Physiology Exam 4 Module 12 (Respiratory System)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
1
New cards
oxygen, CO2
•The main function of the respiratory system is to ***supply the body tissues with ____*** ***and dispose of*** ***____*** generated by cellular metabolism.
2
New cards
ventilation
•Respiration includes:
1\.Pulmonary ________ (exchange of air between atmosphere and alveoli)
3
New cards
external, internal
2\. Gas exchange
•_______ respiration (movement of O2 from lungs into blood; CO2 from blood to lungs)
•_________respiration (movement of O2 from blood into tissue cells; CO2 from cells into blood) (relates to circulatory)
•_______ respiration (movement of O2 from lungs into blood; CO2 from blood to lungs)
•_________respiration (movement of O2 from blood into tissue cells; CO2 from cells into blood) (relates to circulatory)
4
New cards
alveoli
tiniest structure of lungs?
5
New cards
larynx
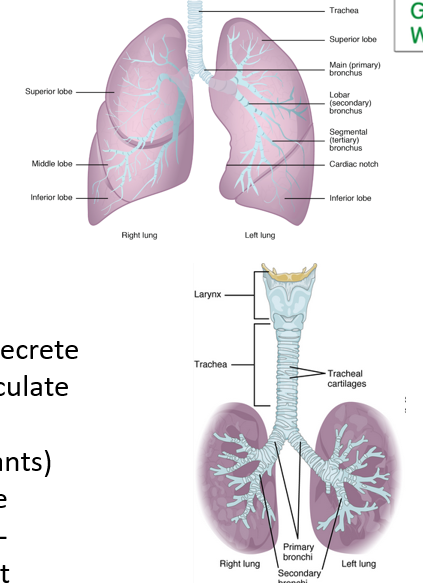
upper airway:
Air comes in and travels to ______-(where vocal cords are)
Air comes in and travels to ______-(where vocal cords are)
6
New cards
alveoli
Airway ends in alveolar sacs
__**_______**__**:** sites of gas exchange with the blood
7
New cards
respiratory
zones:
•________ zone (where the gas exchange happens)
•Conducting zone (everything else)… Particulates (dust, foreign contaminants) stick to mucus in the conducting zone
•________ zone (where the gas exchange happens)
•Conducting zone (everything else)… Particulates (dust, foreign contaminants) stick to mucus in the conducting zone
8
New cards
cilia
•Epithelial surfaces contain ***______*** that secrete mucus and keeps lungs clear of particulate matter
9
New cards
37
•Air is __ degrees (Celsius) in respiratory zone – temperature and moisture is constant
10
New cards
capillaries
•The alveoli are tiny, hollow sacs supplied by ***________***
•Size of the Surface area of alveoli in contact with capillaries is big
•Allows for **quick** diffusion
11
New cards
epithelial
•***Type I alveolar cells***: flat _______ cells forming a continuous layer.
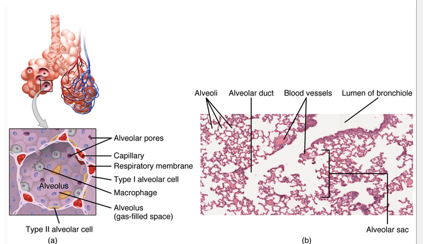
12
New cards
surfactant
•*Type II alveolar*: specialized cells that produce ***________***.
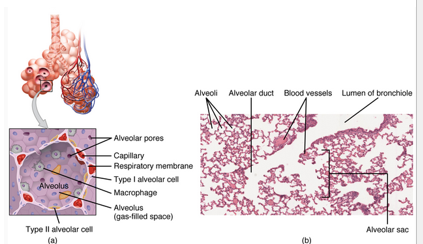
13
New cards
thorax
lungs & diaphragm
•Respiratory system is located in the _______
•Neck to diaphragm
•Wall of thorax includes intercostal (between the ribs) muscles
•Respiratory system is located in the _______
•Neck to diaphragm
•Wall of thorax includes intercostal (between the ribs) muscles
14
New cards
volume
•Lungs
•Passive, elastic structures whose ________fluctuates
•Volume depends on difference in pressure inside and outside of lungs
15
New cards
boyles
•**______ law:** pressure in alveoli (intrapulmonary) decreases below atmospheric-air will move from atmosphere to alveoli, high to low pressures
16
New cards
atmospheric
4 pressure types
\
•All pressures are relative to ***______pressure*** (760 mmHg at sea level) Patm(the air that surrounds the body)
•Volume of lungs is made to change through Boyle’s Law. An inversely proportional relationship between pressure & volume. (i.e. increasing V, reduces P & vice versa)
•P1V1=P2V2
17
New cards
alveolar
4 pressure types
\
•***Intra-________ pressure (Intrapulmonary aka inside the lungs)*** changes to drive the movement of air.
•Palv is the pressure in the alveoli.
\
•***Intra-________ pressure (Intrapulmonary aka inside the lungs)*** changes to drive the movement of air.
•Palv is the pressure in the alveoli.
18
New cards
inspiration
•Palv is less than Patm = _______
19
New cards
expiration
•Palv greater than Patm = _________
20
New cards
intrapleural
4 pressure types
**________: pressure in pleural space, Pip**
•It fluctuates with breathing, but it is always less than Palv (or intrapulmonary).
**________: pressure in pleural space, Pip**
•It fluctuates with breathing, but it is always less than Palv (or intrapulmonary).
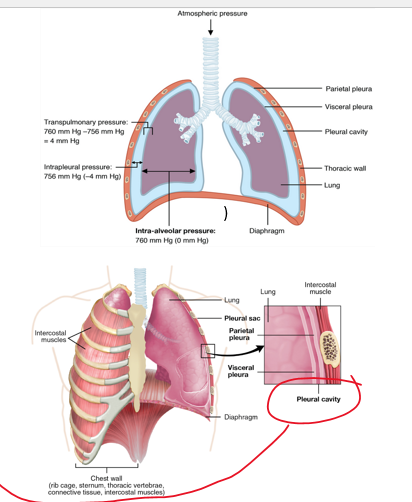
21
New cards
transpulmonary
4 pressure types
\
**_______: holding lungs open Ptp=Palv- Pip**
•Difference in pressure allows lungs to stick to the chest wall (keeps them in place)
\
**_______: holding lungs open Ptp=Palv- Pip**
•Difference in pressure allows lungs to stick to the chest wall (keeps them in place)
22
New cards
may need to rewatch part of the video on this
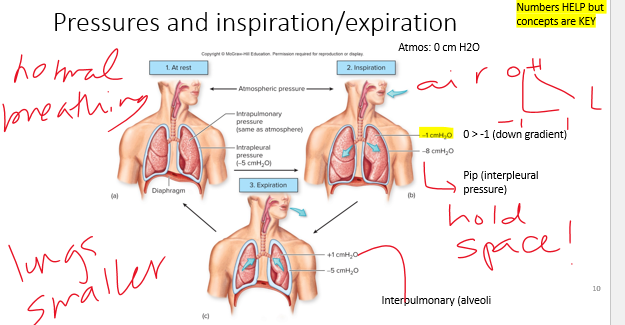
23
New cards
motor
inspiration vs expiration
inspiration:
•Movement of air from external environment into alveoli of the lungs
•Initiated by skeletal muscle & ***______ neurons*** firing action potentials to ***intercostal muscles*** (between ribs) and diaphragm (flattens @ base of thoracic cavity)
inspiration:
•Movement of air from external environment into alveoli of the lungs
•Initiated by skeletal muscle & ***______ neurons*** firing action potentials to ***intercostal muscles*** (between ribs) and diaphragm (flattens @ base of thoracic cavity)
24
New cards
diaphragm
inspiration vs expiration
Inspiration:
•***__________*** contracts and provides the most important inspiratory muscle
Inspiration:
•***__________*** contracts and provides the most important inspiratory muscle
25
New cards
active
inspiration vs expiration
•Enlarging thoracic cavity allows lungs to enlarge and cause increase in size of alveoli (nervous, muscular)
•_____ movement
•Enlarging thoracic cavity allows lungs to enlarge and cause increase in size of alveoli (nervous, muscular)
•_____ movement
26
New cards
decrease
inspiration vs expiration
expiration
* Air from alveoli to external environment
* Motor neurons ***_____ action potentials*** to diaphragm and intercostals, muscles relax
expiration
* Air from alveoli to external environment
* Motor neurons ***_____ action potentials*** to diaphragm and intercostals, muscles relax
27
New cards
passive
inspiration vs expiration
* Air in alveoli gets compressed as lungs become smaller, air moves out, Palv > Patm
* _______ movement of lungs
* Air in alveoli gets compressed as lungs become smaller, air moves out, Palv > Patm
* _______ movement of lungs
28
New cards
respiratory
integration & communication of systems
•Receive information regarding ___________ system
•Nervous system processes information and responds
•Muscles move and respiration occurs
•Receive information regarding ___________ system
•Nervous system processes information and responds
•Muscles move and respiration occurs
29
New cards
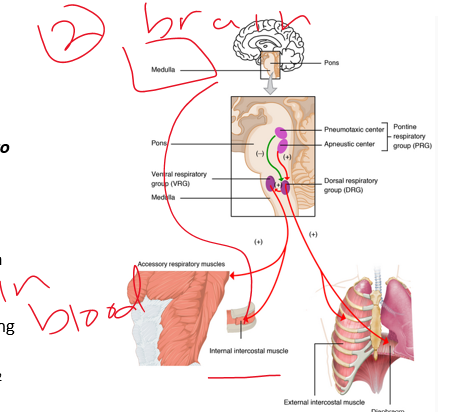
medulla oblongata
neural input
•Respiratory rhythm generated in **_______ _________** Same location for major cardio control centers
•Motor Neurons-Breathing depends on these muscle movements, especially diaphragm
30
New cards
oxygen
receptors
•The carotid bodies are strategically located to ***monitor ______ supply to the brain***
•Called __peripheral chemoreceptor__: responding to changes in H+ concentrations
•Indirectly affects ventilation by affecting chemoreceptor sensitivity to PCO2, PO2 follows changes
•The carotid bodies are strategically located to ***monitor ______ supply to the brain***
•Called __peripheral chemoreceptor__: responding to changes in H+ concentrations
•Indirectly affects ventilation by affecting chemoreceptor sensitivity to PCO2, PO2 follows changes
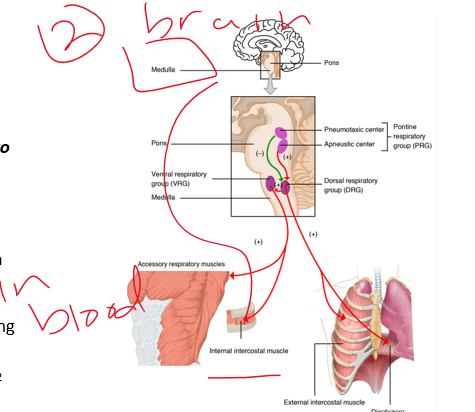
31
New cards
H+
receptors
1\.Know ___
2\.Know Co2 and O2 concentrations
3\.go out to lungs to adjust ventilation (rate)
1\.Know ___
2\.Know Co2 and O2 concentrations
3\.go out to lungs to adjust ventilation (rate)
32
New cards
constant
Input from the receptors modifies rate and depth of breathing so these variables remain ________.
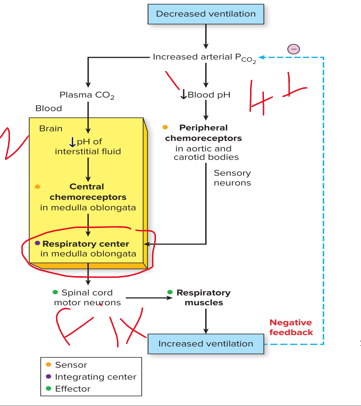
33
New cards
inspiration
•When muscles contract in the chest wall the chest expands - _______
•Diaphragm is contracted downward and the thoracic cavity is large
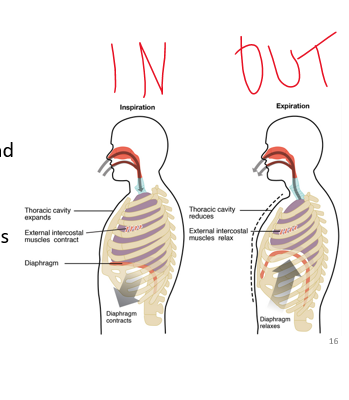
34
New cards
•Opposite occurs for expiration: muscles ______ and the recoil drives passive expiration back out
35
New cards
daltons
partial pressures: proportional to the concentration for that gas
•*_________ Law:* pressure each gas exerts is independent of the pressure of other gases
•The total pressure of the mixture is the sum of the individual, *partial pressures*.
•Written as: Partial pressure of O2 is PO2
pulmonary = lungs
•*_________ Law:* pressure each gas exerts is independent of the pressure of other gases
•The total pressure of the mixture is the sum of the individual, *partial pressures*.
•Written as: Partial pressure of O2 is PO2
pulmonary = lungs
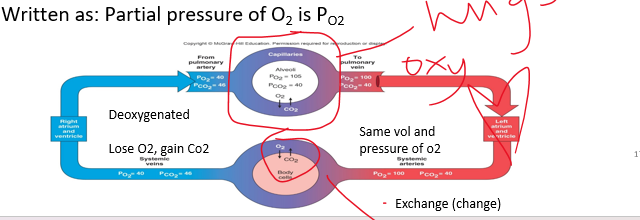
36
New cards
higher
•Alveolar PO2 is ______ than blood, so oxygen diffuses from alveoli into plasma. High to low concentrations
•This induces (simple) diffusion of oxygen to erythrocytes
•Cells obtain more O2 by activity
37
New cards
tissue
\
•During exercise, more O2 is used, decreasing ______ PO2, this increases blood to tissue PO2 gradient.
Oxyhemoglobin: binding oxygen with hemoglobin
Deoxyhemoglobin: produced when oxyhemoglobin releases oxygen
•During exercise, more O2 is used, decreasing ______ PO2, this increases blood to tissue PO2 gradient.
Oxyhemoglobin: binding oxygen with hemoglobin
Deoxyhemoglobin: produced when oxyhemoglobin releases oxygen
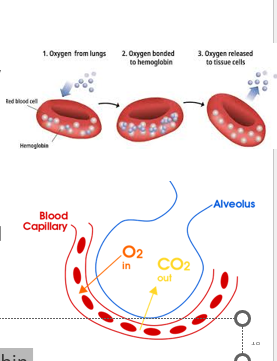
38
New cards
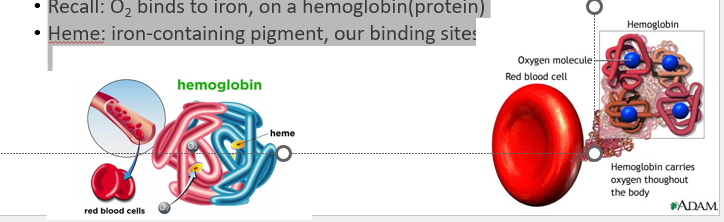
plasma, hemoblobin
Oxygen in blood 2 forms:
•Dissolved in _________ and erythrocyte cytosol (recall no organelles there)
•Combined with _______ molecules in erythrocyte (Majority)
•Recall: O2 binds to iron, on a hemoglobin(protein)
•Heme: iron-containing pigment, our binding sites!
•Dissolved in _________ and erythrocyte cytosol (recall no organelles there)
•Combined with _______ molecules in erythrocyte (Majority)
•Recall: O2 binds to iron, on a hemoglobin(protein)
•Heme: iron-containing pigment, our binding sites!
39
New cards
lungs
•Loading (in the _____ ) & Unloading (systemic):
•(tissues) Deoxyhemoglobin + O –> oxyhemoglobin (lungs)
40
New cards
high
•What affects the movement of oxygen to the hemoglobin (loading)?
•____ PO2 and affinity for pulmonary to capillaries (H to L gradient)
•____ PO2 and affinity for pulmonary to capillaries (H to L gradient)
41
New cards
concentration,ph
\
•What affects the movement of oxygen on the hemoglobin to the tissues (unloading)?
•______ : Systemic tissues are Low in 02 , 02 in capillaries is high
•Affinity – change that lower ___ or create higher temps decrease affinity of 02 on RBC
•Affinity should be sufficient to hold the bond of oxygen to the iron on the hemoglobin but not so high that it prevents unloading (for example if too highly affinity then only 2 O2 , may unload)
•What affects the movement of oxygen on the hemoglobin to the tissues (unloading)?
•______ : Systemic tissues are Low in 02 , 02 in capillaries is high
•Affinity – change that lower ___ or create higher temps decrease affinity of 02 on RBC
•Affinity should be sufficient to hold the bond of oxygen to the iron on the hemoglobin but not so high that it prevents unloading (for example if too highly affinity then only 2 O2 , may unload)
42
New cards
dissolved
Only _________ O2 contributes to PO2 of blood
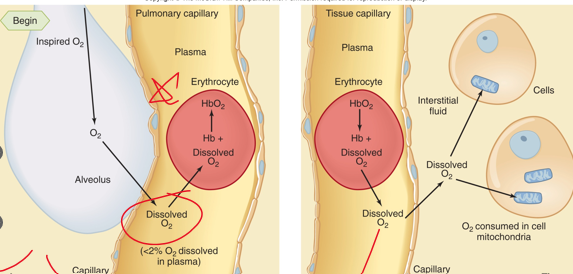
43
New cards
plasma
•CO2 is a waste product, it produces H+ which gives it a toxicity
•H+ in large amounts changes pH
•Forms of transport:
1\.10% dissolves in _____

44
New cards
hemoglobin
2\.Some react with __________
Carbon dioxide binds on the …. to form **carbaminohemoglobin**
Carbon dioxide binds on the …. to form **carbaminohemoglobin**

45
New cards
HCO3-
3\.60-65% is converted to ______, where we get the Hydrogen ions that alter pH levels

46
New cards
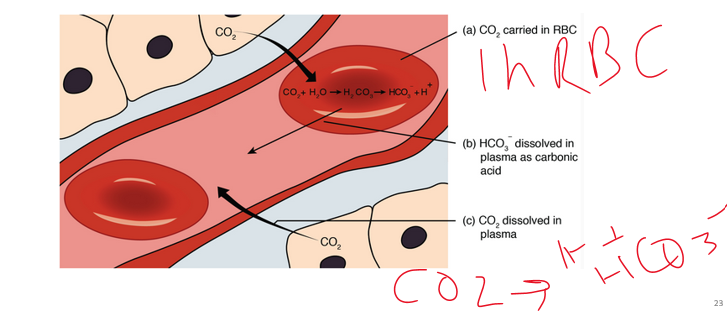
acid
Carbon Dioxide movement in Tissues and lungs
Carbonic anhydrase catalyzes the reaction to form carbonic ______ at high PCO2
Carbonic anhydrase catalyzes the reaction to form carbonic ______ at high PCO2
47
New cards
deoxyhemoglobin
•H+ in red blood cell buffered by __________,
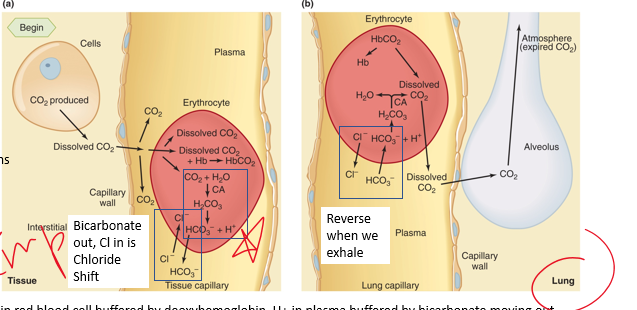
48
New cards
bicarbonate
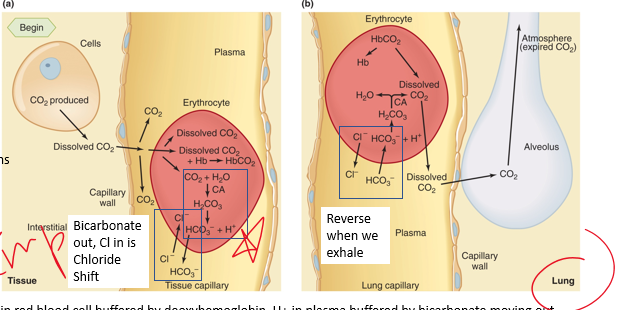
chloride shift:
\
H+ in plasma buffered by _______ moving out
•Bicarbonate builds up in cell, leaves down its gradient
\
\
H+ in plasma buffered by _______ moving out
•Bicarbonate builds up in cell, leaves down its gradient
\
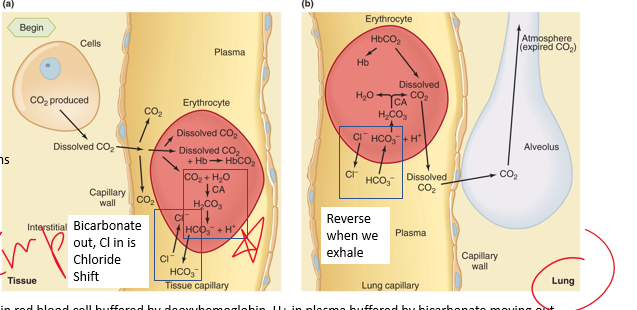
49
New cards
cl-
_________ shift cont
•___ is attracted into cell with movement of bicarbonate and trapping of H+
•___ is attracted into cell with movement of bicarbonate and trapping of H+
50
New cards
7\.35-7.45
•Range for pH of blood: ______ (Homeostasis)
•Maintained through Lungs-CO2 and Kidneys- Bicarbonate
51
New cards
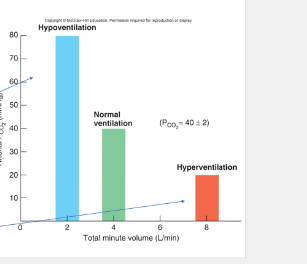
acidosis
**________:** When plasma H+ concentration increases, pH drops below 7.4
•Arterial H+ concentration increased due to carbon dioxide: ***respiratory acidosis***
52
New cards
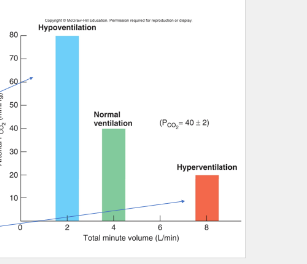
alkalosis
**________:** When plasma H+ concentration decreases, pH rises above 7.4
•***respiratory alkalosis*** results from decreased arterial PCO2 and H+ concentration
53
New cards
hypoventilation
• **____________**
•Low pH, cause of respiratory acidosis
•Alveolar ventilation can’t keep up! Too slow
•High CO2
54
New cards
hyperventilation
• **__________**
•High pH, cause of respiratory alkalosis
•Alveolar ventilation too fast
•Low CO2