ESS Topic 5: Soil Systems and Terrestrial Food Production Systems and Societies
1/62
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
Inputs of a soil system
organic material, infiltration, energy, precipitation
Storages of a soil system
organic matter, nutrients, air, minerals, water
Transfers of a soil system
leaching, translocation
Transformations of a soil system
decomposition, weathering, evaporation
Outputs of a soil system
Uptake by plants, erosion
Soil texture
shape of particles, aeration, retention of nutrients
What is soil structure
size and proportion of soil particles
Field Capacity
Maximum amount of water a soil can hold
Porosity
amount of space between soil particles
Permeability
Ease at which gases & liquids can pass through soil
Clay characteristics
High water retention, low drainage, low organic matter, high nutrients, low aeration, low primary productivity, low biota
Sand characteristics
Low water retention, high drainage, low organic matter, low nutrient capacity, high aeration, low primary productivity, low biota
Loam characteristics
Medium water retention, medium drainage, medium organic matter, high nutrient capacity, medium aeration, medium primary productivity, high biota
Agribusiness
all businesses associated with intensive agricultural production
Commercial agriculture
Large scale production of crops & livestock for sale
Subsistence agriculture
Small-scale farming for self-sufficiency to grow for a family
Cash cropping
Growing for the market, NOT to eat yourself
Increasing demand of food is caused by
Increasing population, Climate change damaging crops, Water scarcity
Where does food waste happen in MEDCs?
Household level, retail level
Where does food waste happen in LEDCs?
Farm level; lack of storage, lack of refrigeration, loss during transportation
Factors influencing food production systems
Level of education and skills, Religious impacts, Farming environment, Government subsidies to promote certain food types, Level of mechanics farmers can afford, Demands of certain foods
Arable
Cultivation of crops
Pastoral
Rearing of animals
Commercial
Products sold to make profit
Subsistence
Products consumed by cultivators
Nomadic
Farmers move seasonally with their herds
Sedentary
Remain in same place throughout the year
How to increase sustainability in food production: Human behavior
Reduce meat consumption, improve accuracy of food labels, increase consumption of organically grown products, improve technology of agriculture
How to increase sustainability in food production: Monitoring and control
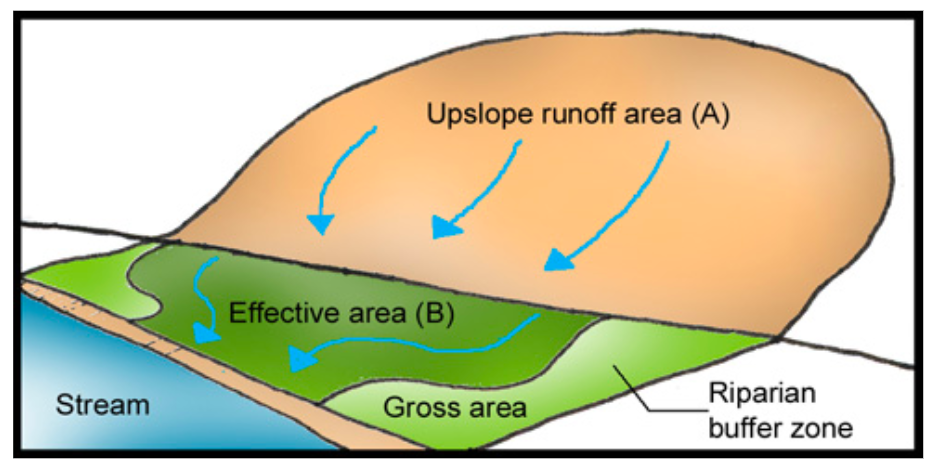
Governmental, non-governmental bodies to regulate practices, planting of buffer zones to regulate runoff
Four stages of soil in succession
Colonization, establishment, stabilization, climax
What happens during colonization stage
Lichens and weathering breaks apart rock, soil begin to form
What happens during establishment stage
Soils become richer as decomposition occurs. Mosses and lichens disappear. Simple organisms form.
What happens during stabilization stage
Horizons form from taller trees growing & shrubs dying
What happens during climax stage
Well-developed soil
What happens when wind
Top layer of soils are removed by wind
Results of when wind
Depletes soil nutrients, soil becomes more fiable (breakable)
What happens when water goes through soil
Sheet wash (removal of thin layers of soil), gullying (rapid, deep cutting of soil)
Results of when water
Causes landslides
Human processes that deplete soil
Overgrazing, deforestation, irrigation
What results when overgrazing
Depletes soil nutrients, increase in soil erosion due to lack of vegetation
What results when deforestation
Soil erosion from water and wind due to lack of vegetation
When too much irrigation
Overdose of water = runoff
Four ways of reducing soil fertility
Soil erosion, toxification, salinization, desertification
Human 👩🏻🌾 causes of soil erosion
dry-land farming
Consequences of soil erosion
Increased pollution, loss of most fertile topsoil
Causes of toxification
Acid rain, pesticides
Consequences of toxification
Increases soil acidity
Causes of salinization
Irrigation water contains salt, evaporation leaves salt
Consequences of salinization
Low crop yield, dead plants, ruined land
Causes of desertification
Effects of harsh climate
Consequences of desertification
reduces productivity, long time to recover
Management strategy: Soil Conditioners — what is it
Helps improve soil structure by increasing aeration, water holding capacity, and nutrients
Management strategy: Soil Conditioners — pros
Allows slow release of nutrients, better absorption by plants
Management strategy: Soil Conditioners — cons
Needs constant monitoring & adding
Management strategy: Cultivation techniques — what is it?
Terracing (cutting layers on slope), contour plowing (plowing along lines of land), alley cropping (planting rows of trees to create alleys)
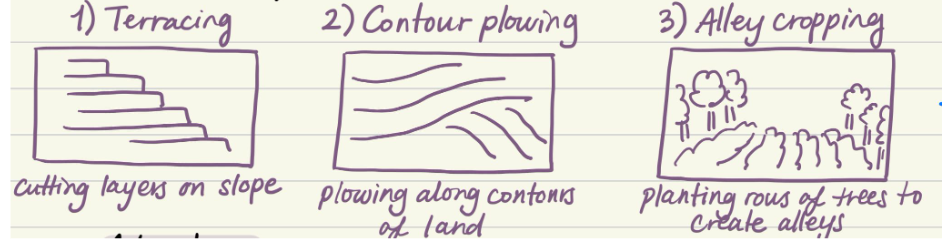
Management strategy: Cultivation techniques — pros
Reduces water runoff, provide share, retain moisture, saves fuel
Management strategy: Cultivation techniques — cons
Increase in pests and diseases thus needs pesticide, expensive equipment
Management strategy: Irrigation — what is it?
Water
Management strategy: Irrigation — pros
Reduces evaporation, salinization
Management strategy: Irrigation — cons
Slower, less productive yield
Management strategy: Crop rotation — what is it
Rotation of crops to avoid monoculture
Management strategy: Crop rotation — pros
Allows soil to improve naturally
Management strategy: Crop rotation — cons
Hard to manage