Lecture 13 - Carbon
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
Two main forms of Carbon
Organic and Inorganic
Inorganic Carbon
• Main reservoir is in atmosphere in form of Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
Dissolving CO2 gas in water can result in a variety of forms • Carbon dioxide, carbonic acid, bicarbonate and carbonate
• Bicarbonate Equilibrium
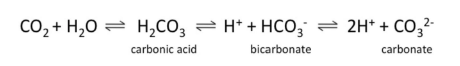
Inorganic Carbon - pH
Amount of carbon forms depends on pH (H+ ions) • Determines acid neutralizing or buffering capacity • Greater dissolved bicarbonate = greater buffering capacity
• Increase in CO2 in atmosphere is increasing acidity of aquatic ecosystems
Organic Carbon
Carbon chains bonded with other elements • Usually hydrogen and oxygen • Can be particulate or dissolved
Particulate Organic Carbon
• Particulate further divided into fine particulate (FPOM) and coarse particulate (CPOM)
• Particulate can be living or dead organic material
• Key source of food for heterotrophic organisms
Dissolved Organic Carbon
• Two major classes • Humic vs Non-humic
• Humic – by-products of breakdown of cellulose, tannins and lignins
• Non-humic – sugars, carbohydrates, amino acids, etc. → broken down by heterotrophs to yield humic compounds
Transformation of Carbon
Cycling of carbon dominated by photosynthesis and respiration
• Formation of Organic Carbon
Photosynthesis - CO2 + H2O + light energy → CH2O + O2
• Breakdown of Organic Carbon • Respiration - CH2O + O2 → CO2 + H2O + chemical energy
• involves oxidation of large organic molecules (most efficient)
• Carbon cycling can also involve •Anaerobic processes
• Oxidation with other molecules (e.g., nitrate and sulfate)
• Fermentation
• Methanogenesis