Anatomy Exam 2 - Mizzou, Anatomy Exam 2 - Mizzou (Hill)
1/389
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
390 Terms
Functions of the Skeletal System (5)
Support: entire body
Protection: Viscera (organs)
Movement: Attachment for the muscles
Hemopoiesis: Blood cell production
Energy & Mineral Reserves: bones have calcium
-need for it leads to osteoporosis
Are bones organs?
Yes - bones consist of various types of tissue -- Including blood
Is the skeleton internal or external?
Internal
Where do bones meet?
At joints
Skeleton consist of
Bones, cartilages, joints, and ligaments
How many named bones are there?
206
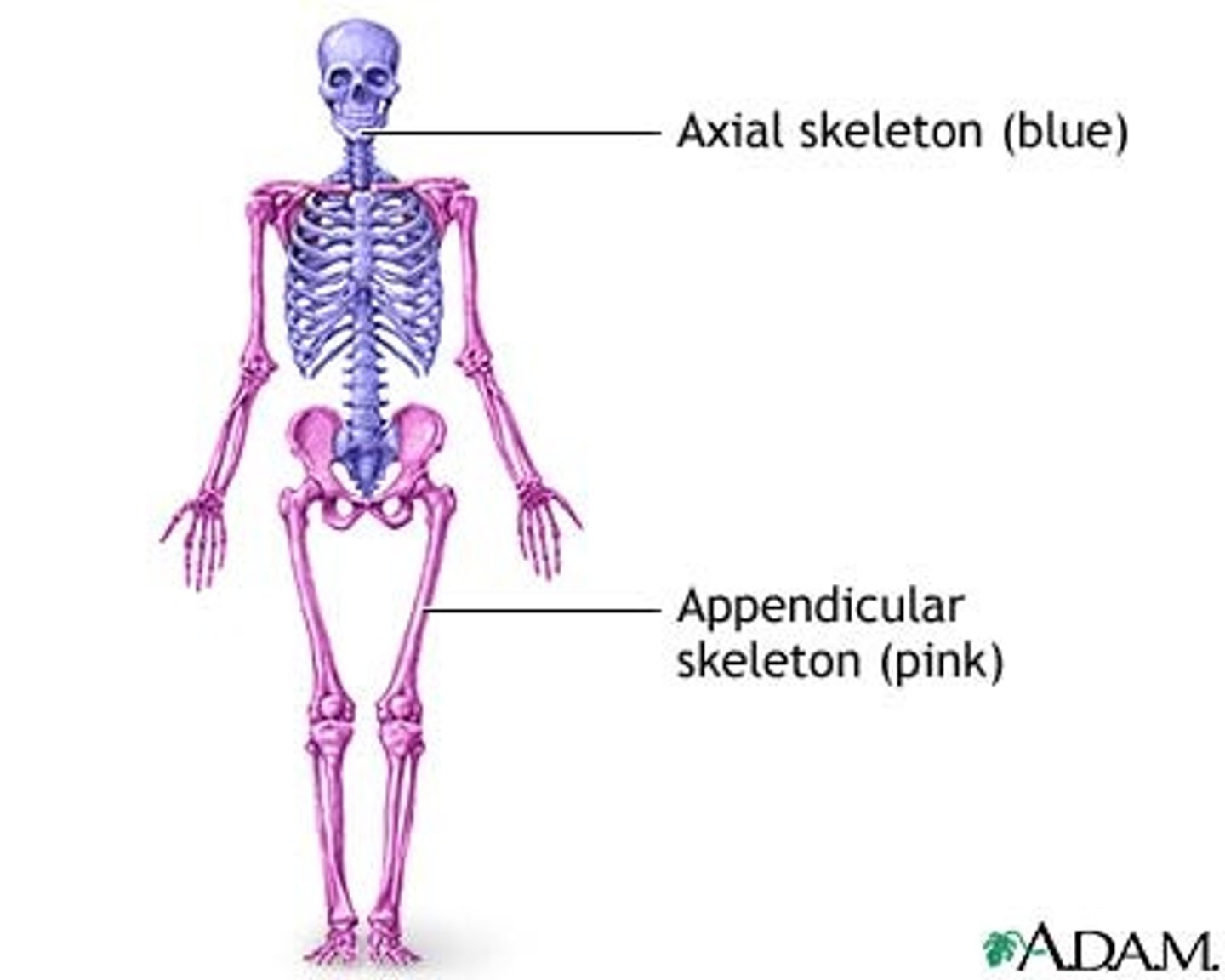
Skeleton subdivides into what?
Axial & appendicular
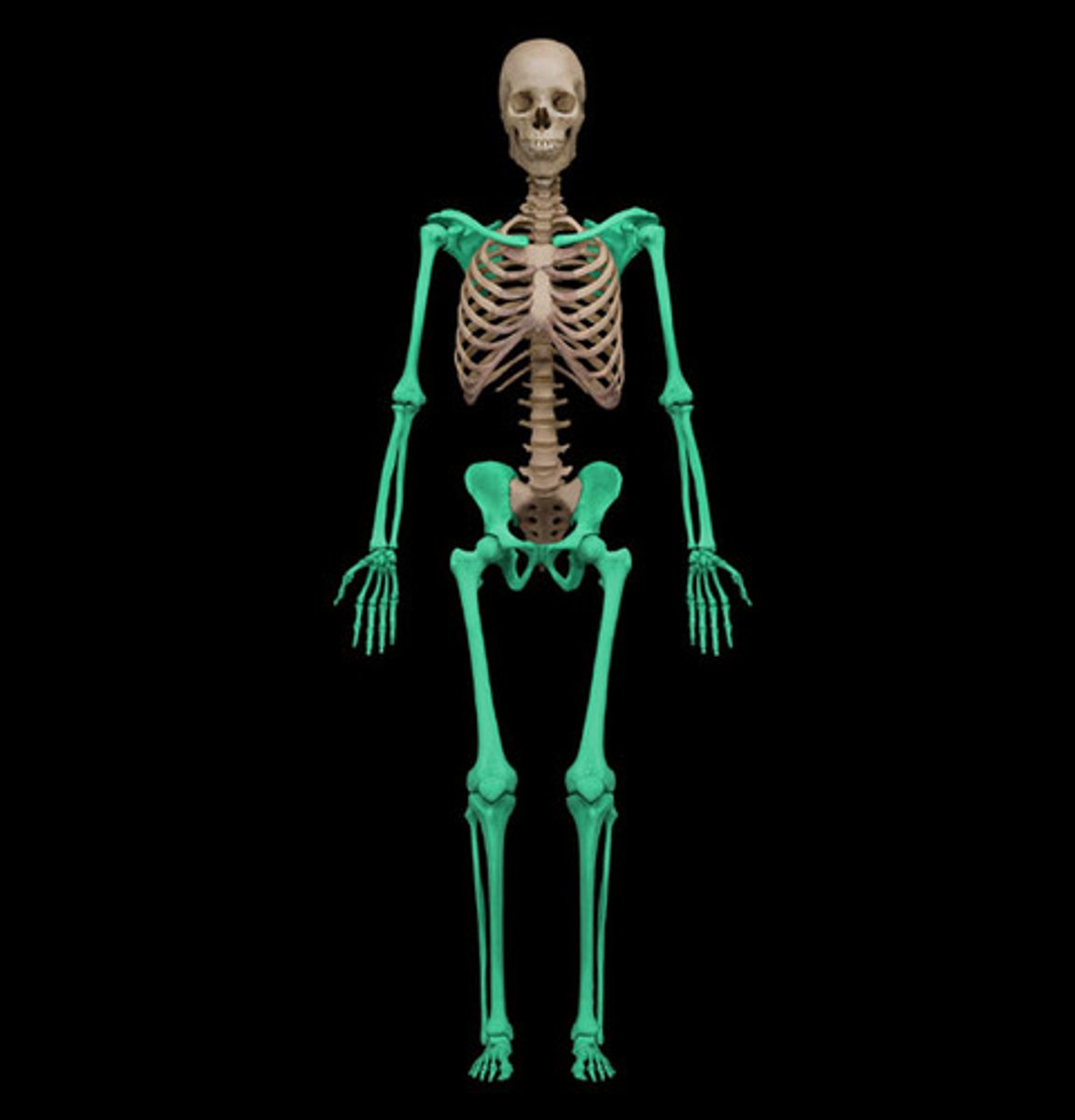
Axial Skeleton includes
Includes: Skull, vertebral, column, thoracic cage(sternum and ribs)
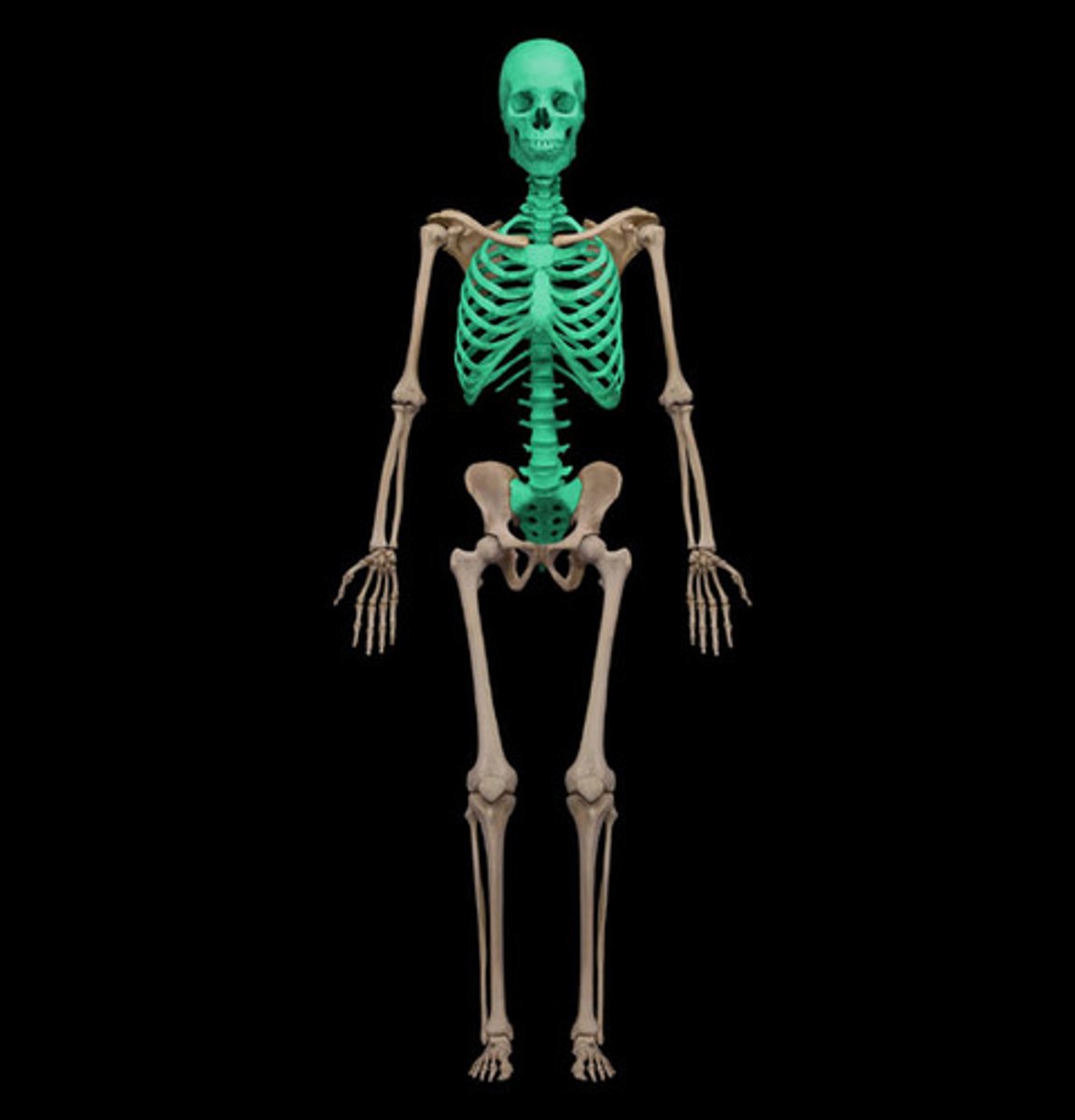
Appendicular Skeleton includes
Includes: pectoral girdle, upper limb, pelvic gridle, lower limbs
Axial & Appendicular Skeleton
Axial Skeleton amount of bones
80 named bones
Axial Skeleton Functions
-Supports head, neck, and trunk
-protects brain, spinal cord, thoracic organs
Bone Markings
characteristics on the surface of the axial and appendicular bones that indicate attachments, articulations or openings for nerves and blood vessels, explains Boundless.
Examples: Foramen, fossa, process, meatus, canal
Foramen (foramina) & example
a hole in a bone (typically for nerves or blood vessels)
Examples: foramen magnum, infraorbital foramen)
Fossa (fossae) & example
a depression in a bone
Examples: mandibular fossa, lacrimal fossa
Process & examples
projection from bone, narrow or wide, protrudes from surrounding bone
ex.: styloid or mastoid process
Meatus & examples
a hole or tube-like structure
(e.g. auditory meatus)
Canal & examples
a groove or tube-like structure
(e.g. optic canal)
Cartilage Tissue Structure
Avascular (no blood supply)
Cell Type: chondrocytes (in lacunae)
Cartilage Functions
Support soft tissues
Model for formation of bone
Gliding surface at articulations
-avascular so no blood supply
-have chondrocytes in lacunae
-cartilage in NOT soft bone
Three types of cartilage
Hyaline, elastic, fibrocartilage
Hyaline Cartilage
-most common kind of cartilage. Has tiny nearly invisible collagen fibers called fibrils
-found:
ends of long bone, costal cartilages, respiratory structures, fetal Skelton
-has a glassy appearance under microscope
Fibrils
Tiny nearly invisible collagen fibers
Elastic Cartilage
Similar to hyaline but lots of elastic fibers. Very resilient and flexible, tolerates repeated bending
Elastic Cartilage is found where?
in pinna (outer ear) and epiglottis
-has a mesh like appearance
Fibrocartilage
has little ground substance & matrix has thick, dense collagen fibers.
Resists strong compression
Fibrocartilage is found where?
in inter-vertebral disks, knee joint, public symphysis
-it helps absorbs shock in joints
Bone Tissue
Much denser than cartilage, very little fluid. Resists compression and tension; very strong. Well vascularized, so it heals/remodels easy. Made of organic and inorganic materials
-bone tissue is where bone has mineralize
Osteoblasts & Osteoclasts
Bone is constantly being built up or broken down - growth, strengthening, remodeling, healing, maintenance.
Osteoblasts
Builds new bone
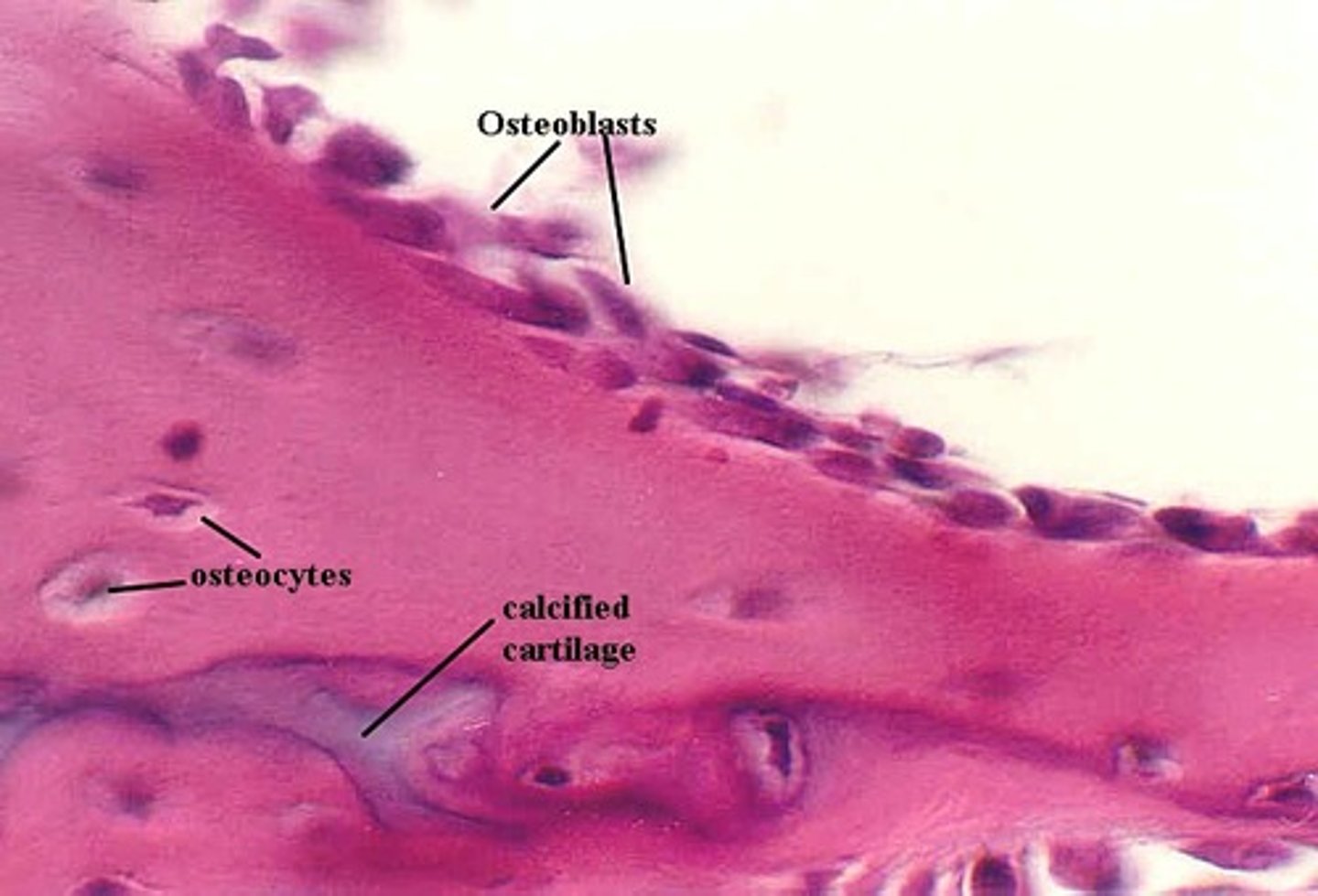
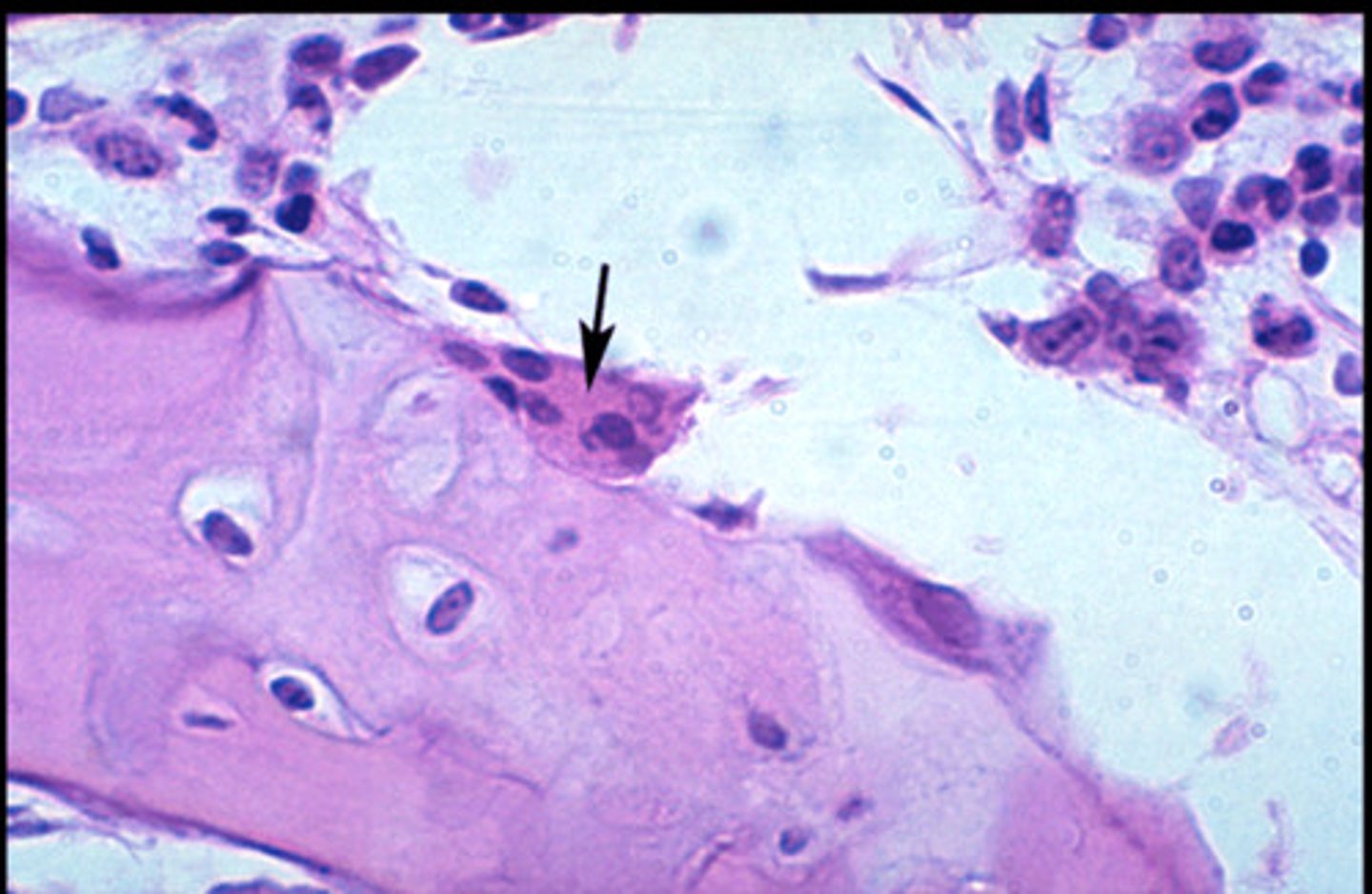
Osteoclasts
Break down (consume) bones and are mature bone cells
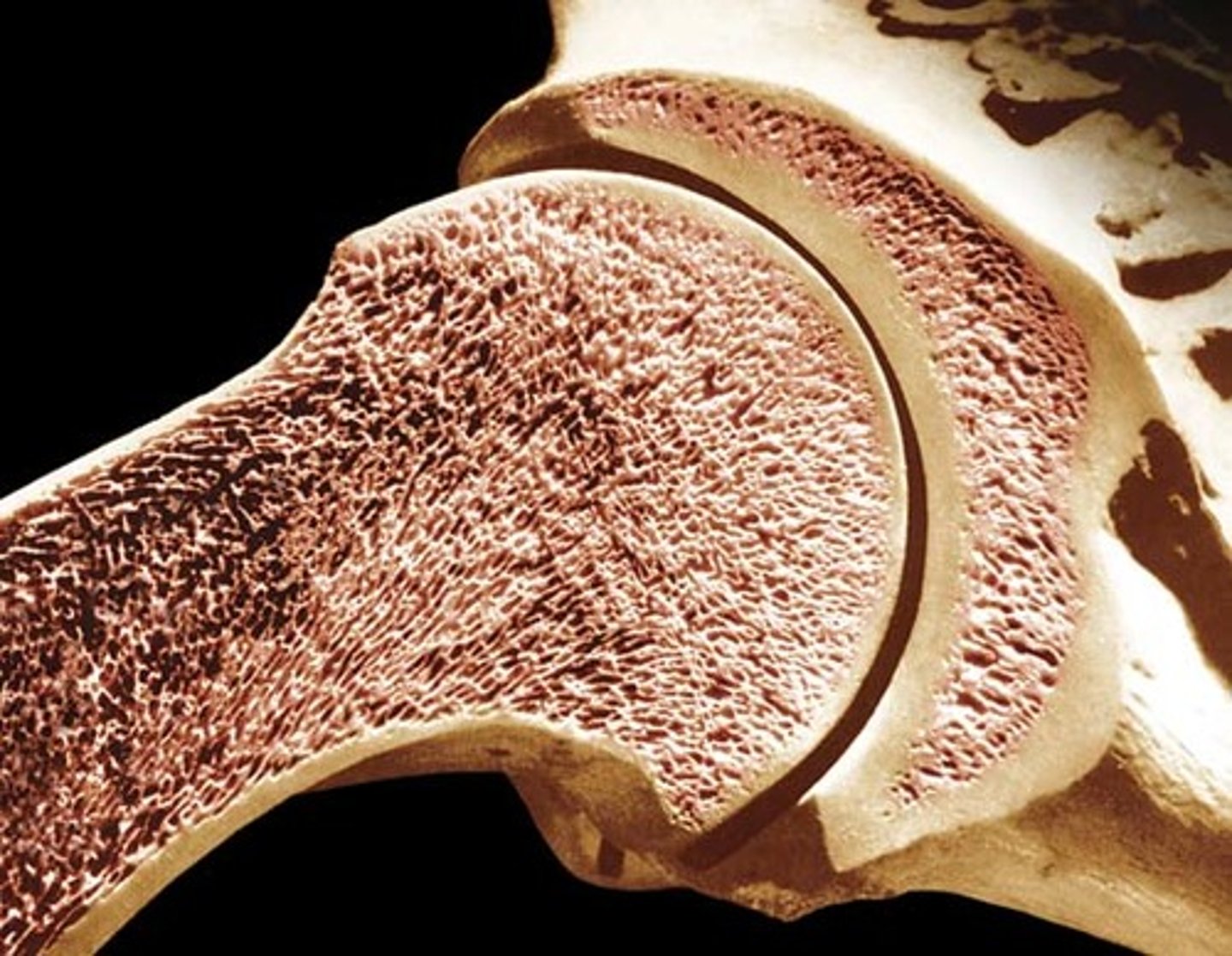
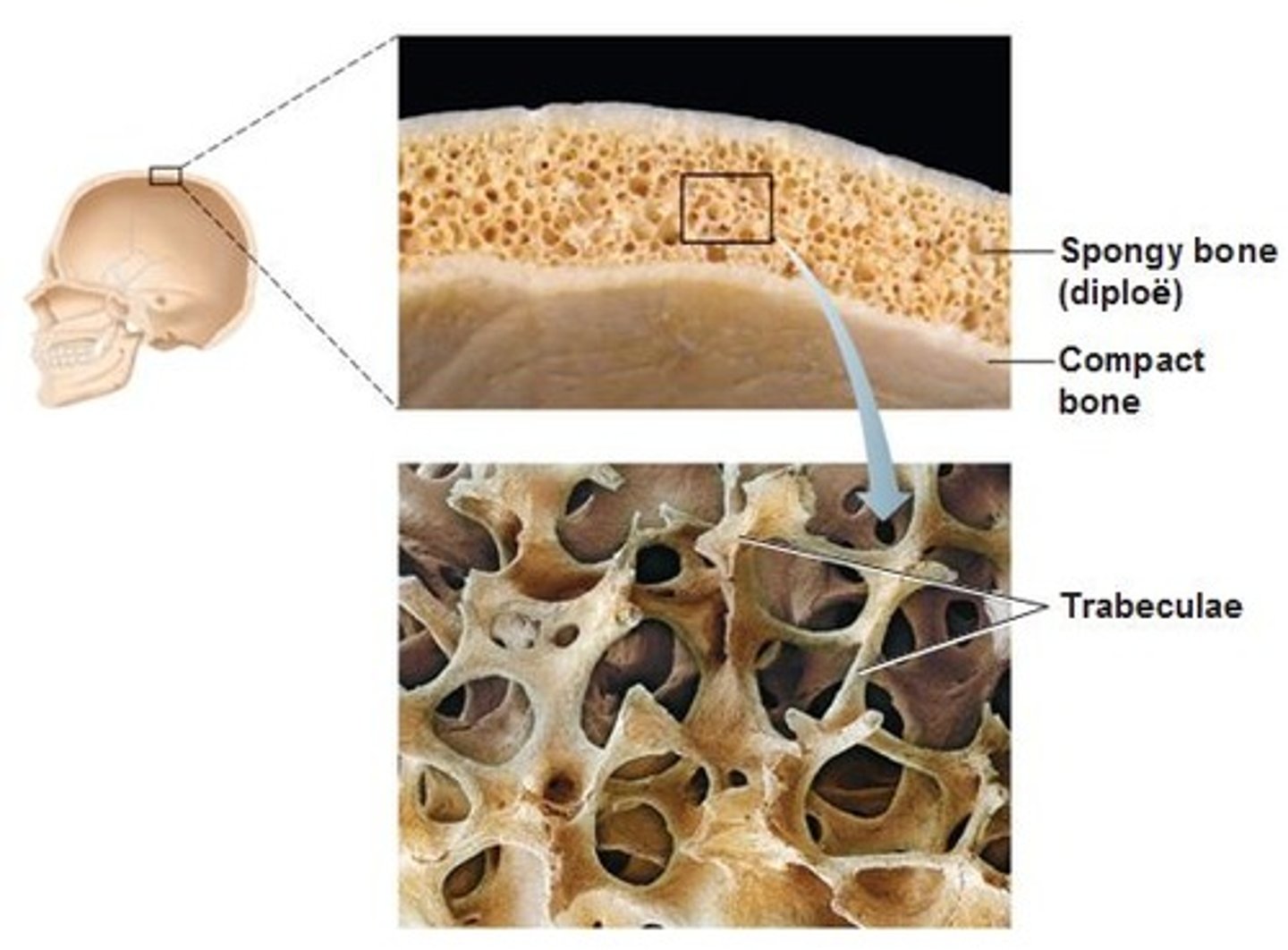
Spongy Bone
(Trabecular bone)
Inside bones
Better at shock absoption
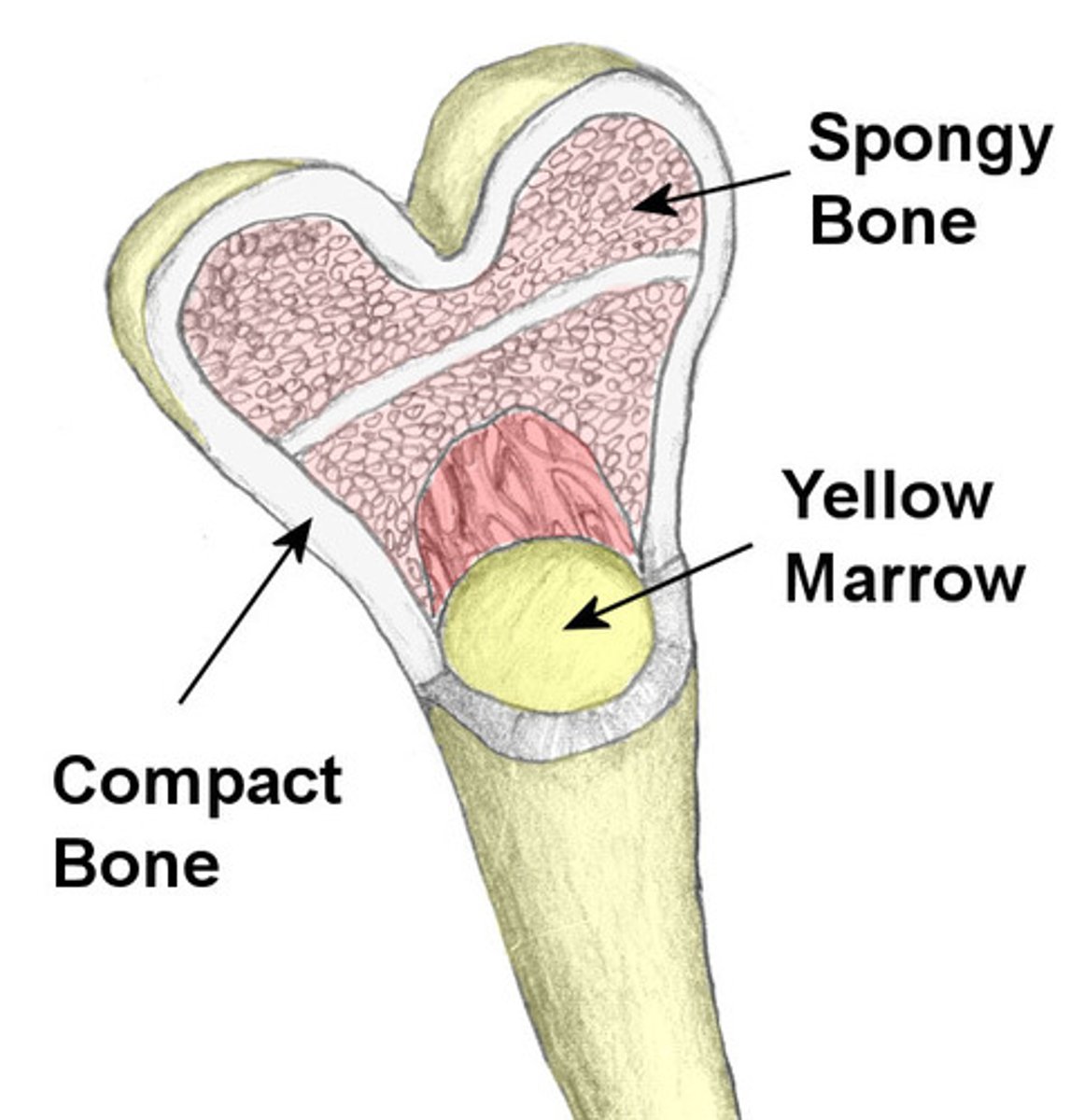
Compact Bone
(Cortical)
Smooth, dense, external portion of bones
Strong, rigid
Compact Bone Structure
Osteon - structure unit
Osteon
-Made up of concentric tubes are called lamellae
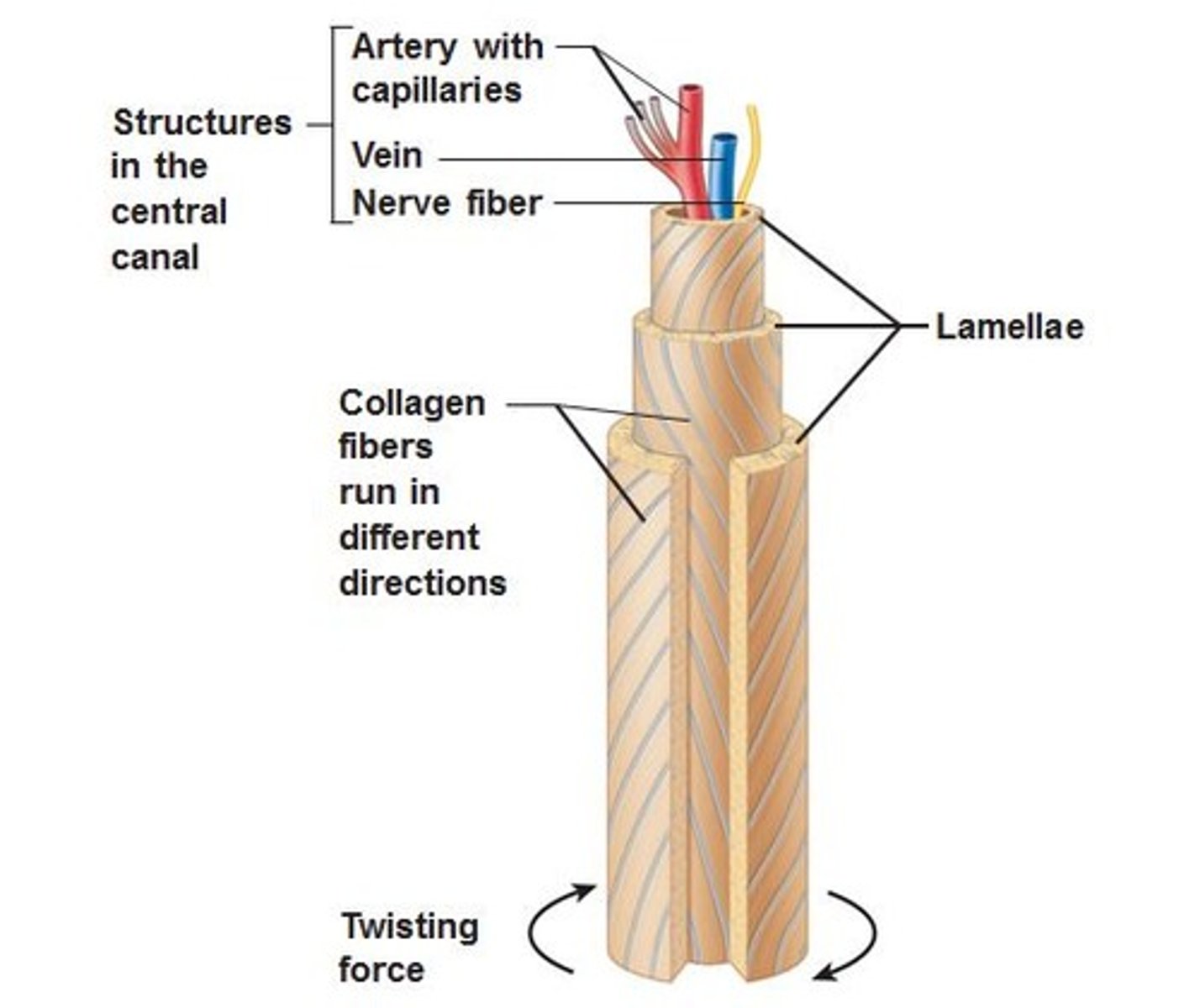
-Oriented parallel to the long axis and main compression stresses
- Haversian (central) canal runs through the core of each osteon and provides blood supply, nutrients, nerves
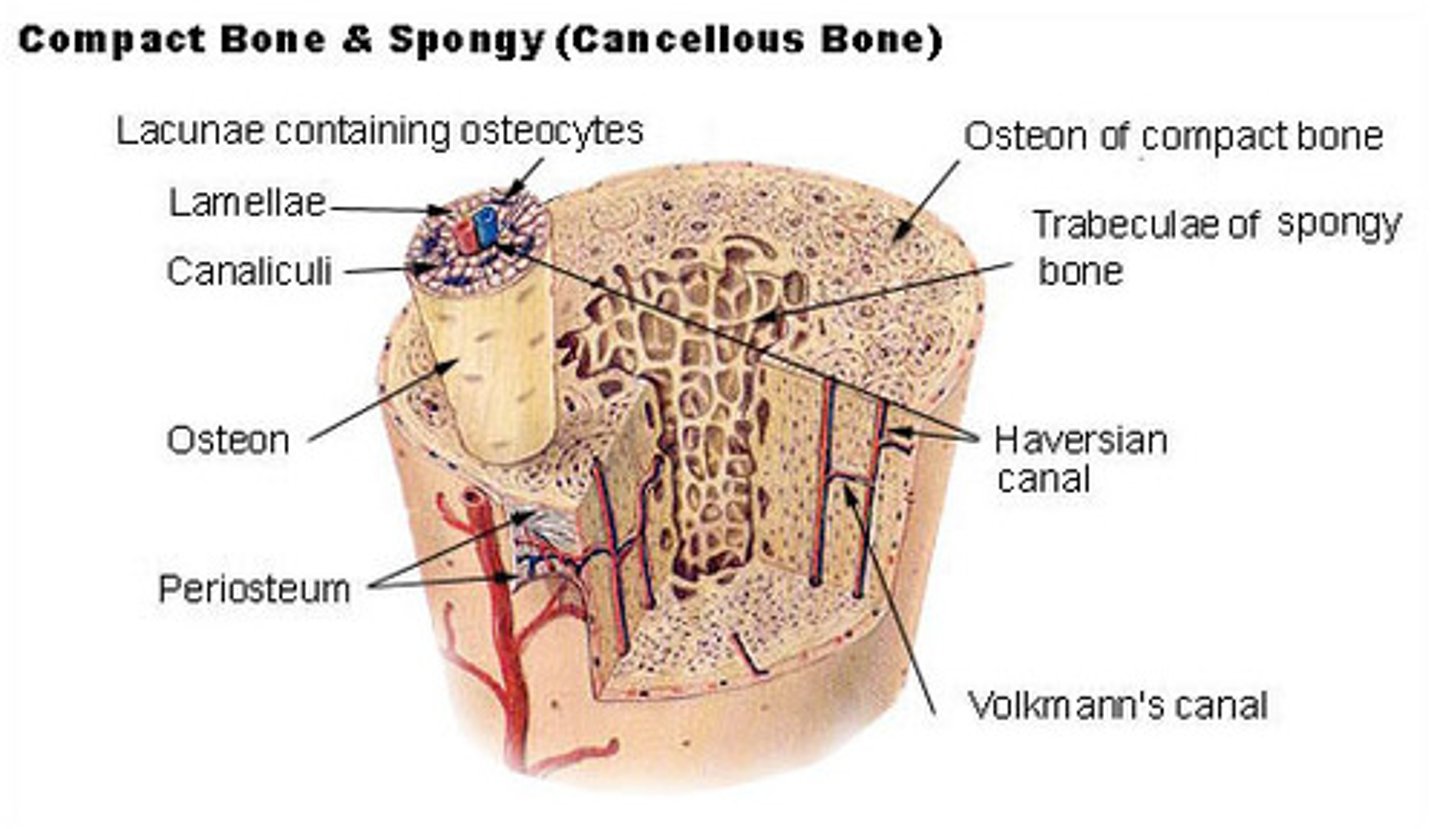
Haversian (central) canal
runs through core of each osteon & provides blood supply, nutrients, nerves
Bones shapes and sizes
Long bone - humerus, metacarpals, femur
Short bone - talus
Flat bone - sternum, skull
Irregular bone - vertebra, ehtopoid, sphenoid
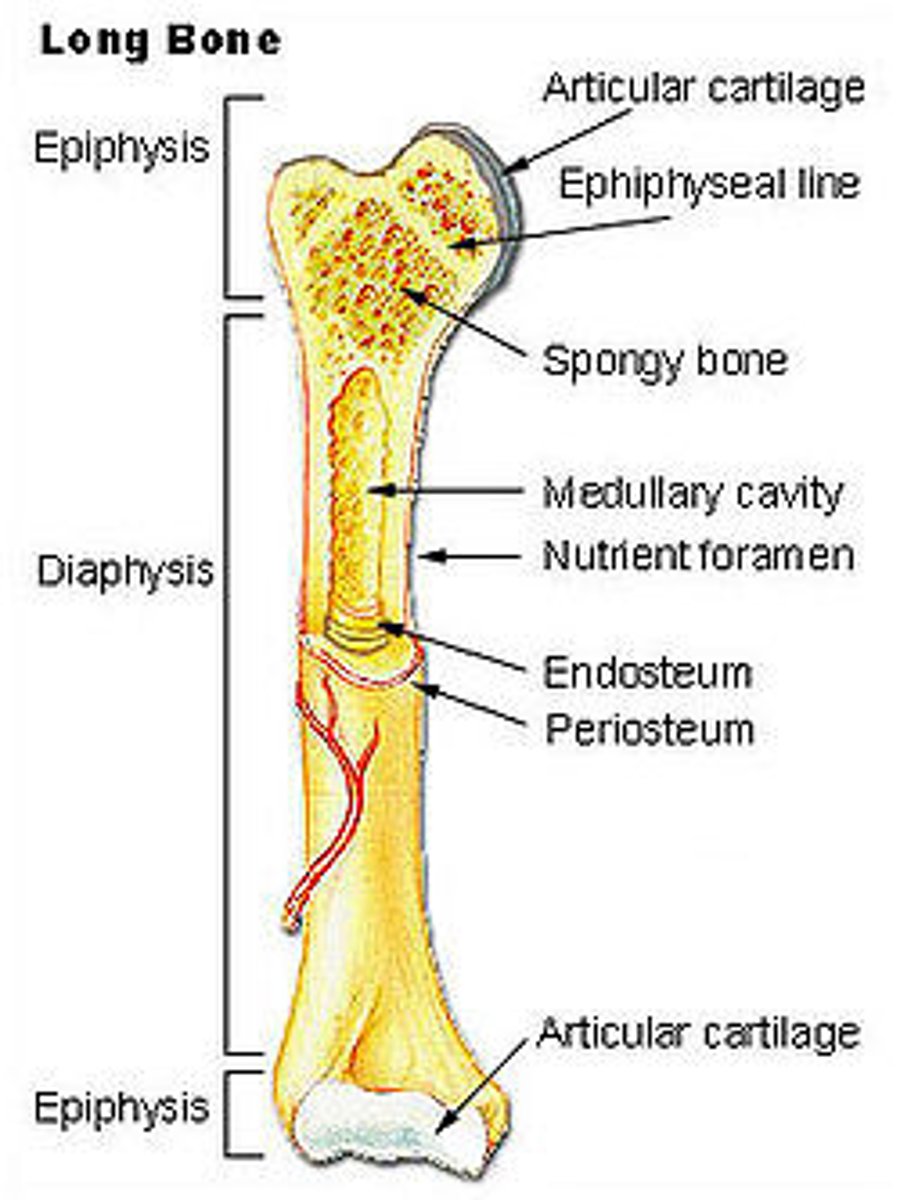
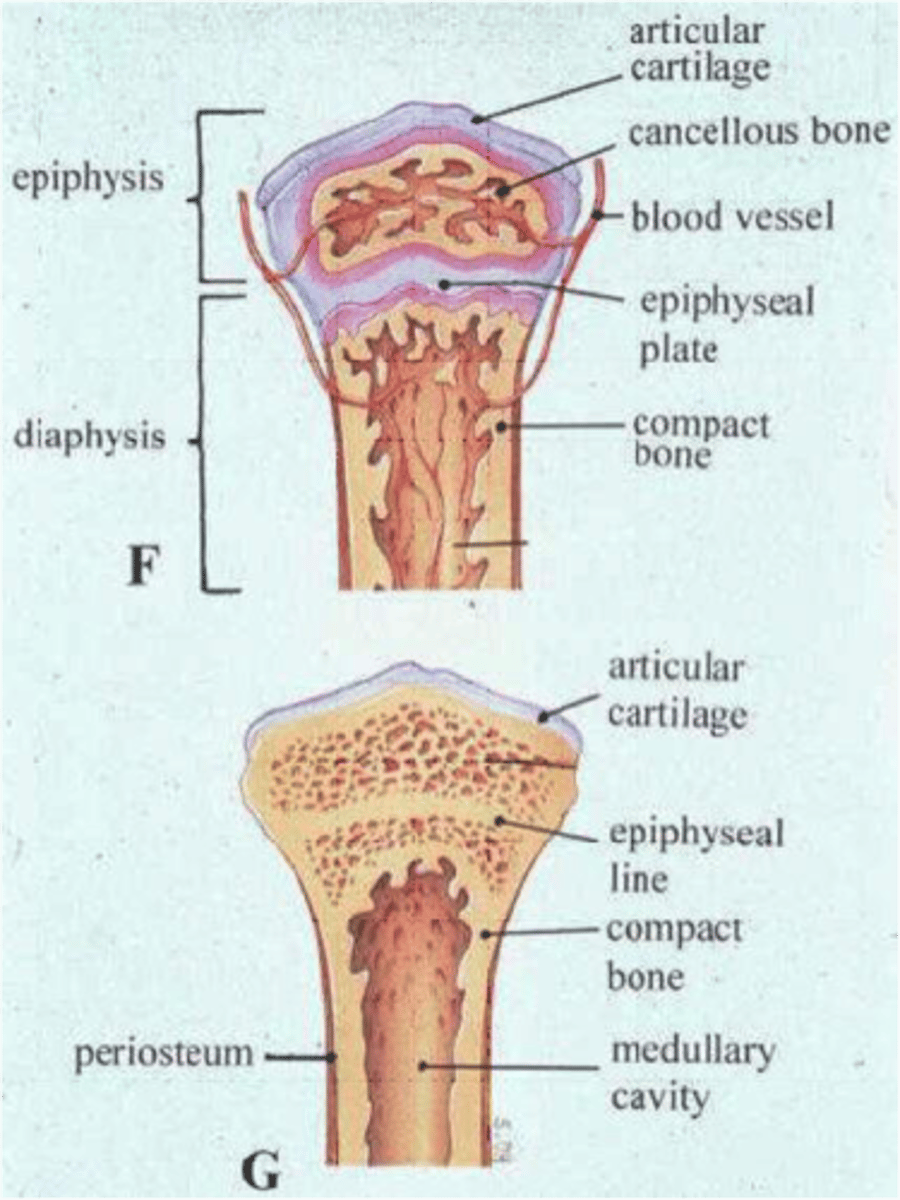
Structure of a Long Bone
Epiphysis - ends
Epiphyseal Line - growth plate
Diaphysis - shaft
Compact bone - superficial
Spongy bone - deep
Articular cartilage is on ends
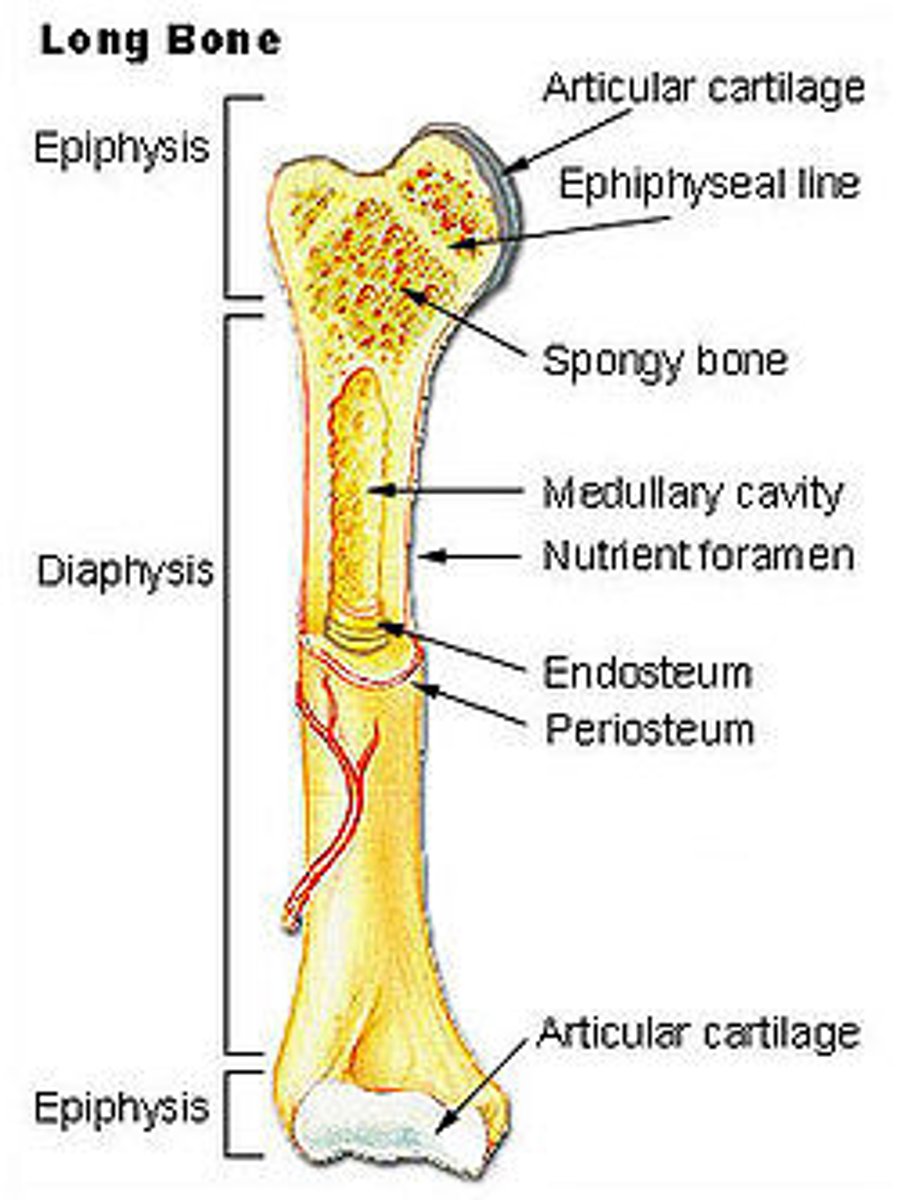
Structure of the diaphysis of a Long Bone
Periosteum - sheath on outside of bone
Endosteum - lines internal cavity
Medullary Cavity - Bone marrow
Nutrient Arteries - Feed bone
Flat, Irregular, and Short Bones
-Compact bone with periosteum on outside
-Spongy bone with endosteum inside
-Contain marrow but don't have a marrow cavity
Bone Development & Growth
-Begins in the embryo & continues through life (more slowly in the adult)
-Before week 8, skeleton made of hayaline cartilage or mesenchyme
-Before week 8, bone tissue begins to replace most cartilage & mesenchyme
Osteogenesis/Ossification
Process of bone formation
-May be endochondral or intramembranous
Two types of Ossification
- Intramembranous Ossification
- Endochondral Bone Ossification
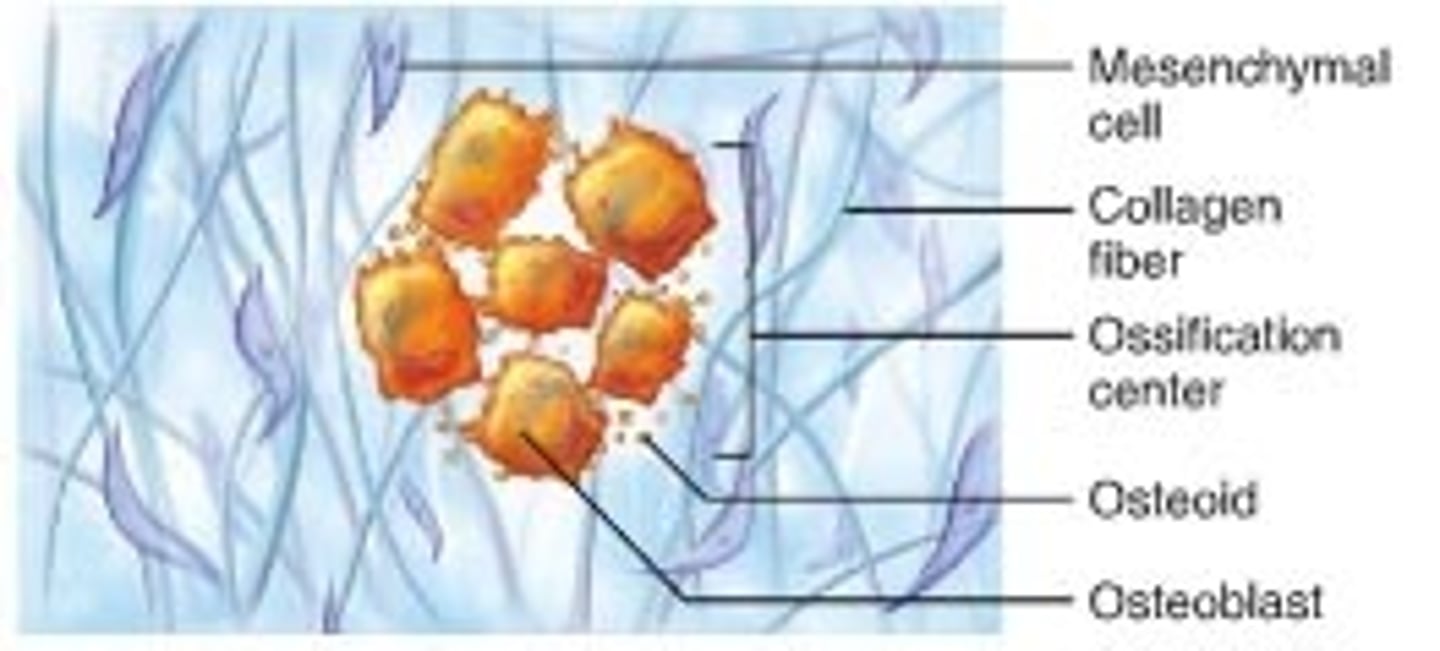
Intramembranous Ossification
-Bone grows within a membrane
-Forms many flat bones (bones of the skull) as well as maxillae, zygomatic, mandible & center of clavicle
Endochondral Bone Ossification
-Most of the bones of the skeleton form this way
1) Skeleton begins as Hyaline Cartilage model
2) Bone replaces cartilage
3) Epiphyseal (growth) plates ossify eventually
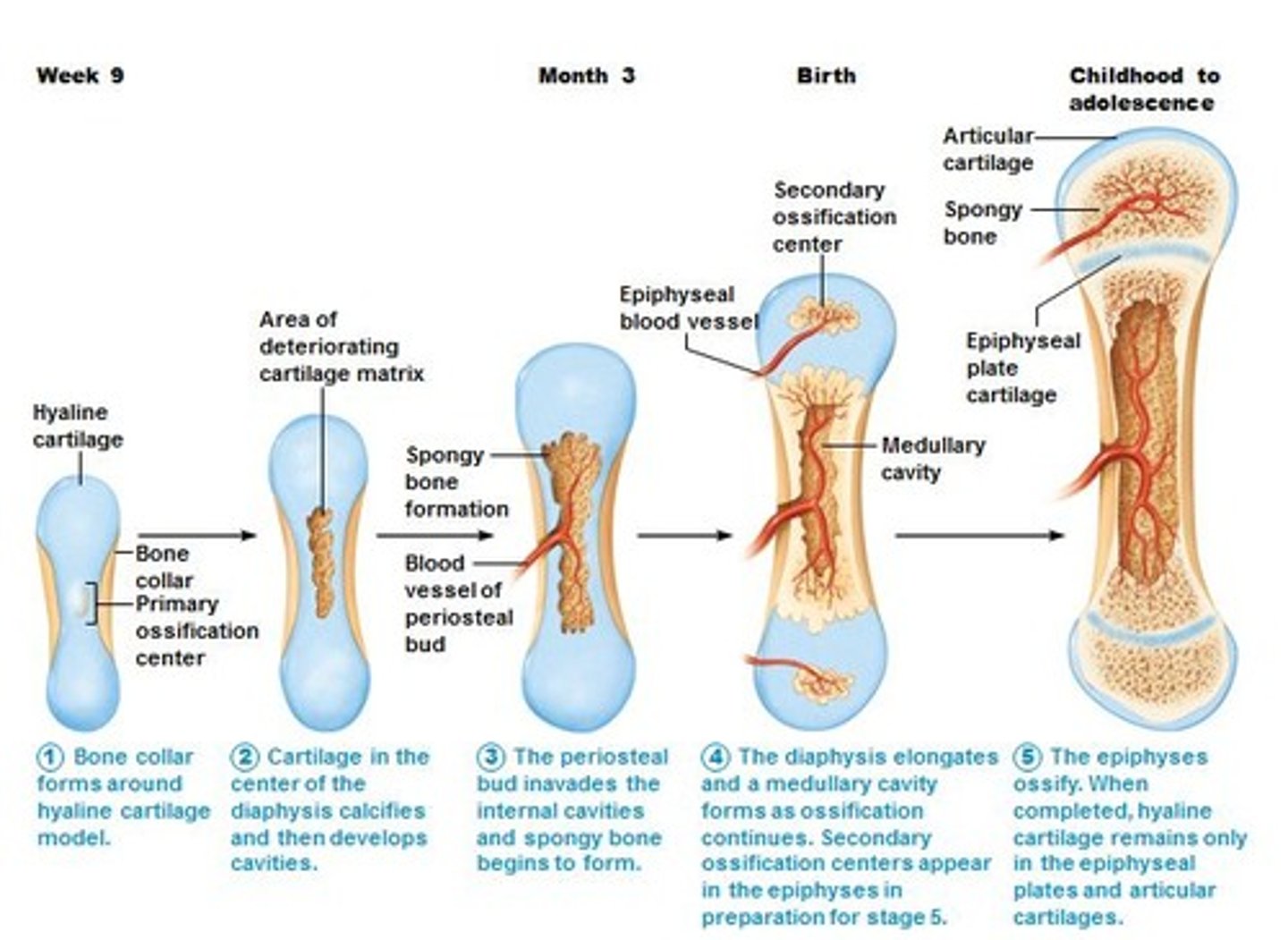
Closure of the Epiphyseal Plates
Cartilage is gradually replaced by bone tissue on both sides of the epiphyseal plate (primary center of ossification at diaphysis & secondary centers of ossification in epiphyses)
-When centers of ossification meets (a epiphyseal plate), growth stops
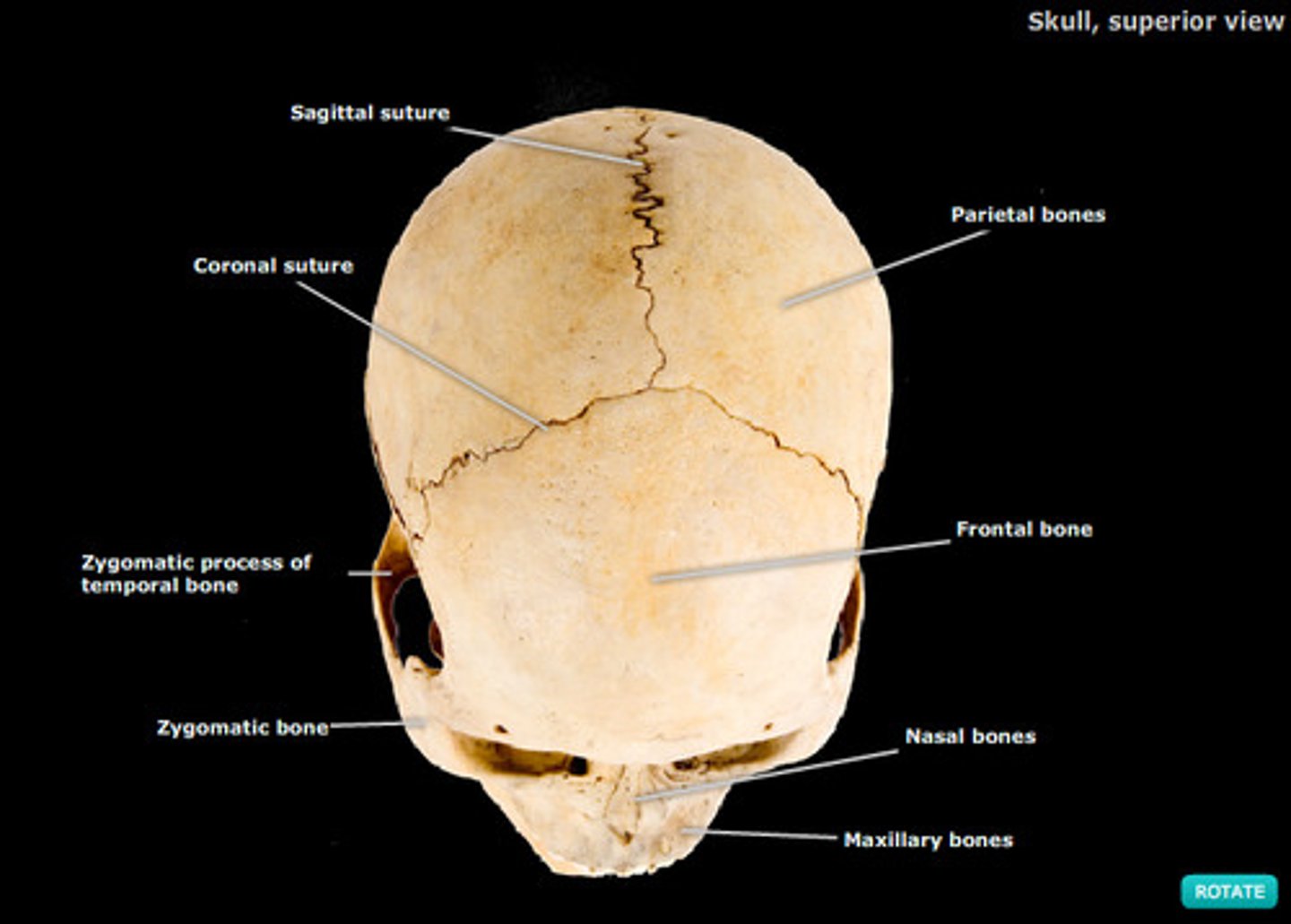
Skull
- 28 Bones - very complex
- Most are "flat" bones, formed via intramembranous ossification(when bones form w/in a membrane)
- united by sutures (interlocking, immovable joints)
sutures of the Skull
1. Coronal Suture- b/t frontal and parietal; corresponds w the coronal view
2. Squamous suture-b/t the parietal bone and temporal bone
3. Lambdoid suture-b/t the occipital bone and parietal bone
4. Sagittal Suture- b/t the parietal bone along the midline; corresponds to the saggital plane
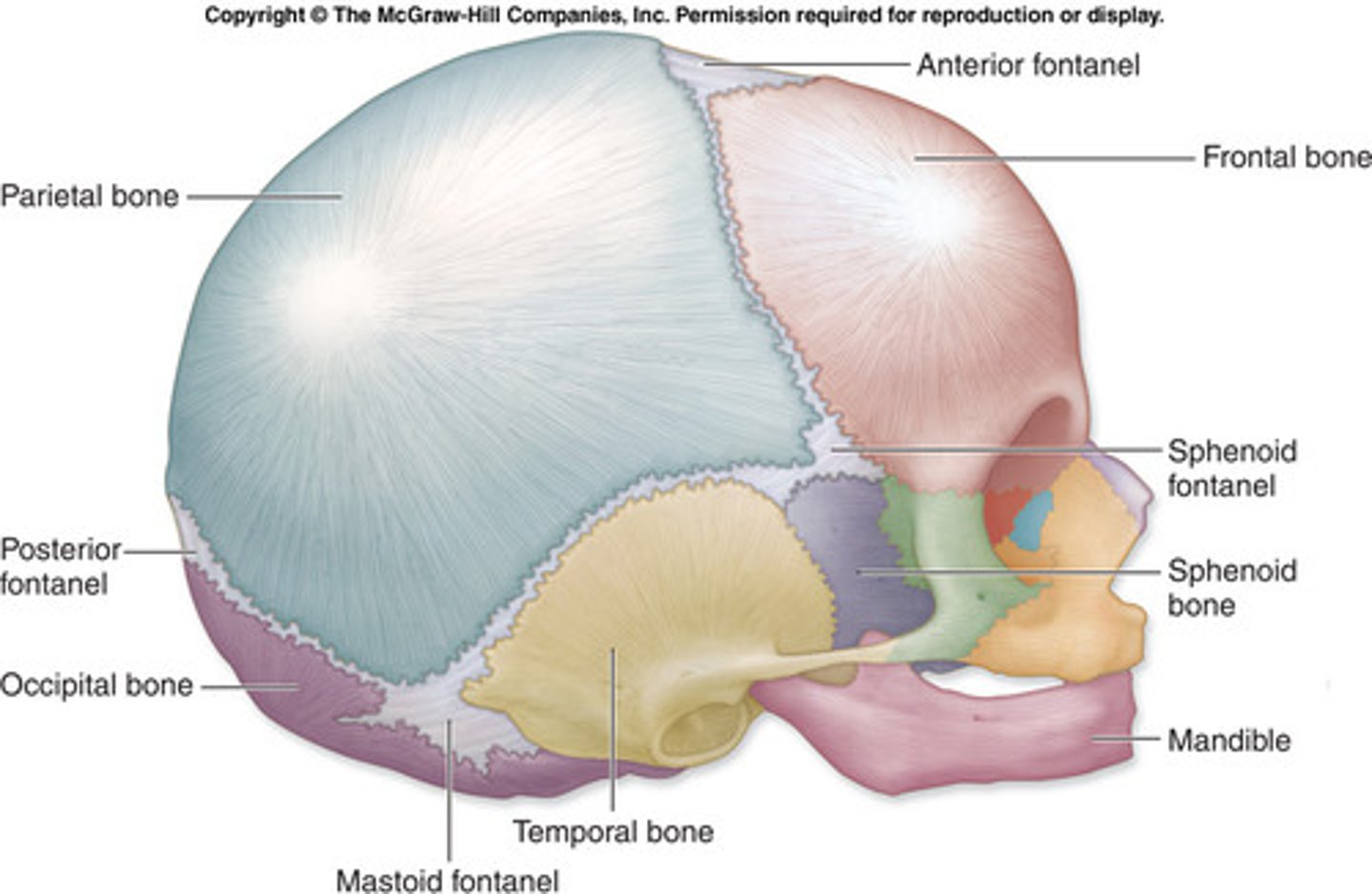
Fetal/Infant Skull & sutures
-not fused in infant skull bones
- Connected by flexible connective tissues to allow head to deform during birth & allow rapid brain growth
- Areas between bones are called fontanelles (soft spots) & fuses over times
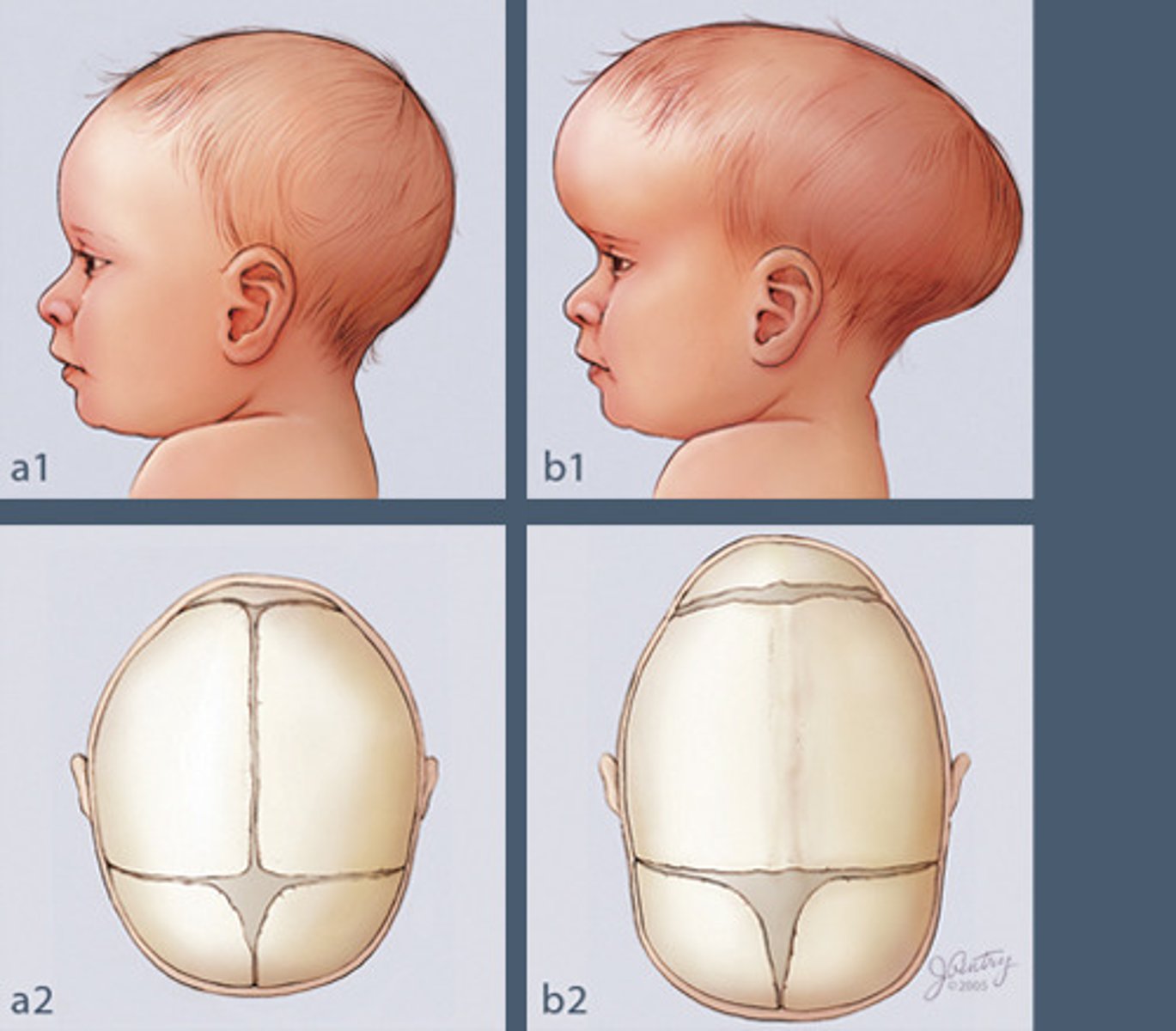
Craniosynostosis
pre-mature fusion of skull bones, leads to unusual cranial vault shape
-sagital synostosis is when the sagittal suture fuses to early and the head long from anterior to posterior
-coronal synostosis is when the coronal suture fuses too early and their head is too short along the anterior/ posterior surface
these require plastic surgery
what are the divisions of the Skull
Subdivides into cranial & facial divisions
Cranial bone functions
Protect brain
provides attachments sites for some head/neck muscles
Facial bone functions
form the framework of face
opening the passage of air & food
Hold the teeth
anchor muscles of face
what is the cranium subdivided into
Vault(calvarium) = superior, lateral & posterior bones of skull (includes forehead)
Base = inferior part of cranium
Cranium is made up of
8 Bones
- Frontal (forehead)
- Occipital
- Sphenoid
- Ethmoid
- 2 Parientals (left & right)
- 2 Temporals (left & right)
Parietal Bone
Made up most of superior part of skull, extend posteriorly & laterally
**Note: Sagittal suture (between two parietal bones), lambdoid surure (between parietal & occipital bones)
Occipital Bone
-forms Posterior part of cranium & cranial base
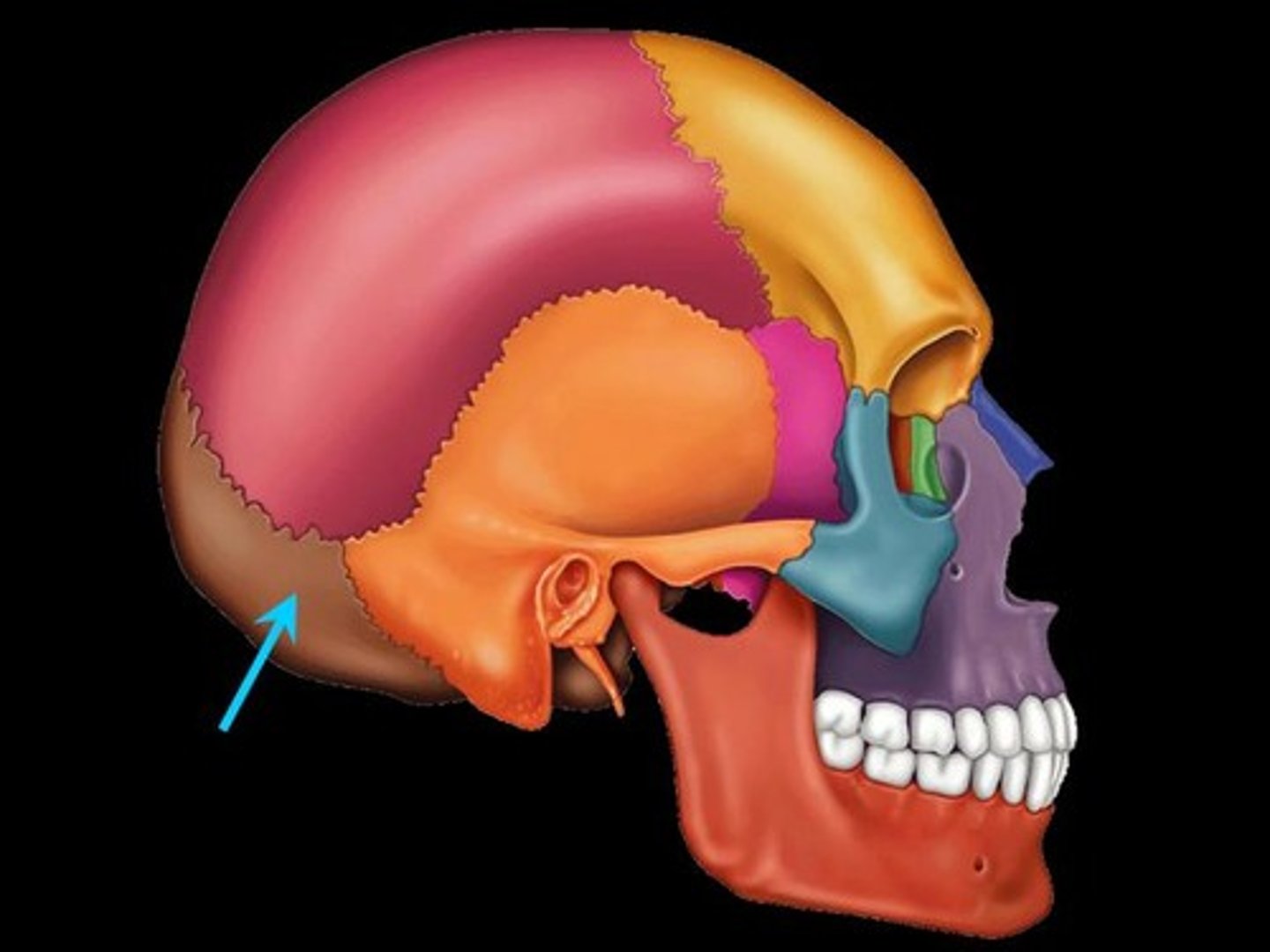
foramen magnum
-main feature of occipital bone
-large opening in occipital bone that allows the spinal cord to pass & connect the brain
occipital condyles
articulate with the atlas
Temporal Bones
Paired temporal bones (left and right sides) house opening to ear, forms the base of cheekbone.
what are the 3 main regions of the temporal bone
petrous
tympanic
squamous
Temporal Bones Regions- petrous
-Petrous is best seen internally, contains middle and inner ear cavities. Petrous=hard.
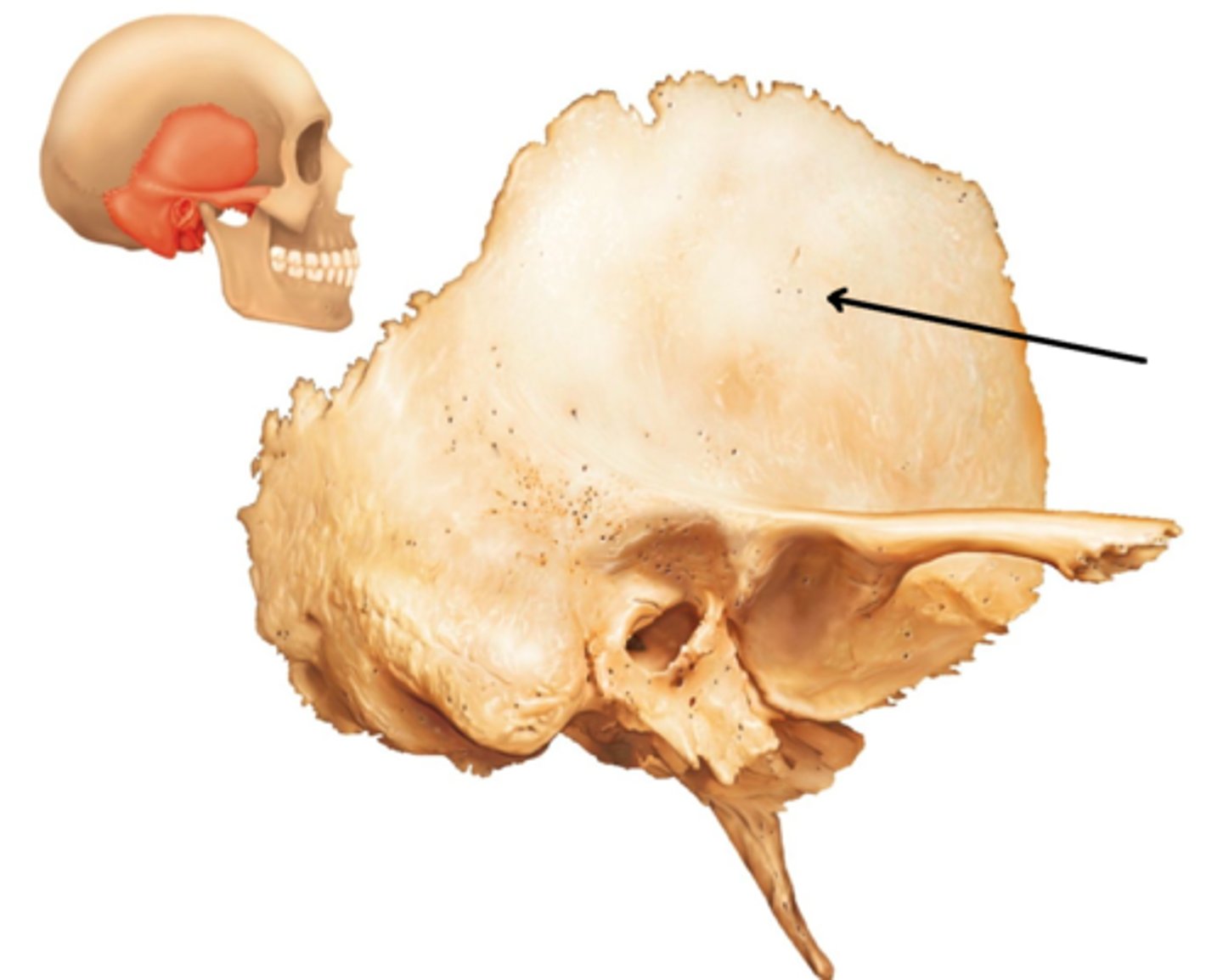
external acoustic meatus
opening in the tympanic region leading to the middle & inner ear
squamous portion
is the vertical portion (part of cranial vault).
Temporomandibular Joint (jaw joint)
where the condyle of the mandible articulates with temporal bone at the mandibular fossa just anterior to the external auditory meatus
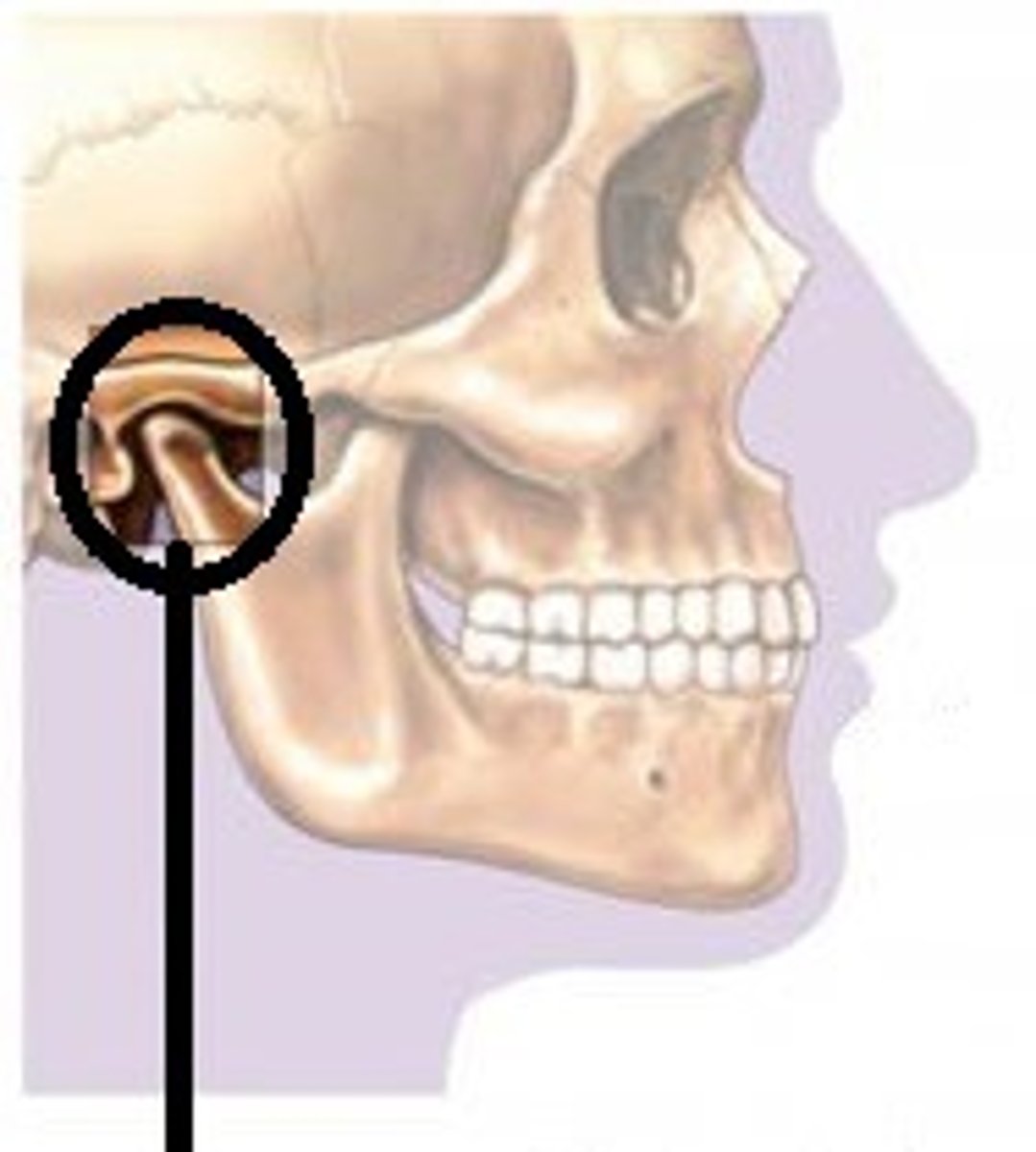
Middle Ear Cavity (inside temporal bone)
3 ear ossicles in the middle ear: from lateral to medial they are: malleus, incus and stapes. Bones are really small.
Sound waves cause vibrations of these bones that are transmitted to the inner ear (cochlea).
Sphenoid
Large and wing-shaped/ butterfly shaped
-seen on the lateral parts of the skull and deep w/in the orbits
Landmark: Sella turcica - bony depression that holds the pituitary gland.
Sphenoid is the only cranial bone that articulates with every other cranial bone.
Ethmoid Bone
Just anterior to the sphenoid is the ethmoid bone.
Ethmoid takes up most of the area between the nasal cavity and the orbits.
Forms some boundaries of the nasal cavity, also separates nasal cavity from the brain.
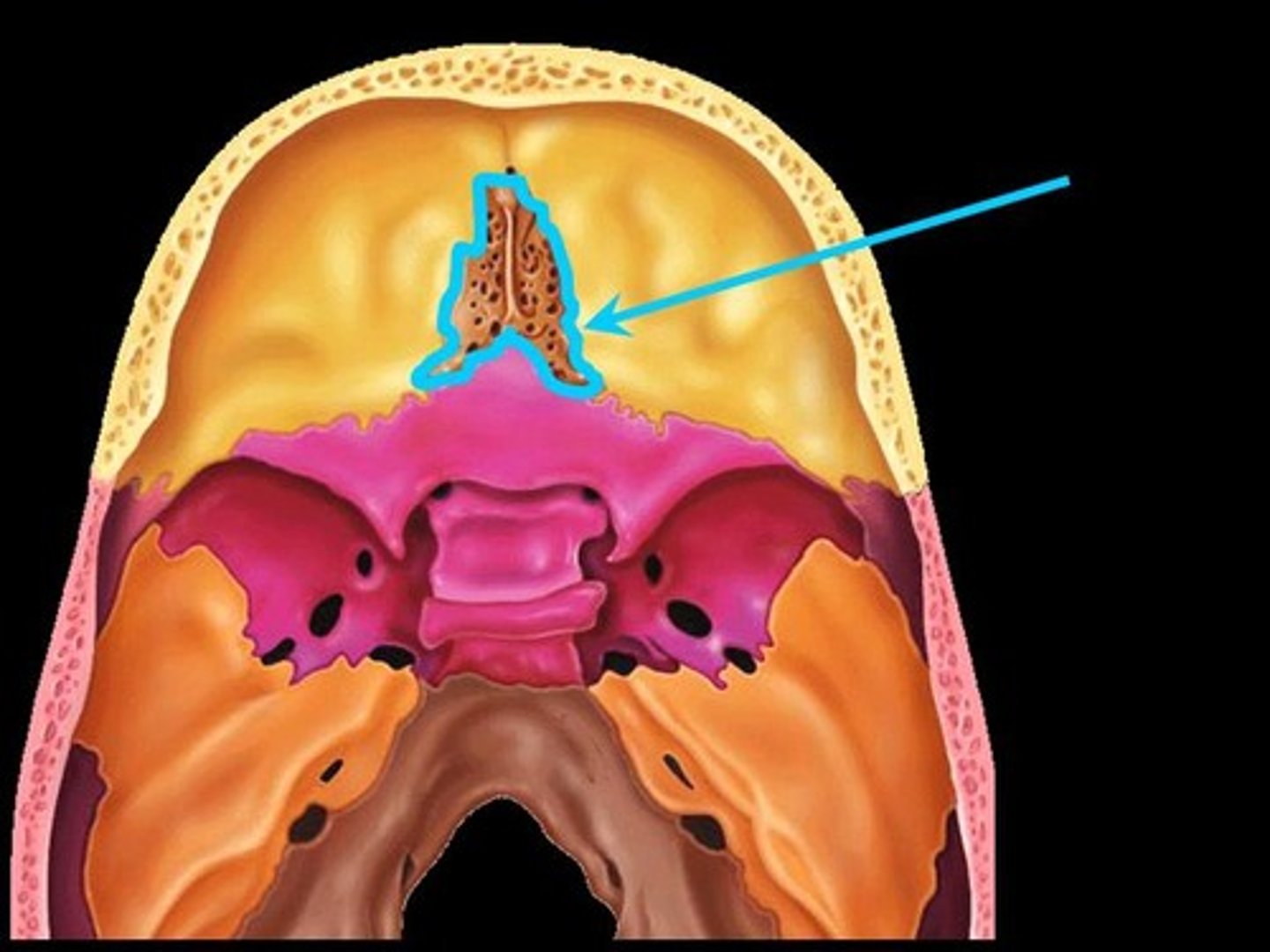
Ethmoid
- Crista galli attaches to cribriform plate; separates nasal cavity from brain, site of attachment for dura mater (membrane covering brain)
- Cribriform plate helps form the roof of nasal cavities; foramina allow passage of olfactory nerves into brain.
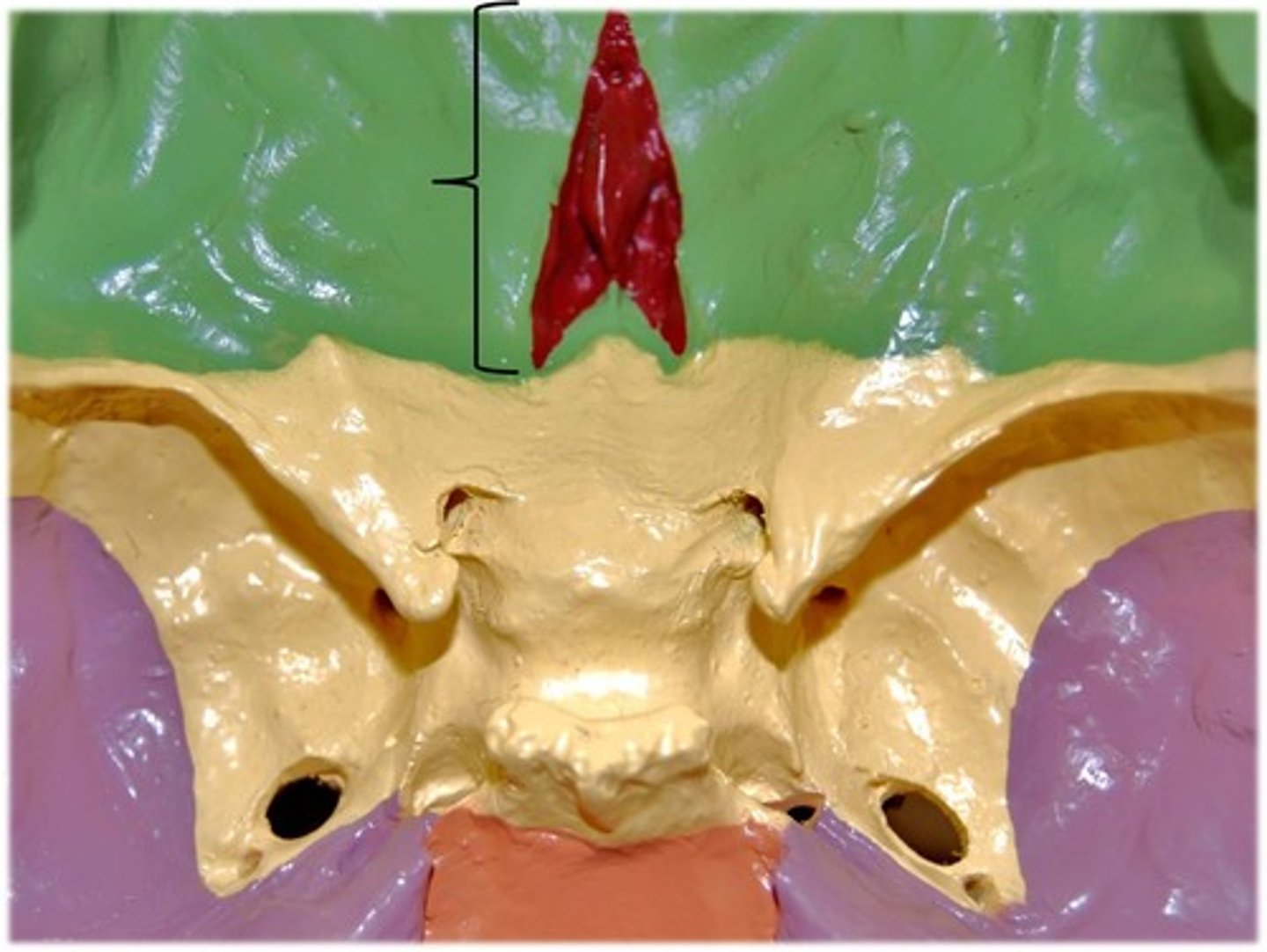
Facial Skeleton
14 Bones of the Face
Mandible (unpaired)
Vomer (unpaired)
2 Nasals
2 Lacrimals
2 Maxillae
2 Zygomatics
2 Palatine bones
2 Inferior nasal conchae
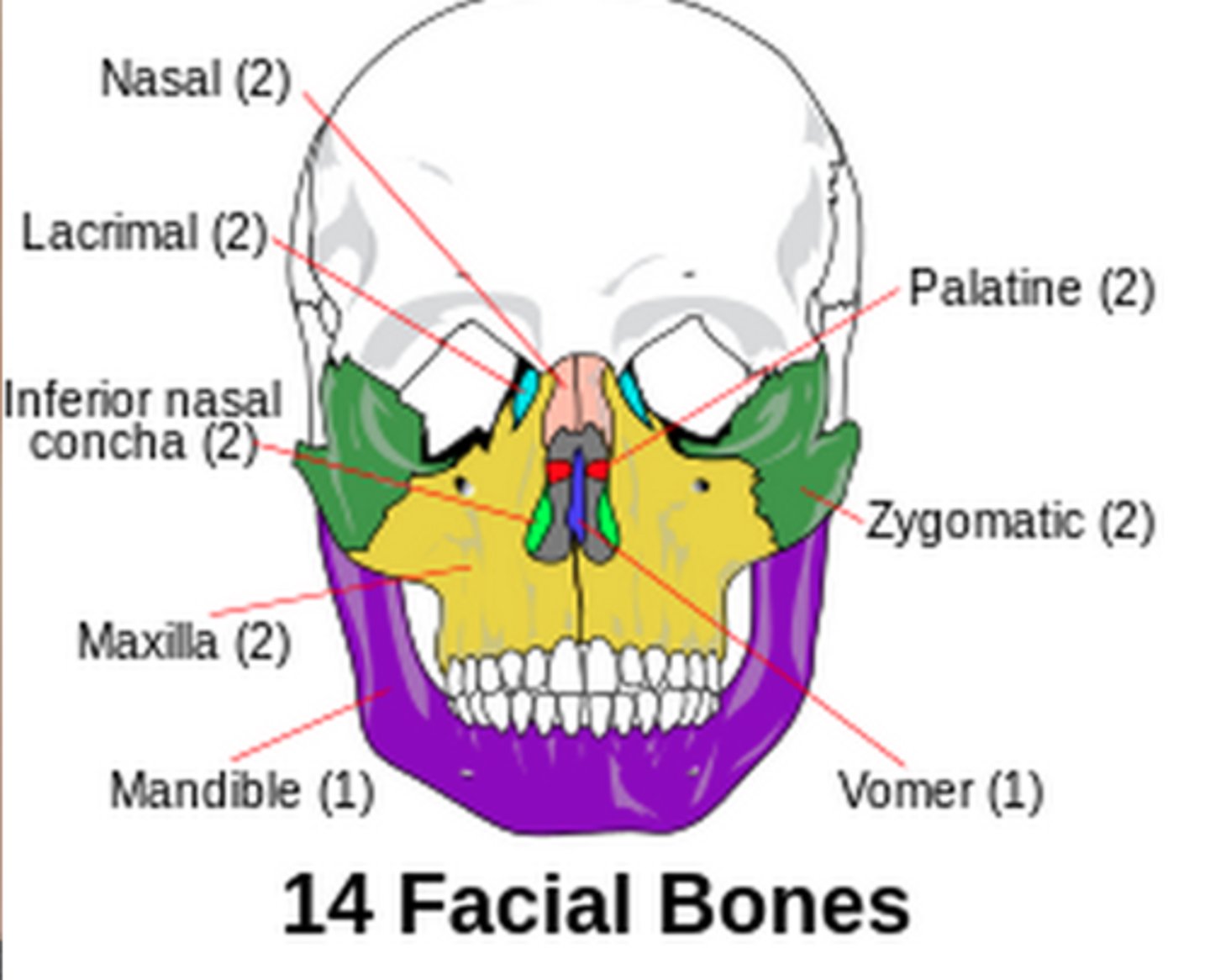
Bones of the Facial Skeleton
-Lacrimal bones (paired):
Lacrimal groove allows tears to drain into nasal cavity
-Inferior nasal concha
(paired)
-Vomer-w/in nasal cavity and on midline
(unpaired)
-Nasal bones (paired)
form bridge of nose
attach to cartilages
that form nose.
-Zygomatic bones
(paired) form
cheekbones
-Maxillae- form upper jaw
(paired)
-Mandible- form lower jaw
(unpaired)
Maxilla(e)
Maxillary bones form upper jaw (paired, left & right).
Articulate with all other facial bones except mandible.
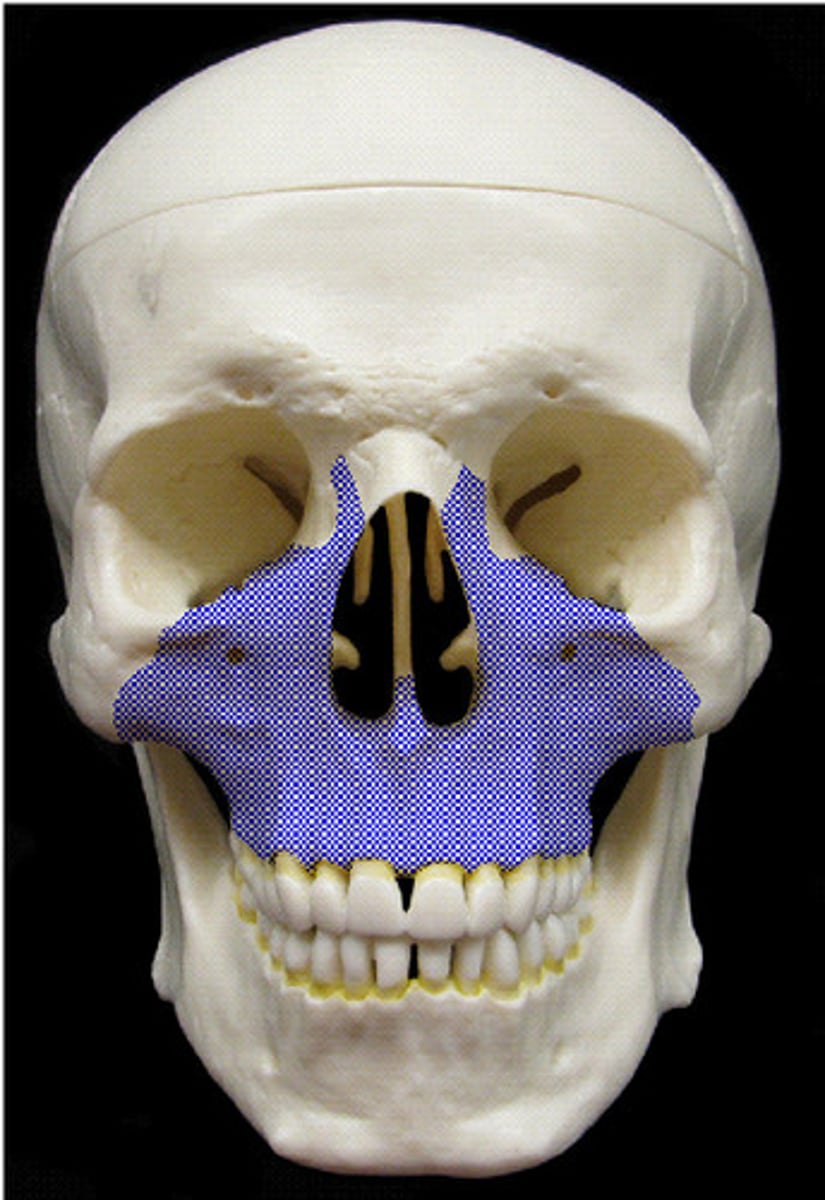
what are the 3 parts of the maxillae
Alveolar processes-contains teeth.
Frontal processes- extend upward to reach frontal bone
Zygomatic processes- of maxilla articulate with zygomatic bone
Orbit
-has about 7 bones
-Supports the eyes & muscles that move the eyes. Orbit also contains fat and lacrimal glands (tear producing glands).
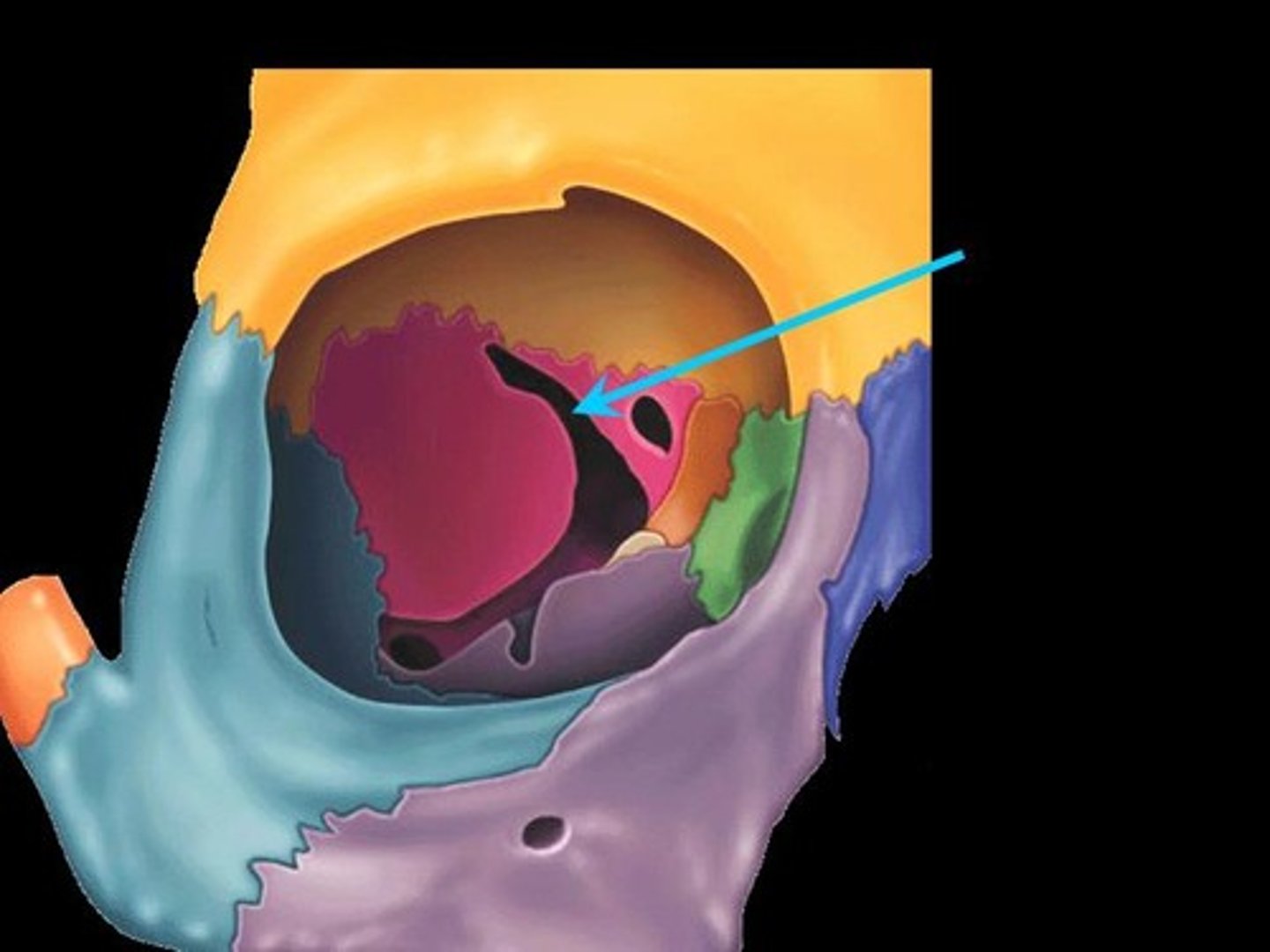
what are the bones that form the wall of the orbit
frontal, sphenoid, zygomatic, maxillary, palatine, lacrimal & ethmoid bones(look at notes for this).
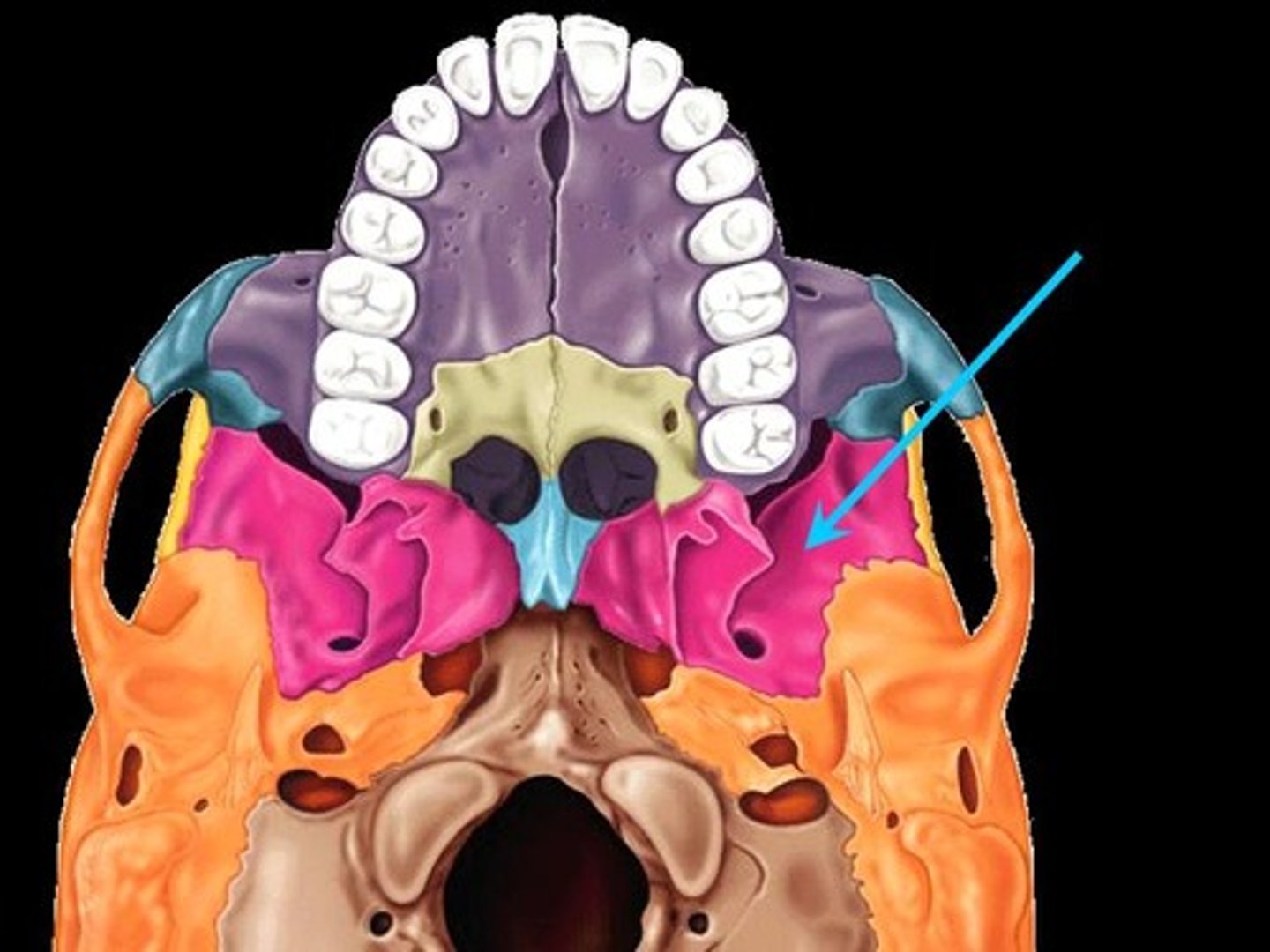
what are the lateral walls of the nasal cavity made of N
nasal bones, nasal conchae (superior, middle (these are part of ethmoid bone), inferior(is its own bone), maxillae, palatines - these form part of the nasal walls.
what is the floor of the nasal cavity made of
= hard palate. Formed by palatine process of maxillae, horizontal plate of palatine.
what is the hard palate composed of
maxillary bones and the palatine bone.
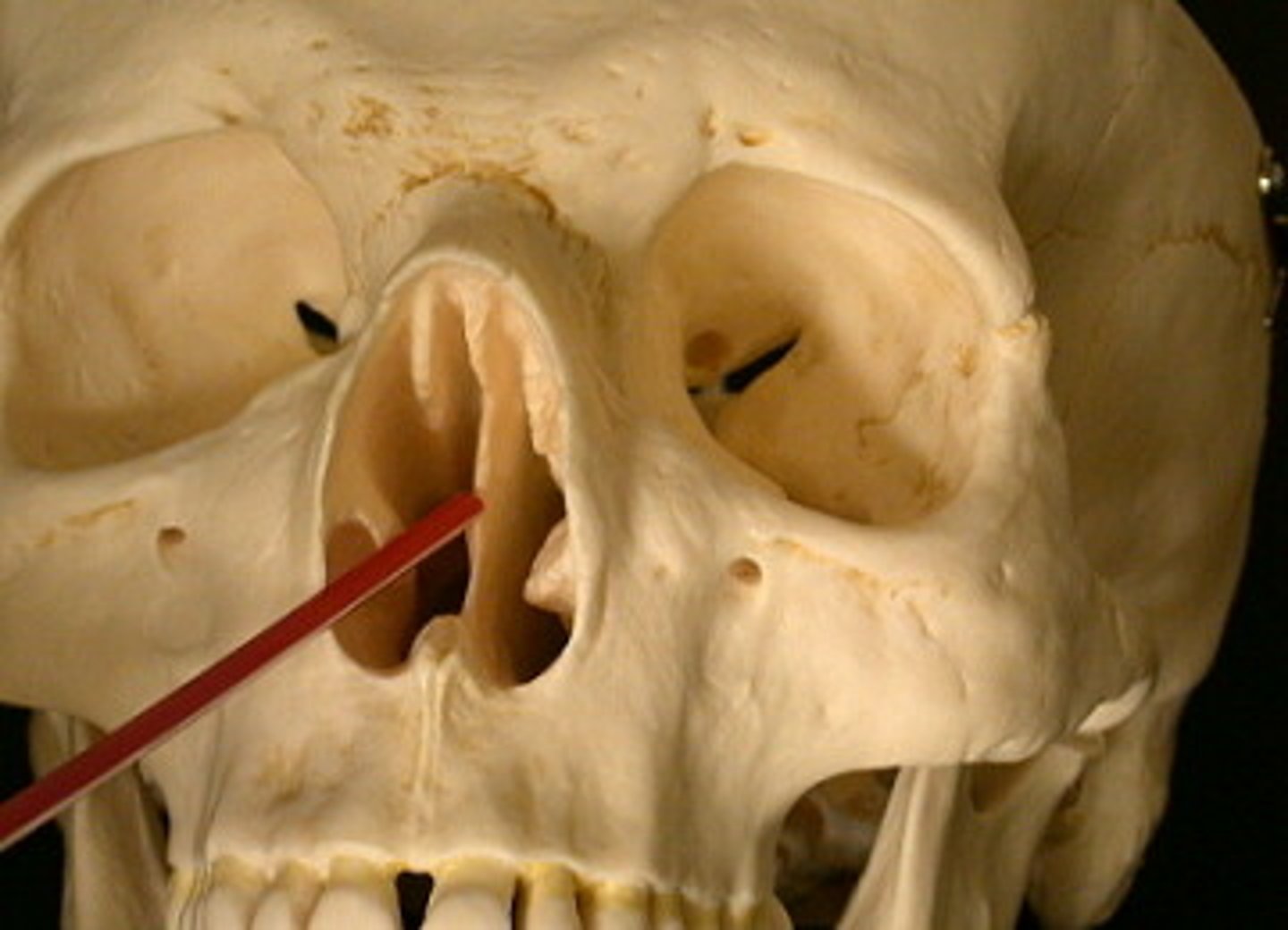
what does the vomer form
inferior portion of nasal septum
Cleft Palate
-Failure of the 2 sides of the palate to join during development leads to cleft palate. --Severity varies.
-Opening between mouth and nasal cavity makes effective nursing difficult so they have to use special equipment to do that.
-Can be repaired surgically with good outcomes.
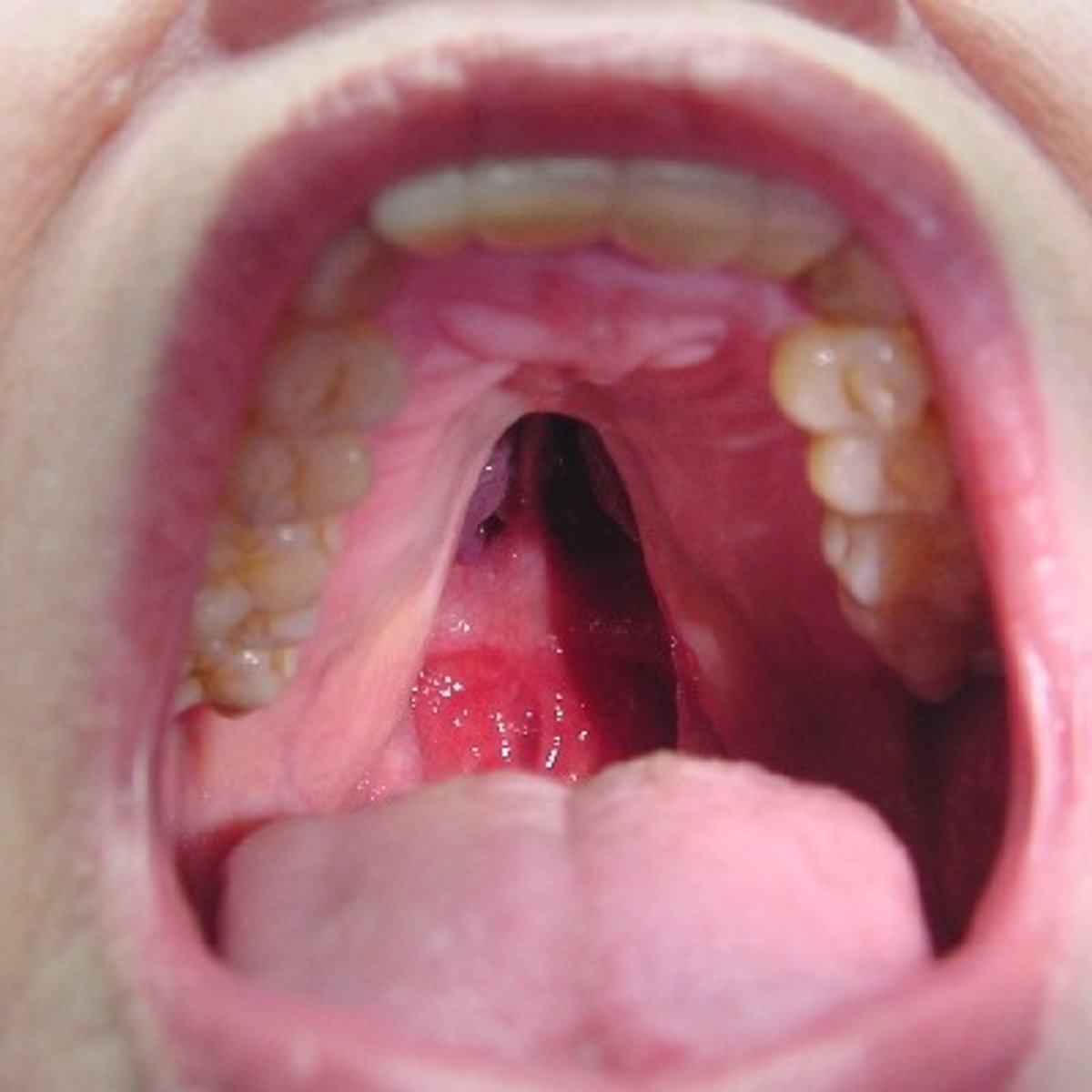
what is the largest and strongest bone in the face
mandible
what does the body of the mandible contain
lower teeth
what are are the tooth sockets on
the superior border(alveolar processes)
mandibular symphysis
(not visible) is where the two halves of the body join to form the chin (=mental protuberance).
where do vessels and nerves enter the mandible? exit?
mandibular foramen
exit- mental foramen inferior to teeth
what does the condyle of the mandible articulate w
temporal bone at mandibular fossa to form the tempomandibular joint (TMJ,both sides)
what does the coronoid process of the mandible serve as
attachment site for the temporalis muscle, a major chewing muscle
Fetal/Infant Face
-Cranium is proportionately huge relative to the face in infancy & early childhood.
-By age 2, skull is 3/4 adult size.
-Between ages 6-13, face grows outward & develops more "adult" proportions; body size begins to catch up with head.
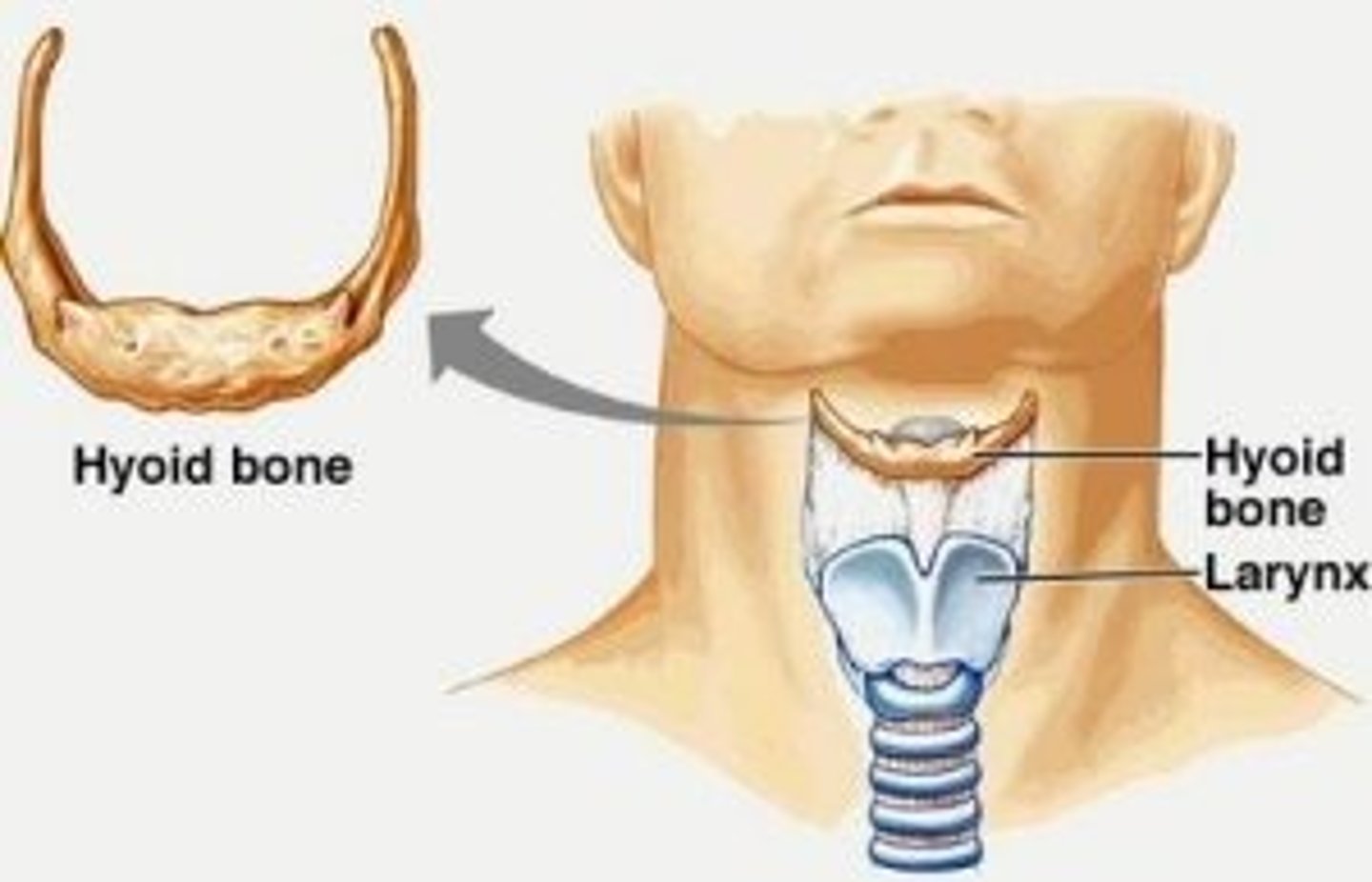
Hyoid
"Free floating" bone in neck inferior to mandible.
Only bone in skeleton that does not articulate with any other bone.
Acts as base for tongue, site of muscle attachments for muscles that move the larynx.
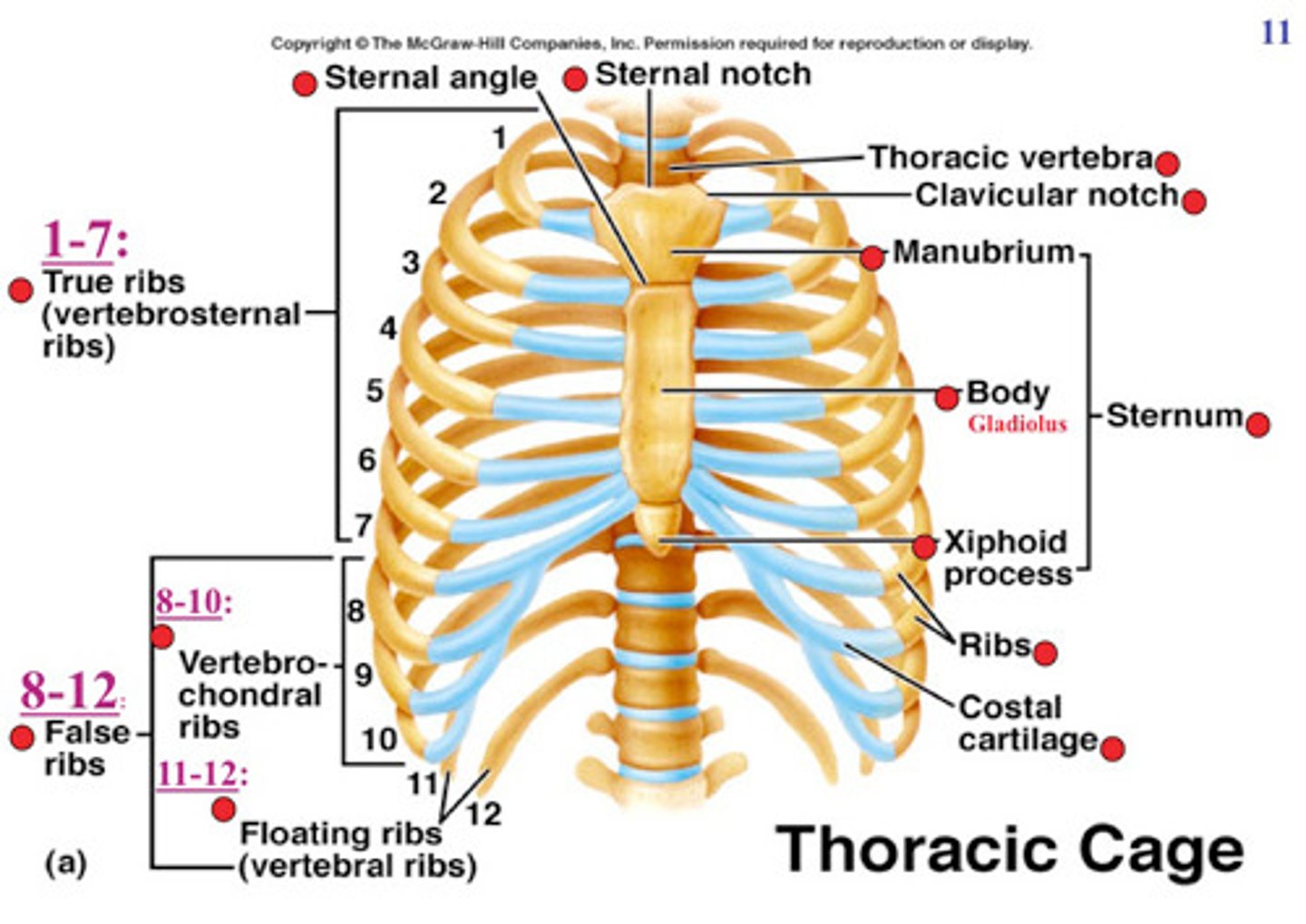
what does the thoracic cage include
thoracic vertebrae, ribs, sternum, and costal cartilages
thoracic cage protects what
heart
lungs
other organs
thoracic cage supports what
pectoral girdle and provides attachment points
intercostal spaces hold muscles that aid in what
breathing.
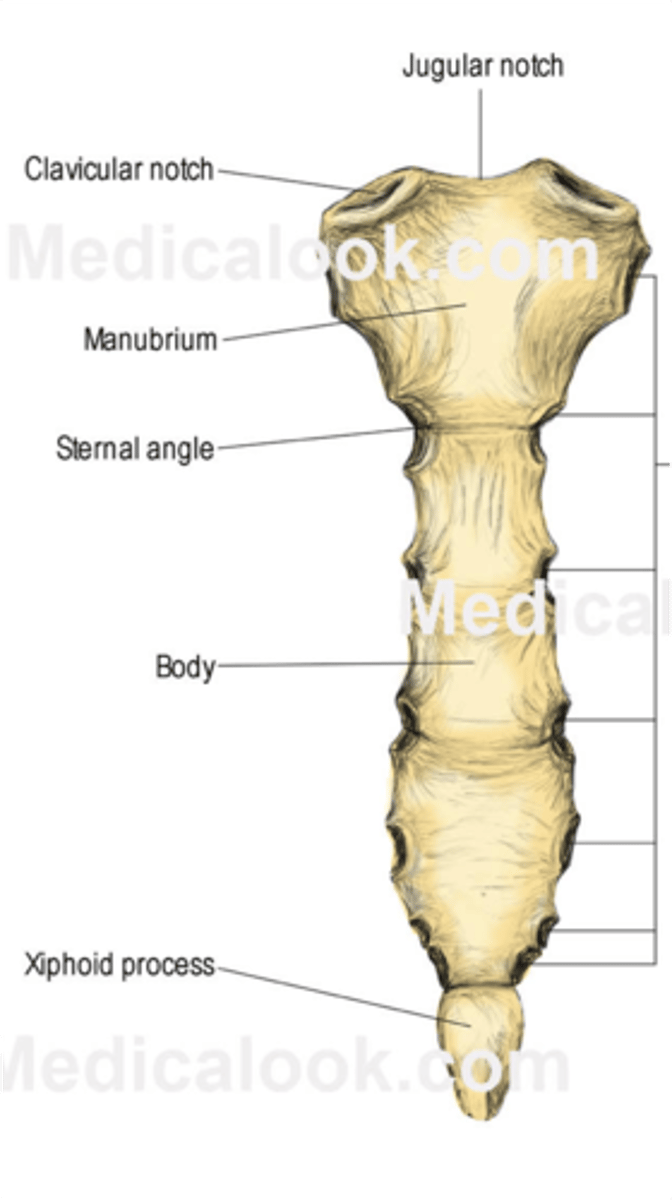
Sternum(breast bone)
3 bones
-- Manubrium
-- Body
-- Xiphoid Process
Articulates with:
-- Clavicles superiorly
-- Ribs & costal cartilages inferiorly
-Sternal angle is important landmark for thoracic anatomy.
-xiphisternal joint (joint b/t body and diploid process)
-xiphoid bone
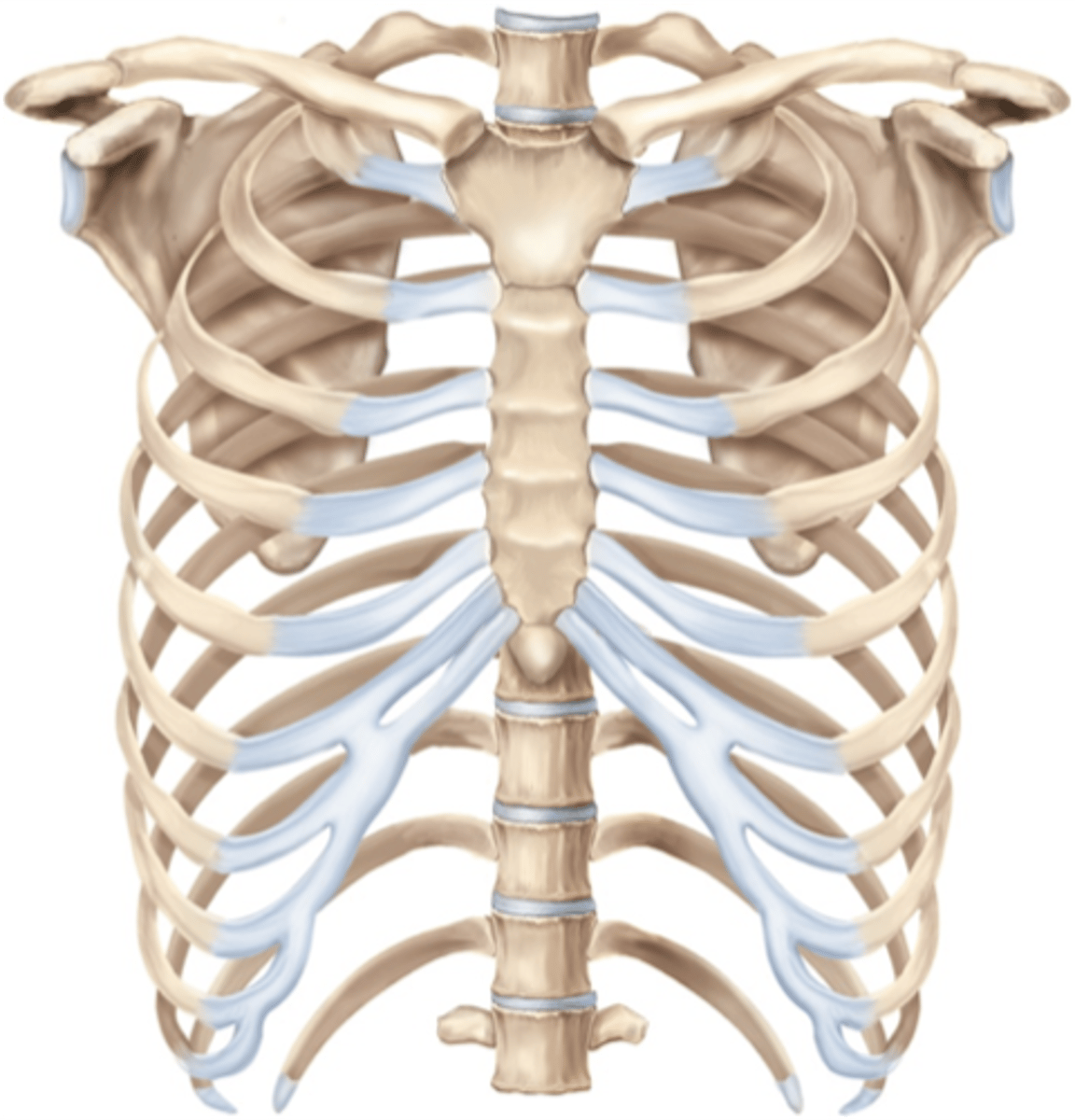
Rib Cage
Function: protect internal organs, aid in respiration.
-12 pairs of ribs.
-All ribs attached posteriorly to thoracic vertebrae
-1st 7 attach to sternum by costal cartilages (true ribs).
-8-10 are false ribs - do not have a direct attachment to the sternum. They attach via a shared costal cartilage.
-11 and 12 are "floating ribs" - they do not attach anteriorly to the sternum.
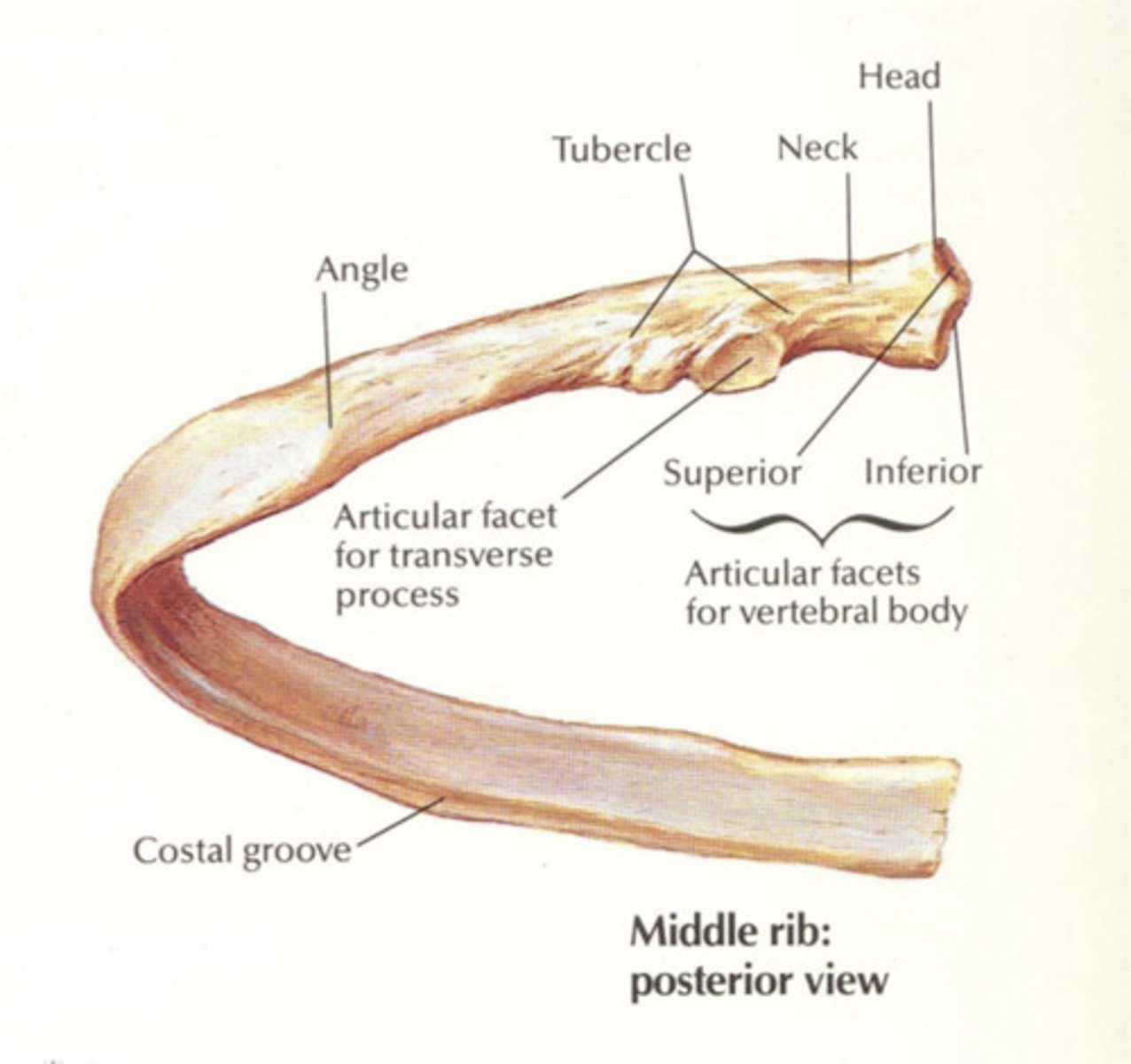
Rib Structure
-Main part of rib is the shaft (body).
-Rib articulates with the vertebra at the head and tubercle
-"Neck" (not labeled) is a thinner region between the head and tubercle. Head has -2 "facets" - one facet articulates with the body of "its" vertebra; one articulates on the body of the vertebra superior to it.
-Tubercle articulates with a facet on the transverse process of the vertebrae.
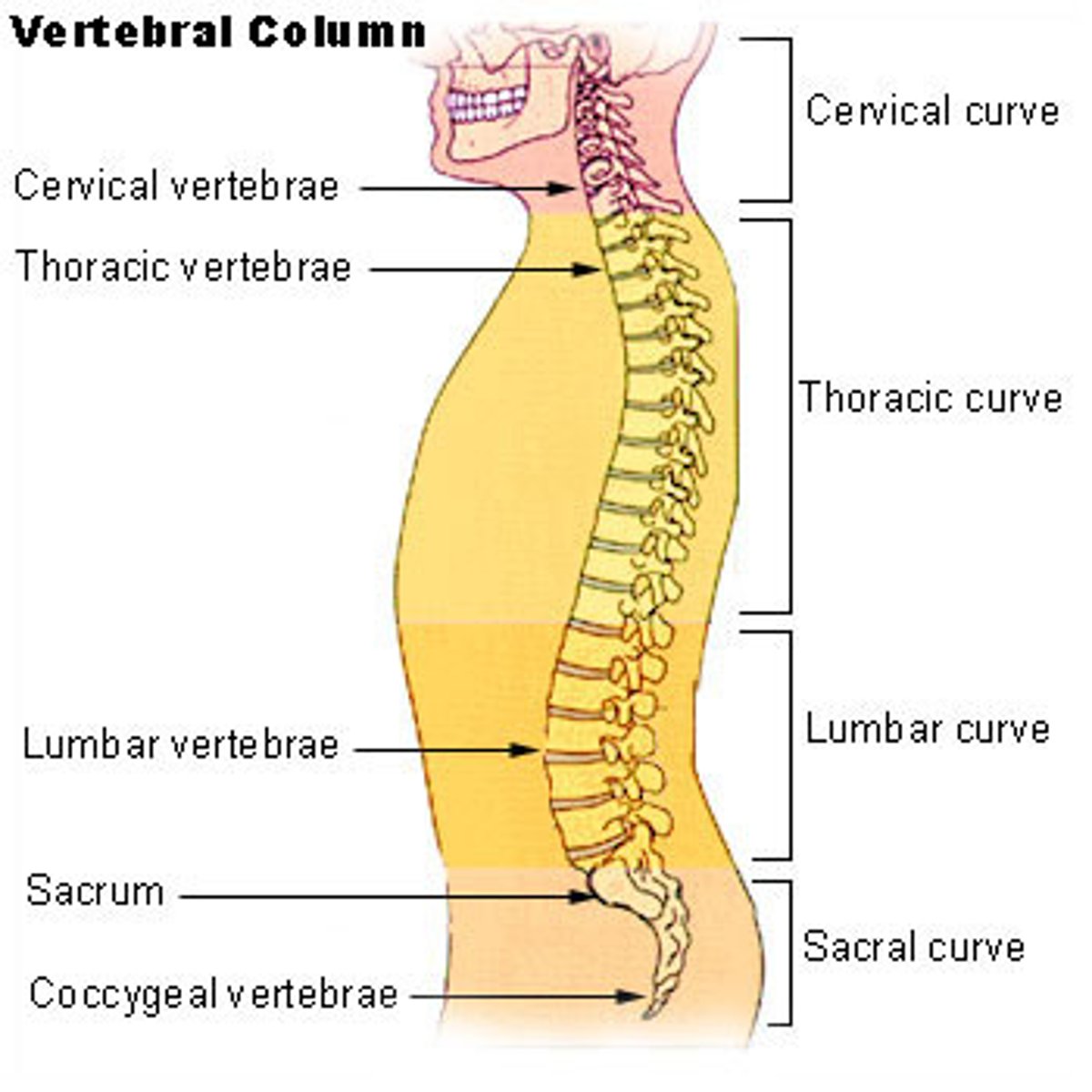
Vertebral Column
26 vertebrae- from superior to inferior...
-- 7 Cervical-in neck
-- 12 Thoracic
-- 5 Lumbar-lower back
-- 5 Sacral (will fuse into 1)
-- 4 Coccyx (will fuse into 1)
Functions:
-- Protect spinal cord
-- Supports body axis
-- Attachment points for ribs & muscles of neck & back.
-- Anchor pectoral & pelvic girdles
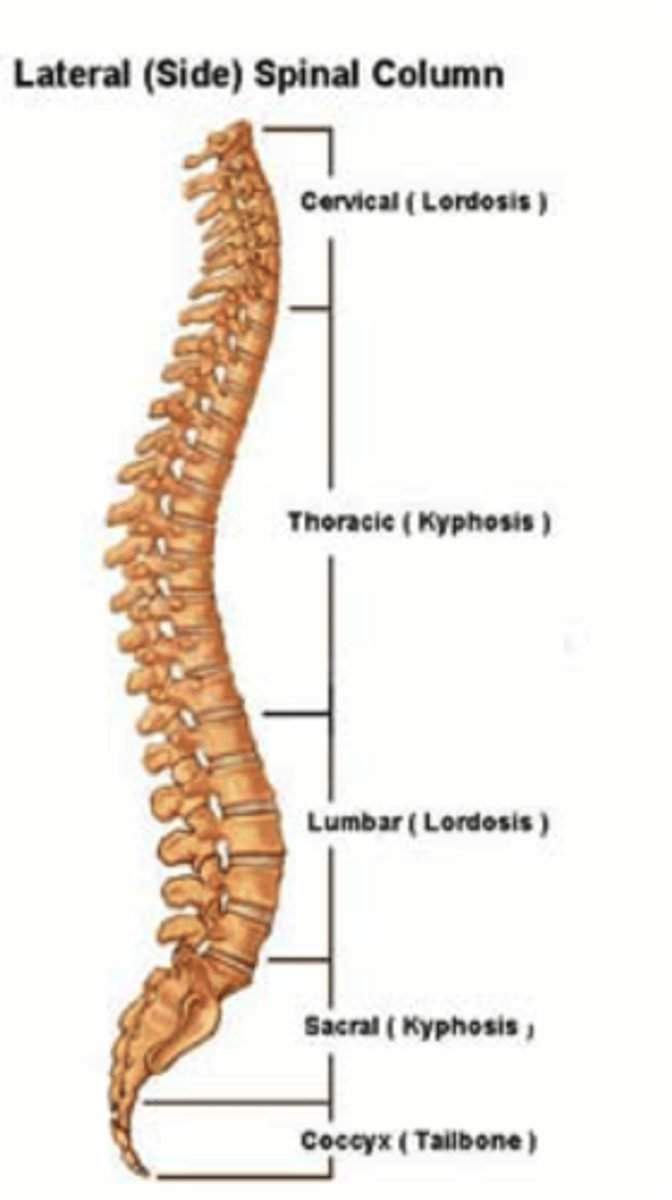
Curves of the Spine
-Vertebrae become larger as move inferiorly to support weight
-Sacrum articulates with hip bones of pelvis, passes weight to appendicular skeleton specifically the lower legs.
-Curves increase flexibility; also position center of gravity over axis of body
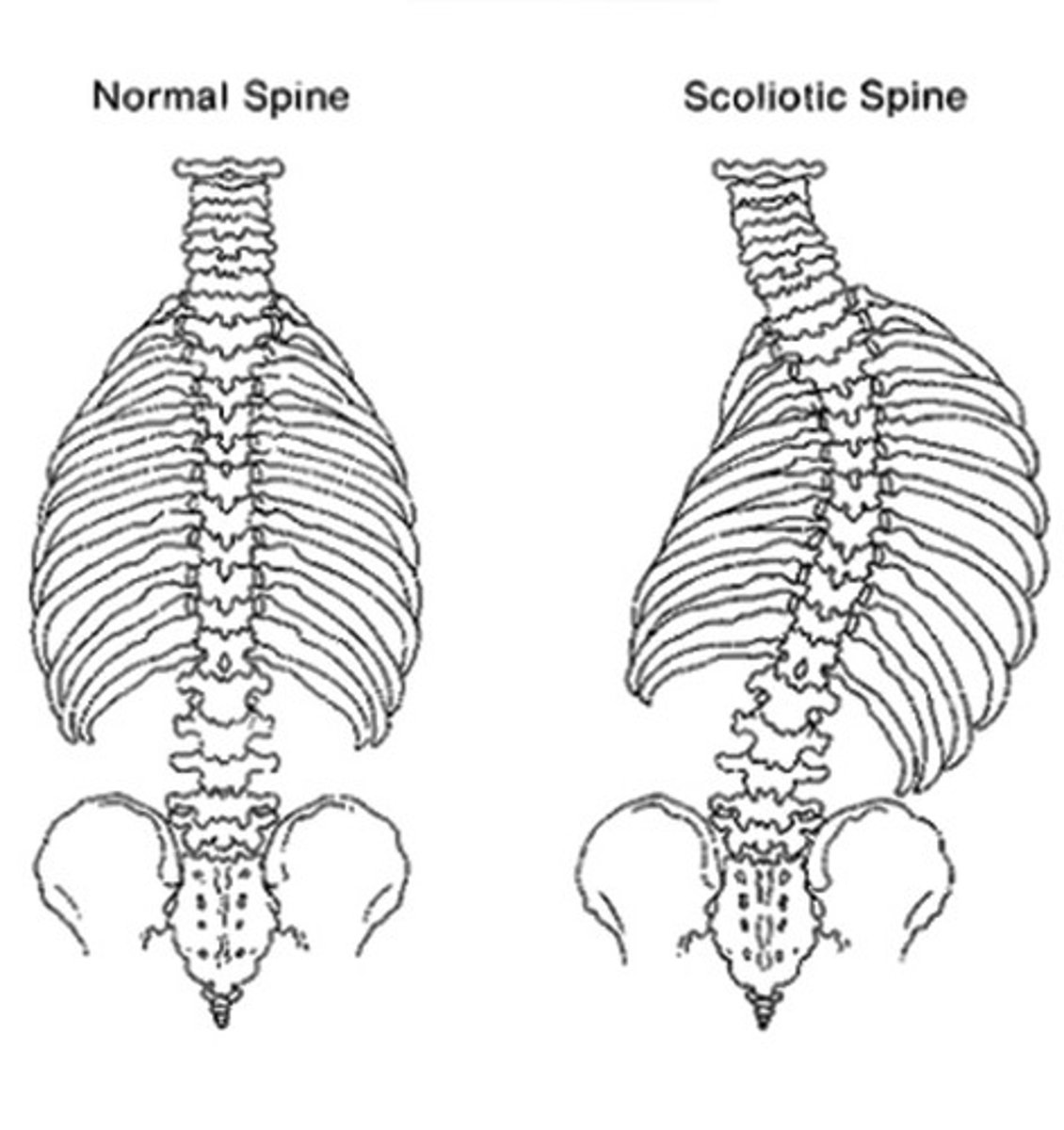
Curves of the Spine: Scoliosis
-Scoliosis - lateral curvature of the spine.
Usually treated with body braces or surgery when young
Lateral curvature is abnormal!!.
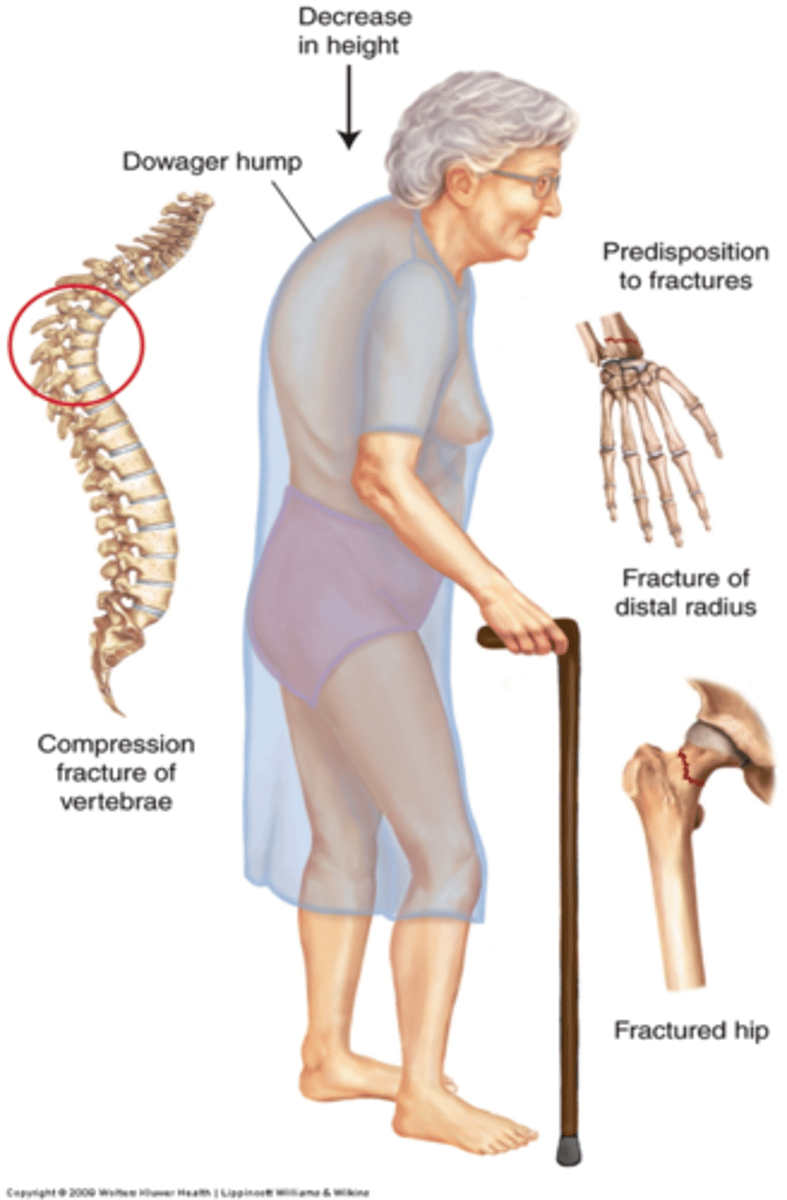
Kryphosis (Dowager's Hump)
-Excessive curvature of the thoracic spine.
-Typically the result of vertebral body factures caused by osteoporosis.