Flexible Containers
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Value of Flexible Packaging
-less material
-less weight
-portability
-technology advancement closing the gap on rigids
Components/functions
- Bags/Pouches
- Seals/fitments
- Printing/Labels
Converting Process Definition
Transform raw materials in the form of polymer pellets or film substrates (including paper and foil) into a final packaging structure
Common Layers
- Barrier
- Sealant
Typical Substrates - Printing
- Paper
- OPP
- PET
- Monolayers are surface printed
Printing Challenges
- Surface quality: treatment
- Dimensional stability
- Gravure and Flexography are the 2 main processes (roll to roll printing)
Barrier Materials
- Metallized films
- Glass coated films
- PA (Nylon)
- Oriented films (OPP & PET)
- Coated films
- Foil
Common Sealant Layers
LLDPE, LDPE, CPP
LLDPE
whole range of modified sealants for sealing through contaminants to peelable seals
LDPE
when no serious demands such as heat and chemicals are involved
CPP
higher temp applications require polypropylene
Shrink Materials -- Labels and Sleeves
- PVC
- PET
- OPS
- PLA
Materials - Fitments
- Made of PP or PE: must be compatible w/ sealant layer
- Injection molding for precision
- Zippers are extrusion molded
- Can be pre-applied to pouch or as pouch is being formed and filled
Purpose of Fitments
dispensing, reclosing, aeration
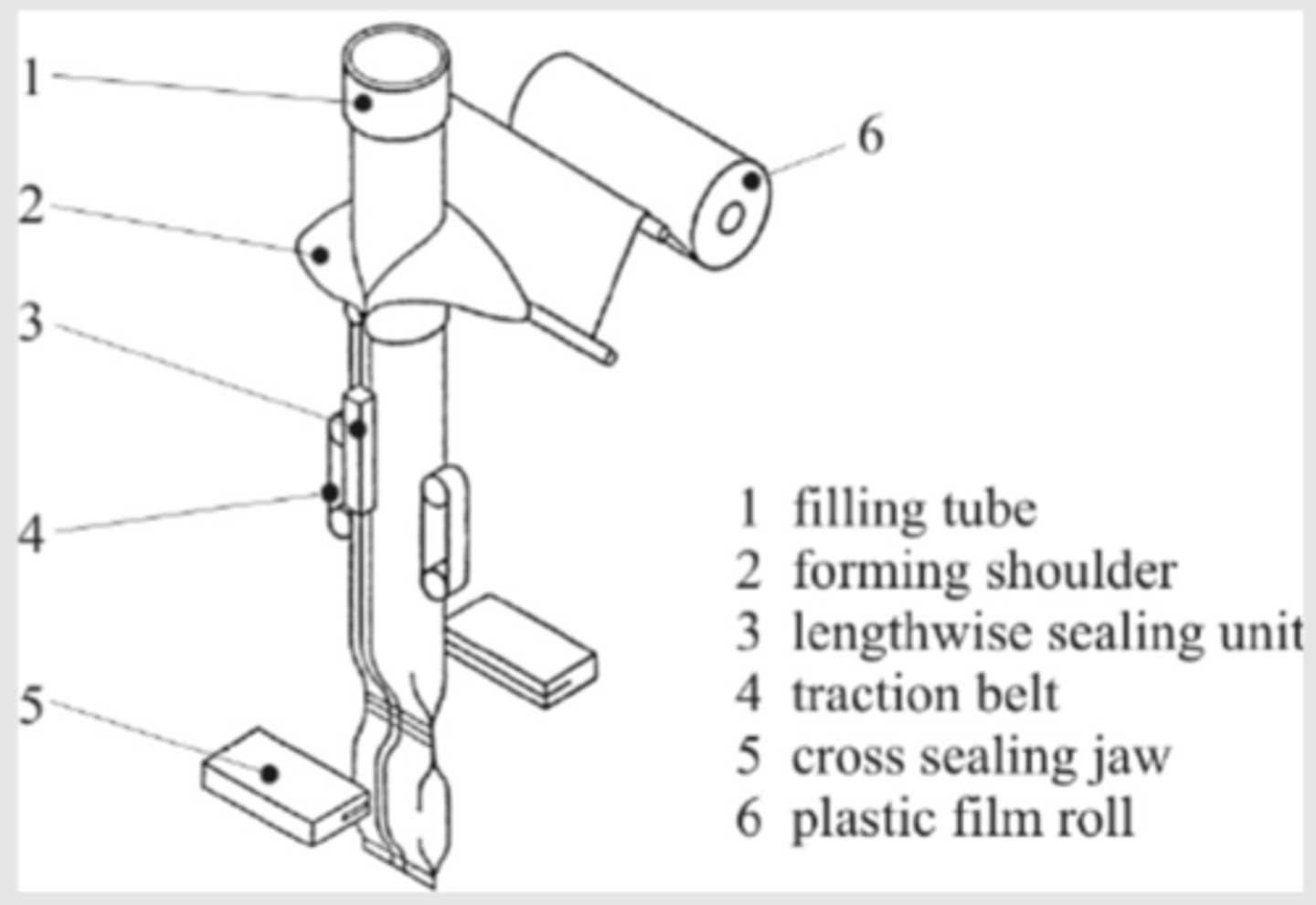
VFFS - Vertical Form Fill and Seal
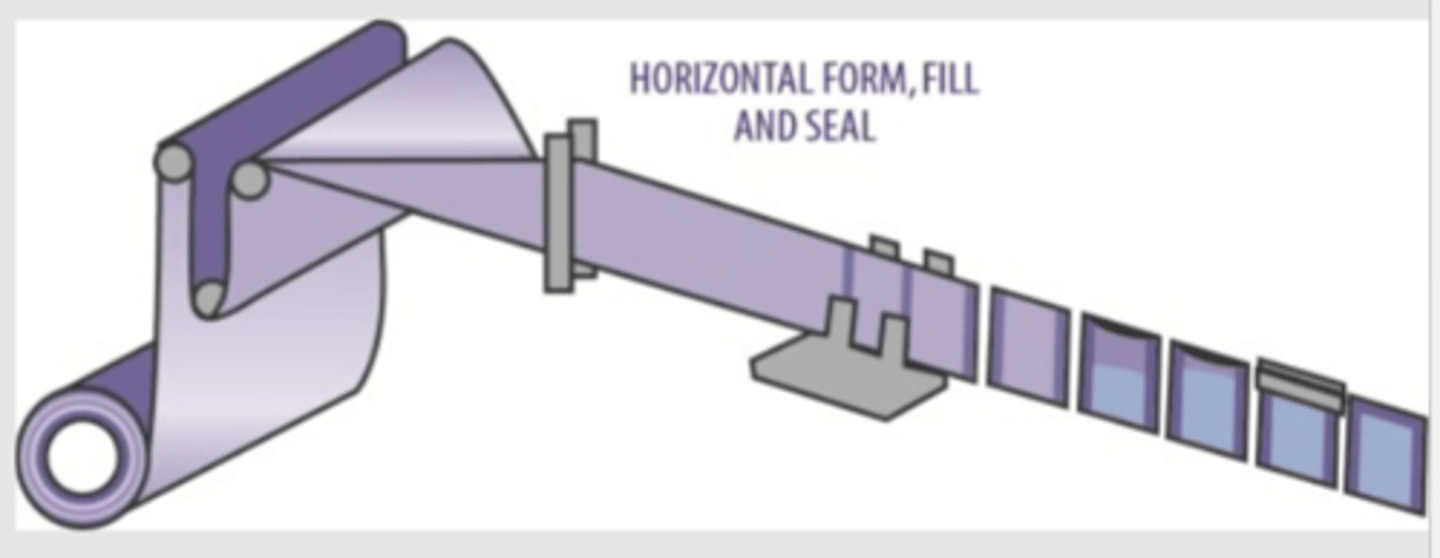
HFFS - Sachet
Pre made pouches
-stand up with a separate gusset
-stand up with a folded bottom
-box pouch
-4 side seal flat
Seal Jaw Design
serrations
Fin or lap seal
lap seal saves material but the outer and inner have to seal
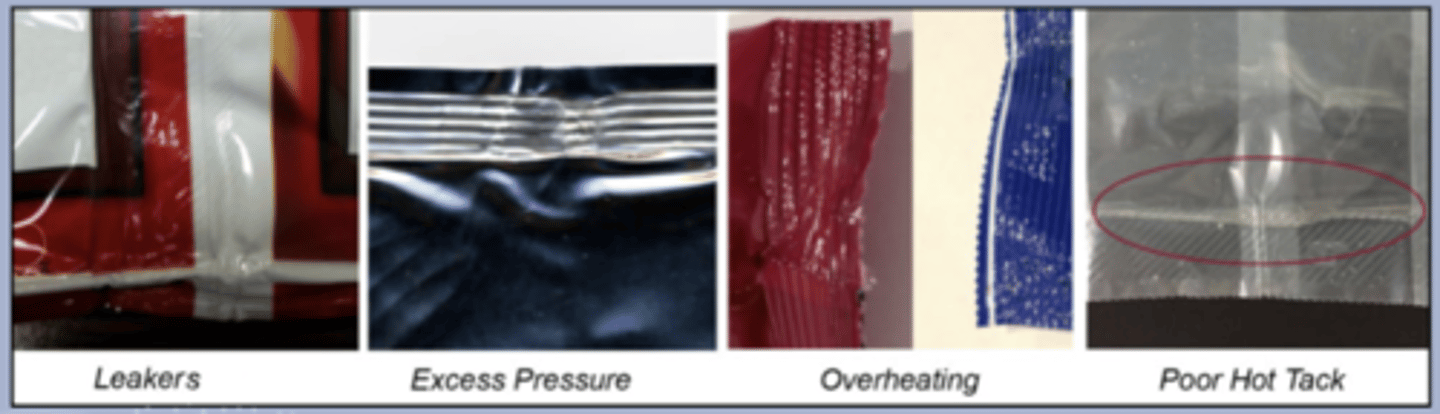
What are the most vulnerable areas of seals
folded areas
Seal Failures & Defects
Package Validation is directly related to
safety
Safety
extractables, toxicity, retained solvents, heavy metals
Barrier
porosity, microbial barrier, gas transfers, light transmission
Durability
flexural, bond strength, tensile, puncture, tear, thickness