College Psychology Chapters 1-3
1/66
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Mr. Charron - FVL
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
What is psychology?
The scientific study of behavior and natural processes. It’s goal is to describe, predict, and explain behaviors.
Empiricism
Our knowledge originates in experience
Structuralism
What exists
Introspection
To sit down and think
Functionalism
How we function
Neuroplasticity
How the brain changes/adjusts to experiences
Neurons
Building blocks of neural information center
Cell body
Each has one
Dendrite
Receive and integrate information
Axon
Passes message to other axons
Glial cells
Spidery “glue cells”
Threshold
Signals by a minimum intensity
Refractory period
Resting pause
All-or-none response
The level of stimulation will not affect it. It will either respond or it won’t.
Myelin sheath
Fatty tissue that insulates and speeds up the impules of axons
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
Communication to muscles and brain regions is slow, with diminished muscle control and impaired cognition.
Synapse
Meeting point between neurons
Neurotransmitters
Chemical messengers
Reuptake
Excess neurotransmitters finally drift away and are broken down by enzymes or reabsorbed by the sending neuron.
Acetylcholine
Enables muscle function, learning and memory
Dopamine
Influences mood/emotion
Seratonin
Affects mood
Norepinephrine
Helps control alertness and arousal
GABA
Major inhibitory transmitter
Glutamate
Exitory and memorial
Endorphins
Inhibity
Endorphin
Natural chemicals produced by the body that act as painkillers and mood enhancers. They help reduce pain, improve mood, and promote a sense of well-being.
Agonist
Increases a neurotransmitter’s action
Antagonist
Decreases a neurotransmitter’s action
Sensory neurons
Transmit sensory information from the body's sensory organs to the central nervous system (CNS)
Motor neurons
Transmit signals from the central nervous system to muscles and glands, allowing for voluntary and involuntary movements
Sympathetic mode
Fight or flight response
Parasympathetic mode
Rest and digest
Endocrine system
Sends molecules as messages through bloodstream (hormones) that go to various glands
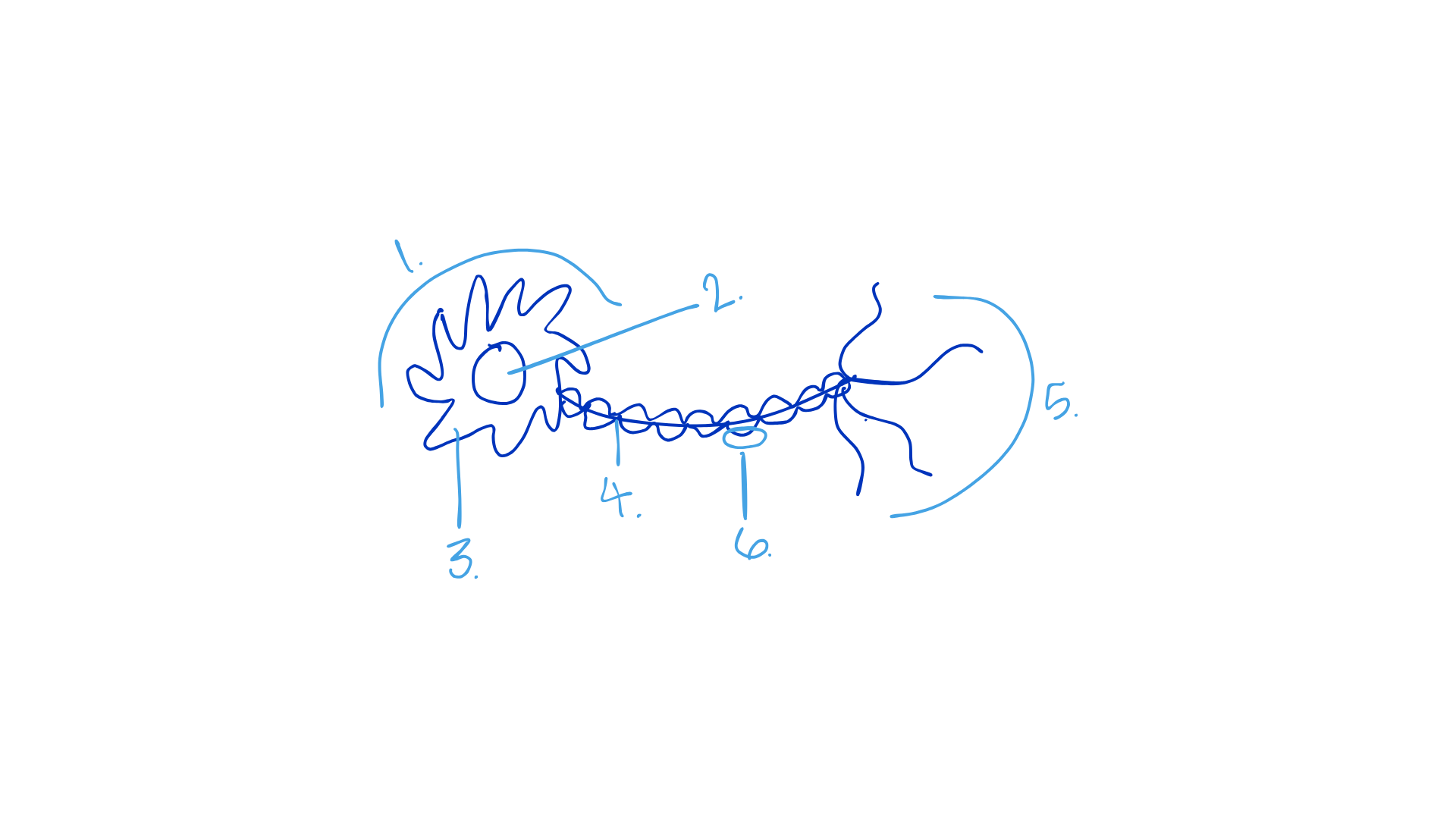
Label these!
Cell body
Nucleus
Dendrites
Axon
Terminal of the axon
Myelin sheath
Cerebellum
“Little brain” helps coordinate voluntary movement, also enables nonverbal learning, judgement of time, memory
Medulla
Controls the most basic functions such as breathing and heartbeat
Pons
Coordinate automatic and unconscious movements
Reticular Formation
Nerve network in the brainstem that enables alertness, arousal from coma to wide awake
Thalamus
“inner chamber” all sensory messages go through this
Hypothalamus
Governs bodily maitnence
Amygdala
Neuron clusters that enable aggression and fear
Hippocampus
Holds conscious, explicit memories
Corpus collosum
Axon fibers connecting the two cerebral hemispheres
Motor cortex
Stimulating this region in the right or left will cause movement on the opposite
Somatosensory
Recieves information from skin senses
Visual cortex
Recieve. segement, and integrate visual info.
Auditory cortex
Processing auditory information

Lobes of the brain
Frontal
Parietal
Temporal
Occipital
Functions of frontal lobe
Speaking, problem solving, muscle movements, making plans and judgement
Functions of parietal lobe
Includes the sensory cortex, controls touch, sensory and perception
Functions of the temporal lobe
The auditory processing areas
Functions of the occipital lobe
Visual areas, recieve visual information from the opposite visual field
What the Phineas Gage incident helps us understand:
Frontal lobe damage changes personality completely
What happens if the motor cortex is damaged?
Paralysis of some kind
What parts of the brain, if injured would cause death?
Medulla - we would be incapable of basic human functions
Consciousness
Our subjective awareness of ourselves and our environment
What 2 things make up consciousness
Awareness of self
Awareness of environment
Hypnosis
Altered state of consciousness
Cognitive neuroscience
Brain activity linked with mental processes
Etymology
The study of the origin and history of words, including their meanings and changes over time.
Selective attention
Where our awareness focuses
Inattentional blindness
Focusing on only one thing
Change blindness
Phenomenon where individuals fail to notice significant changes in their visual environment
Parallel processing
Your mind taking care of routine business
Sequential processing
A cognitive process that involves completing tasks in a step-by-step manner, following a specific order.
Flashcard: Brain Plasticity
The brain's ability to change and adapt by forming new neural connections throughout life, allowing for learning, memory, and recovery from injury.