IB Biology - Water and Nucleic Acids
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Why is water the medium of life?
chemical reactions take place between molecules disolved in solution. All these chemical reactions need to be in a aqueous state (where water is a liquid).
What is a polar covalent bond?
unequal sharing of electrons
What is a consequence of the polar covalent bond?
The oxygen will pull the electron closer and give it a partial negative charge.
Draw a water molecule, including the partial charges
held together by covalent bonds (two hydrogens one oxygen)
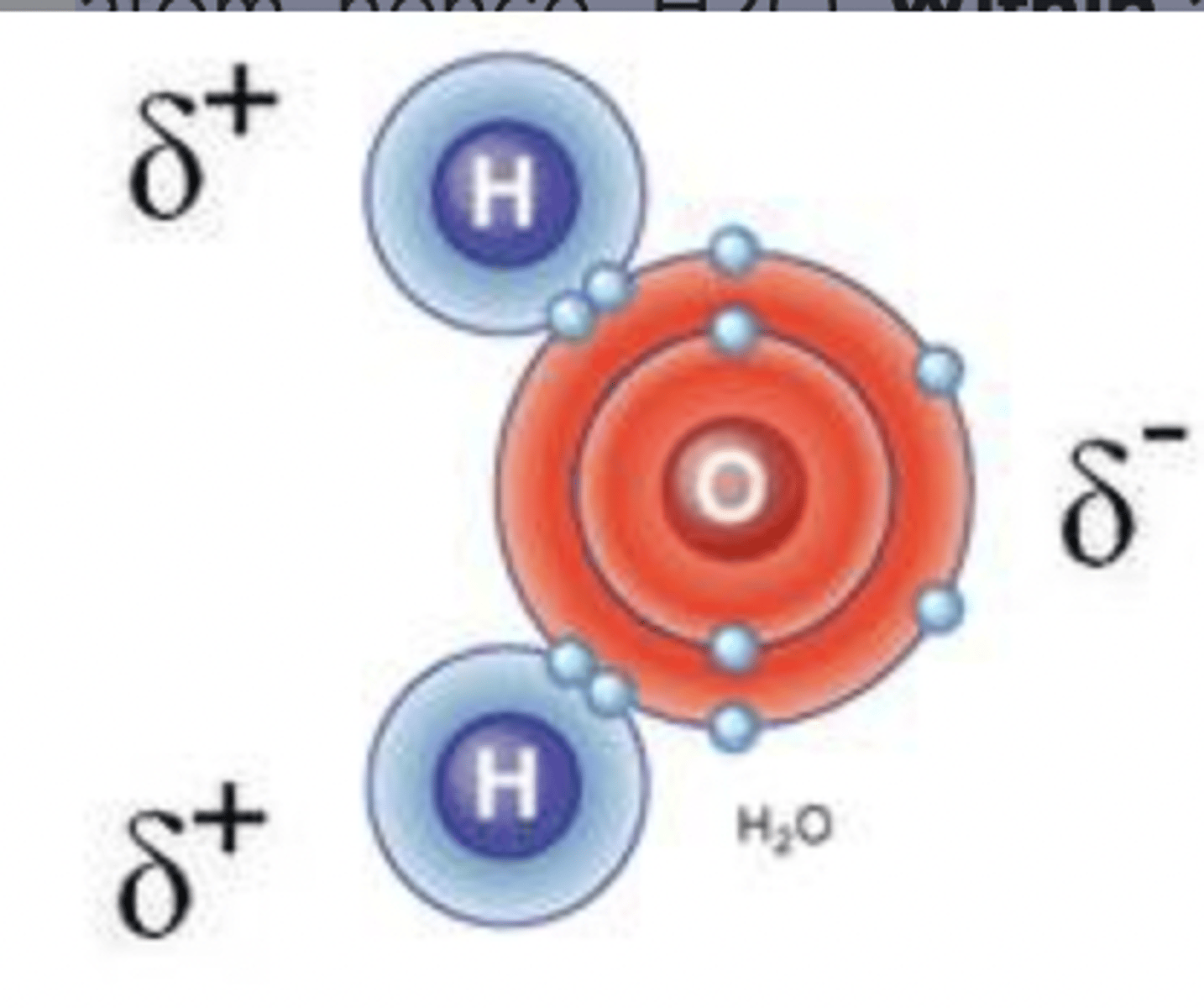
What is a hydrogen bond?
the attraction between a hydrogen atom with a partial positive charge and another atom with a partial negative charge
Draw a hydrogen bond between water molecules
hydrogen bonds would not exist without the covalent bonds covalent bonds create the conditions necessary for the formation of partial charges and dipole moments within molecules.
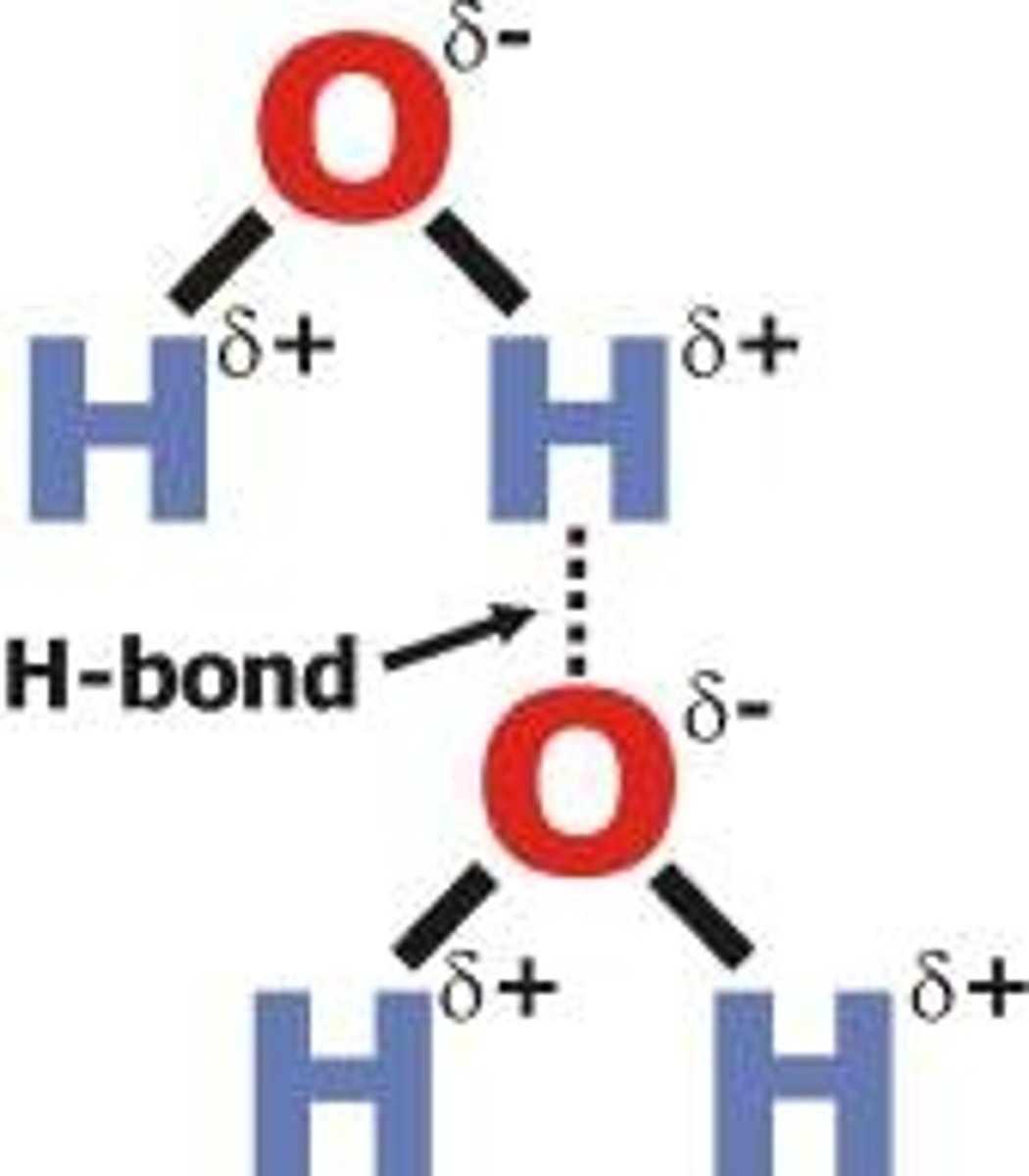
Describe cohesion
-The attraction between two similar molecules.
-Cohesion forms surface tension
-Surface Tension can support small objects
-Creates Viscosity
Explain how cohesion helps water move through the xylem in plants
cohesion helps water stick together like a chain, and this chain of water is pulled up through the plants pipe system (xylem).
Transpiration
The movement of water vapor out of a plant and into the air (against gravity).
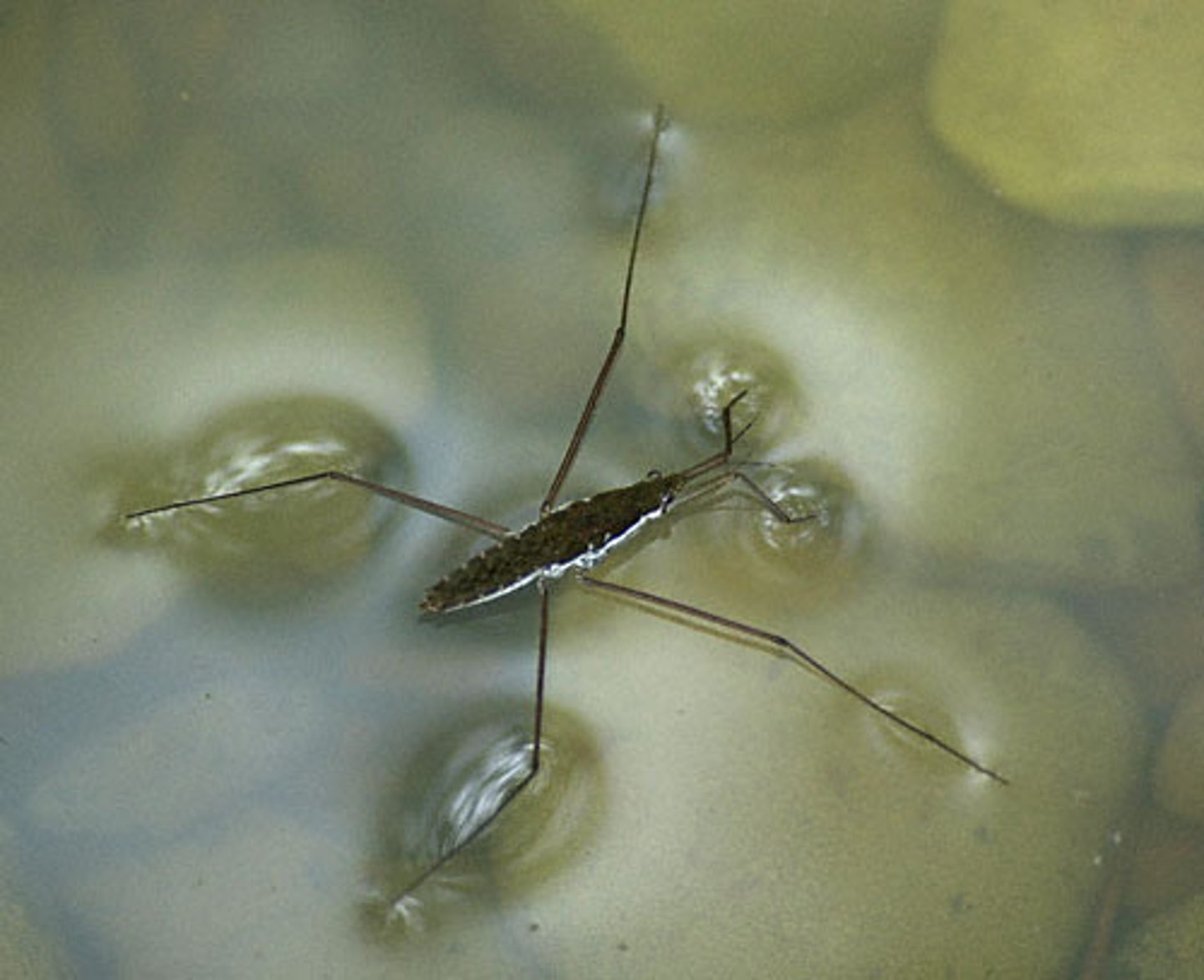
Explain how cohesion allows the surface of water to be used as a habitat.
Cohesion on some animals, such as bugs, can create water tension. The bugs legs are pushing down on the water surface, however the tension of the cohesion between the water molecules is greater then the force of the bugs leg.

What is adhesion?
An attraction between molecules of different substances. Water sticking to something else that is not water.
Describe capillary action
With capillary action, it is possible for a liquid to overcome the force of gravity due to cohesive forces within the liquid itself and also adhesive forces with the liquid and the walls of the tube.
Describe how capillary actions is useful to plants
It helps by pulling the water up through the xylem, from the roots towards the leaves. It is slowly and steadily moving up to make sure that the plant has a constant supply of water.
Solvent
A liquid substance capable of dissolving other substances
Solute
the substance that is dissolved
Solution
A mixture that forms when one substance dissolves another.
Hydrophilic
water loving, water can only dissolve things that are hydrophilic. Polar molecules are hydrophilic meaning they will dissolve into a solution.
Hydrophobic
water hating, hydrophobic substances cannot dissolve in water. Non-polar substances that dont have a charge exp. lipids.
Define metabolism
all the reactions that happen in our cells that require molecules to be in a solution.
explain why metabolic reactions happen in solution
metabolic reactions happen in solution because they need something to dissolve into.
describe transport in plants
Roots take in water, water moves up through the xylem. Phloem is the plants "delivery system". They are networks of tiny tubes that carry the sugars from the leaves to other parts of the plants.
buoyancy
a force exerted upwards onto an object or substance.
Viscosity
A liquid's resistance to flowing
thermal conductivity
The ability of an object to transfer heat
specific heat capacity
the energy required to raise the temperature of one gram of a substance by one degree Celsius
Explain what is meant by "DNA is hereditary material of all organisms"
DNA carries the genetic information that gets passed down from one generation to the next in every living organism.
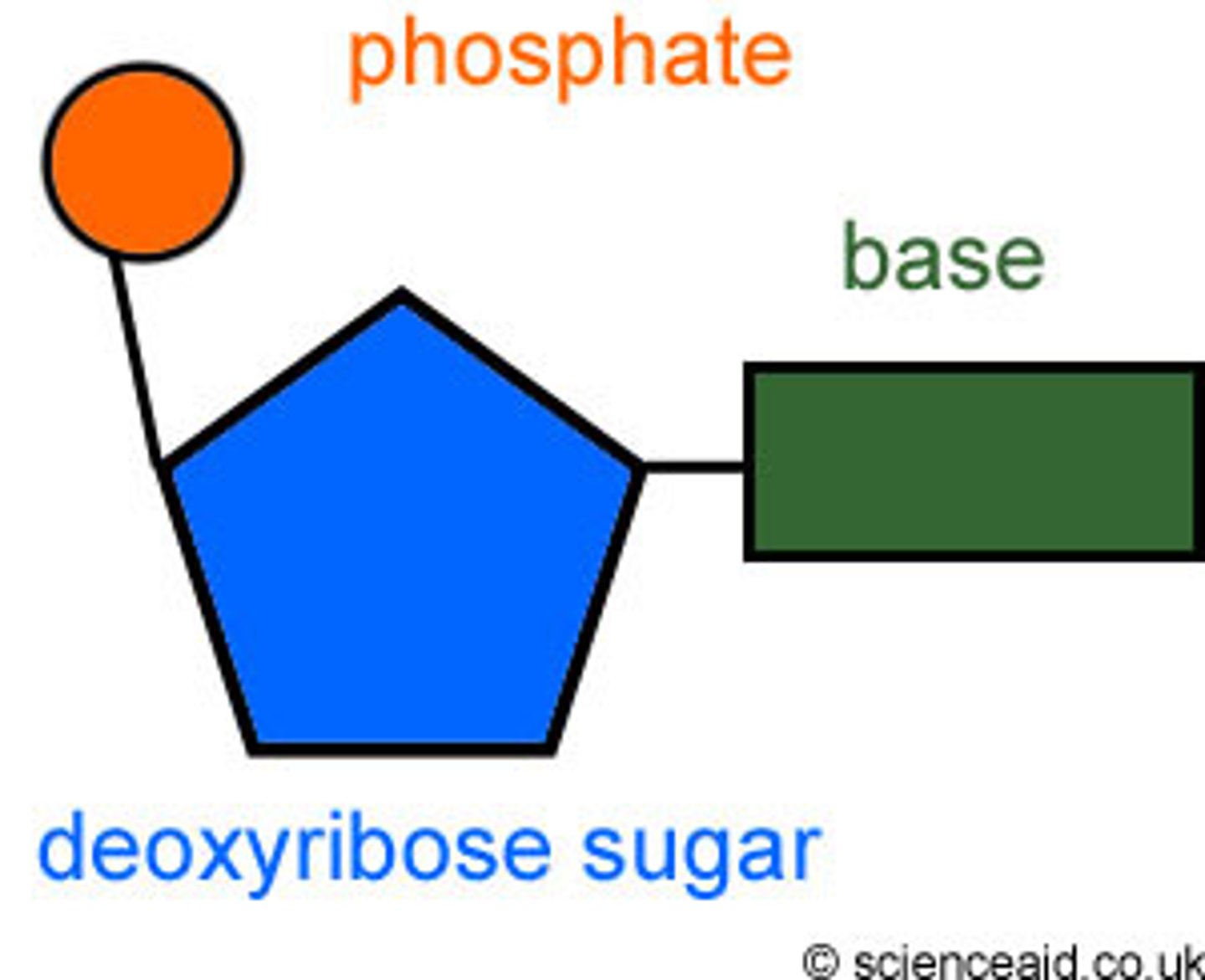
Draw and label a nucleotide
- Circle: phosphate.
- Solid line: covalent bonds.
- Pentagon: sugar (deoxyribose).
- Rectangles: bases (Adenine : Thymine & Guanine : Cytosine).
- Dotted line: H-bonds.
- One length across : nucleotide.
draw and label a chain nucleotide
Nucleotides are linked together by covalent bonds between the phosphate of one nucleotide and the sugar of another.
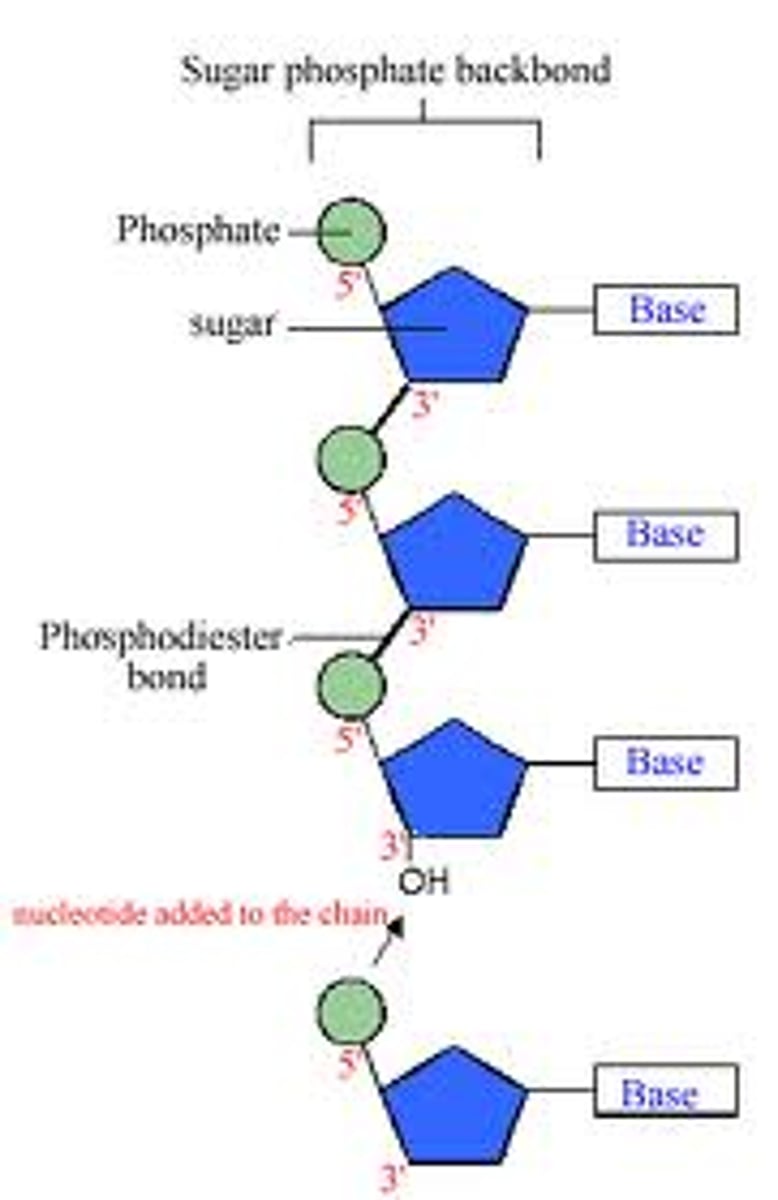
sugar-phosphate backbone
The alternating chain of sugar and phosphate to which the DNA and RNA nitrogenous bases are attached
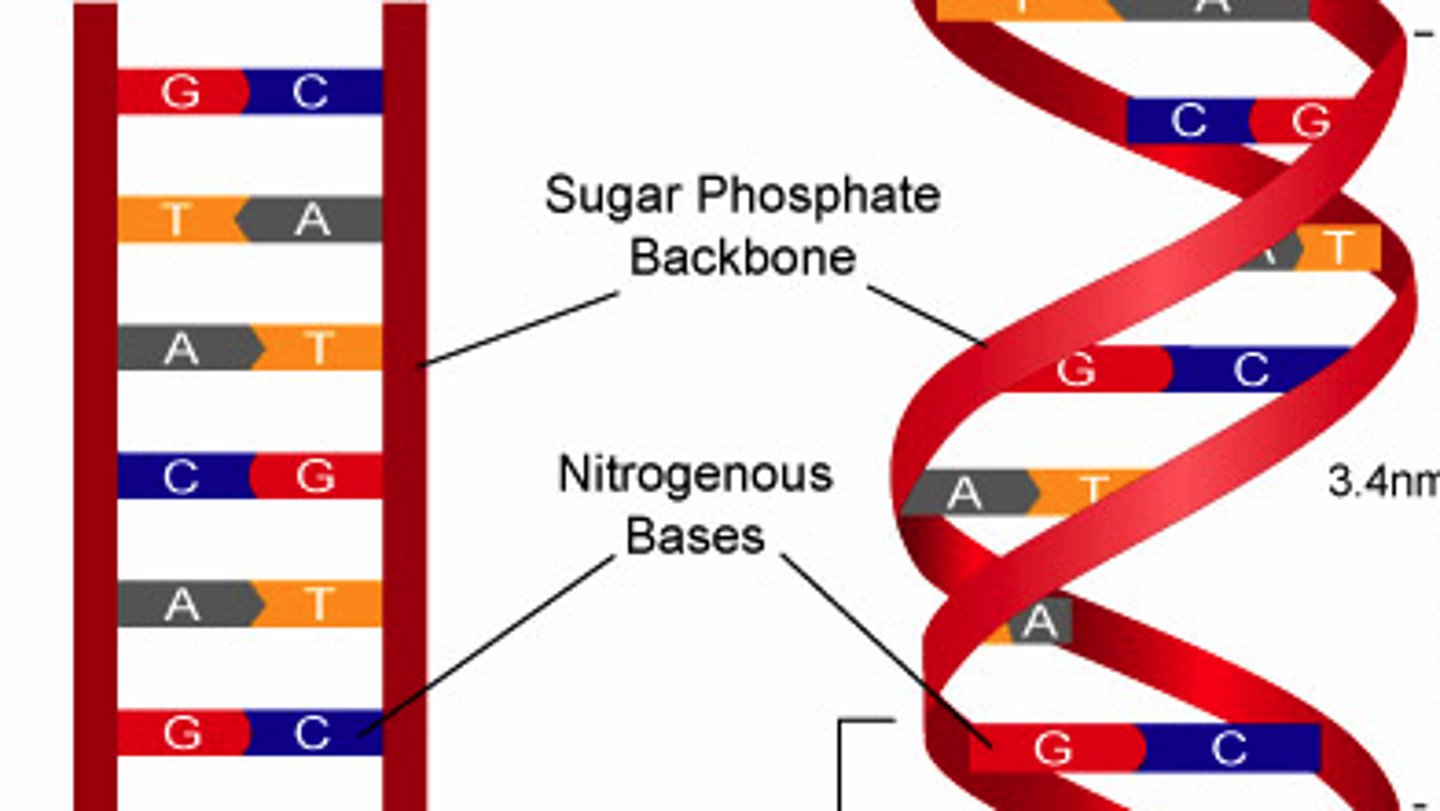
Bases of DNA
Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, Cytosine
Bases of RNA
Adenine, Uracil, Guanine, Cytosine
The ________ determines the genetic code.
Sequence of bases
Explain condensation reaction
a removal of water (the molecule H20) to create a covalent bond.
Draw a diagram that represent condensation reactions to join two nucleotides together.
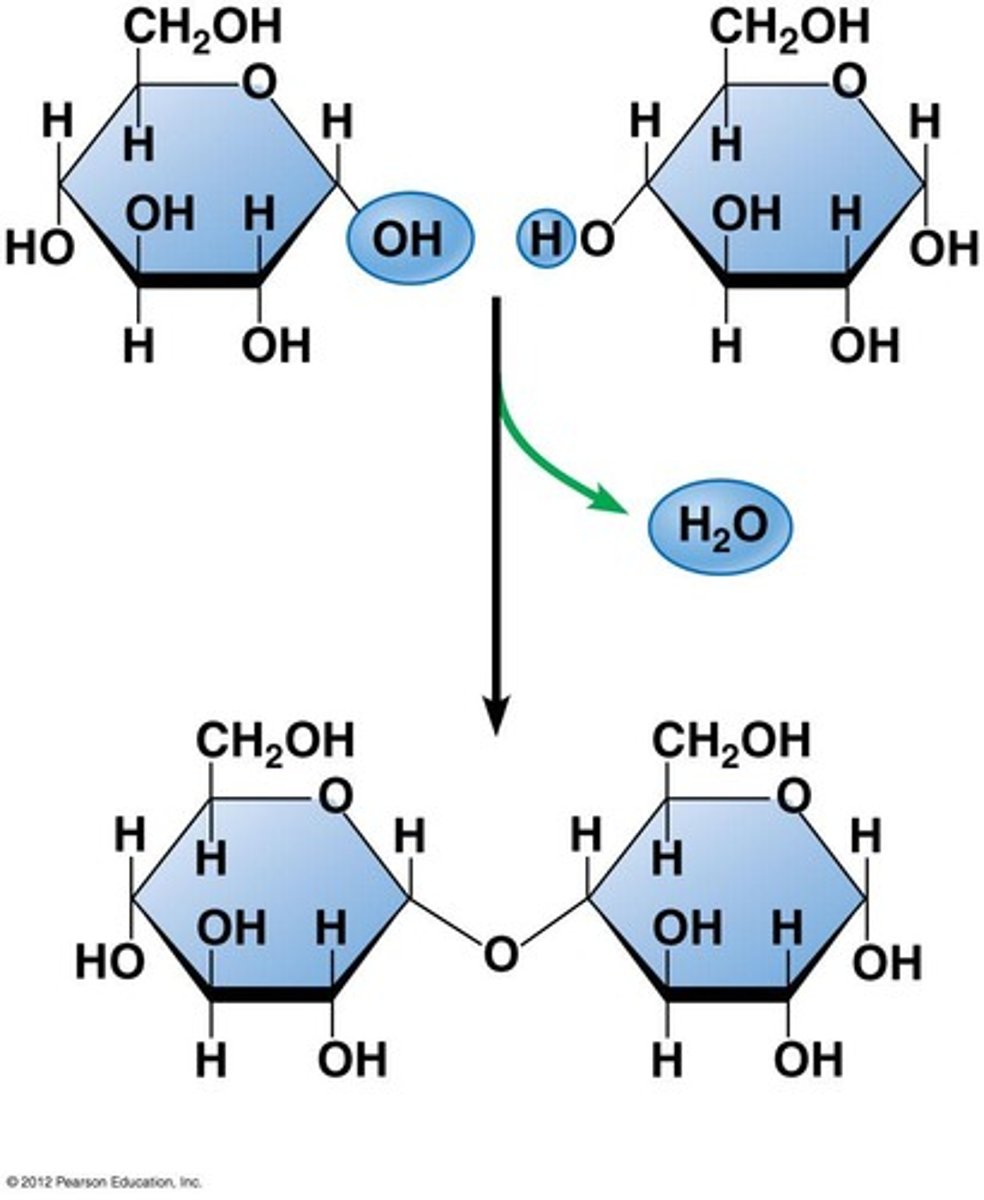
How many water molecules are produced when 46 nucleotides are joined together?
45, everytime you make a bond you remove a water molecule.
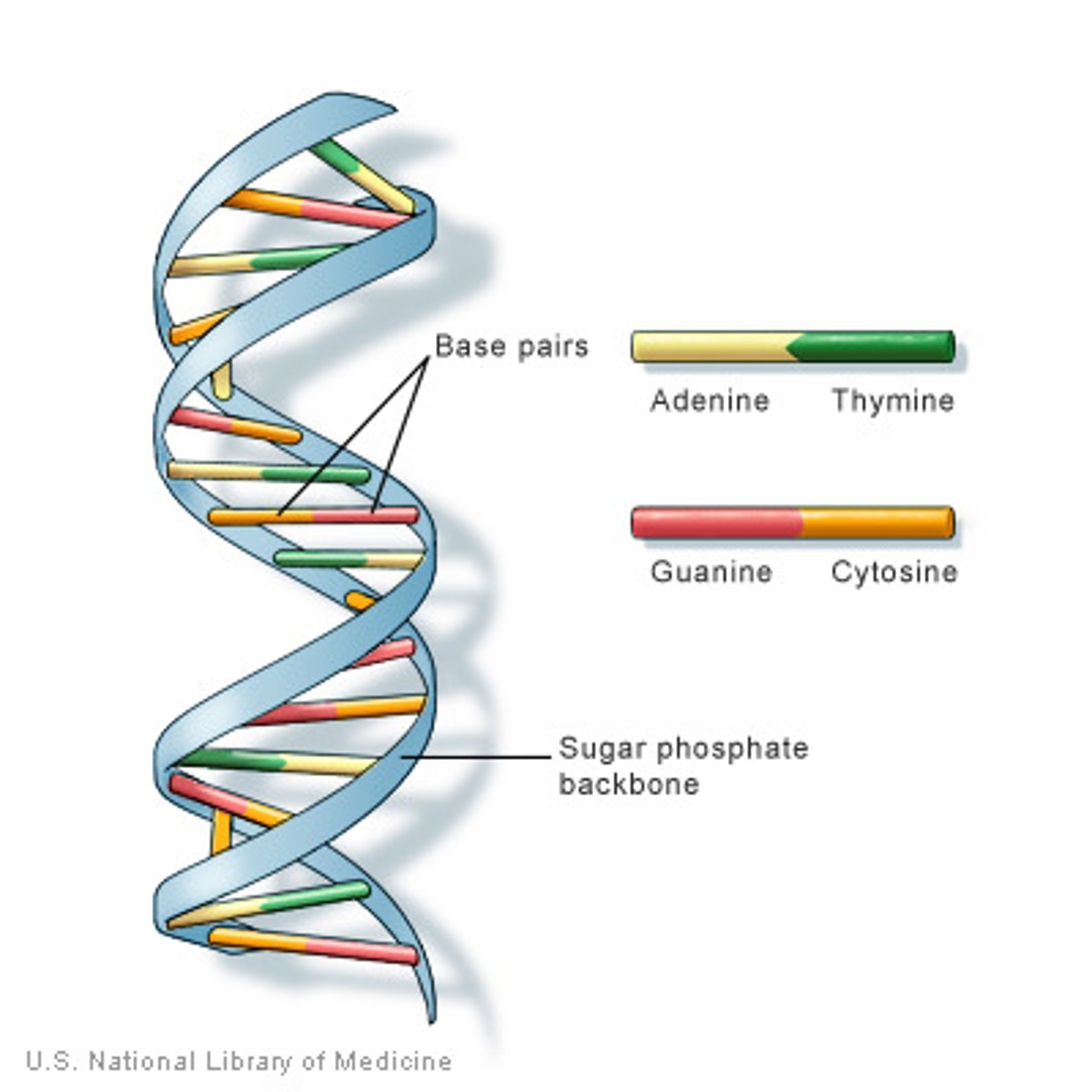
What is complimentary base pairing?
DNA: A-T, C-G
RNA: A-U, C-G
What is antiparallel?
strands run in opposite directions
What holds the two strands of DNA together?
hydrogen bonds
Draw the double helix structure of a DNA molecule.
RNA
single-stranded nucleic acid that contains the sugar ribose, adenine pairs with uracil.
DNA
A double-stranded, helical nucleic acid molecule capable of replicating and determining the inherited structure of a cell's proteins, adenine pairs with thymine.
semiconservative DNA replication
each daughter DNA molecule is composed of one original strand and one new strand
DNA to RNA to protein
central dogma
DNA replication
DNA unzips into two parts and splits with the cell. In it's new home each side of the DNA strand attack to matching nucleotides to create 2 exact copies. It is important in puberty and other times of growth as it is the reproducing of your cells.
gene expression
The process by which information encoded in DNA directs the synthesis of proteins or, in some cases, RNAs that are not translated into proteins and instead function as RNAs.
describe how cells are able to store such large amounts of genetic information
we can put them in different patterns and different lengths and they create many possible sequences.
what is the universal genetic code?
No matter what organism, they all use the same genetic code to understand their genetic instructions and make proteins. The sequence of DNA is different but how it's interpreted is the same.
how does the universal genetic code provide support for common ancestry?
it suggests that we all come from a common ancestor because we're all using the same genetic code to read and understand our DNA.