstone shaped bones that form the bridge of the nose and don't contain sinuses.
nasal
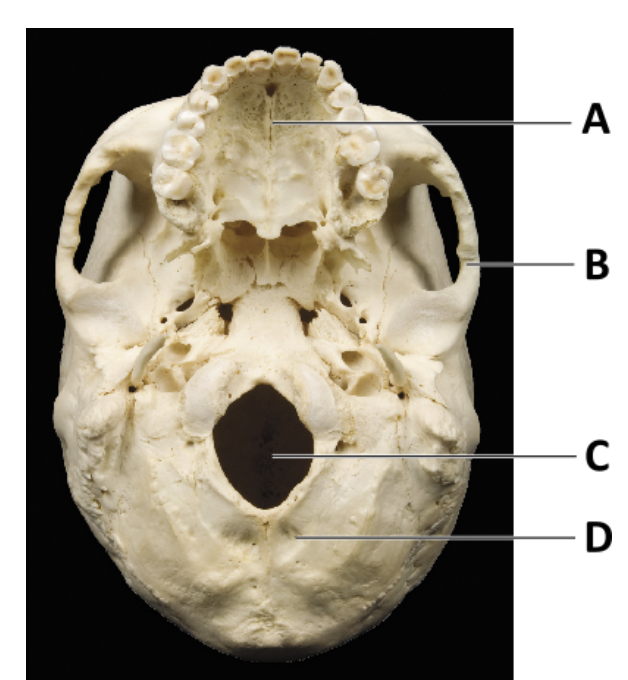
Which of the following bones are indicated by letters A, B, and D (in order)?
maxilla, temporal, and occipital
Which of the following bones is not a facial bone?
Zygomatic
Ethmoid
Inferior nasal concha
Maxillary
Ethmoid
The ethmoid bone forms the area of the cranium between the nasal cavity and the orbits.
ethmoid
What bone forms part of the nasal septum?
Maxillary
Vomer
Nasal bone
Inferior nasal concha
Vomer
Which facial bones makeup the central portion of the bridge of the nose?
Lacrimal
Nasal
Maxillary
Zygomatic
Nasal
The ______ is a thin bone in the nasal cavity forming part of the nasal septum.
vomer
The 2 tombstone shaped nasal bones are found above the nasal cavity. They form a continuous bony bridge that connects the ?
2 sides of the face.
What is the anatomical name for the facial bones known as "cheekbones"?
Zygomatic bones