Sorting, Graph, Dynamic programming, Searching, Recursion,
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Questions which are related to the title
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
What is recursion?
A function that calls itself to solve a smaller version of the problem.
What are the two cases in a recursive function?
Base case (terminates recursion)
recursive case (function calls itself).
Difference between recursion and iteration?
Recursion uses function calls and stack memory;
iteration uses loops without extra stack overhead.
Give examples of problems solved with recursion
Fibonacci
Factorial
Tree traversals
Graph traversals (DFS/BFS)
Towers of Hanoi."
What is sorting?
Sorting arranges elements of a list in a specific order (ascending or descending).
What is the best complexity possible for comparison-based sorting?
O(n log n).
Name two non-comparison sorting algorithms.
Counting Sort
Radix Sort.
What is a stable sort?
A sorting algorithm that preserves the relative order of equal elements
Which algorithms are recursive and which are not?
Recursive → QuickSort, MergeSort;
Non-recursive → Selection Sort, Insertion Sort."
What is searching in computer science?
The process of finding an item with specified properties in a collection.
Why is searching important?
To retrieve data efficiently from large datasets.
What are the main types of searching algorithms?,
Linear Search
Binary Search
Interpolation Search
Hash-based search."
What is the complexity of Linear Search?
O(n).
What is the complexity of Binary Search?
O(log n) (on sorted data).
What is a graph?
A pair (V, E) where V is a set of vertices and E is a set of edges."
What is the difference between directed and undirected graphs?
Directed graphs have edges with a direction (u→v)
Undirected graphs have bidirectional edges (u,v)."
What is a spanning tree?
A subgraph that connects all vertices with minimum edges and no cycles.
Which algorithm finds the shortest path in a graph with positive weights?
Dijkstra’s Algorithm.
"Which algorithm finds all-pairs shortest path, even with negative weights?
Floyd–Warshall Algorithm.
What is Dynamic Programming (DP)?
A method that solves problems by breaking them into subproblems, storing results to avoid recomputation.
What are the two key properties of DP problems?
Optimal substructure
Overlapping subproblems.
What are the two approaches of DP?
Bottom-up (tabulation)
Top-down (memoization).
Give classic examples of DP problems.
Longest Common Subsequence
Knapsack
Matrix Chain Multiplication
Fibonacci
Bellman-Ford
TSP
How is DP different from Divide & Conquer?
Divide & Conquer solves independent subproblems,
DP handles overlapping subproblems using memoization.
What is the average and worst case of QuickSort?
Average = O(n log n)
Worst = O(n²). Trick → avoid worst case by using random pivot."
What is the time complexity of MergeSort?
O(n log n).
Recurrence → T(n) = 2T(n/2) + O(n).
Trick to quickly compare sorting algorithms?
Insertion → small n, nearly sorted;
MergeSort → guaranteed O(n log n);
QuickSort → fastest in practice but avoid bad pivots;
HeapSort → good for memory-constrained."
How does Binary Search work?
Repeatedly divide sorted array into halves until element is found or interval is empty.
What is the recurrence relation for Binary Search?
T(n) = T(n/2) + O(1) → O(log n)
Trick for choosing searching algorithm?
If array is sorted & static → Binary Search;
if dynamic (many insert/delete) → Hashing or Trees.
What is the recurrence for Fibonacci using recursion?
T(n) = T(n-1) + T(n-2) + O(1) → O(2^n).
How to optimize recursive Fibonacci?
Use Dynamic Programming (memoization) → reduces to O(n).
What is the time complexity of BFS and DFS?
O(V + E).
Trick to remember BFS vs DFS?
BFS = Queue (level order)
DFS = Stack (depth-first).
Which algorithm finds the Minimum Spanning Tree (MST)?
Kruskal (greedy with edges)
Prim (greedy with vertices)
Trick: Prim = Grow a tree
Kruskal = Join forests.
Formula for Longest Common Subsequence (LCS)?
if X[i] = Y[j];
LCS[i][j] = LCS[i-1][j-1] + 1 ;
else max(LCS[i-1][j], LCS[i][j-1]);Trick for recognizing DP problems?
Look for overlapping subproblems and optimal substructure.
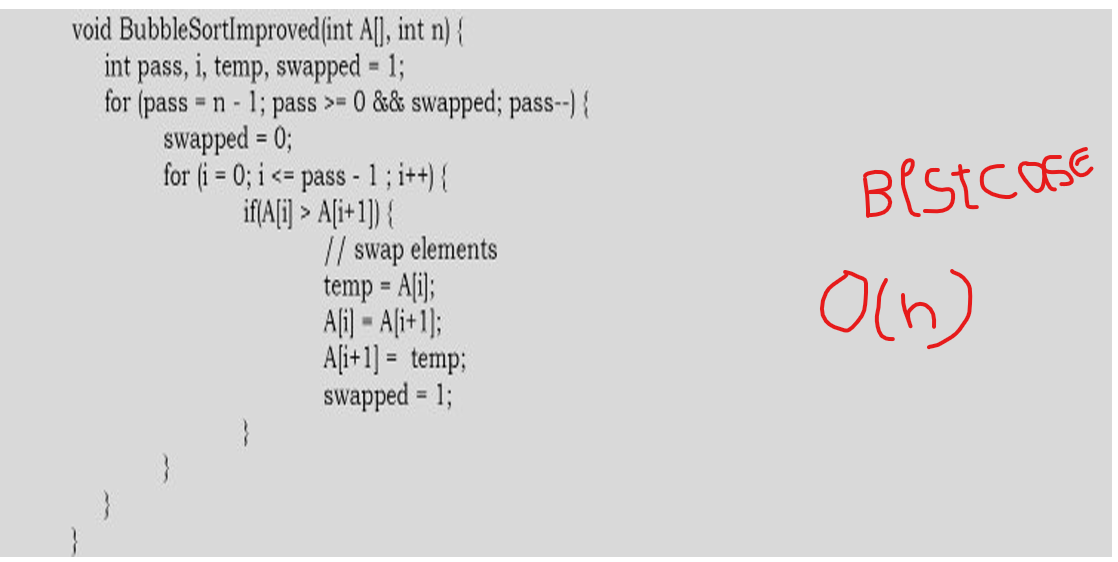
Bubblesortimplementation
Bubble sort is the simplest sorting algorithm. It works by iterating the input array from the first element to the last, comparing each pair of elements and swapping them if needed. Bubble sort continues its iterations until no more swaps are needed.
Selectionsort
Find the minimum value in the list
Swap it with the value in the current position
Repeat this process for all the elements until the entirearray is sorted
