Functional groups
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
alkAnes
default (just C-H's) - methane (cooking fuel)
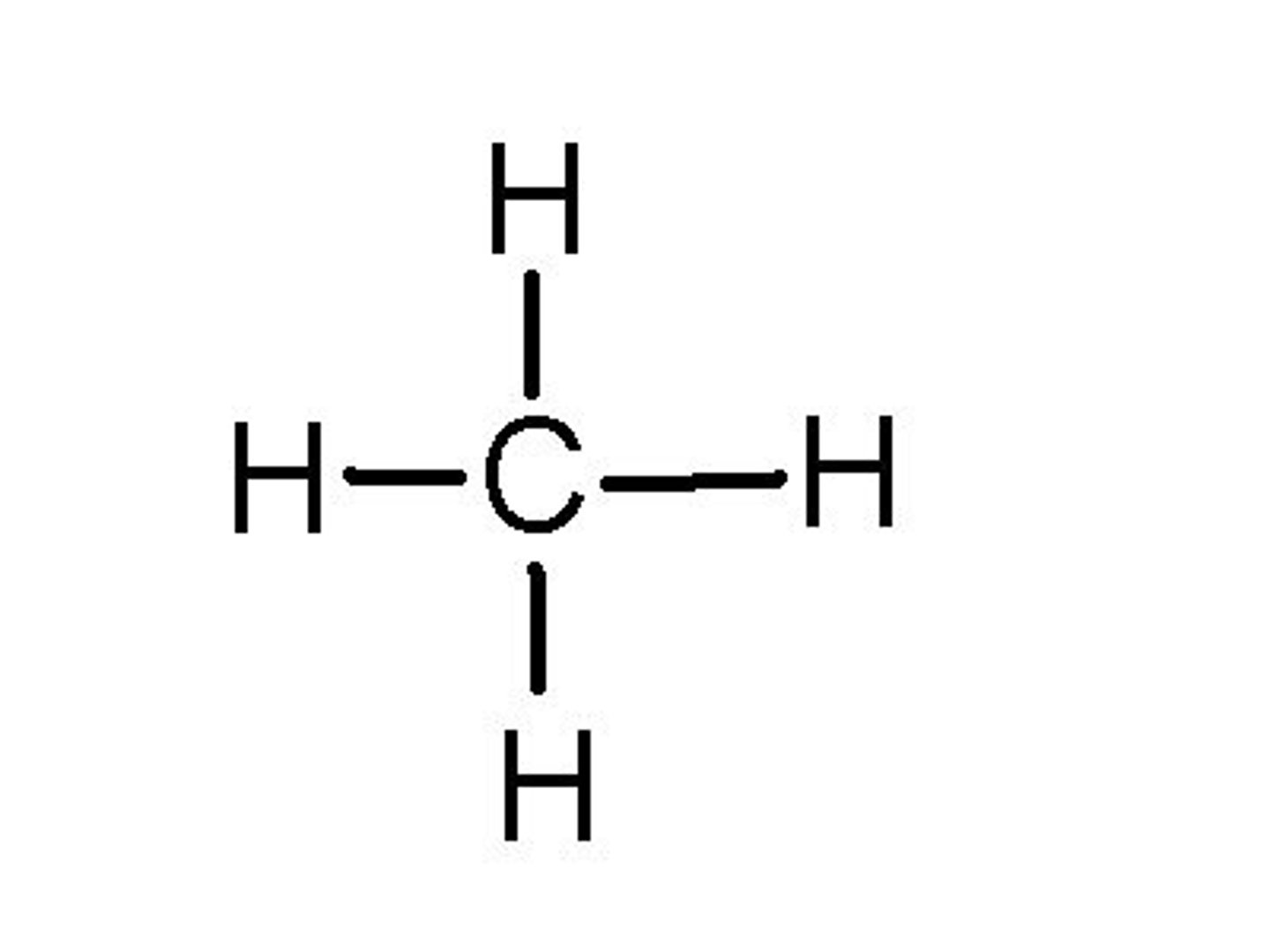
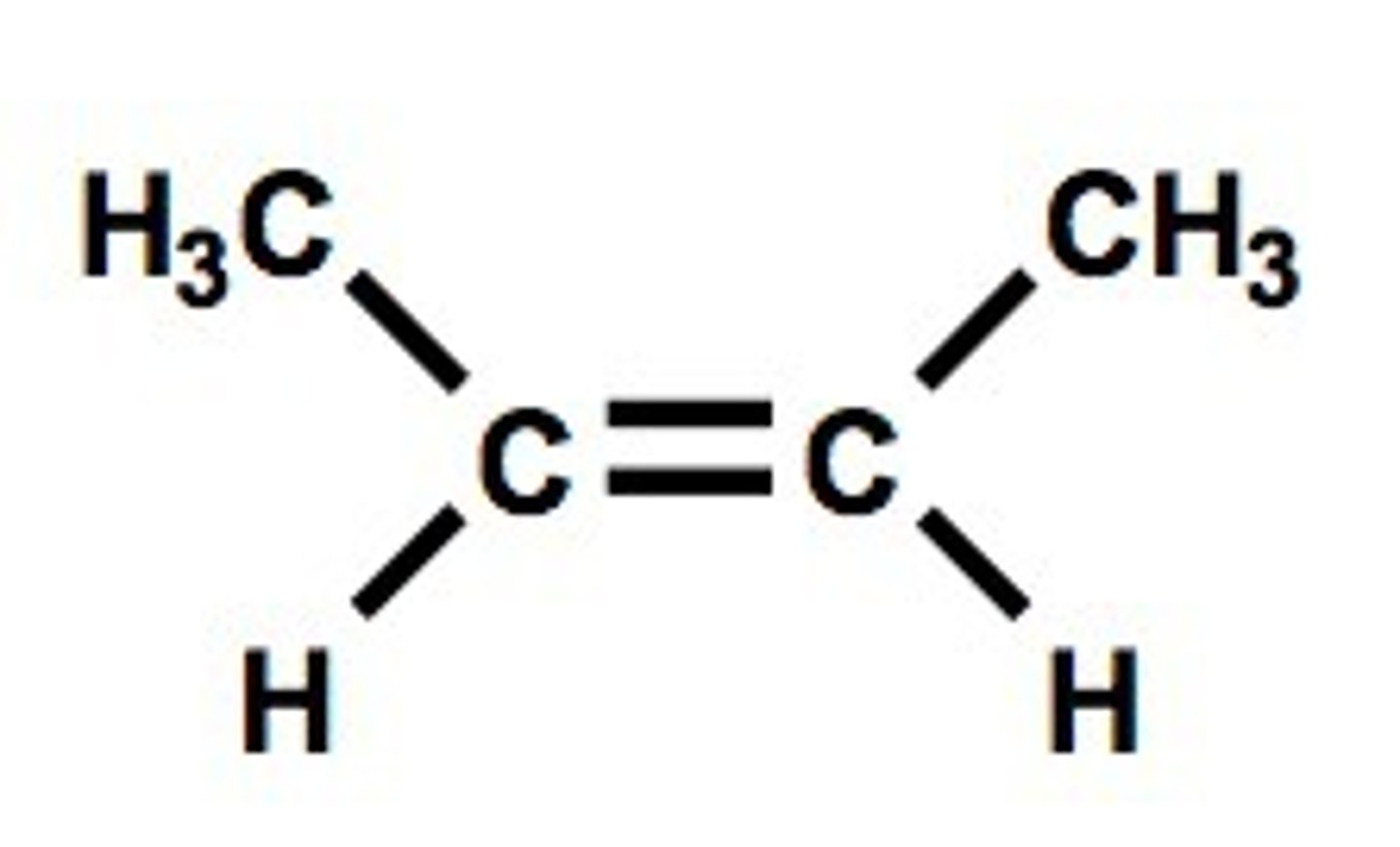
alkEnes
carbon- carbon double bonds (butene- plastic production)
alkYnes
carbon- carbon triple bonds
(propyne- fuel)
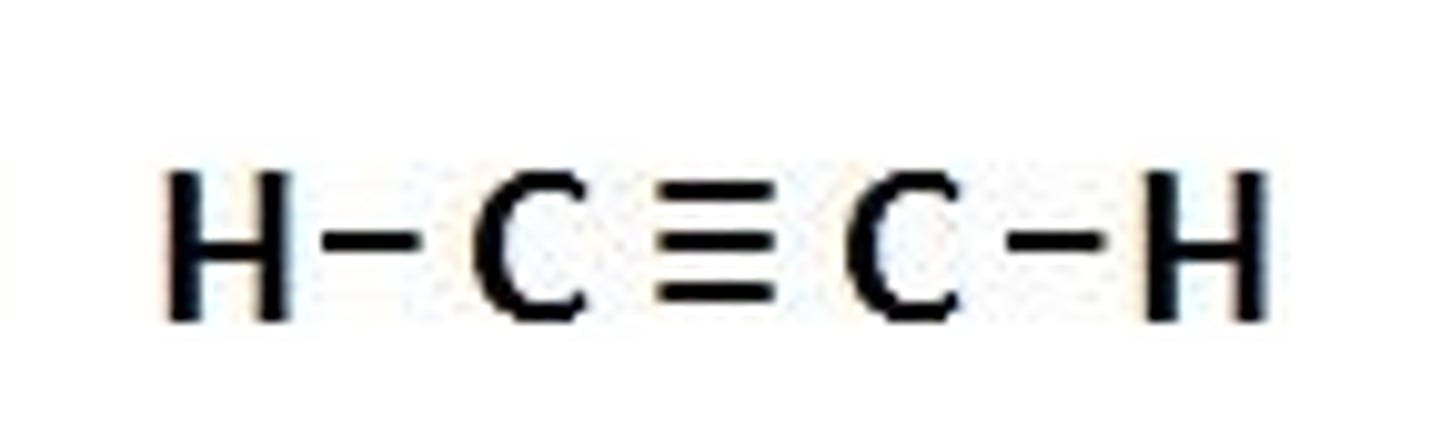
cis- trans isomers
stereoisomers that have the same molecular formula and sequence of bonded atoms, but they differ in the spatial arrangement of their atoms.
- cis means same
- trans means opposite
Example : Trans-2-butene: with two methyl groups
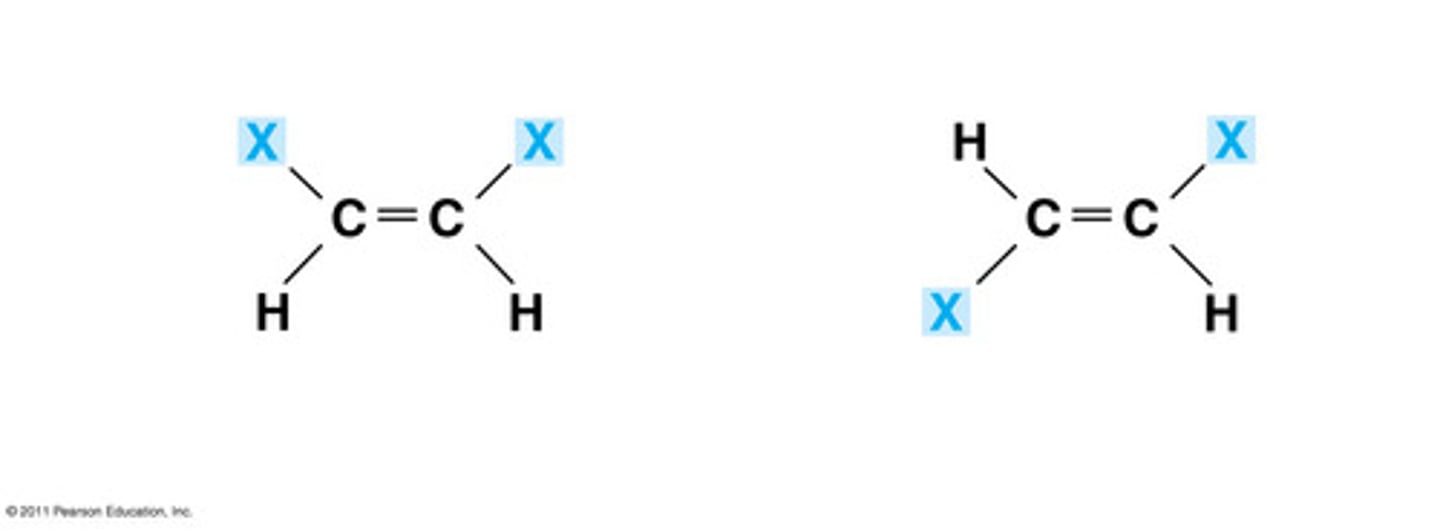
cis- trans isomers - geometric
rotation around a double bond is not possible - only when you have alkenes (double bonded carbon)
exsample: Trans-2-butene: with two methyl groups
cycloalkene
cyclic hydrocarbon that contains a carbon-carbon double bond within the ring structure.
exsample-
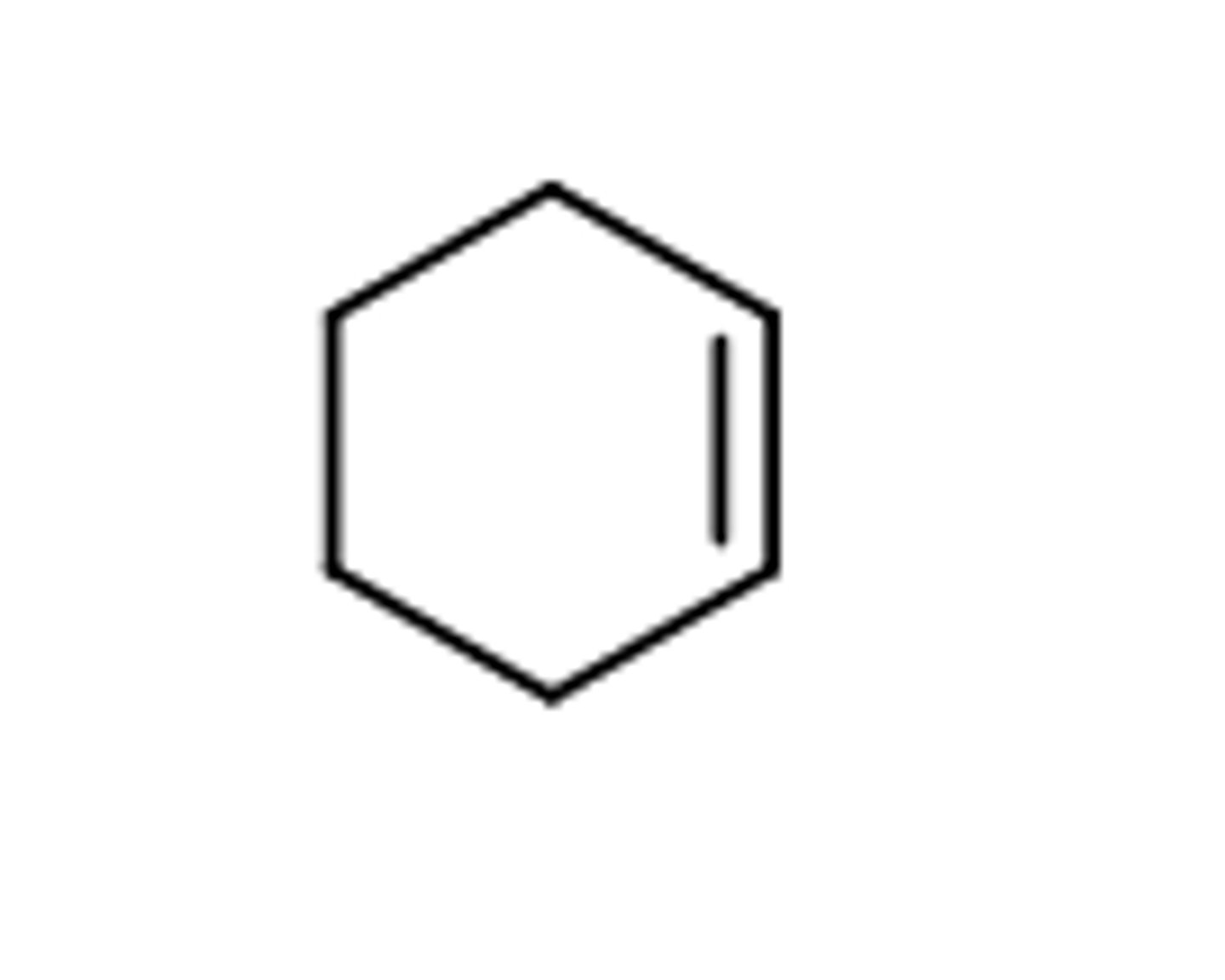
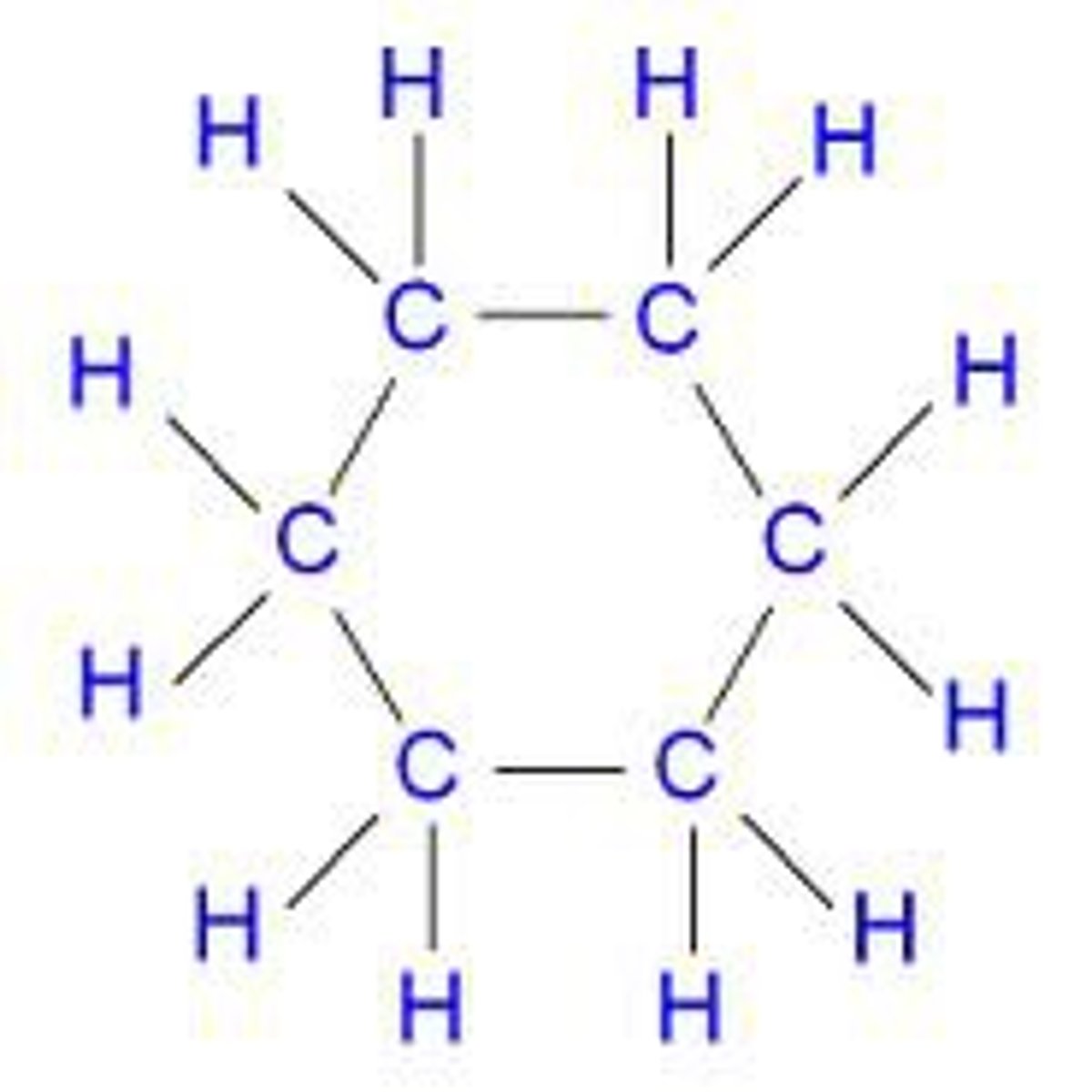
cycloalkane
cyclic (ring-shaped) saturated hydrocarbons, meaning they consist of carbon and hydrogen atoms arranged in a ring with only single bonds between the carbon atoms.
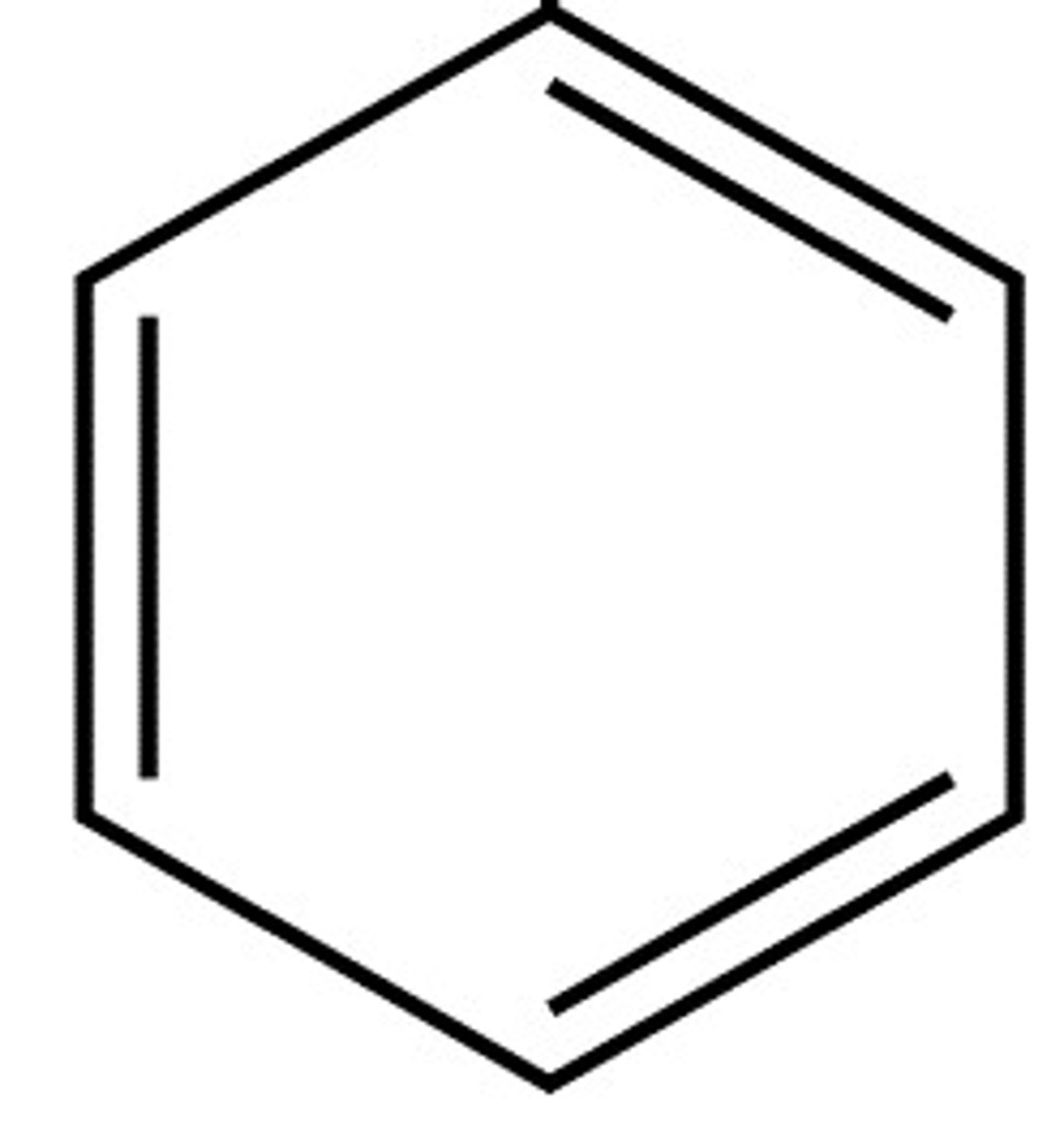
Aromatric
alternating double bonds (benzene- plastic production)
alkyl halides
alkanes with halides
- carbon chain where one or more hydrogen atoms in an alkane are replaced by halogen atoms (fluorine, chlorine, bromine, or iodine)
exsample: bromoethane
- used to make pharmaceuticals
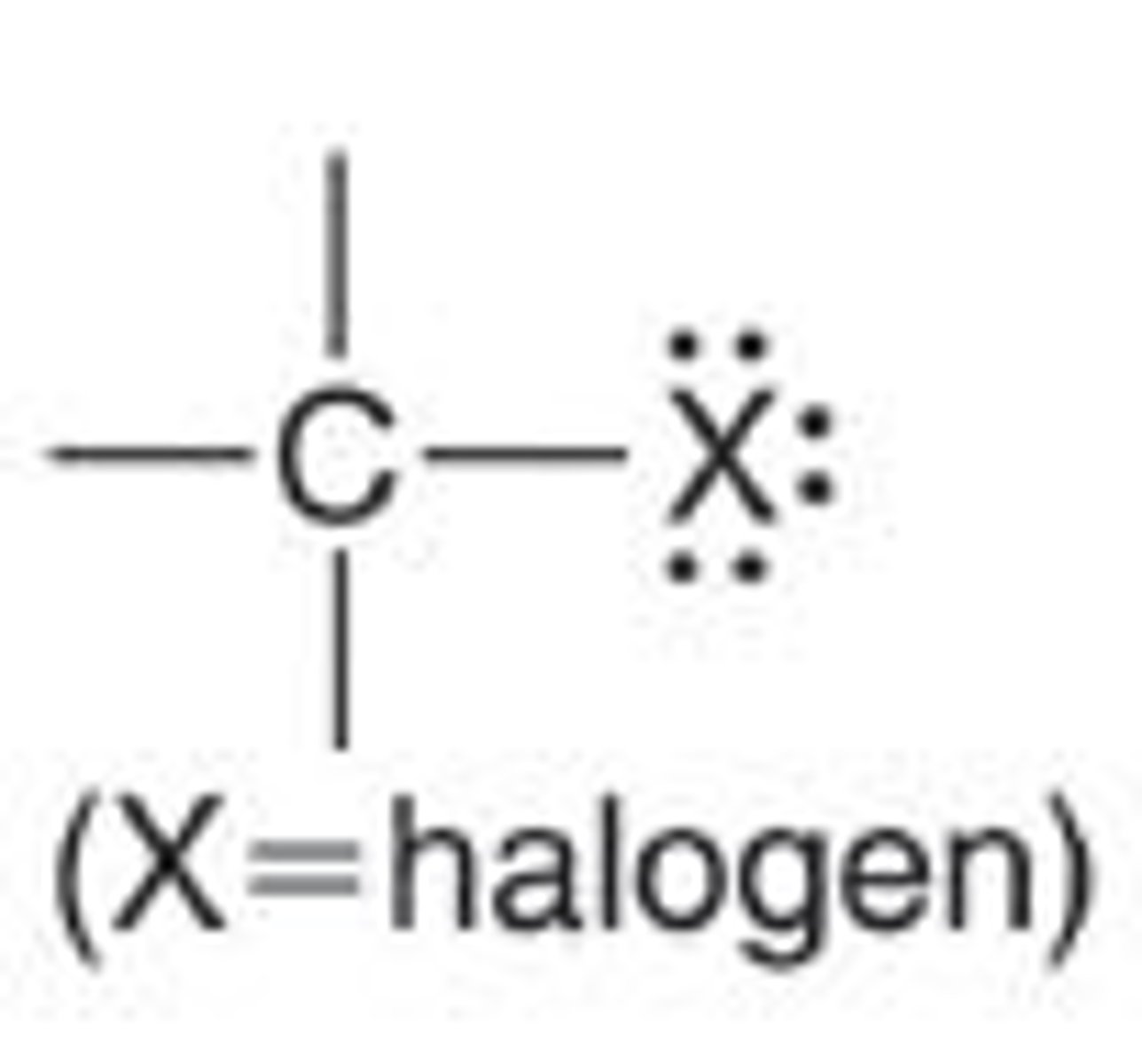
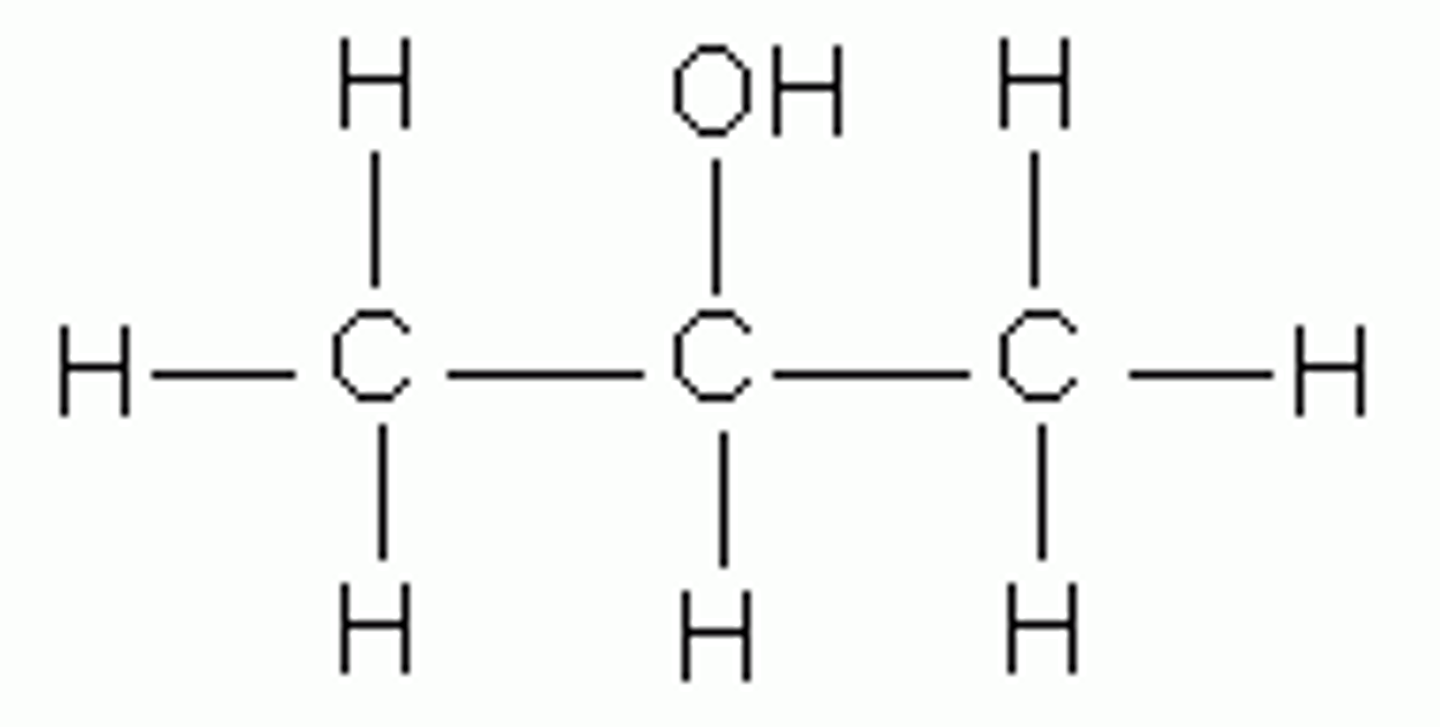
Alcohols
OH bond to carbon
- ethanol ( fuel)
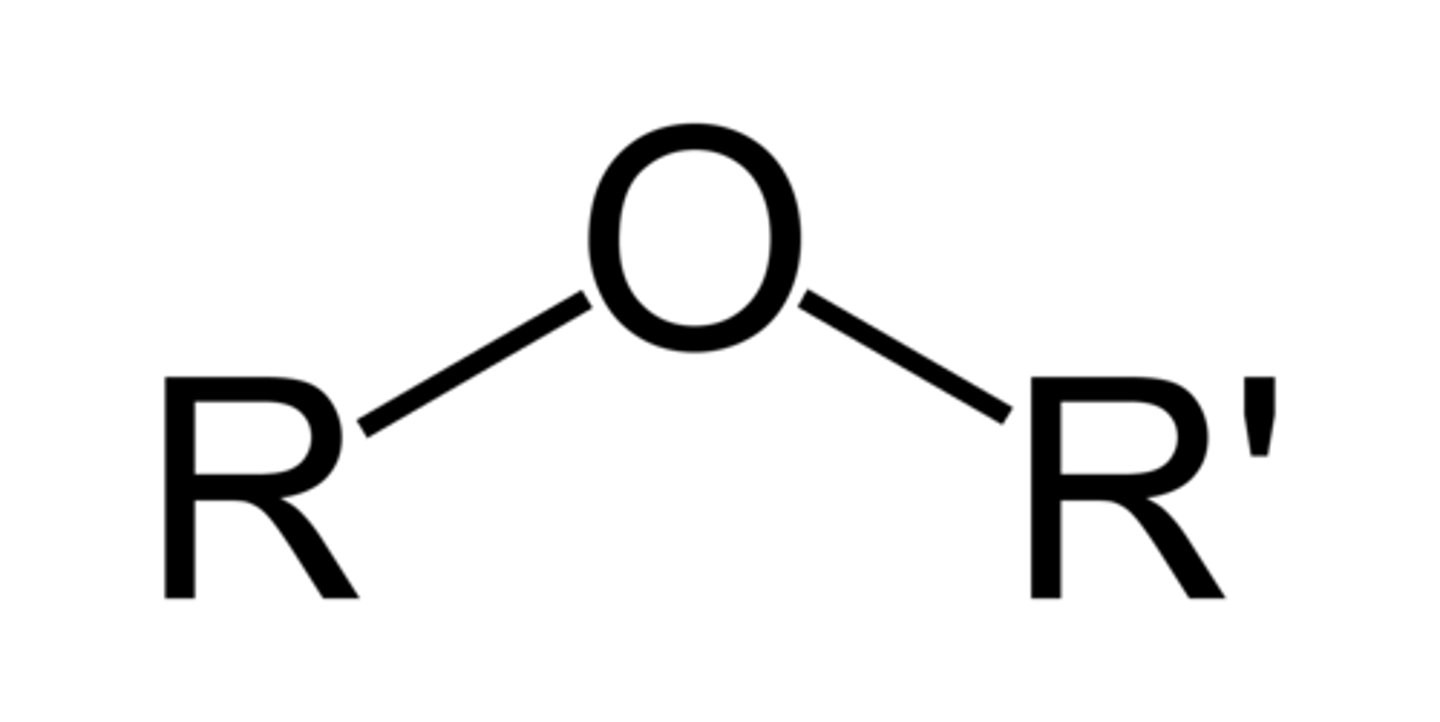
Ethers
bringing oxygen bond
- dimethyl (medication)
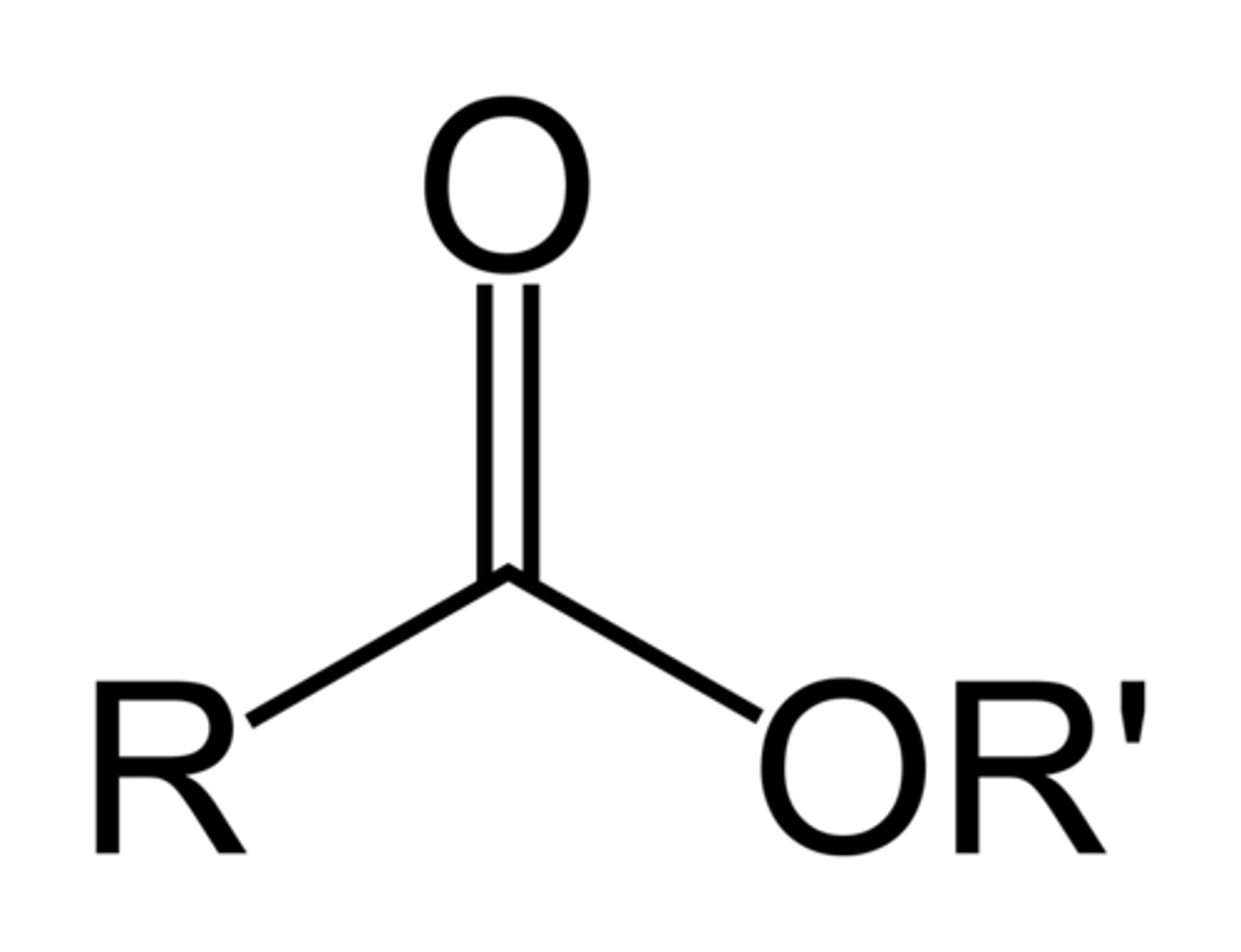
Ester
acid+ alcohol
- propyl methanoate (flavoring agent)
aldehydes
- terminal carbon :the carbonyl group (carbon double bonded to oxygen ) is attached to a carbon atom within the carbon chain
ex: formaldehyde (preservative)
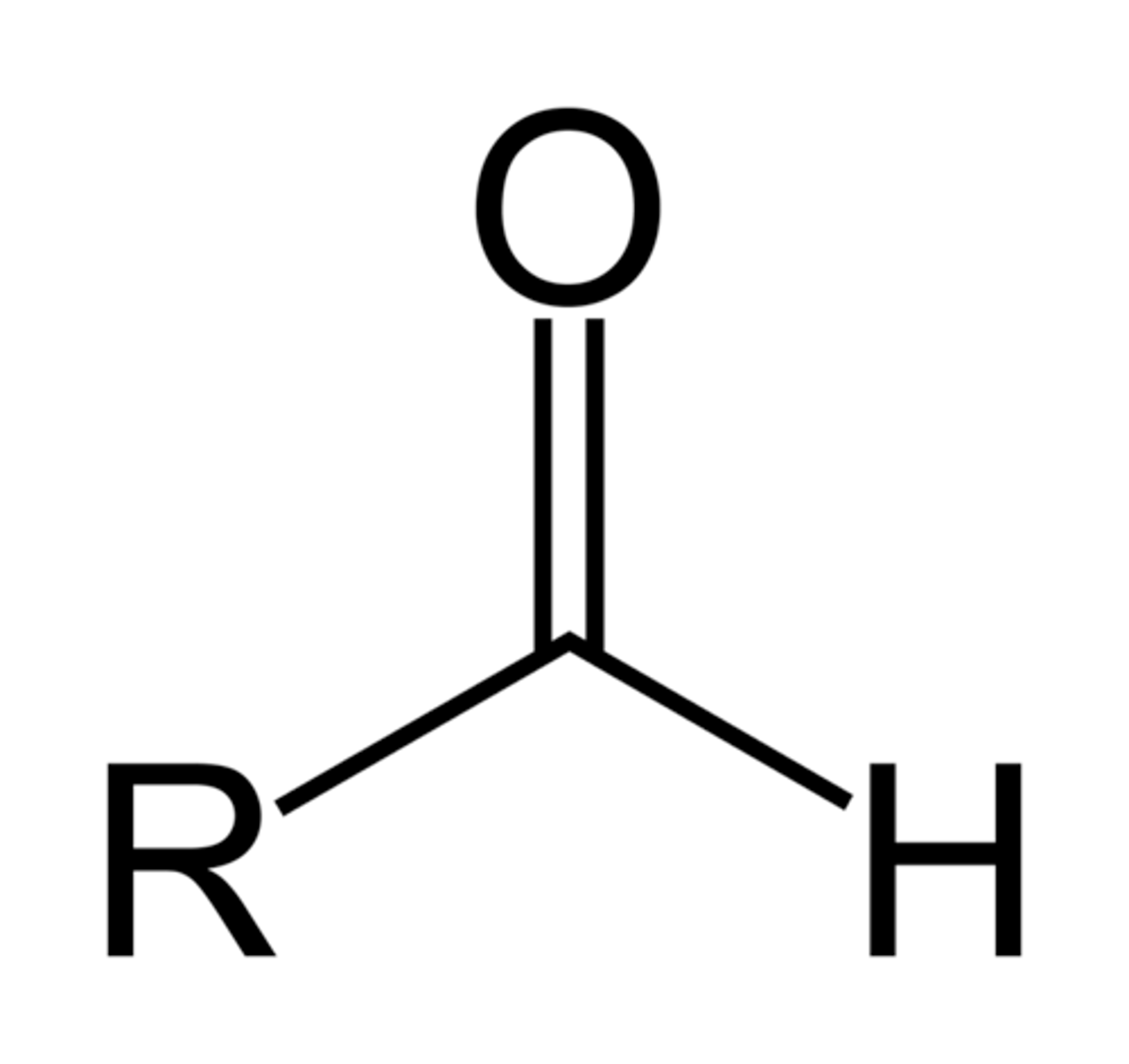
ketones
(C=O) bonded to two carbon atoms
ex- acetone
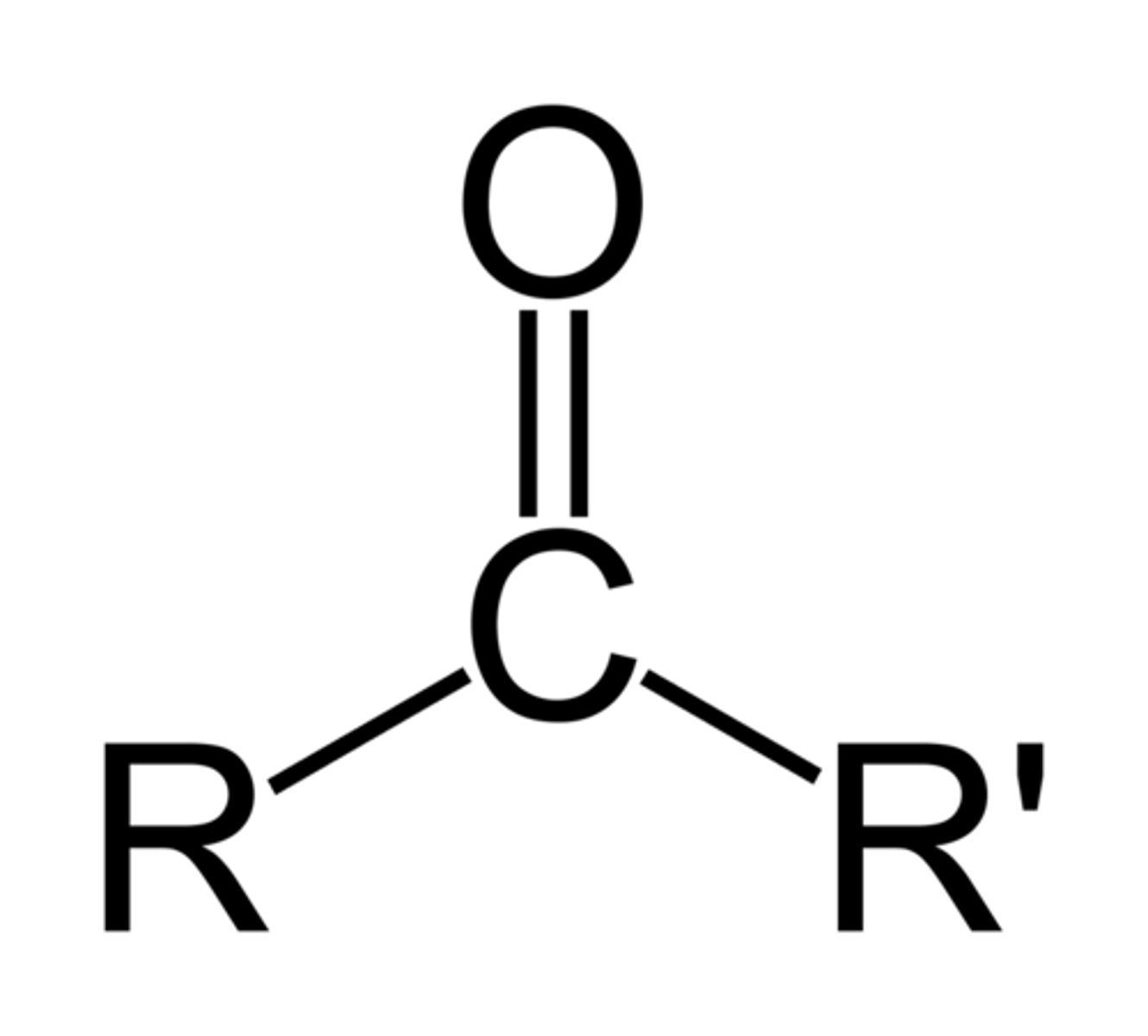
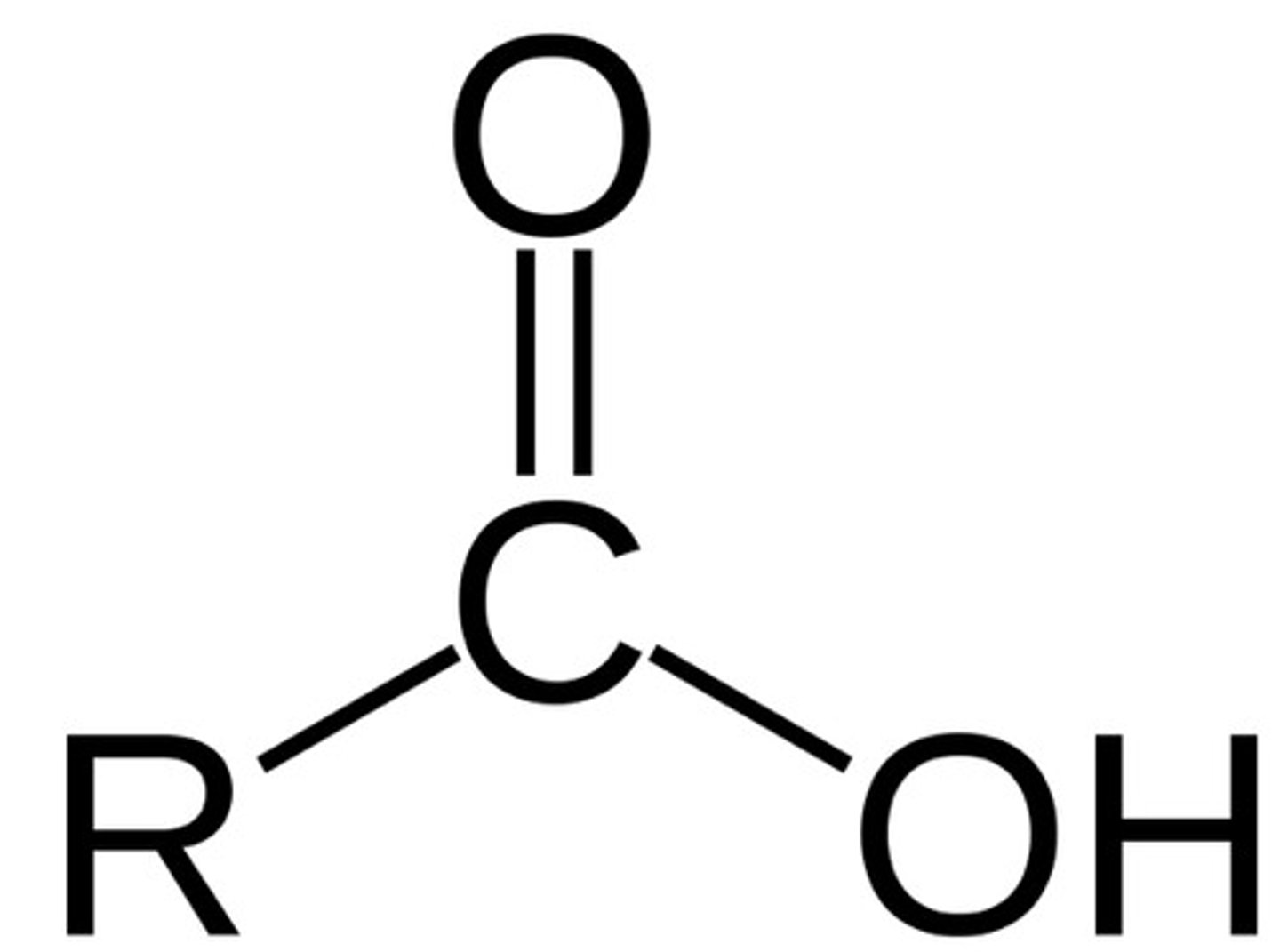
carboxylic acid
(-COOH)
ex: amino acid (building block of protiens)
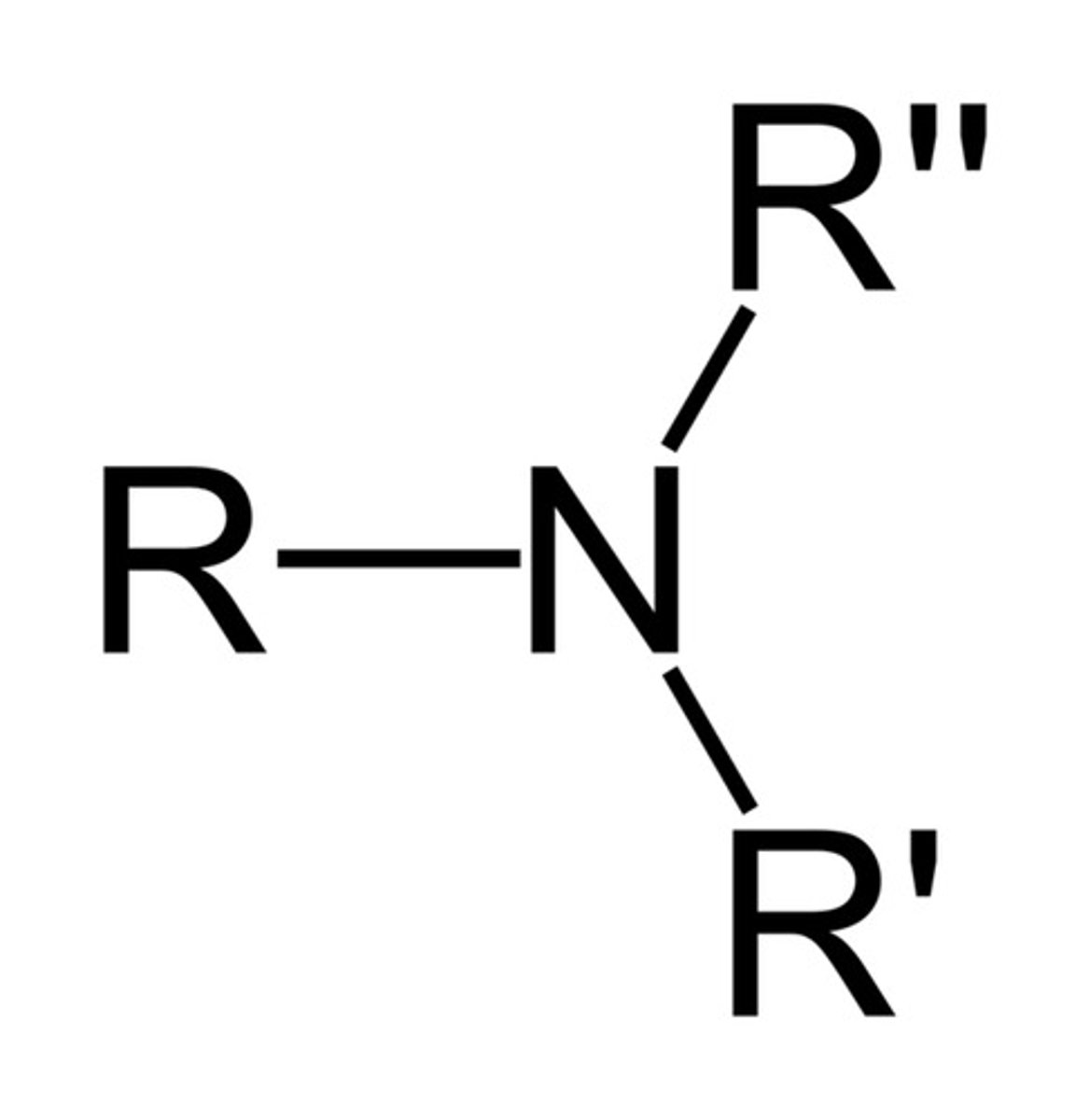
amine
n-c and n-h bonds (nitrogen lone pair
ex ammonia (fertilizer)
ammonium
amine + protons
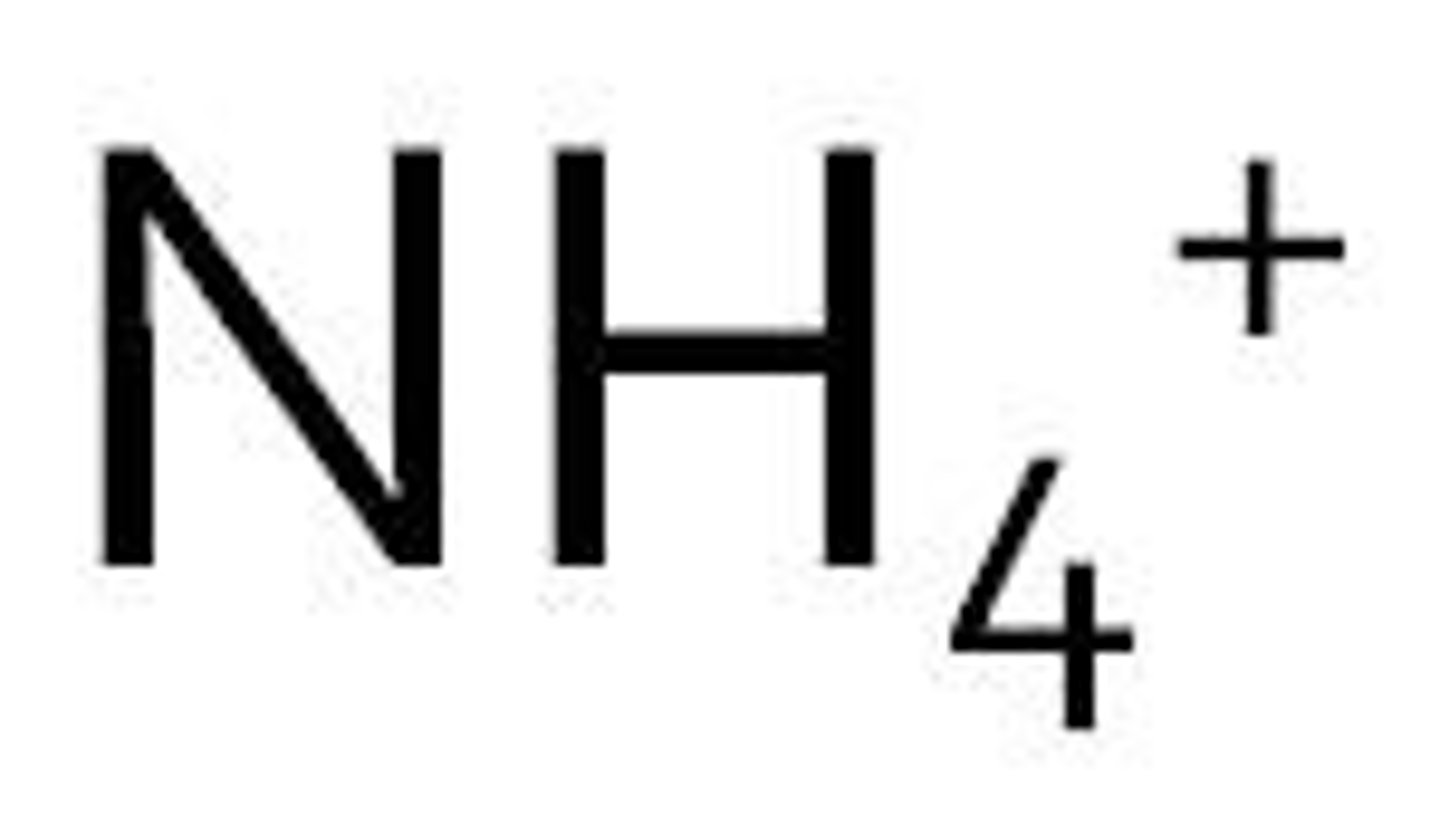
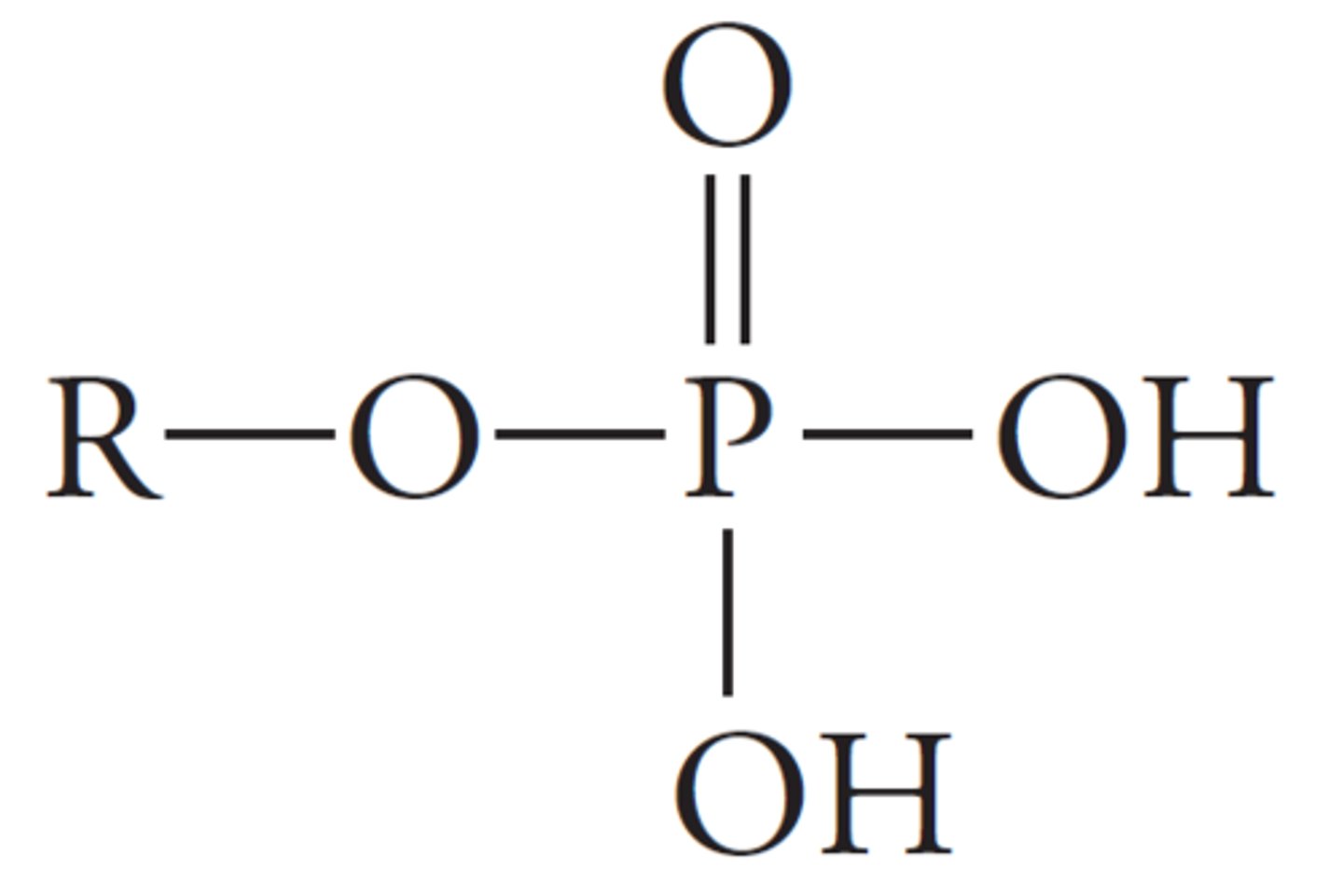
phosphate derivatives
phosphorus atom bonded to four oxygen atoms, where one of those oxygen atoms is also bonded to another atom.
ex DNA