Critical Care Exam 1 Practice ?s Pain/Sedation/Delirium
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
Your patient is receiving morphine for pain management. Give the type of medication and what is the #1 thing to look out for?
opioid, respiratory depression
Your patient is going to be receiving morphine (opioid) for pain management. Before you give it, what 4 things do you want to monitor before giving it?
HR
BP
Respiratory Status (must be more than 10 breaths)
LOC
Your patient wants more morphine. Upon assessment, their respiratory rate was 9. Can you give it?
No must be over 10 breaths
What can opioids do to your bowels that you must assess before giving it?
Constipation
Your patient has sleep apnea. Is it safe to give morphine?
No, opioids can cause respiratory depression
If your patient is on opioids and you’re watching BP, what can you do to keep it okay?
maintain fluid status
Before administering IV morphine to a critically ill patient, which assessments are essential for the nurse to perform?
Select all that apply.
A. Respiratory rate
B. Blood pressure
C. Oxygen saturation
D. Pain intensity
E. Bowel movement pattern
ABCD
The nurse is preparing to administer IV morphine to a patient in the ICU. Which action is most appropriate?
A. Administer the medication as a rapid IV push
B. Dilute and administer slowly over several minutes
C. Give the medication during ambulation
D. Withhold the medication if the patient is sedated but in pain
B
After administering IV morphine, which assessments should the nurse prioritize?
Select all that apply.
A. Level of consciousness
B. Respiratory rate
C. Capillary refill
D. Blood pressure
E. Pain relief
ABDE
A patient receiving IV morphine becomes difficult to arouse and has shallow respirations. What is the priority nursing action?
A. Increase oxygen delivery
B. Stimulate the patient and reassess
C. Administer naloxone
D. Document findings and continue to monitor
C
For overdose on morphine or opioids, what do you give?
naloxone
When you give opiods/narcotics via IV, what do you always want to do?
Push slowly!
How many mg is morphone usually given via IV?
1-2mg
The provider prescribes morphine 1–2 mg IV every 2 hours PRN pain for a critically ill patient. Which nurse response is most appropriate?
A. Question the order because the dose is too low to be effective
B. Administer 1 mg IV and reassess pain
C. Administer 2 mg IV immediately
D. Hold the medication until pain reaches 7/10
B (safe to use, 1-2mg and reassess)
What opioid is of choice for a patient with an MI and why?
morphine, decreases workload of the heart, vasodilator
Hydromorphone (dilaudid) what type of drug and what is the safe dose and why?
opioid, 0.25 - 1mg, stronger
Fentanyl (Sublimize) what is a safe dose and why?
25 - 50mcg, very strong!
What is the severe side effect of fentanyl (Sublimize) to watch for if pushed too fast?
Chest Wall Rigidity (can make CPR difficult)
What opioid works very quickly and rapid onset but doesn’t last long?
Fentanyl
When giving fentanyl, what BIG side effects do you need to watch?
bradycardia and itchy nose
You have to give a patient Narcan (naloxone) to reverse respiratory depression. What side effects should you watch out for (think you are reversing)?
sudden pain, tachycardia, increased blood pressure, sweating, ANGRY
Your patient is being weaned off opioids. What drug could you use?
Tylenol
You're weaning your patient off opioids and using Tylenol. What other name for the drug and what is the total amount you can use per day?
acetaminophen, 4 grams a day
Long term use of Tylenol, can cause ____ damage
liver damage
When giving NSAIDs for pain, what BIG things to watch for?
kidney damage, GI bleeding
Your patient is at high risk for bleeding. Should you give them an NSAID
no, can cause bleeding
A critically ill patient is started on enteral tube feedings. Which nursing actions are priority to prevent complications?
Select all that apply.
A. Verify tube placement per facility policy
B. Elevate the head of bed 30–45°
C. Check gastric residual volume before each feeding
D. Assess bowel sounds before starting feedings
E. Monitor blood glucose levels
ABE
A patient receiving continuous tube feeding suddenly develops coughing and oxygen desaturation. What is the priority nursing action?
A. Increase oxygen flow
B. Stop the feeding and place the patient upright
C. Check gastric residual volume
D. Notify the provider
B, aspiration!
Your patient is on enteral feeding. What can be done to prevent aspiration?
HOB up 30-45 degrees
Your patient is on enteral feeding. What can be done to prevent tube occlusion?
always flush with 30ml of water
For TPN nutrition, what do you want to monitor since this feeding has dextrose?
check blood glucose (hyperglycemia risk)
When you discontinue TPN nutrition, what do you want to assess for after which your patient could be at risk of? (think of dextrose)
hypoglycemia
What is the best or safest position for central line insertion and why?
Trendelenburg, prevent an air embolism
What needs to be done to check for correct position of a central line?
chest X-Ray
The nurse is assisting with central venous catheter insertion. Which actions are appropriate to ensure correct and safe insertion?
Select all that apply.
A. Place the patient in Trendelenburg position
B. Use maximal sterile barrier precautions
C. Have the patient perform a Valsalva maneuver during insertion
D. Clean the insertion site with chlorhexidine
E. Obtain a chest x-ray before using the line
F. Flush all lumens immediately after insertion
ABCDE
How often should you change the dressing on a central line or picc line?
every 24 hours
Normal sodium concentration
135 - 145
Normal potassium concentration
3.5 - 5.2
Your patient is hyponatremic. What should you implement?
seizure precautions
What IV fluid can be used to correct hyponatremia because of its sodium content most similar to the human body?
lactated ringers
For hypernatremia, what should your patient consume more of?
water! to dilute sodium
Hypokalemia can cause what to the heart?
ventricular dysrhythmias
On an EKG, hyperkalemia can cause what?
peaked T waves and wide QRS complexes
Normal calcium concentration
8.5 - 10.5
What calcium imbalance can cause more muscle excitability (think opposite)?
hypocalcemia
What calcium imbalance can cause less muscle excitability (think opposite)?
hypercalcemia
Normal concentration of magnesium
1.5 - 3
Your patient has a 1.0 magnesium level. What 3 things would you expect?
tremors, seizures, tetany (speeds up)
Your patient has a 3.5 magnesium level. What 3 things would you expect?
CNS depression, weak reflexes, muscle weakness (slows down)
What scale is most commonly used to measure patient agitation and sedation on ventilators?
RASS
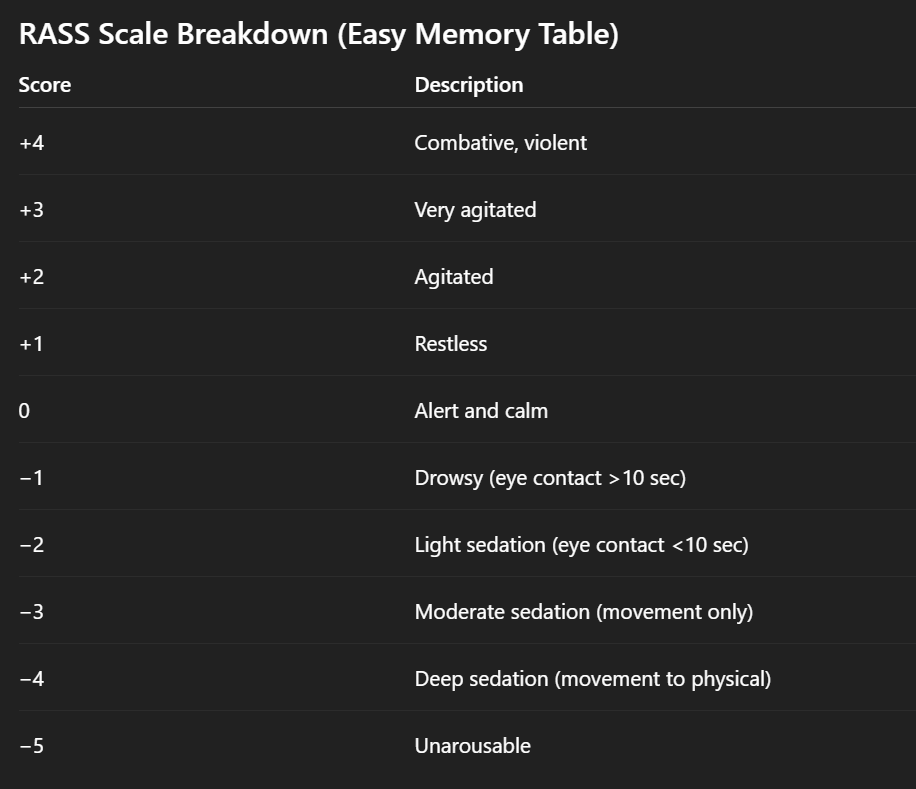
A nurse is assessing a mechanically ventilated patient in the ICU. The patient opens their eyes to verbal stimulation, makes eye contact for less than 10 seconds, and then drifts back to sleep. Which RASS score should the nurse document?
A. +2 (Agitated)
B. 0 (Alert and calm)
C. −2 (Light sedation)
D. −4 (Deep sedation)
C. −2 (Light sedation)

The nurse is assessing a patient receiving continuous IV propofol. The patient does not respond to verbal commands but withdraws their arm when the nurse applies a sternal rub. Which RASS score should the nurse document?
A. −2 (Light sedation)
B. −3 (Moderate sedation)
C. −4 (Deep sedation)
D. −5 (Unarousable)
C. −4 (Deep sedation)
A nurse assesses a ventilated patient and documents a RASS score of −5. What is the priority nursing action?
A. Reassess the patient in 4 hours
B. Administer PRN benzodiazepine
C. Notify the provider and prepare to titrate sedation
D. Increase stimulation and reorient the patient
C. Notify the provider and prepare to titrate sedation
If you put your patient on deep sedation, what must be true?
MUST have a patent airway
If your patient is over sedated, what are some things to look out for?
Ulcers, DVTs, PE, Pneumonia, Ileus
A mechanically ventilated ICU patient has been deeply sedated with propofol for 5 days. The nurse notes a RASS score of −4. Which complications should the nurse monitor for as a result of prolonged over-sedation? Select all that apply.
A. Stress ulcers
B. Deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
C. Pulmonary embolism (PE)
D. Pneumonia
E. Seizures
ABCD
What to look out for if your patient is undersedated?
pull out tubes/lines, hazardous
A mechanically ventilated patient is receiving a low-dose sedative infusion. The nurse notes that the patient is pulling at the endotracheal tube, attempting to climb out of bed, and becomes visibly anxious when approached. The RASS score is +3. Which risks should the nurse anticipate due to undersedation? Select all that apply.
A. Accidental extubation
B. Increased oxygen consumption
C. Hemodynamic instability
D. Pressure ulcers
E. Ventilator-associated pneumonia
ABC
What class of medications do we use for sedation?
benzodiazepines
What is the main prototype for benzodiazepines for muscle spasms?
Diazepam (Valium)
What benzodiazepine do we use primarily for seizures at 0.5-1mg IV push?
lorazepam (Ativan)
What benzodiazepine is used the most 1-2mg IV push?
Versed (midazolam)
For benzodiazepine what do you need to do if you push via IV to prevent respiratory depression?
push SLOWLY
What 3 things to watch for benzodiazepines when used for sedation?
lower BP, lower LOC, respiratory depression
When giving benzodiazepines what must you check since these can cause impairment when secreted?
liver function tests
Your patient is on benzos for sedation and is experiencing respiratory depression. What should you give to reverse this?
Romazicon (flumazenil)
What drug is primarily used for sedation for patients on a ventilator? (think Michael Jackson drug)
propofol (diprivan)
Does propofol have a slow or rapid onset?
RAPID 1-2 minutes, 2-4 min half life
Concentration of propofol?
10,000mcg/ml
Your patient is on propofol. How often should you change the tubing and why?
every 12 hours, high infection risk
What is the BIGGEST side effect of propofol?
hypotension (assess BP and sedation level)
What syndrome can propofol cause where cardiac arrest, hyperkalemia, metabolic acidosis, rhabdomyolysis?
Propofol Infusion Syndrome
What can propofol cause to the muscles?
Rhabdomyolysis - breakdown of muscle
After propofol, what medication can we give to wean them off since it doesn’t cause resp depression?
precedex (dexmedetomidine)
What withdrawal can cause seizures and is threatening?
benzodiazepine withdrawal
What withdrawal can be uncomfortable and painful?
opiate
What is the delirium detection tool used?
CAM
A 72-year-old patient in the ICU after cardiac surgery becomes increasingly confused, agitated, and unable to maintain attention. The nurse suspects delirium. Using the Confusion Assessment Method (CAM) for the ICU, which finding would most strongly support a diagnosis of delirium?
A) The patient has a history of mild cognitive impairment.
B) The patient demonstrates acute onset of mental status changes and fluctuating course, plus inattention.
C) The patient is oriented to person, place, and time but appears anxious.
D) The patient reports hallucinations but is calm and cooperative.
B, it’s abrupt not chronic (that’s dementia)
Identify type of delirium: restless, agitated, combative
Hyperactive
Identify type of delirium: sleepy, lethargic, mumbling
hypoactive
What common risk factor can cause delirium in the elderly?
UTI
Name the ABCDEF bundle for delirium prevention?
Awakening
Breathing Trials
Careful Choice of Sedation (lowest amount)
Delirium Assessment (CAM)
Early progressive exercise and mobility
Family integration throughout
Propofol or Precedex sedation for a delirium patient?
precedex
Your patient is withdrawing from alcohol. What would you expect after 24 hours?
shaky, agitation, diaphoretic, hyperactive
Your patient is withdrawing from alcohol. What would you expect after 48-72 hours?
Increased vital signs, hyperactive, confused, tremors, SEIZURES
What are the huge two drugs with benzos is given to patients on alcohol withdrawal?
Thiamine and Folic Acid
What does thiamine do for alcohol withdrawal
prevents neuro complications and prevent Wernicke’s Encephalopathy
What does folic acid do for alcohol withdrawal
folic acid deficiency