C9 - Chemistry of the Atmosphere
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
when was the earth formed
4.6 billion years ago
Can scientists be sure what gases made up the early atmosphere?
No
what is the most common scientific theory for the earth’s existance?
intense volcanic activity, releasing gases that made earth;s early atmosphere similar to mars’ and venus’ today.
lots of CO2
little-no oxygen
small amounts of other gases eg. ammonia and methane
nitrogen built up gradually as it is unreactive
This scientific theory is similar to the conditions in which planets today?
Mars
Venus
Volcanic activity releases…
…water vapour.
What then happens when volcanoes release water vapour?
The water vapour condenses as the earth cools
how were oceans formed?
volcanic activity released water vapour, condensed as the earth cooled and formed oceans.
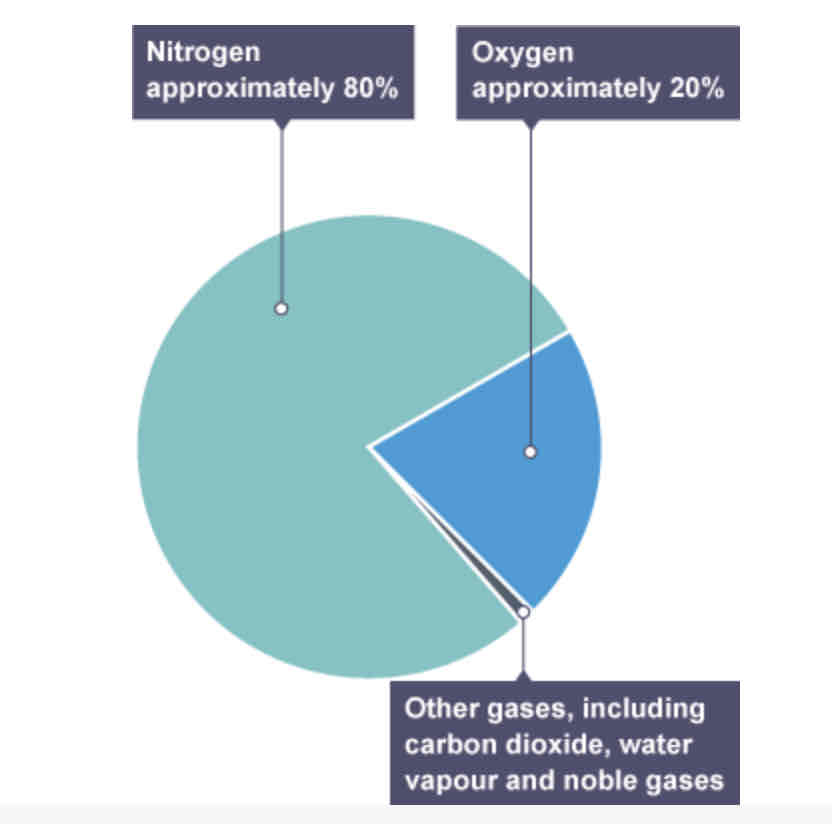
gas content in air NOW
80% nitrogen
20% oxygen
<1% other gases (CO2, H2O, noble gases)
has remained fairly stable for 200million years
how did oxygen increase in the atmosphere?
photosynthesis by primitive plants and algae released oxygen, which gradually built up in the atmosphere and eventually allowed animals to evolve
Photosynthesis equation
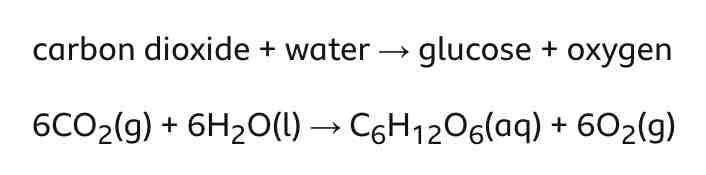
When did algae first evolve?
2.7 billion years ago
Soon after algae first evolved…
…oxygen began to exist in the atmosphere.
How did the amount of CO2 in the atmosphere decrease?
carbon dioxide is a very soluble gas and so it readily dissolves in oceans to form soluble carbonate compounds. This means the amount of CO2 in the atmosphere decreased.
How were sedimentary rocks formed?
The carbonate compounds were then precipitated as sedimentary rocks eg. limestone.
How were fossil fuels formed?
it was absorbed from the oceans by photosynthetic algae and plants, and organisms like these were turned into fossil fuels (which contain carbon), eg. crude oil.
how was coal formed?
Formed from trees in dense forests and low-lying wetland areas. Flooding caused wood from forests to be buried, preventing oxidation. Compression and heating over millions of years turned wood into coal.
how was crude oil formed?
simple plants and tiny animals living in oceans or lakes. these organisms died, remains sank to bottom, buried under sediment, lack of oxygen prevented oxidation. over millions of years, heat and pressure turned the organisms into crude oil and natural gas.
What are the 2 reasons why CO2 in the atmosphere decreased?
dissolved in oceans
used by primitive plants in oceans for photosynthesis
why are greenhouse gases necessary for earth?
without them, mean temperature on Earth would be -18*C, too cold to support life
what do greenhouse gases do?
absorb heat radiated from the earth
release energy in all directions, keeping the Earth warm
This is called the greenhouse effect.
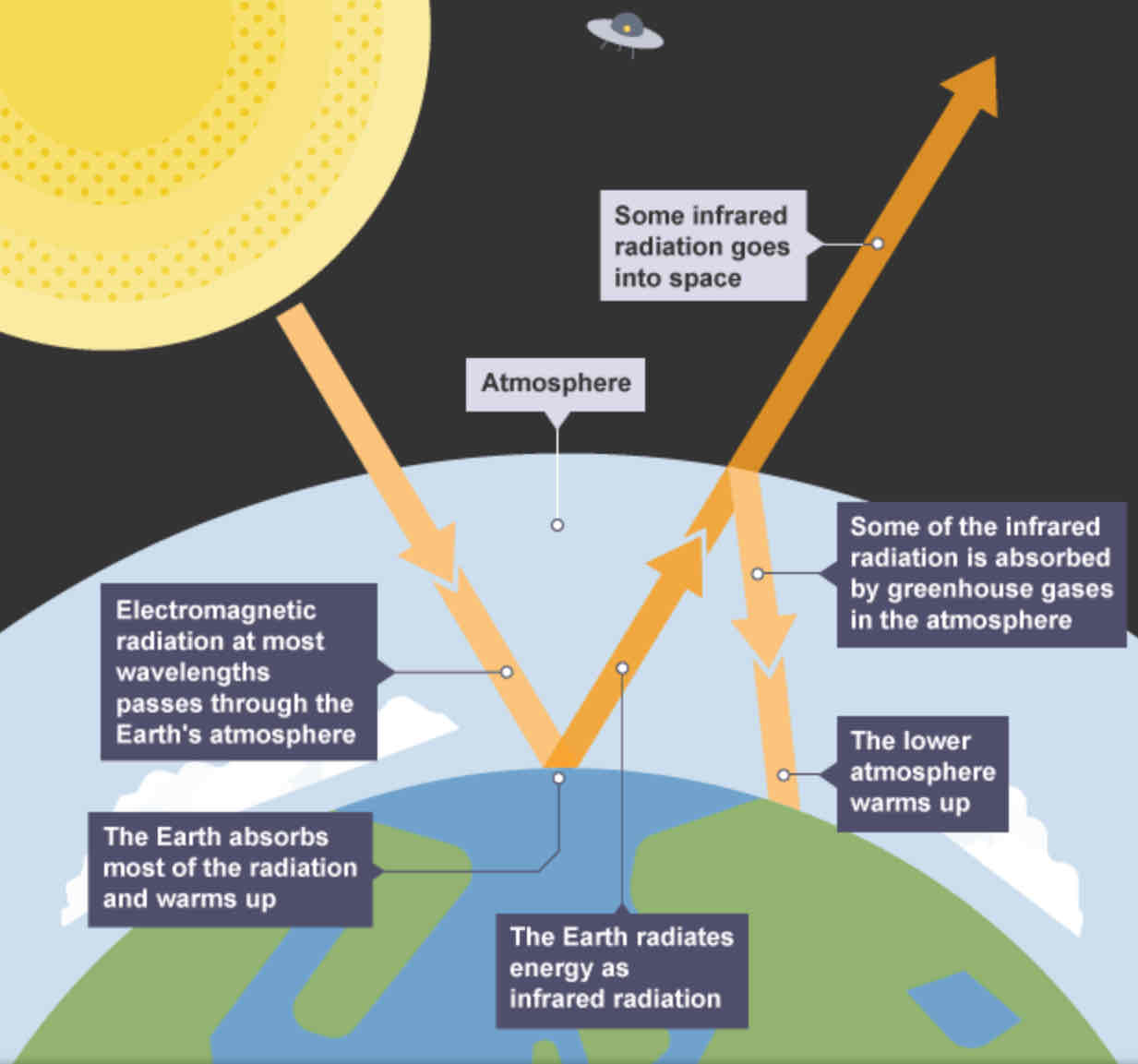
Greenhouse effect - diagram
examples of 3 most abundant greenhouse gases present in Earth’s air?
water vapour
carbon dioxide
methane
explain the greenhouse effect in detail.
Electromagnetic radiation (from sun) at most wavelengths passes through Earth’s atmosphere.
Earth absorbs most of the radiation and warms up.
Earth radiates energy as infrared radiation.
Some of the infrared radiation goes into space.
Some of the infrared radiation is absorbed by greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
The lower atmosphere warms up.
what should be considered when evaluating quality of evidence of research?
is who did the research trustworthy?
did the person who funded the research cause bias?
did the data’s collection and analytical methods cause uncertainties?
which organisation is publishing the evidence?
human activities increasing amount of greenhouse gasses?
farming cattle releases methane
farming rice in paddy fields releases methane
burning fossil fuels releases carbon dioxide
deforestation releases carbon dioxide and decreases its absorption through photosynthesis
Why do scientists believe humans are responsible for the increase in greenhouse gasses and therefore global warming?
Majority of evidence in peer-reviewed journals supports the theory that human activities are the cause.
What do some people believe the cause of climate change is?
Natural factors
Cycles of climate change
What may the media sometimes present?
Articles and opinions that are…
Simplified
Inaccurate
Based on only some evidence
Biased
What is important in creating an accurate article?
For new evidence to be shared with as a any people as possible, so other scientists can check the results and interpretations, and repeat the experiment themselves.
climate
average weather conditions over longer periods and larger areas.
weather
the day-to-day condition of the atmosphere in a small area.
What must you compare when talking about global warming?
Data from many years (climate), of else you cannot make a judgement about the changing climate.
The Earth’s climate has been constantly changing since…
…since the Earth was formed, 4.6 billion years ago.
What were examples of changes in climate in the past?
Several ice ages
Periods of much warmer temperatures
What were these changes in climate caused by before?
Volcanic eruptions
Changes in energy that reaches the earth from the sun
When did the cause of climate change shirt from being natural to being caused by humans?
200 years ago
is climate change natural
yes, up until 200 years ago it was caused by volcanic eruptions and changes in energy that reaches the Earth from the Sun.
Are global warming and climate change different?
Yes
global warming
the rise in the average temperature of the earth’s surface. has only been occurring in the past 200 years.
Climate change
The long-term alteration of weather patterns. This has always been happening.
Which one of global warming and climate change is then caused by human activities?
Global warming
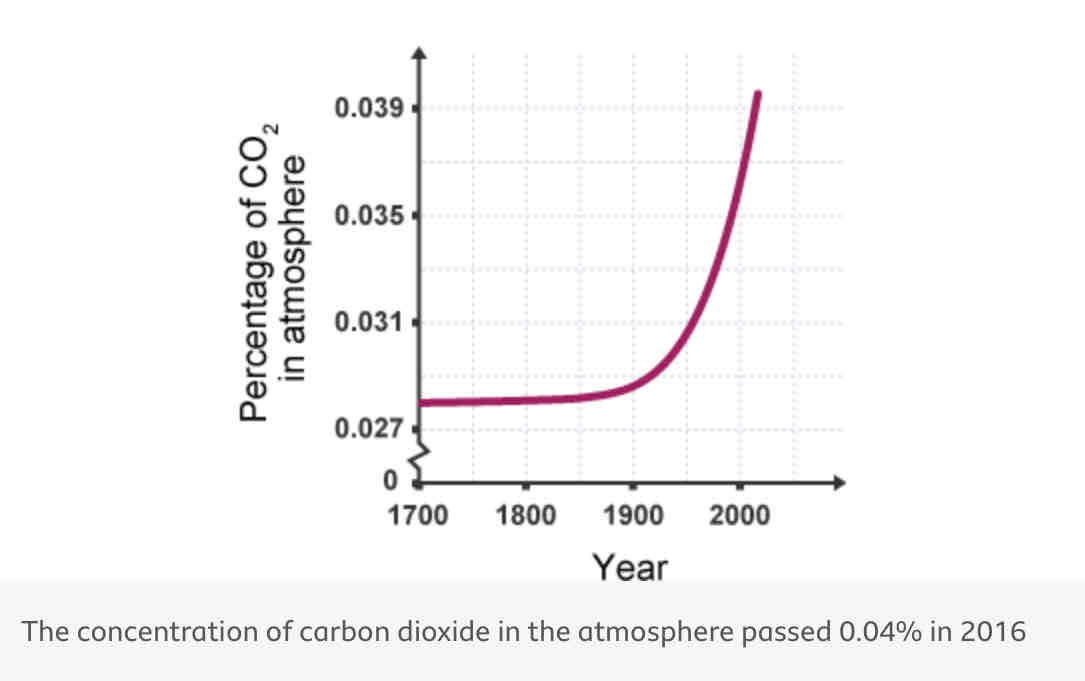
Relationship between carbon dioxide and global warming
Strong correlation
effects of global warming
glaciers and polar ice melting
sea levels rising
patterns of rainfall changing, causing floods or droughts
habitats changing
as temperature rises, seawater warms up and expands
what is ‘carbon footprint’ of something
the total amount of carbon dioxide and other GGs emitted over the full cycle of a product’s production and shipment or the total amount of carbon dioxide released by all the activities a person takes part in over the period of a year.
What would h carbon footprint of a car include?
machinery used to extract metal from Earth’s crust and process it
power stations which generate electricity used to manufacture the car
the car itself when it drives for many years
the machinery which is used to dispose of or recycle a car
What would the carbon footprint of a person in one year include?
total amount of CO2 released into the atmosphere by all of the activities they take part in
the manufacture, use and disposal of all products and resources they use
What are common things which increase your carbon footprint? (5)
using fossil-fuelled electricity at home for lighting, electronic devices etc.
using a gas-powered boiler a home for heating and hot water
Travel to school by bus or car (most likely runs on fossil fuels)
Eat beef or rice farmed with methods releasing methane
travel abroad once per year on an aeroplane
Why does using a gas-powered boiler increase your carbon footprint?
Produces CO2
how can someone improve their carbon footprint? (3)
fit solar panels to reduce amount of fossil fuel generated electricity used.
use a bicycle instead of a car.
improve home insulation (eg. double glazing) to reduce amount of gas burned in the boiler
Why might it be difficult for individuals to decrease their carbon footprint? (2)
too expensive
may work too far from home to cycle
What do most fuels contain?
Carbon and/or Hydrogen
What happens when hydrogen atoms are present in a fuel?
They are oxidised to water.
Is water a pollutant?
No
complete combustion of hydrocarbon fuels
When lots of oxygen is present, the carbon atoms are completely oxidised to CO2, and the maximum amount of energy is released.
CO2 and water are produced.
complete combustion of a hydrocarbon fuel occurs when…
…there is a good supply of oxygen
incomplete combustion of a hydrocarbon fuel occurs when…
…there is a poor supply of oxygen.
incomplete combustion of hydrocarbons
There is a poor supply of oxygen, so carbon may or may not be oxidised, to form CO or a particulate carbon (soot), or a mixture of both. Less energy is released.
problems with incomplete combustion
carbon monoxide is poisonous - it binds to haemoglobin in RBCs and prevents them from carrying oxygen to the cells in your body.
CO is colourless and odourless, so it is difficult to tell if you are breathing it in.
particulate carbon can cause health issues as it irritates lining of the lungs, so can cause cancer and worsen asthma. can
particulate carbon cause global dimming, reducing rainfall.
global dimming
gradual reduction un radiation energy reaching Earth’s surface from the sun. this is due to small particles in the atmosphere produced bu human activities eg. burning fossil fuels.
Atmospheric pollutants that can be produced from burning fossil fuels:
carbon dioxide
carbon monoxide
particulate carbon (soot)
unburned hydrocarbons
sulfur dioxide
nitrogen oxides
Where does Carbon dioxide, CO2 come from?
Complete combustion of any fuel containing carbon atoms.
Where does Carbon monoxide, CO come from?
Incomplete combustion of any fuel containing carbon atoms.
Where does Particulate carbon, C (soot) come from?
Incomplete combustion of any fuel containing carbon atoms.
Where do Unburned hydrocarbons come from?
Hydrocarbon fuel molecules which have not been oxidised at all.
Where does Sulfur dioxide, SO2 come from?
Combustion of a fossil fuel which contains sulfur impurities.
Where do Nitrogen oxides, NOx come from?
Oxidation of atmospheric nitrogen inside the engine of a car, lorry, etc.
What is acid rain?
A dilute solution of sulfuric acid, H2SO4.
why is sulfur dioxide a pollutant?
Sulfur atoms in fuels oxidised to SO2, then further oxidised to form sulfur trioxide gas (SO3) in the atmosphere.
This dissolves in rainwater to form acid rain.
this kills plants and animals, especially those in aquatic habitats. also damages manmade objects such as buildings and statues.
Sulfur oxidation reaction
sulfur + oxygen → sulfur dioxide
S + O2 → SO2
Sulfur dioxide oxidation reaction
sulfur dioxide + oxygen → sulfur trioxide
2SO2 + O2 → 2SO3
Acid rain formation reaction
sulfur trioxide + water → sulfuric acid
SO3 + H2O → H2SO4
Is nitrogen present in fossil fuels?
No
why are NOx gasses pollutants?
High pressure and temperature in car engines can cause nitrogen and oxygen in air to react to form oxides of nitrogen (NO or NO2, grouped by general formula NOx).
These can cause acid rain or react with other pollutants in the atmosphere to produce photochemical smog.
photochemical smog
a type of air pollutant that appears as a visible smoky fog and is very harmful to health - can cause asthma attacks or death.