Ocular Disease II: Cataracts and Lens Disorders
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
Cataract
A dense cloudiness that forms in the normally clear ocular lens, leading to visual loss when located on the visual axis.
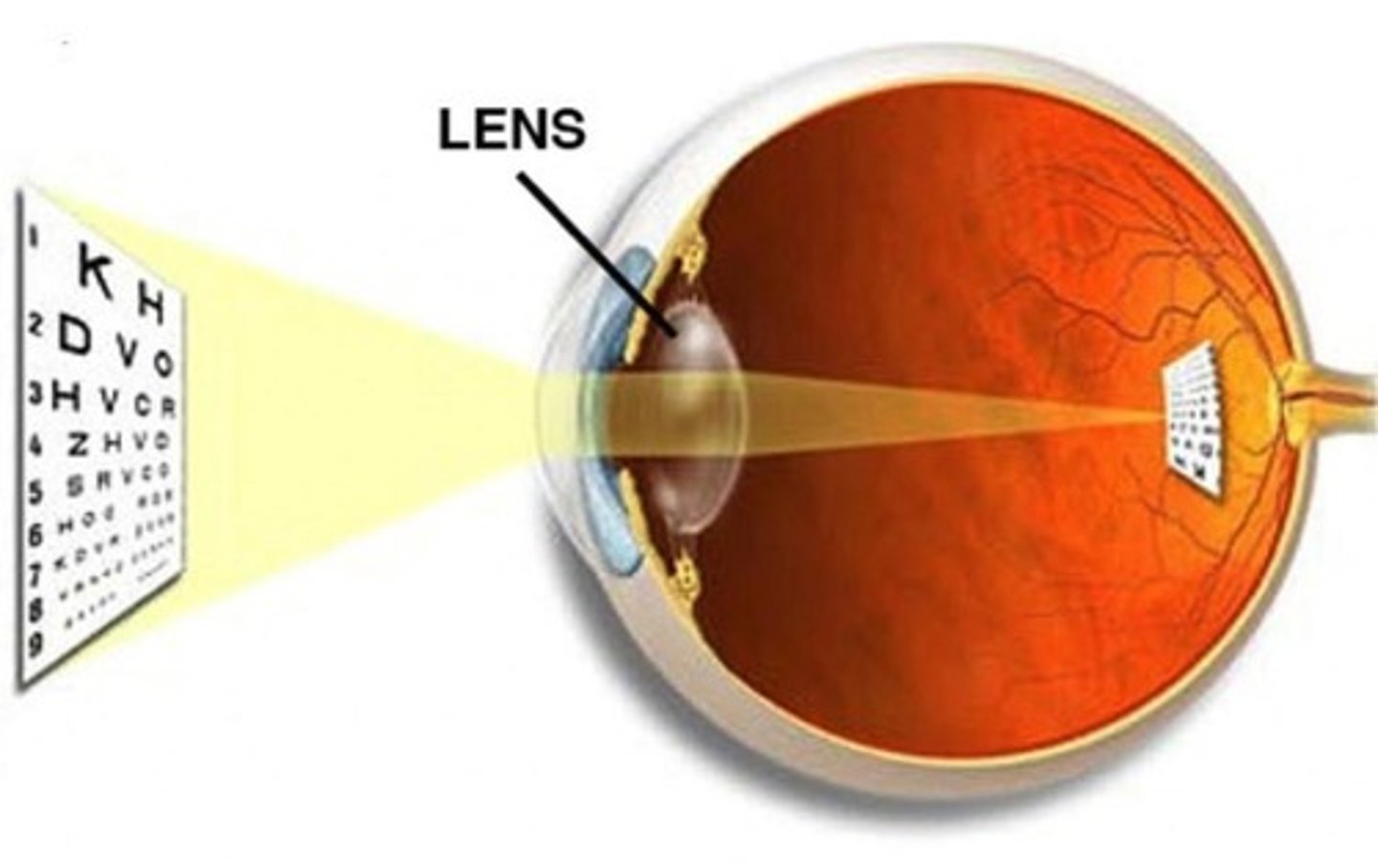
Crystalline Lens
A biconvex, optically transparent intraocular structure that transmits light to the retina with minimal scattering.
Accommodation
The process involving the relaxation and contraction of ciliary muscles to change the focal distance to the retina.
Zonular Fibers
Suspensory ligaments that attach the lens to the ciliary body and determine its degree of accommodation.
Presbyopia
A condition characterized by the gradual decline in the ability to focus on near objects, often requiring corrective lenses.

Cataract Causes
Factors leading to cataracts include age-related degeneration, congenital issues, infections, radiation, drugs, trauma, and diabetes mellitus.
Visual Acuity
The clarity or sharpness of vision, commonly decreased in patients with senile cataracts.
Glare
Disabling brightness experienced by patients, particularly noticeable during the day or with oncoming headlights at night.
Macular Degeneration
A progressive eye disease that affects the macula, leading to loss of central vision.
Diabetic Retinopathy
A diabetes-related condition that affects the blood vessels of the retina, potentially leading to vision loss.
Retinal Detachment
A serious condition where the retina separates from the back of the eye, requiring immediate medical attention.
Retinitis Pigmentosa
A genetic disorder that leads to the degeneration of the retina, causing progressive vision loss.
Central Serous Chorioretinopathy (CSCR)
A condition characterized by the accumulation of fluid under the retina, leading to visual distortion.
Retinal Vein Occlusion
A blockage of the veins that carry blood away from the retina, potentially causing vision loss.
Retinal Artery Occlusion
A blockage of the arteries supplying blood to the retina, often resulting in sudden vision loss.
Hypertensive Retinopathy
Damage to the retina caused by high blood pressure, which can lead to vision impairment.
Contrast Sensitivity
The ability to distinguish between an object and its background, which can decrease in brightly lit environments.
Myopic Shift
A change in vision where the progression of cataracts increases the dioptric power of the lens, leading to mild to moderate nearsightedness.
Monocular Diplopia
A visual disturbance where a person sees double images in one eye, often due to changes in the lens that create a 'lens within a lens' effect.
Senile Cataract
An age-related condition characterized by progressive clouding and thickening of the lens, leading to vision impairment.
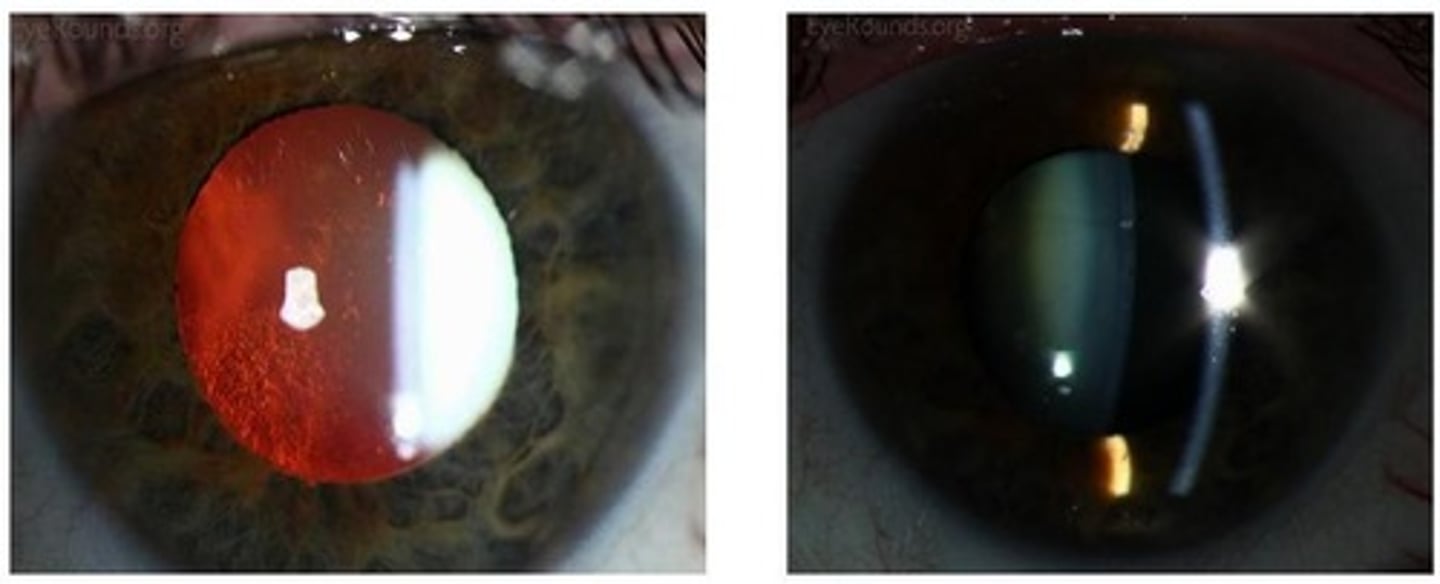
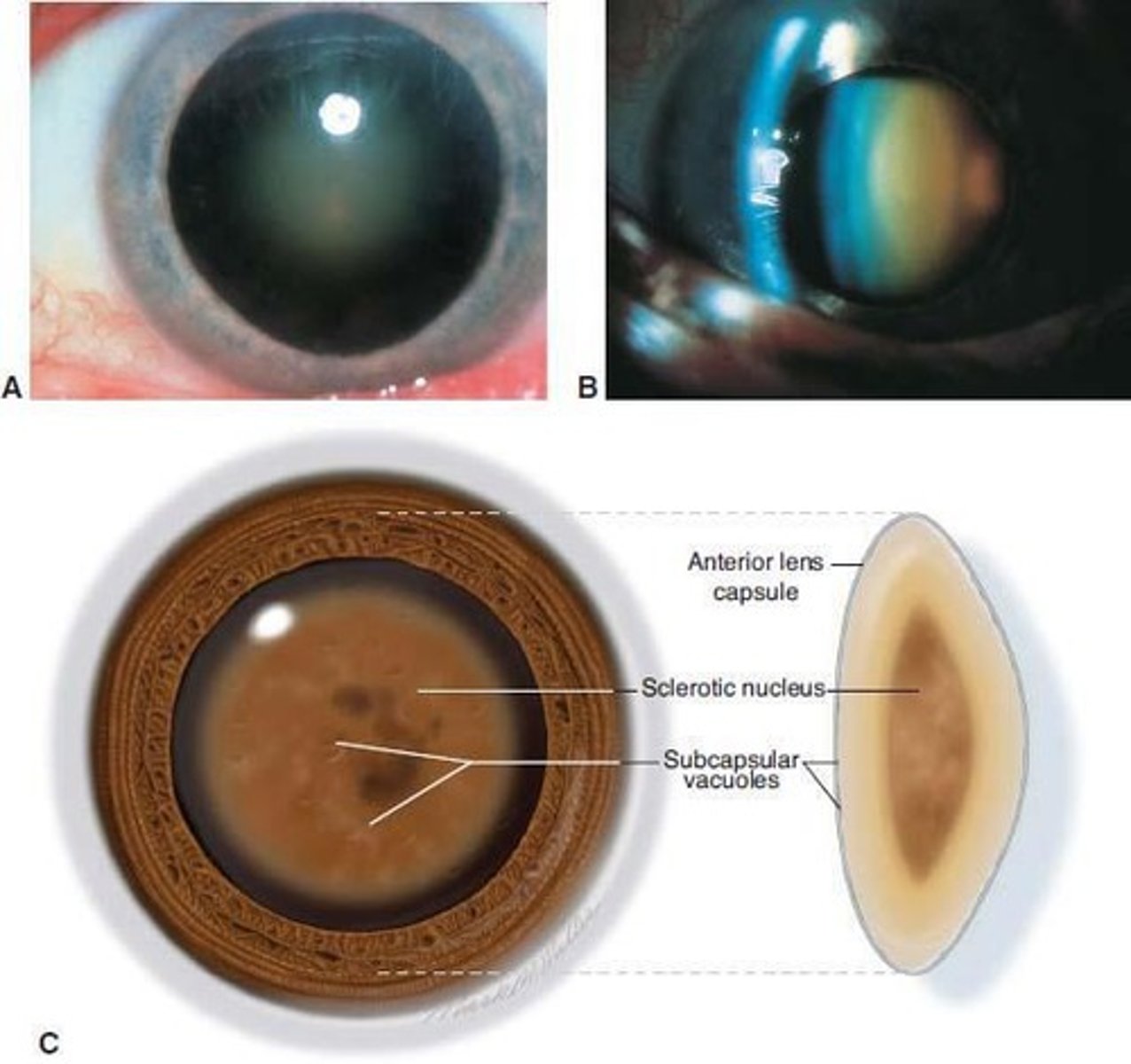
Nuclear Sclerotic Cataract
A type of cataract marked by yellowing and hardening of the central lens, often leading to decreased distance vision and temporary improvement in near vision.
Brunescent Cataract
An advanced form of nuclear cataract where the lens becomes very opaque and brown.
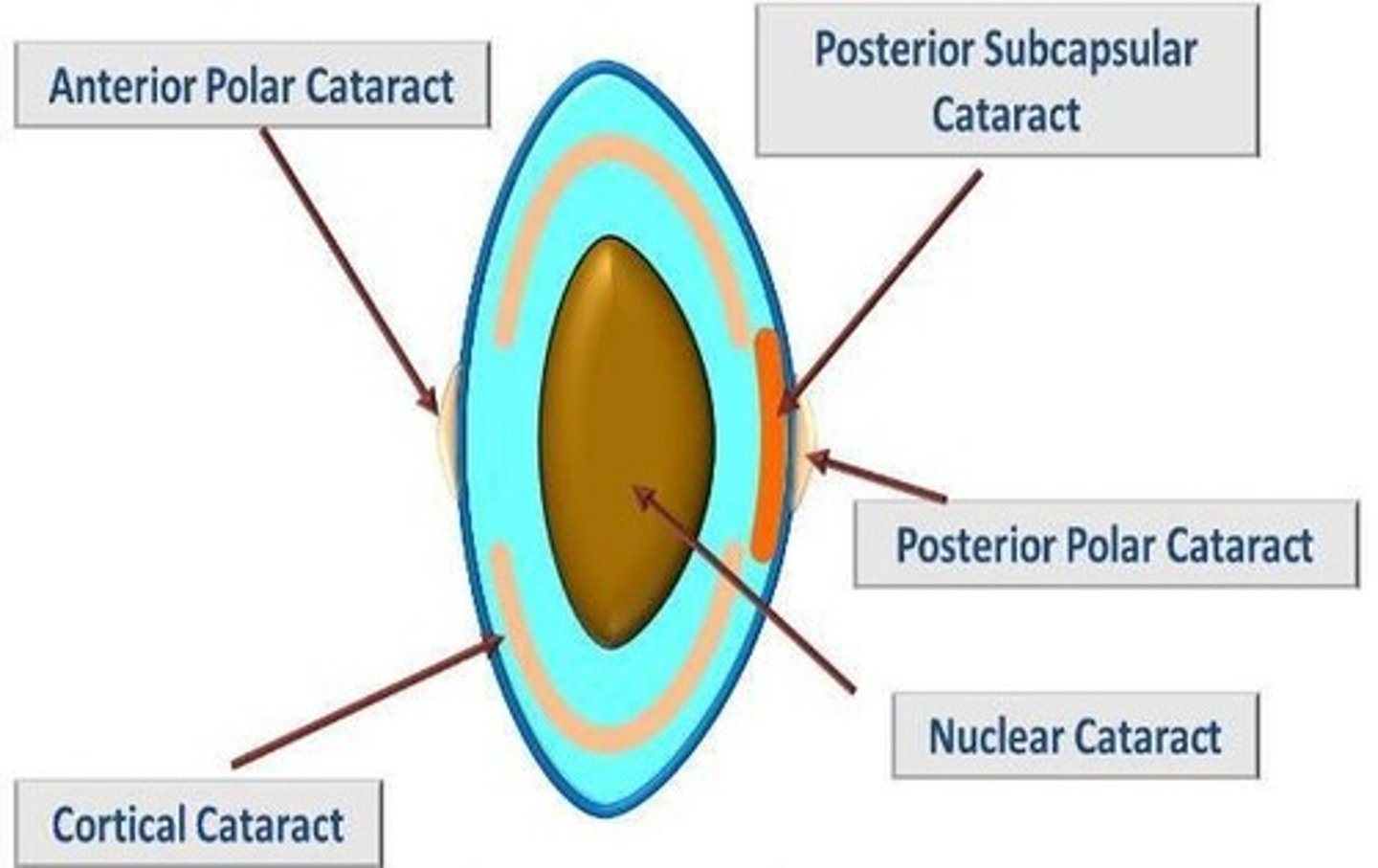
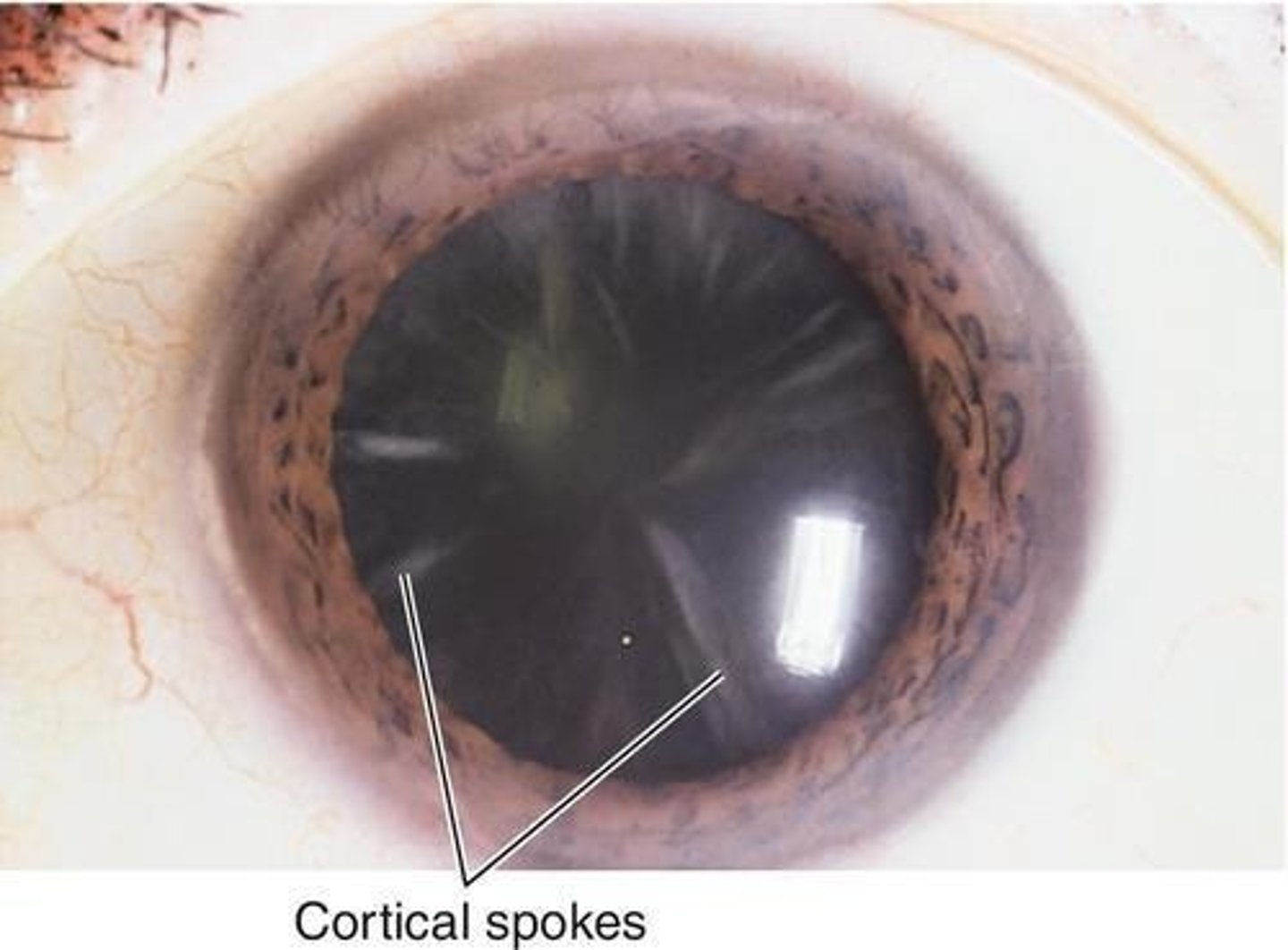
Cortical Cataract
A cataract characterized by wedge-shaped opacities at the lens periphery that can interfere with central vision as they progress.
Cortical Spokes
Wedge-shaped opacities in the lens that can compromise visual acuity, especially when they encroach upon the visual axis.
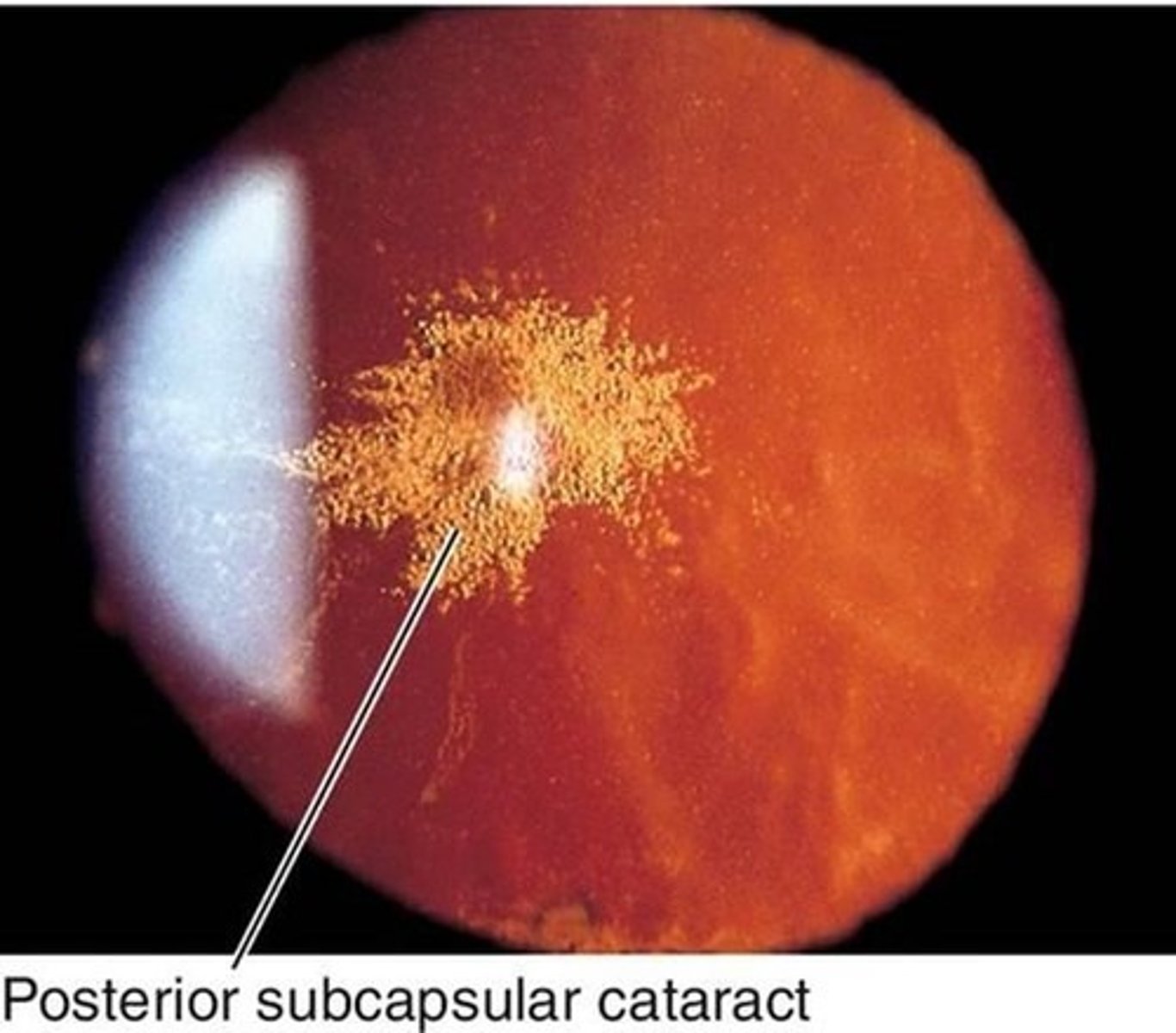
Posterior Subcapsular Cataract
A type of cataract that forms at the back of the lens, often affecting reading vision and causing glare.
Temporary Second Sight
A phenomenon where patients with nuclear sclerotic cataracts may temporarily experience improved near vision as their distance vision declines.
Degenerative Cataract
A common type of cataract that develops with age, leading to gradual vision impairment.
Visual Axis
The line of sight that extends from the eye to the object being viewed, which can be affected by cataracts.
Glare Sensitivity
Increased sensitivity to bright lights, often experienced by individuals with cortical cataracts, especially while driving at night.
Opacity
A condition where the lens becomes cloudy, impairing vision, which is a hallmark of cataract formation.
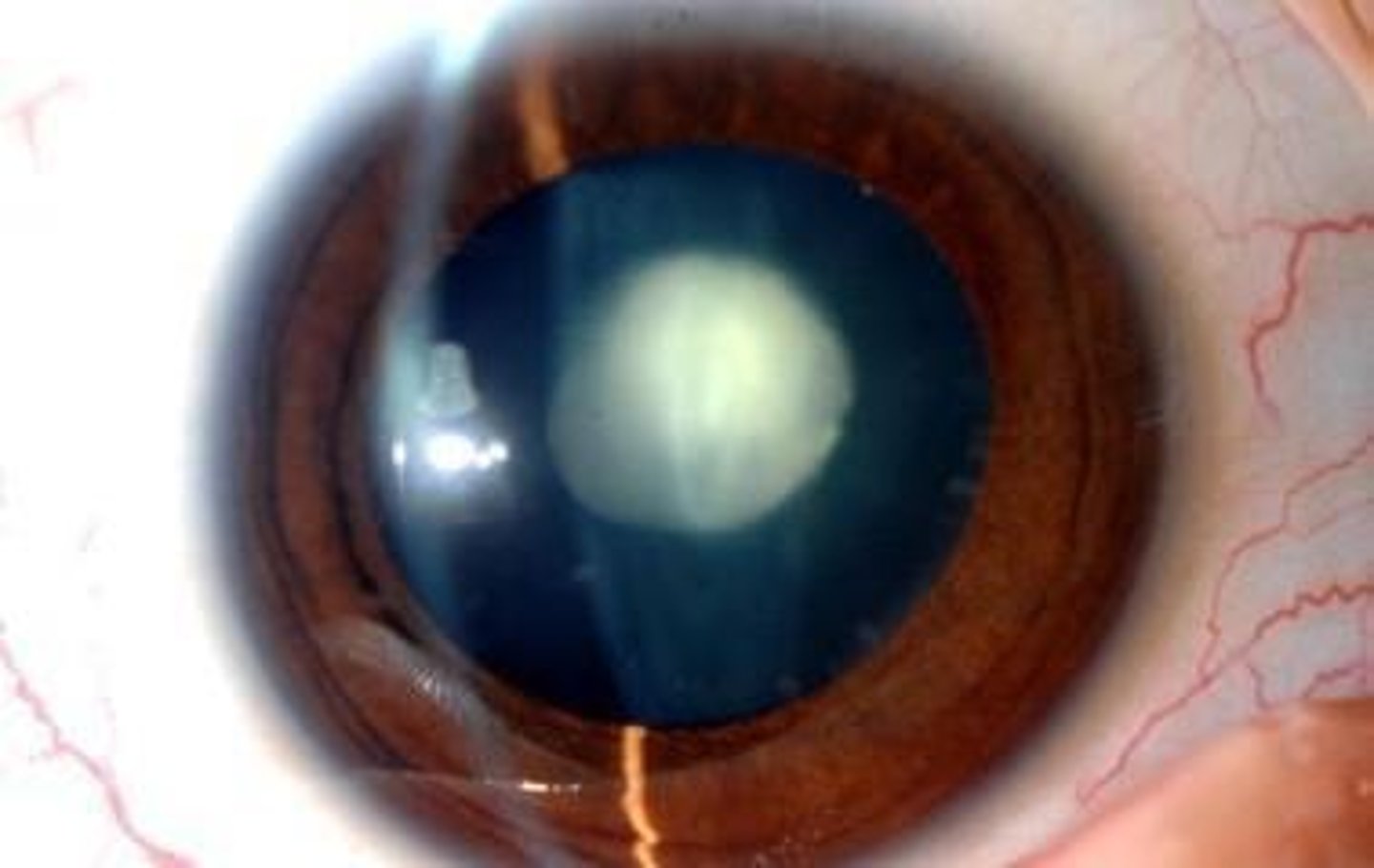
Lens Fibers
Cells that make up the lens of the eye, which can become opacified in cataract development.
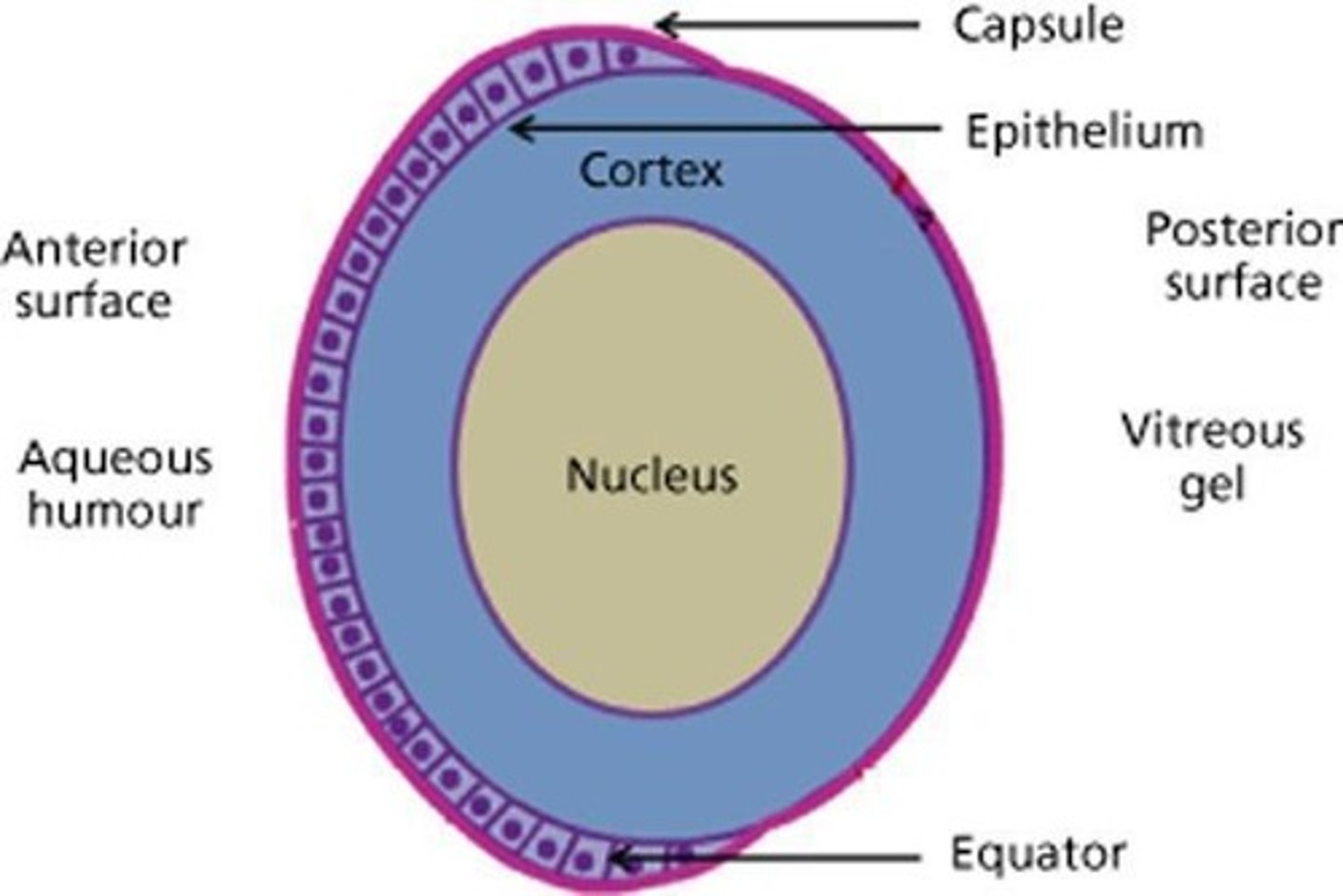
Posterior Subcapsular Cataract (PSC)
A type of cataract characterized by granular and plaque-like opacities located in the most posterior cortical layer of the lens, directly under the lens capsule.
Location of PSC
The opacities are found in the back outer layer of the lens, often centrally located.
Age of Onset
This cataract type tends to occur in younger patients compared to other types like cortical or nuclear sclerotic cataracts.
Combination with Other Cataracts
Often occurs in conjunction with nuclear or cortical cataracts in later stages.
Retroillumination
Easily noticed on retroillumination due to their central location, which may interfere with funduscopy.
Progression Rate
The progression of this cataract is variable but generally occurs more rapidly than in nuclear sclerosis.
Symptoms
Near vision is often more affected than distance vision.
Contributory Factors
Can be a complication of conditions such as chronic uveitis, steroid administration, vitreoretinal surgery, external eye trauma, and systemic conditions like diabetes mellitus.
Glare Disability
Central location of PSC can lead to severe glare disability.
Irregular Opacities
May present with irregular opacities resembling the surface of the moon.
Anterior Subcapsular Cataract (ASC)
Similar to PSC but located in the front center of the lens, often associated with trauma.
Anterior Polar Cataract (APC)
A small opacity in the anterior capsule of the lens, generally not visually significant and managed without surgery.
Posterior Polar Cataract (PPC)
Characterized by well-demarcated white opacities in the central posterior subcapsular area, complicating surgical removal.
Mixed Cataract
Occurs when more than one type of cataract is present in a lens, typically starting as a pure type.
Traumatic Cataract
Clouding of the lens that may occur due to blunt or penetrating ocular trauma, leading to damage of lens fibers.
Congenital cataract
An opacification of the lens present at birth or shortly after, which can be caused by genetic disorders, metabolic issues, or maternal infections.
Diabetic snowflake cataract
A rapid-onset cataract characterized by grey-white subcapsular opacities, often associated with uncontrolled diabetes.
Hypermature cataract
A dense cataract that obscures the red reflex and contains milky fluid within the capsule due to degeneration of the lens cortex.
Mature cataract
A cataract that is completely opaque, obscuring the red reflex, and can appear white or brunescent.
Immature cataract
A cataract with variable opacification, where some areas of the lens remain clear.
Incipient cataract
A cataract that is visible on examination but has little clinical significance.
Risk factors for cataract development
Factors that increase the likelihood of cataract formation, including diabetes, steroid use, UV exposure, smoking, and nutritional deficiencies.
Posterior lenticonus
A condition associated with unilateral congenital cataracts, characterized by a conical shape of the posterior lens.
Morgagnian cataract
A specific type of hypermature cataract where the nucleus sinks within the fluid cortex.
Cataract surgery
A painless procedure to restore vision by replacing the clouded lens with a clear artificial lens.
Phacoemulsification
A cataract surgery technique where a small incision is made, and an ultrasonic probe breaks up the cloudy lens.
Intraocular lens (IOL)
An artificial lens implanted in the eye after the removal of the cloudy lens.
Extarcapsular cataract extraction (ECCE)
A surgical method that requires a larger incision to remove the lens in one piece.
Femtosecond Laser-Assisted Cataract Surgery (FLACS)
A technique that uses a laser to assist in cataract surgery, replacing many steps that require a blade.
Capsulotomy
A surgical procedure that involves creating an opening in the capsule that holds the lens of the eye.
Multifocal Intraocular Lens (IOL)
A type of lens that provides correction for both near and distance vision, allowing multiple focal points.
Monofocal Intraocular Lens (IOL)
A lens designed to provide clear vision at one distance, requiring glasses for other distances.
Toric Intraocular Lens (IOL)
A specialized monofocal lens designed to correct astigmatism.
Posterior Capsular Opacification (PCO)
A common complication after cataract surgery where the capsule holding the IOL becomes cloudy, affecting vision.
Yag Laser Capsulotomy
A minimally invasive outpatient procedure using a laser to create an opening in the cloudy capsule to restore clear vision.
Disabling Glare
A visual disturbance often associated with cataracts, particularly posterior subcapsular cataracts, that impairs vision.
Phakic Intraocular Lens
A lens implanted in the eye without removing the natural lens, often used to correct high refractive errors.
Visual Impairment
A decrease in the ability to see that can affect daily activities such as reading and driving.
Surgical Indications
Criteria that determine the need for cataract surgery, including reduced visual acuity and significant visual impairment.
Nuclear Sclerosis
A type of cataract that causes hardening and yellowing of the central part of the lens, affecting distance vision more than near vision.
Diabetic Snowflakes Cataract
A type of cataract associated with diabetes, characterized by snowflake-like opacities in the lens.
Subcapsular Cataract
A type of cataract that forms under the lens capsule, often associated with steroid use or diabetes.
Penetrating Trauma
An injury that disrupts the lens capsule, potentially leading to cataract formation.
Retro-illumination
A diagnostic technique used to visualize cataracts by shining light through the lens.