public goods and common resources
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
definition of excludability?
People who don’t pay can be easily prevented from using a good
definition of rival in consumption?
The same unit of the good cannot be consumed by more than one person at a time (or at all)
definition of non excludable?
People who don’t pay cannot be easily prevented from using a good
definition of nonrival?
More than one person can consume the same unit of the good at the same time
what are the four types of goods?
1. Private goods are excludable and rival in consumption. Eg: wheat that you buy. Membership at MCC
2. Public goods are nonexcludable and nonrival in consumption. Eg: public sewer system, streetlights, ….
3. Common resources are goods that are nonexcludable but rival in consumption. Eg: water in a public well, fruit in a public forest, parking (free).
4. Artificially scarce goods are excludable but nonrival in consumption. Eg: on-demand movies on Amazon Prime, ground entry in Wimbledon.
why can markets only supply private goods efficiently?
Markets cannot supply goods and services efficiently unless they are private goods which are excludable and rival in consumption.
what are the features of a private good?
Provider can charge a price for the good, so that he is at his optimum. Consumers will be willing to pay as much as the good is of value to them.
what is an artificially scarce good?
is a good that is excludable but nonrival in consumption. Example: on-demand movies
why are artificially scarce goods bad?
because it is excludable, sellers charge a positive price, which leads to inefficiently low consumption
leads to inefficiently low consumption
show a graph for a artificially scarce goods?
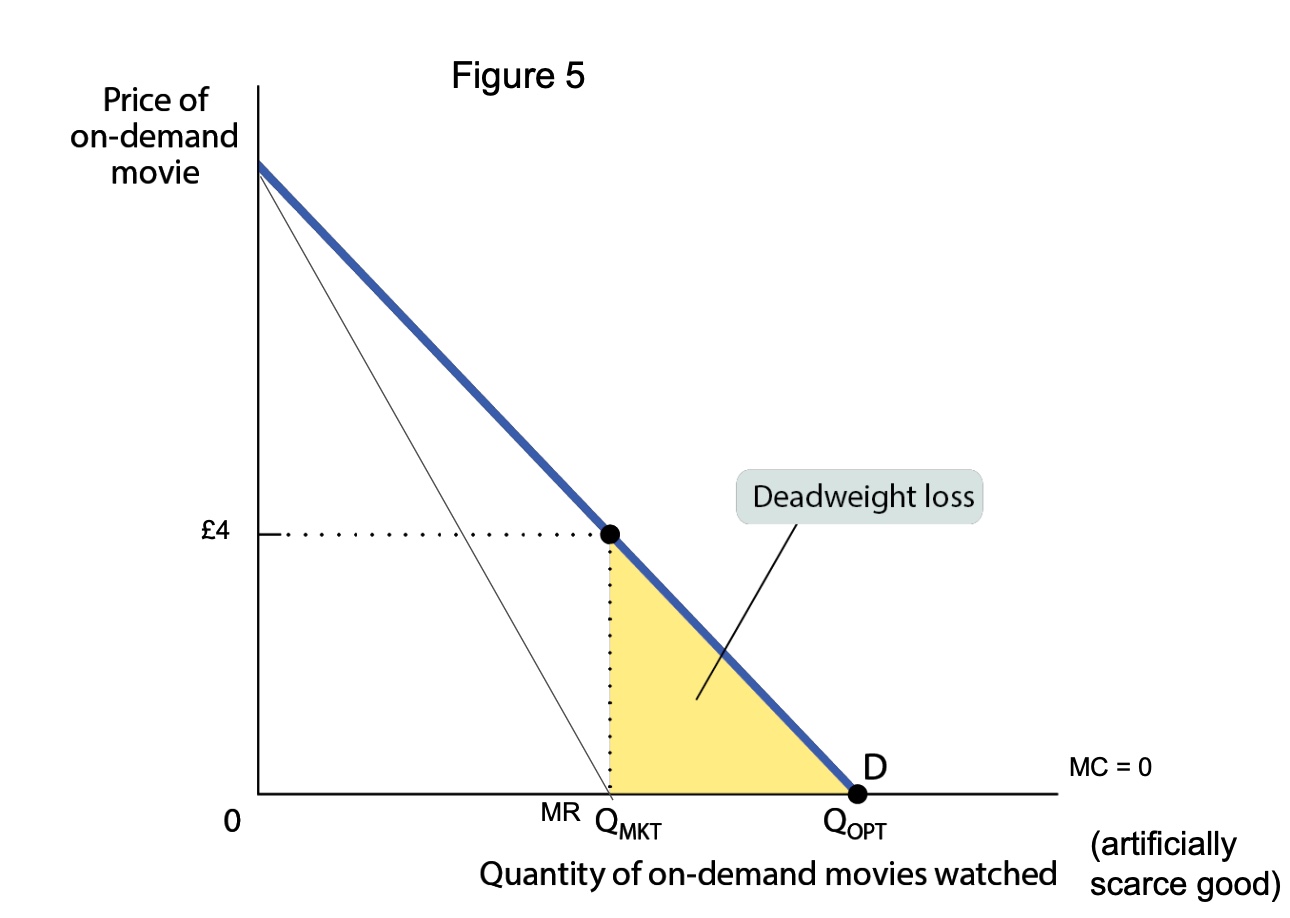
what is the free-rider problem?
many individuals are unwilling to pay (incur the cost) for consumption of nonexcludable goods and instead will take a “free ride” on anyone who does pay
what do non-excludable goods suffer from?
inefficiently low production - they are undersupplied
what is a public good?
is a good that is both nonexcludable and nonrival in consumption
what do public goods suffer from?
free-rider problem
non-rival consumption, it is inefficient to charge people for consuming them
if the government provides the public good, how much should it produce?
Produce the quantity where marginal social benefit of a public good equals marginal cost of producing it.
what does the marginal social benefit of a public good equal?
the sum of individual marginal benefits enjoyed by all consumers
what is the efficient quantity of a public good?
the quantity at which the marginal social benefit is equal to the marginal cost of providing it
is the marginal social benefit of one more unit of a public good always greater than the individual marginal benefit?
yes