Pharmacogenetics: UGT1A, NAT2, TPMT, and OATP1B1 Insights
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What does the UGT1A gene locus encode?
The UGT1A gene locus encodes 9 UGT1A proteins and contains four pseudogenes.
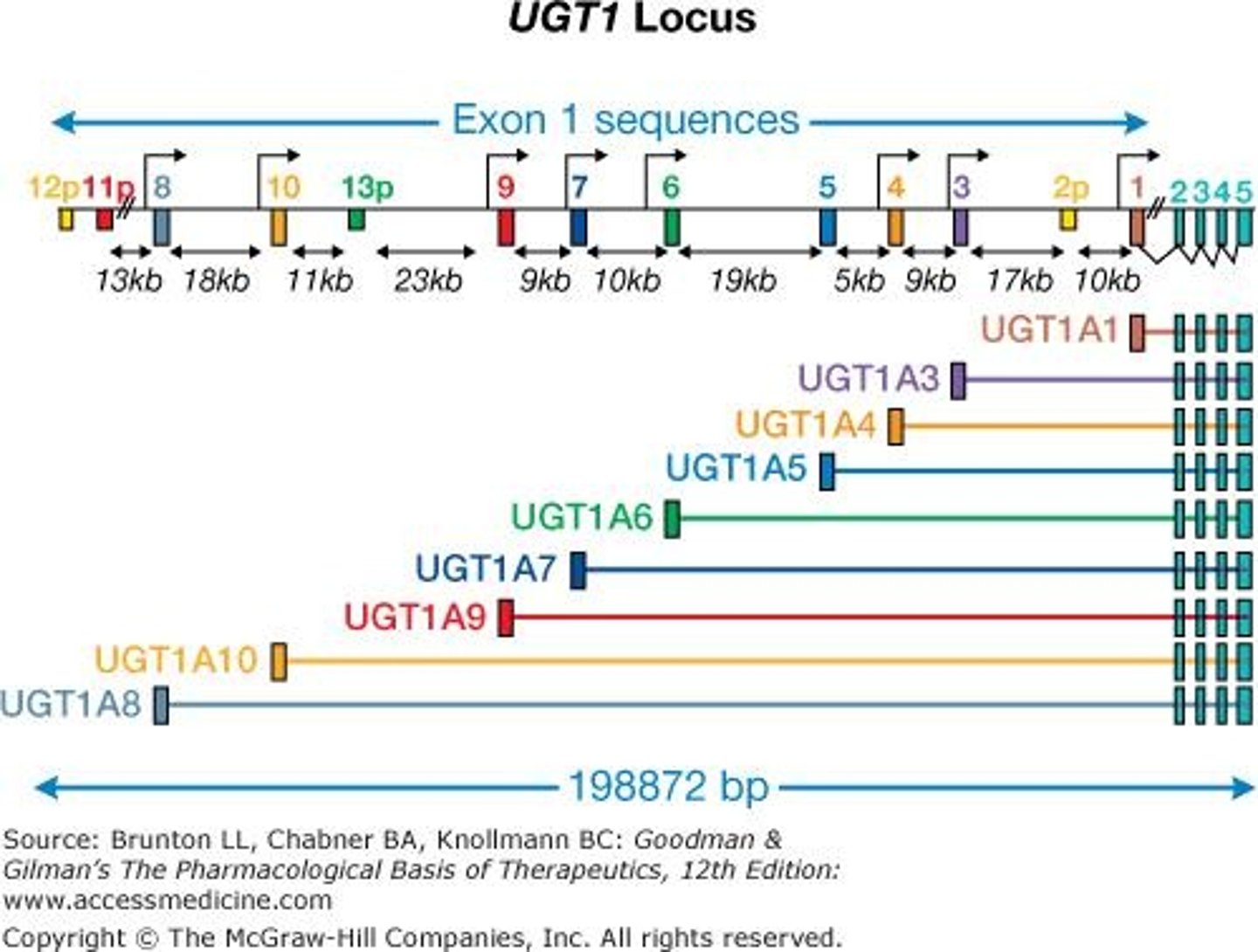
What is unique about Exon 1 in UGT1A isoforms?
Exon 1 is unique to each UGT1A isoform, while Exons 2-5 are shared by all isoforms.
What are some types of UGT polymorphisms?
UGT polymorphisms include TATA repeats and single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs).
What is Crigler-Najjar Syndrome?
Crigler-Najjar Syndrome is an inherited genetic disease resulting from the near complete loss of UGT1A1, leading to impaired bilirubin conjugation and hyperbilirubinemia.
What are the two types of Crigler-Najjar Syndrome?
Type I is a complete deficiency of UGT1A1 (most severe), while Type II is a near complete deficiency.
What are the symptoms associated with Crigler-Najjar Syndrome?
Symptoms include jaundice, potential for kernicterus, lethargy, increased muscle tone, and motor and intellectual disabilities.
How does light therapy help in Crigler-Najjar Syndrome?
Certain wavelengths of light (430-490 nm) convert bilirubin to water-soluble forms that can be eliminated.
What is Gilbert Syndrome?
Gilbert Syndrome occurs when only one copy of the UGT1A1 gene has a mutation, leading to a less severe increase in serum bilirubin levels.
What is the most common polymorphism associated with Gilbert Syndrome?
The most common polymorphism is the UGT1A1*28 allele.
What is the prevalence of Gilbert Syndrome in the US population?
Gilbert Syndrome affects approximately 5-10% of the US population, often in individuals of Asian descent.
What is Atazanavir and its effect on UGT1A1?
Atazanavir is an antiretroviral protease inhibitor that inhibits UGT1A1-glucuronidation of bilirubin, particularly in UGT1A1 poor metabolizers.
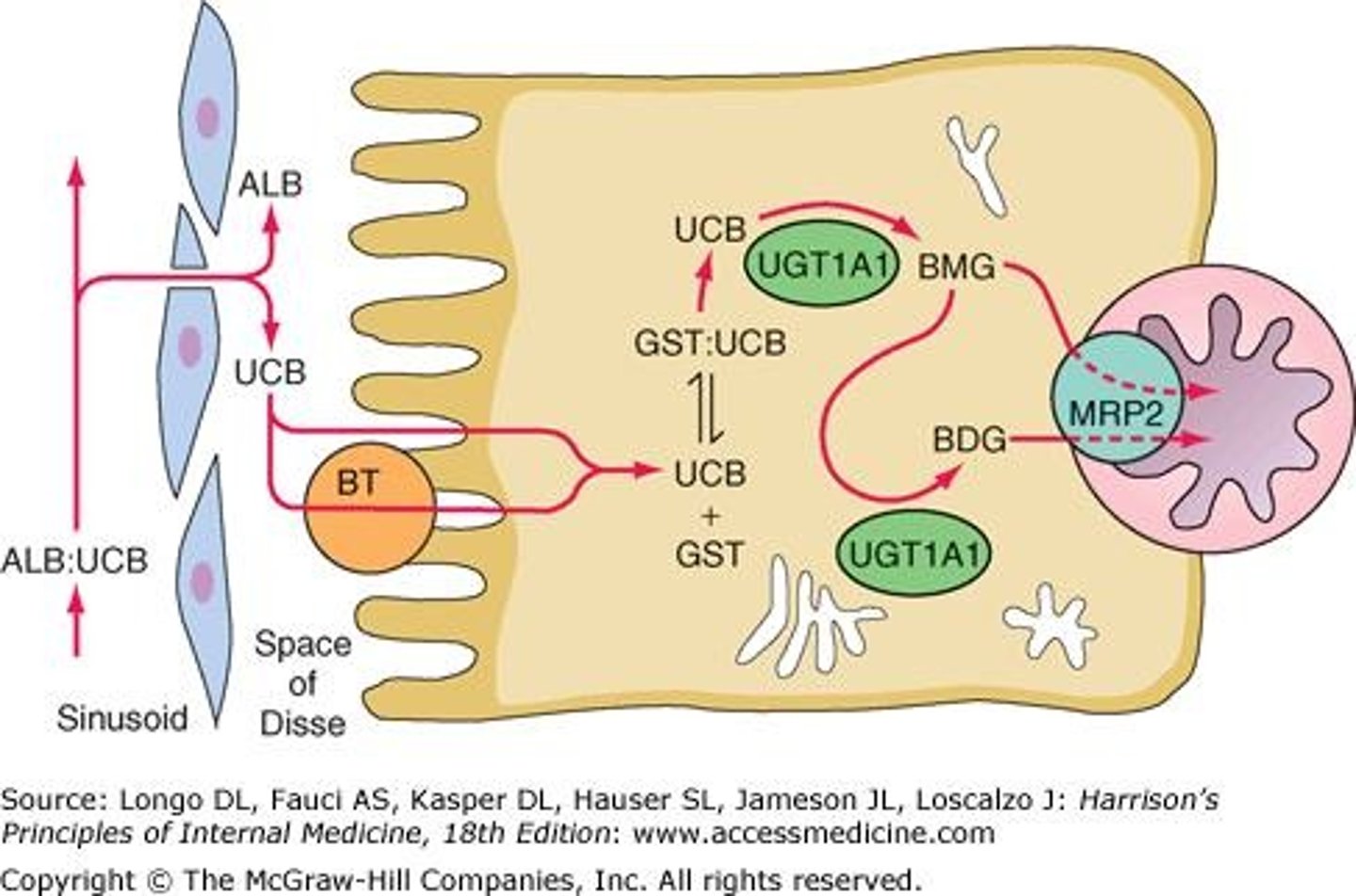
What is the consequence of UGT1A1 inhibition by Atazanavir?
Inhibition leads to indirect hyperbilirubinemia without hepatotoxicity, which may cause patients to discontinue treatment due to jaundice.
What is Irinotecan and its mechanism of action?
Irinotecan (CPT-11) is a prodrug used in chemotherapy that inhibits topoisomerase I, unwinding DNA during replication.
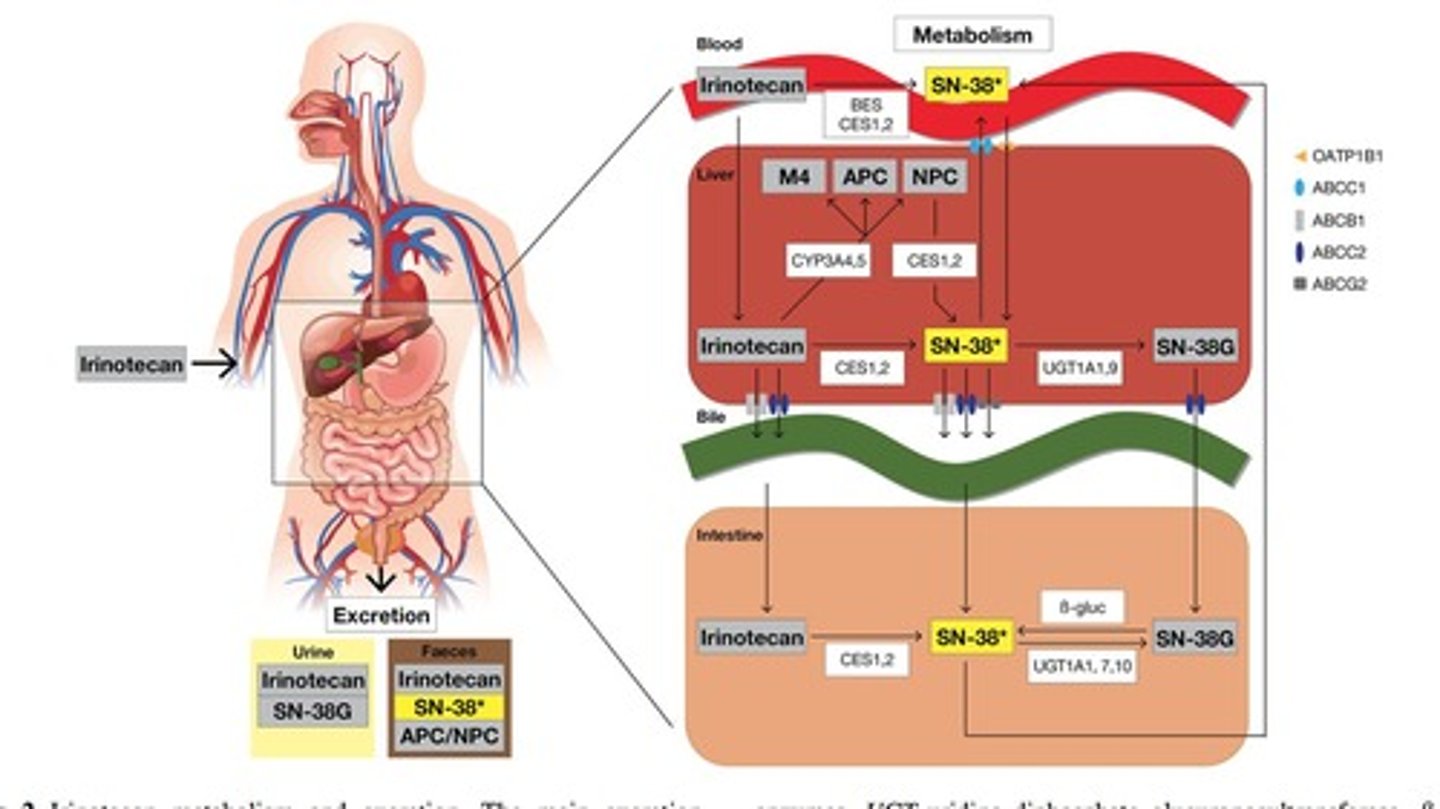
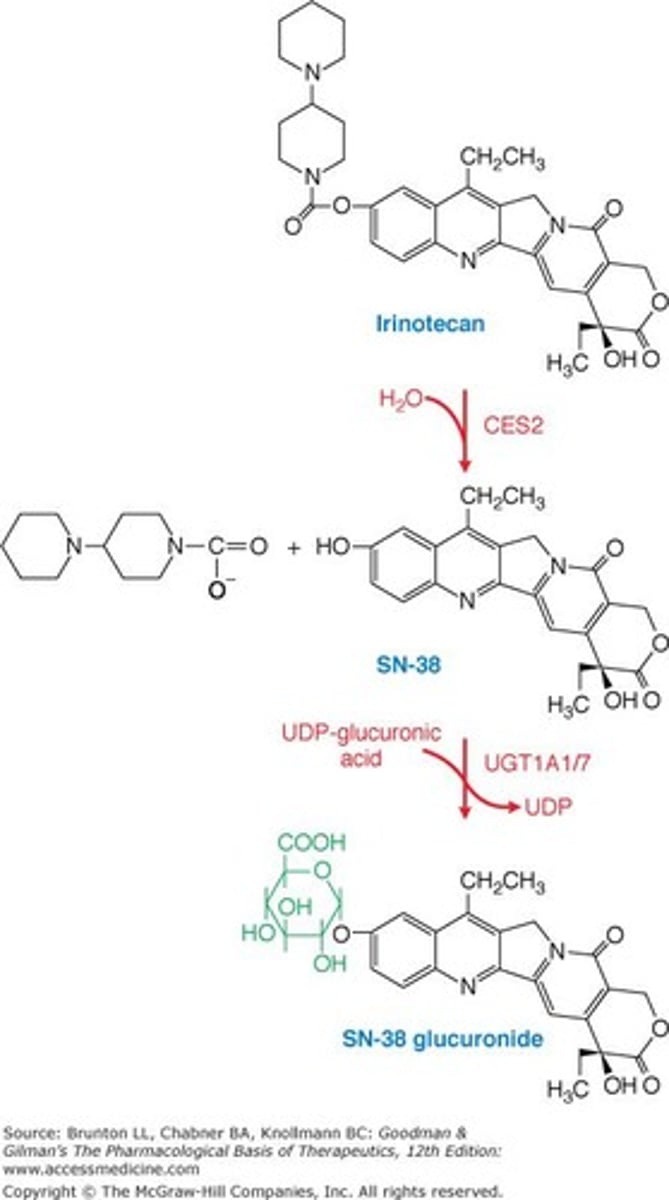
What is the role of UGT1A1 in the metabolism of SN-38?
UGT1A1 inactivates SN-38 to a glucuronide conjugate, which is crucial for its detoxification.
What toxicities are associated with SN-38?
Toxicities include leukopenia, neutropenia, and intestinal cell damage leading to potentially life-threatening diarrhea.
How do UGT loss-of-function SNPs affect SN-38 toxicity?
Patients with Gilbert's or other UGT loss-of-function SNPs are at increased risk of SN-38 toxicities.
What are the acetylator genotypes associated with NAT2?
NAT2 genotypes include fast/rapid, intermediate, and poor/slow acetylators.
What is the risk for slow acetylators when taking isoniazid?
Slow acetylators are at increased risk of isoniazid-induced peripheral neuropathy.
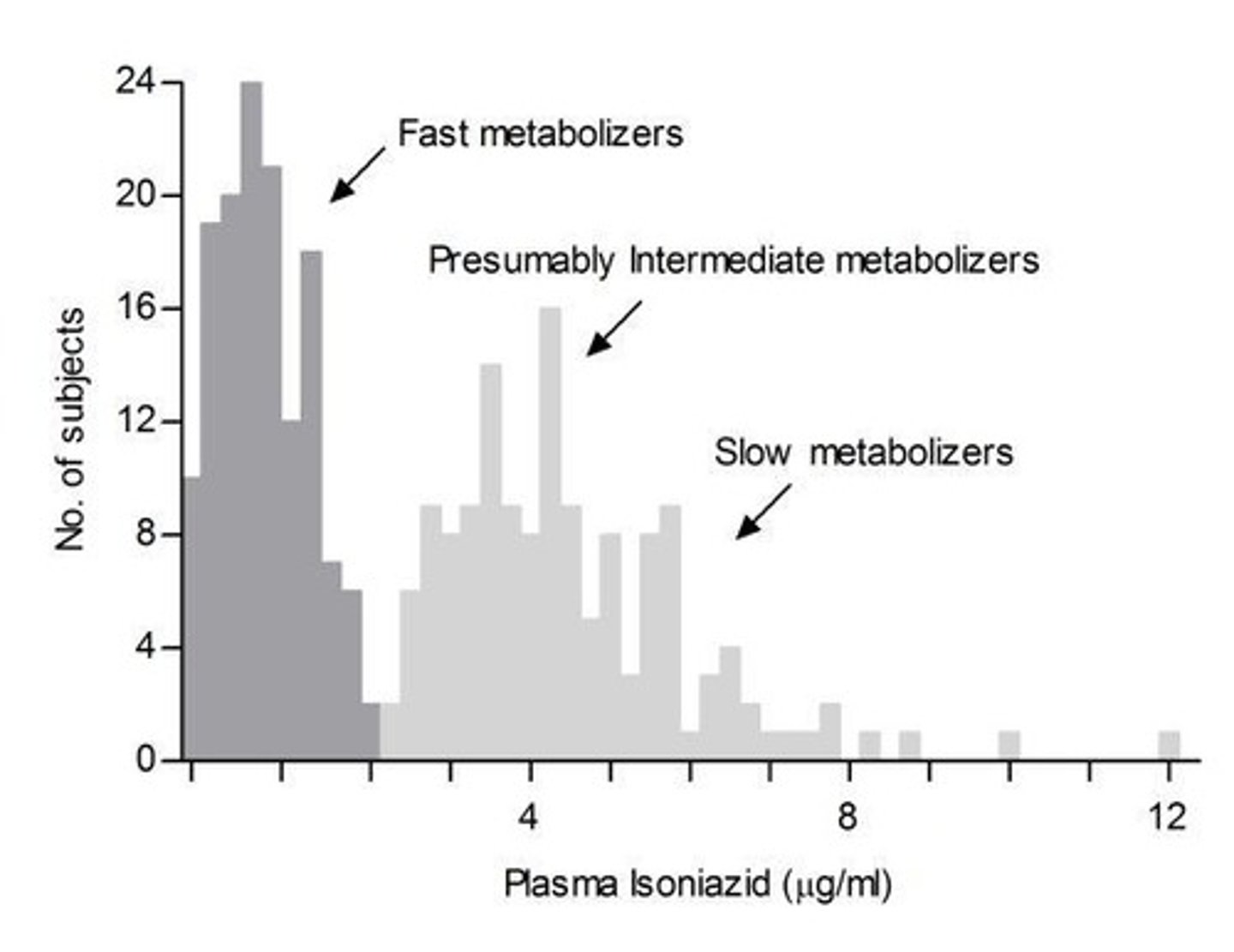
What can prevent isoniazid toxicity in slow acetylators?
Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) can prevent isoniazid toxicity.
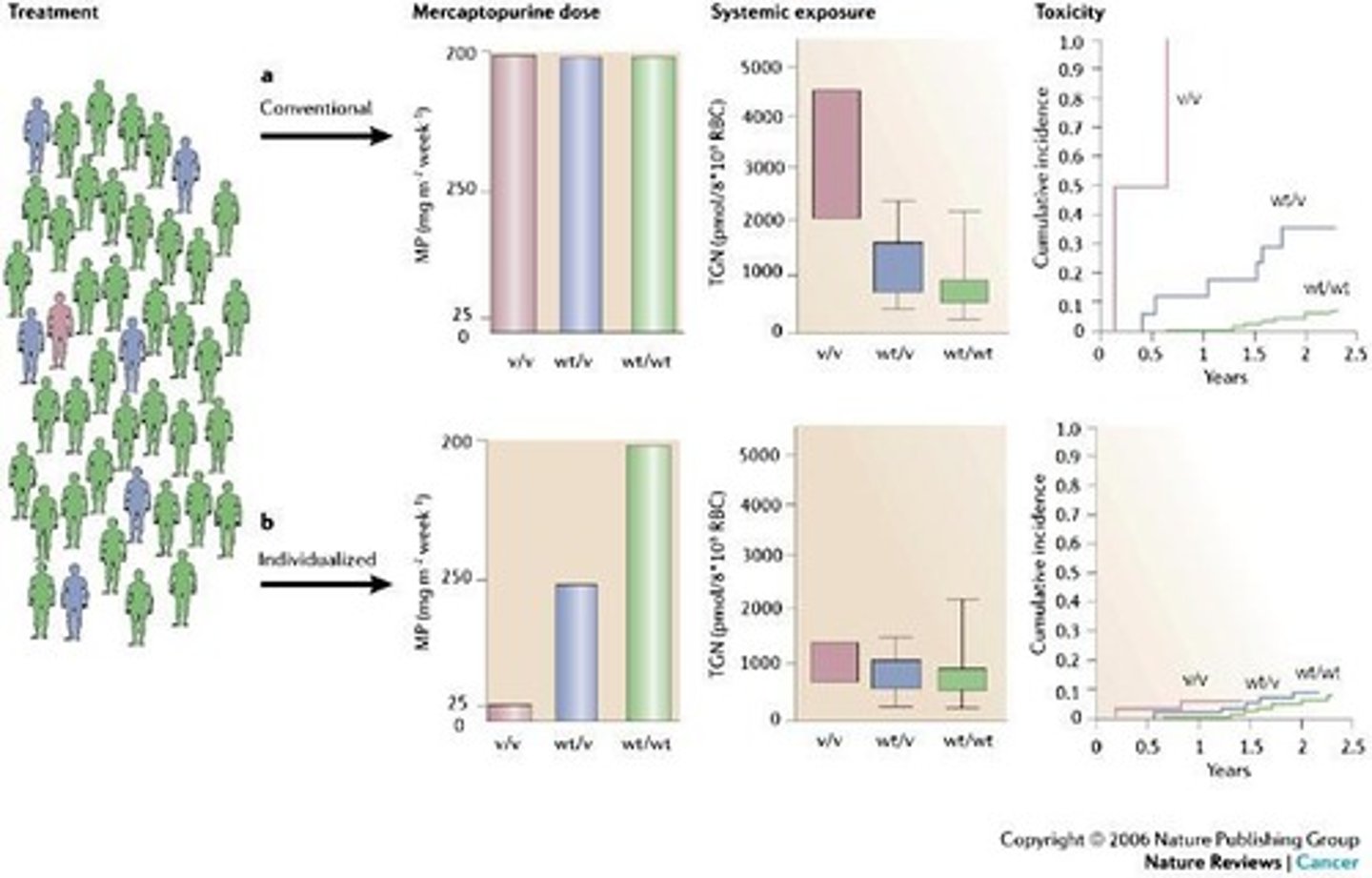
What is TPMT and its role in drug metabolism?
Thiopurine S-methyltransferase (TPMT) metabolizes thiopurines like 6-mercaptopurine, which are used in leukemia and inflammatory bowel disease.

What is the significance of measuring TPMT activity?
TPMT activity is measured in RBCs as a surrogate for drug-metabolizing tissues, but is unreliable in patients who have received RBC transfusions recently.
What are the common alleles associated with TPMT activity?
TPMTH (high activity) includes 1 (wild-type) and 24, while TPMTL (low activity) includes 2, 3A, 3B, 3C, and *4.
What is the relationship between TPMT activity and 6-mercaptopurine toxicity?
Low TPMT activity is associated with increased toxicity from 6-mercaptopurine due to myelosuppression.
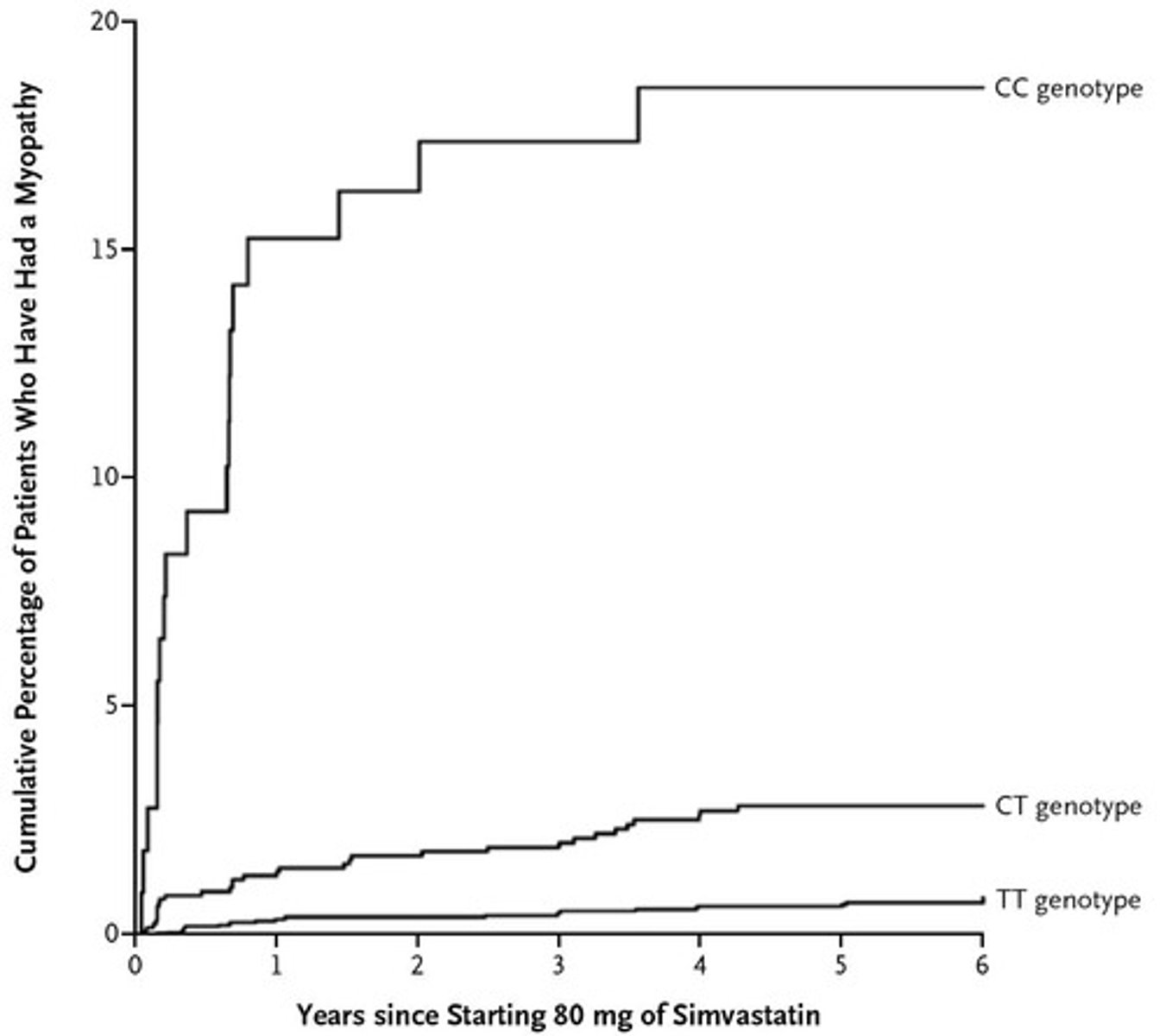
What is the SEARCH study and its focus?
The SEARCH study examined the effectiveness of additional reductions in cholesterol and homocysteine, focusing on simvastatin and its association with myopathy.
What genetic variant is associated with simvastatin-induced myopathy?
A loss-of-function variant in OATP1B1 is associated with reduced hepatic uptake of simvastatin, leading to myopathy.
What is the role of ABCG2 in gout?
SNPs in ABCG2 are associated with a higher risk of gout, particularly in males.
What is the most common ABCG2 SNP associated with drug response?
The Q141K amino acid substitution in ABCG2 is associated with increased risk for gefitinib-induced diarrhea and altered pharmacokinetics.