Permian mass extinction
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
exam 3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Who was most impacted by the Permian mass extinction?
Shallow marine invertebrates
Mass extinction
episodic events in which large numbers of taxa go extinct simultaneously
What was the greatest known extinction?
The Permian Mass Extinction which occurred 252 MYA
What percent of life died during the Permian mass extinction?
95% of marine life and 70% terrestrial
Which taxa were most devastated by the Permian mass extinction event?
Trilobita, Anthozoa, Crinoidea
The permian mass extinction is also known as ____
The great dying
What is the ancestral coral form?
Rugosa
What are the modern coral form?
Scleractinia
When did Scleractinia diverge?
During the mid-triassic
How long did the ocean go without significant reef builders?
25 million years
The permian mass extinction is also known as the ____
Great dying
What caused the mass extinction event?
Volcanic eruption (299-252 MYA) Permian period
What is the result of the permian mass extinction?
Volcanic emissions of CO2. Halogens and halocarbon compounds expelled. Temporary ozone depletion increasing UVB radiation and acid rain.
Massive wildfires broke out from the volcanism and drought destroying much of plant life
Increase in sea surface temperatures
Ocean acidification
When was the Permian period?
299-252 MYA
When was the Permian mass extinction event?
252 MYA
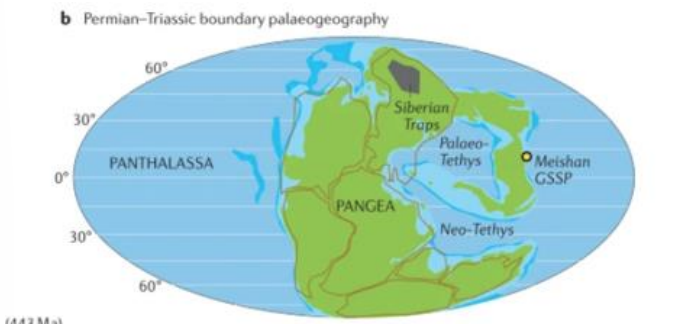
Label the original world
Pangea
Panthalassa
Neo-Tethys/Palaeotethys
Siberian Traps Igneous Province (STIP)
Which organisms were most impacted by the Permian mass extinction event?
Organisms that were at low latitudes, cant run away, have carbonate shells
Where is the site of the volcanic event associated with the permian mass extinction?
The Siberian Traps Igneous Province
What life died out first from the Permian mass extinction event?
Terrestrial life then marine
What is the result of the permian mass extinction?
The eruptions released huge amounts of greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane into the atmosphere. In turn, this triggered global warming which caused a dramatic increase in sea surface temperatures. The rapid warming of the oceans, and ocean acidification over a short period of time resulted in the extinction of marine and terrestrial life.
How much did SST increase and over what period of time?
Increased from 24-30 degrees C to about 35-39 degrees C over 39,000 years
What is the Oceanic Anoxic Event?
The result of the massive volcanic eruption in the Siberian Traps which erupted high quantities of carbon dioxide and sulfur compounds which led to global warming and disrupted ocean circulation. This resulted in anoxic water conditions, oceans were depleted of oxygen, which spread over the majority of the Panthalassa Ocean from the late Permian into the middle Triassic. The water was a hostile environment where most marine organisms could not survive which contributed to mass extinction.
What organisms were vulnerable to the OAE?
Organisms that produced calcium carbonate skeletons or shells. They relied on stable ocean chemistry to build and maintain their calcium carbonate structures, which was compromised leading to their extinction.
What is the cause of metal poisoning in the oceans and why?
Death of organic matter, living organisms are the cause. Living things contain mercury therefore when they die, they release the mercury already contained in their body. Therefore when there was a mass extinction event there was a dramatic increase in mercury to toxic levels in the ocean.
Which groups did well after the permian mass extinction?
Malacostraca
Echinoidea
Chondrichthyes
Osteichthyes
Reptilia
Chordata diverged in the ____
Cambrian
Why do chordata have a difficult ancestry to trace?
Their ancestor was soft bodied therefore their fossil record is not best preserved