Bio 100 Exam 3 Study Set
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
analogous structure
A character found in two taxa that looks similar due to convergent evolution, not because of descent from a common ancestor.
binomial nomenclature
A system of two-part scientific names for an organism, which includes genus and species names.
branch point
A point on a phylogenetic tree where a single lineage splits into distinct new ones.
clade
A group of taxa with the same set of shared derived characters, including an ancestral species and all its descendants.
cladistics
A method used to organize homologous traits to describe phylogenies using common descendent as the primary criterion for classifying organisms.
class
The category in the taxonomic classification system that falls within phylum and includes orders.
domain
The highest level category in the classification system, which includes all taxonomic classifications below it; it is the most inclusive taxon.
family
The category in the taxonomic classification system that falls within order and includes genera.
genus
The category in the taxonomic classification system that falls within family and includes species; it is the first part of the scientific name.
kingdom
The category in the taxonomic classification system that falls within domain and includes phyla.
molecular systematics
Methods of using molecular evidence to identify phylogenetic relationships.
monophyletic group
Organisms that share a single ancestor.
order
The category in the taxonomic classification system that falls within class and includes families.
phylogenetic tree
A diagram used to reflect the evolutionary relationships between organisms or groups of organisms.
phylogeny
The evolutionary history and relationship of an organism or group of organisms.
phylum
The category in the taxonomic classification system that falls within kingdom and includes classes.
rooted
Describing a phylogenetic tree with a single ancestral lineage to which all organisms represented in the diagram relate.
shared derived character
A character on a phylogenetic tree that is shared only by a certain clade of organisms.
sister taxa
Two lineages that diverged from the same branch point.
species
The most specific category of the classification system.
systematics
The science of determining the evolutionary relationships of organisms.
taxon
A single level in the taxonomic classification system.
taxonomy
The science of classifying organisms.
Adaptation
A heritable trait or behavior in an organism that aids in its survival in its present environment.
Adaptive Radiation
A speciation when one species radiates out to form several other species.
Allopatric Speciation
A speciation that occurs via a geographic separation.
Analogous Structure
A structure that is similar because of evolution in response to similar selection pressures, not due to a common ancestor.
Bottleneck Effect
The magnification of genetic drift as a result of natural events or catastrophes.
Convergent Evolution
An evolution that results in similar forms on different species.
Divergent Evolution
An evolution that results in different forms in two species with a common ancestor.
Founder Effect
A magnification of genetic drift in a small population that migrates away from a large parent population carrying an unrepresentative set of alleles.
Gene Flow
The flow of alleles in and out of a population due to the migration of individuals or gametes.
Gene Pool
All of the alleles carried by all of the individuals in the population.
Genetic Drift
The effect of chance on a population’s gene pool.
Homologous Structure
A structure that is similar because of descent from a common ancestor.
Macroevolution
A broader scale of evolutionary changes seen over paleontological time.
Microevolution
The changes in a population’s genetic structure (i.e., allele frequency).
Migration
The movement of individuals of a population to a new location, affecting allele frequencies.
Natural Selection
The greater relative survival and reproduction of individuals in a population that have favorable heritable traits.
Speciation
A formation of a new species.
Sympatric Speciation
A speciation that occurs in the same geographic space.
Variation
The variety of alleles in a population.
codon
Three consecutive nucleotides in mRNA that specify the addition of a specific amino acid or the release of a polypeptide chain during translation.
deoxyribose
A five-carbon sugar molecule with a hydrogen atom rather than a hydroxyl group in the 2' position; the sugar component of DNA nucleotides.
DNA polymerase
An enzyme that synthesizes a new strand of DNA complementary to a template strand.
double helix
The molecular shape of DNA in which two strands of nucleotides wind around each other in a spiral shape.
gene expression
Processes that control whether a gene is expressed.
genetic code
The amino acids that correspond to three-nucleotide codons of mRNA.
helicase
An enzyme that helps to open up the DNA helix during DNA replication by breaking the hydrogen bonds.
mRNA
Messenger RNA; a form of RNA that carries the nucleotide sequence code for a protein sequence that is translated into a polypeptide sequence.
mutation
A permanent variation in the nucleotide sequence of a genome.
nitrogenous base
A nitrogen-containing molecule that acts as a base; often referring to one of the purine or pyrimidine components of nucleic acids.
nontemplate strand
The strand of DNA that is not used to transcribe mRNA; this strand is identical to the mRNA except that T nucleotides in the DNA are replaced by U nucleotides in the mRNA.
phosphate group
A molecular group consisting of a central phosphorus atom bound to four oxygen atoms.
primer
A short stretch of RNA nucleotides that is required to initiate replication and allow DNA polymerase to bind and begin replication.
promoter
A sequence on DNA to which RNA polymerase and associated factors bind and initiate transcription.
replication fork
The Y-shaped structure formed during the initiation of replication.
RNA polymerase
An enzyme that synthesizes an RNA strand from a DNA template strand.
rRNA
Ribosomal RNA; molecules of RNA that combine to form part of the ribosome.
semiconservative replication
The method used to replicate DNA in which the double-stranded molecule is separated and each strand acts as a template for a new strand to be synthesized.
start codon
The AUG (or, rarely GUG) on an mRNA from which translation begins; always specifies methionine.
stop codon
One of the three mRNA codons that specifies termination of translation.
telomere
The DNA at the end of linear chromosomes.
template strand
The strand of DNA that specifies the complementary mRNA molecule.
transcription bubble
The region of locally unwound DNA that allows for transcription of mRNA.
tRNA
Transfer RNA; an RNA molecule that contains a specific three-nucleotide anticodon sequence to pair with the mRNA codon and also binds to a specific amino acid.
The building blocks of DNA are called
nucleotides.
The structure of DNA is called a(n)
double helix
The central dogma of molecular biology states that the information contained within genes flows in which direction?
DNA to RNA to protein
Genes are included on structures called:
chromosomes
DNA replication is called semiconservative because
each resulting DNA molecules is comprised of one new DNA strand and one old strand
RNA differs from DNA because RNA
is single-stranded, whereas DNA is double-stranded
Which base is found in DNA, but not in RNA?
thymine
Which process requires the participation of all three types of RNA?
translation
DNA replication makes a(n) ________ copy of the DNA strand, while transcription makes a(n) ________ copy of the DNA strand.
DNA; mRNA
The sequence of the mRNA that would result from transcribing a DNA template strand with the bases TACGCTAAT would be
AUGCGAUUA.
An intervening sequence of DNA that is not expressed is called a(n)
intron
Which nucleotide bases are present in equal amounts in DNA?
guanine and cytosine
The “t” of tRNA stands for:
transfer
Which statement correctly describes the locations of transcription and translation within a eukaryotic cell?
DNA is transcribed in the nucleus, and then the mRNA transcript is transported to the cytosol to be translated into protein
Which of the following contains the anti-codon?
Transfer RNA
An important difference between mRNA and DNA is:
mRNA can move throughout the cell, whereas DNA stays in the nucleus.
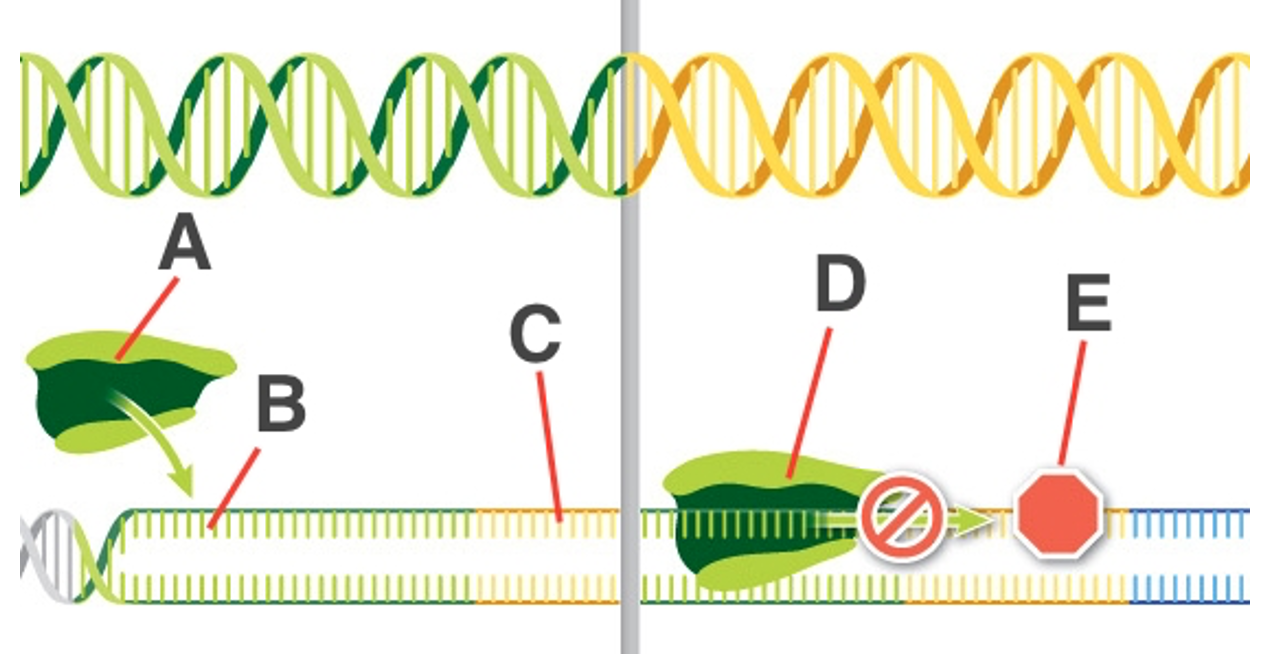
An operon is a group of several genes and elements that control the expression of these genes as a unit. The diagram shows the promoter and operator regions of the operon. Which label on the diagram represents the repressor protein?
E
A chain of ______ results in a polypeptide chain that folds up into a ______.
amino acids… protein
If an mRNA codon reads UAC, its complementary anticodon will be
AUG.
The mRNA has a three-nucleotide sequence called a(n) _________, while the molecule transporting the amino acid has a complementary sequence called a(n) _______________.
codon; anticodon
A gene can be described as:
A series of DNA bases that contain information for production of a protein
Alternate versions of a gene are called _______________. They can code for different ________________ of the same character.
alleles; traits
When two identical alleles for a character are present, the genotype is referred to as:
homozygous
Widow's-peak hairline in humans is dominant to non-widow's-peak hairline. If a person has a widow's-peak hairline, what is his or her genotype?
The genotype is either heterozygous or homozygous dominant
Skin color is coded for by several different genes which results in a range of skin colors from very dark to very light. This is an example of
polygenic inheritance
The filled-in squares of a Punnett square represent
all possible combinations of gametes based on a cross between the two parents
A diploid individual with two identical alleles for a particular gene is said to be:
homozygous for that gene
Determine if the following statement is true or false. Parents with the dominant phenotype cannot have offspring with the recessive phenotype.
False, because both parents could be heterozygous.
In a one-trait testcross, a homozygous dominant individual is crossed with a homozygous recessive individual. Which phenotype will be absent in the F1 generation?
recessive trait.
Albinism (lack of skin and hair pigmentation) is caused by a recessive autosomal allele. A woman and man, both normally pigmented, have an albino child together. For this trait, what is the genotype of the albino child?
homozygous recessive
The phenotype of an organism can best be determined by:
observing the organism
If a heterozygous dominant tall pea plant is crossed with a short pea plant, what is the expected phenotypic ratio?
1 tall:1 short
Which of the following is mismatched?
identical alleles - heterozygous
How can two pea plants that have different genotypes for seed color be identical in phenotype?
One of the two plants could be homozygous for the dominant allele, while the other could be heterozygous.