Lesson 6: Elasticity of Supply
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
Supply Elasticity
A measure of the way in which quantity supplied responds to a change in price
Elastic supply
Small change in price leads to a relatively larger change in output; Coefficients greater than 1
Inelastic supply
Quantity changes very little relative to change in price; Coefficients less than 1
Difference b/w demand elasticity and supply elasticity
If quantities are being PURCHASED= DEMAND elasticity
If quantities are being BROUGHT TO THE MARKET = SUPPLY elasticity
Determinants of Supply
Its production (nature of the business, more easily a firm can adjust to a change in price = more likely the supply is elastic)
Supply Elasticity does not depend on..
number of substitutes, necessity of the product, or percentage of budget used to purchase the product (demand elasticity does), ONLY affected by PRODUCTION CONSIDERATIONS!
Market Period
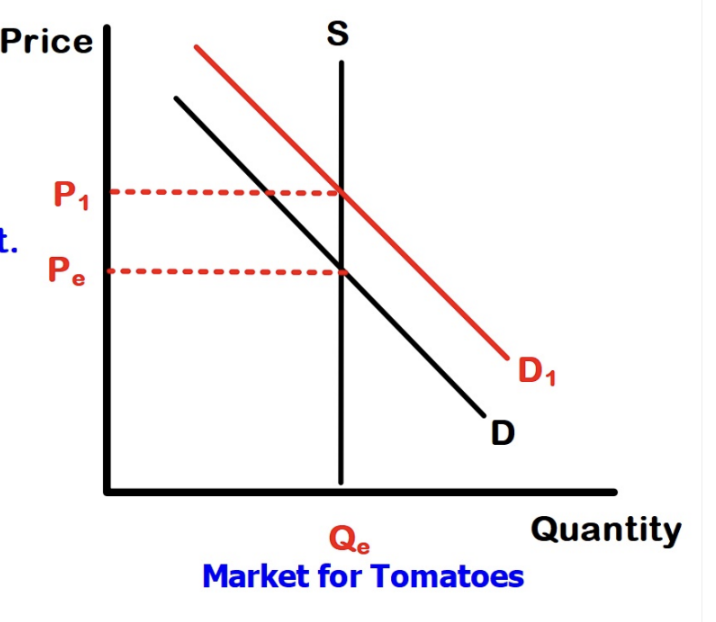
A time period so short that the producer CANNOT respond to the change in price. Insufficient time to change output. Supply is perfectly inelastic (ex. Tomato farmer cannot produce more tomatoes at the end of growing season)
Short Run
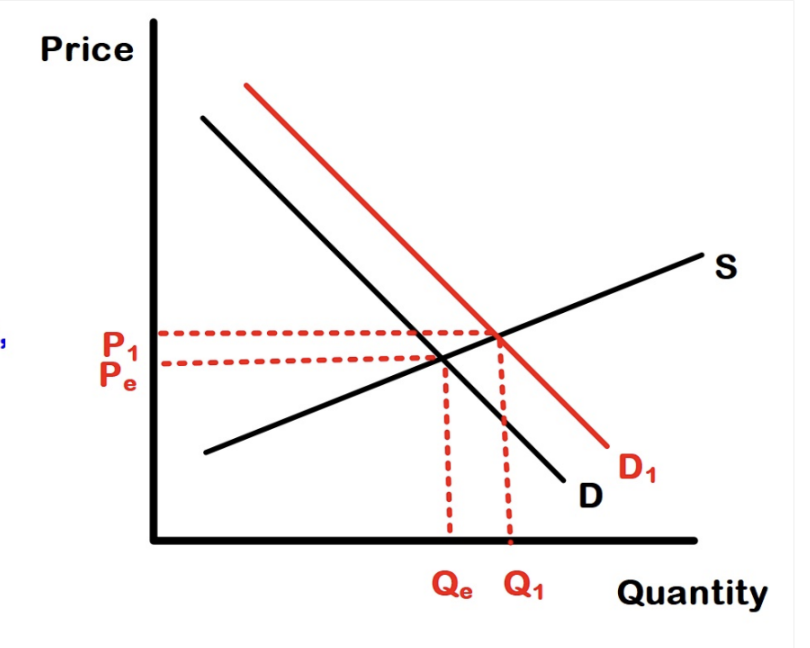
A period of time that will not allow for a change in the physical plant capacity (capital goods) but will allow for some temporary change in output from that physical plant (Ex. Tomato farmer can construct a temporary greenhouse)
Long Run
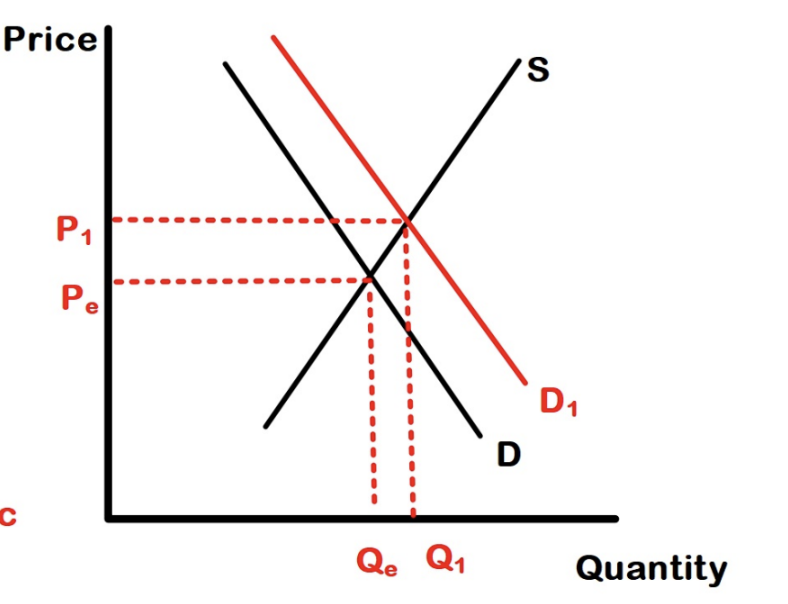
There’s an ample of time to make major adjustments to production-change methods, expand the physical plant, increase capital, hire more workers, etc. (ex. Tomato farmer buys more land)