CogSci 180 Midterm - Brain Basics
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
neuroanatomical orientations
anterior (front)
posterior (back)
dorsal (top of head or back)
ventral (bottom of skull or front of body)
lateral (toward side of body, away from middle)
medial (middle of body, away from side)
coronal or frontal section (parallel to forehead)
sagittal or lateral section (perpendicular to ground)
transverse or axial section (parallel to ground)
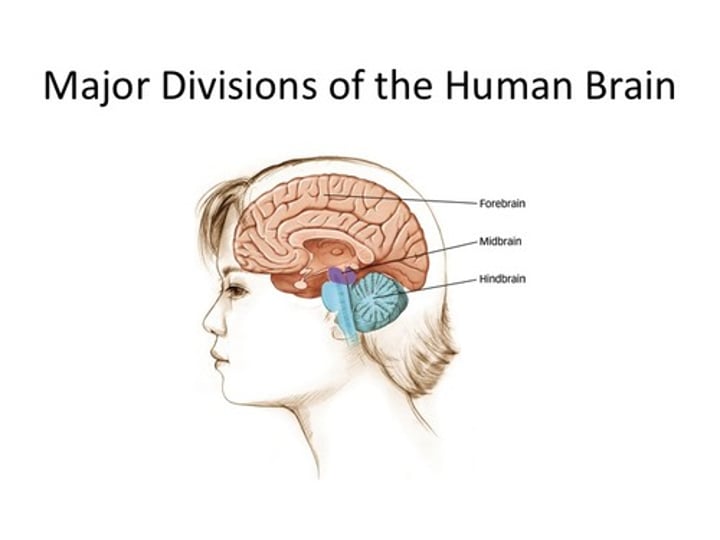
3 divisions of human brain
forebrain - neocortex (rational)
midbrain - limbic brain (emotional)
hindbrain - reptilian brain (instinctual)
cerebral cortex
best distinguishes us from other animals
outermost layer of grey matter (3mm thick)
26 billion neurons
sulci+gyri increase surface area
consists mainly of glia and cell bodies
includes neocortex (lobes) and limbic cortex
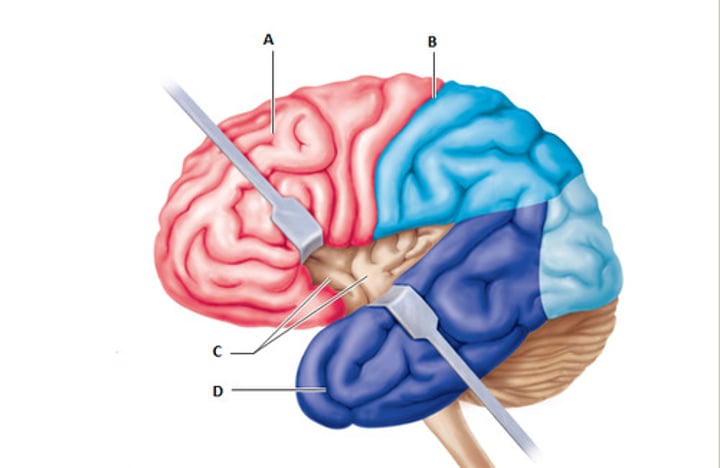
lobes of the brain
frontal (speaking, muscle movement, planning, judgement, emotional control)
- primary motor cortex (voluntary movements)
- prefrontal cortex (plans/judgements)
parietal (body awareness)
- primary somatosensory cortex (body surface mapped onto brain surface)
occipital
- primary visual cortex (receives visual input from opposite visual field)
temporal
- primary auditory cortex (auditory information)
- temporal parietal junction (stim causes out of body exp)
- insula
prefrontal cortex divisions
dorsolateral prefrontal cortex:
working mem, cog flexibility, problem solving, inhibition of rumination/worry
ventromedial prefrontal cortex:
theory of mind, self-perception, risk/fear processing, behavioral ctrl, decision making
includes - rostral ACC, mPFC, subgenual cingulate cortex, orbitofrontal ctx
lateralization of functions
corpus callosum connects
Left (projects to right side of body):
- analysis of info
- recognition of serial events
- language
- math computation
- logical and linear
Right (projects to left side of body)
- synthesis of info
- pattern recognition (holistic)
- identification of emotional expression
- non verbal and holistic
limbic system
assoc w emotions and memory
amygdala
hippocampus
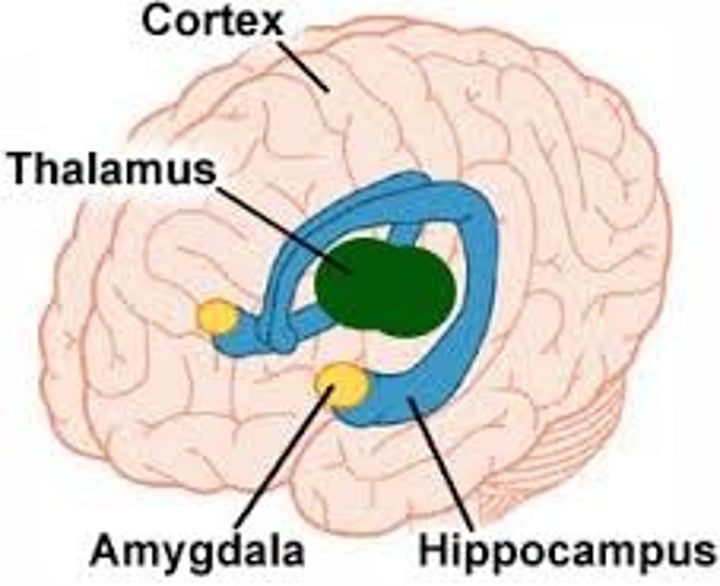
amygdala
linked to emotion, fear/aggression
(conservatives said to have larger)
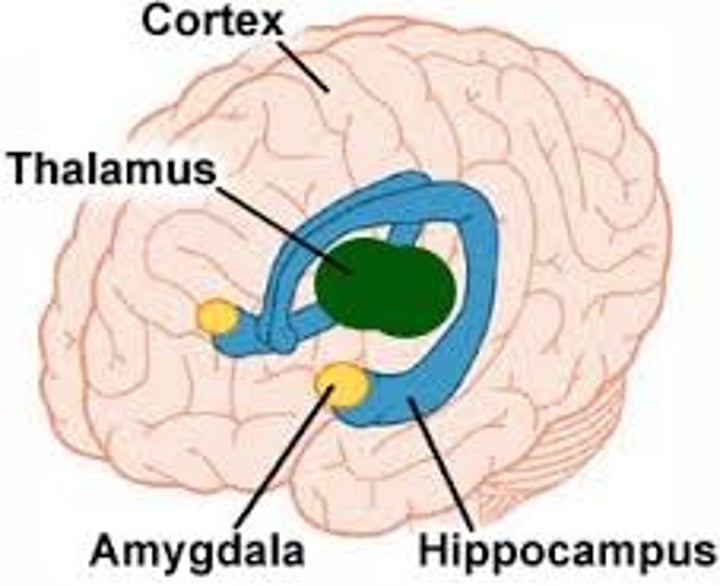
hippocampus
important in memory
anterior hippo, closest to amygdala, involved in regulating behavioral inhibition (PTSD = maybe abnormal anterior hippo activity)
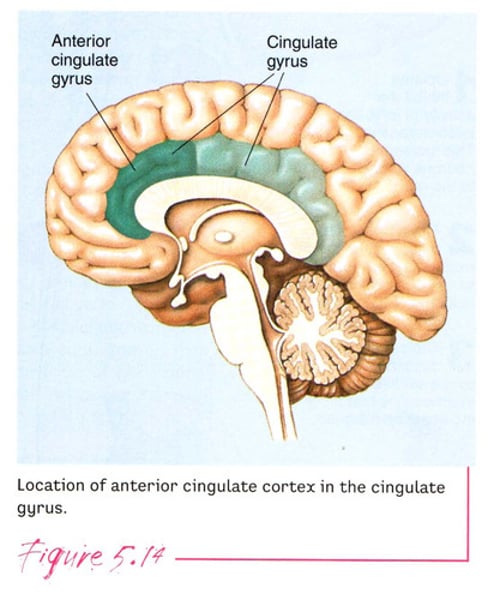
anterior cingulate cortex
collar around front part of corpus callosum
integrates cognitive and affective info
processing of conflicting info
selective attention
pain perception
impulse control
insular cortex
deep within lateral sulcus
functions for body awareness, sense of self, emotion exp, empathy/compassion, addiction
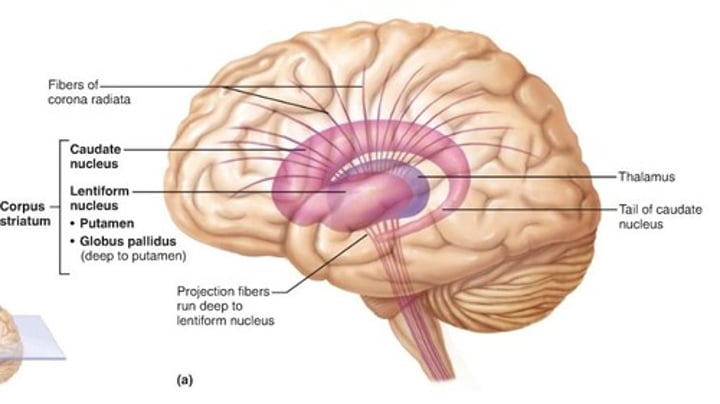
basal ganglia
upper part - caudate nucleus, putamen, globus pallidus for action selection, motor seq, motor inhibition
lower part - NAc for reward learning
nucleus accumbens
lower part of basal ganglia
reward center
VTA/SNc release DA here
brain stem
automatic survival functions (sleep, arousal, heart rate, breathing, blood pressure)
cerebellum
coordinate voluntary movement and balance
plays role in higher learning
network neuroscience
functional connectivity
research can be done when ppl aren't doing anything at all
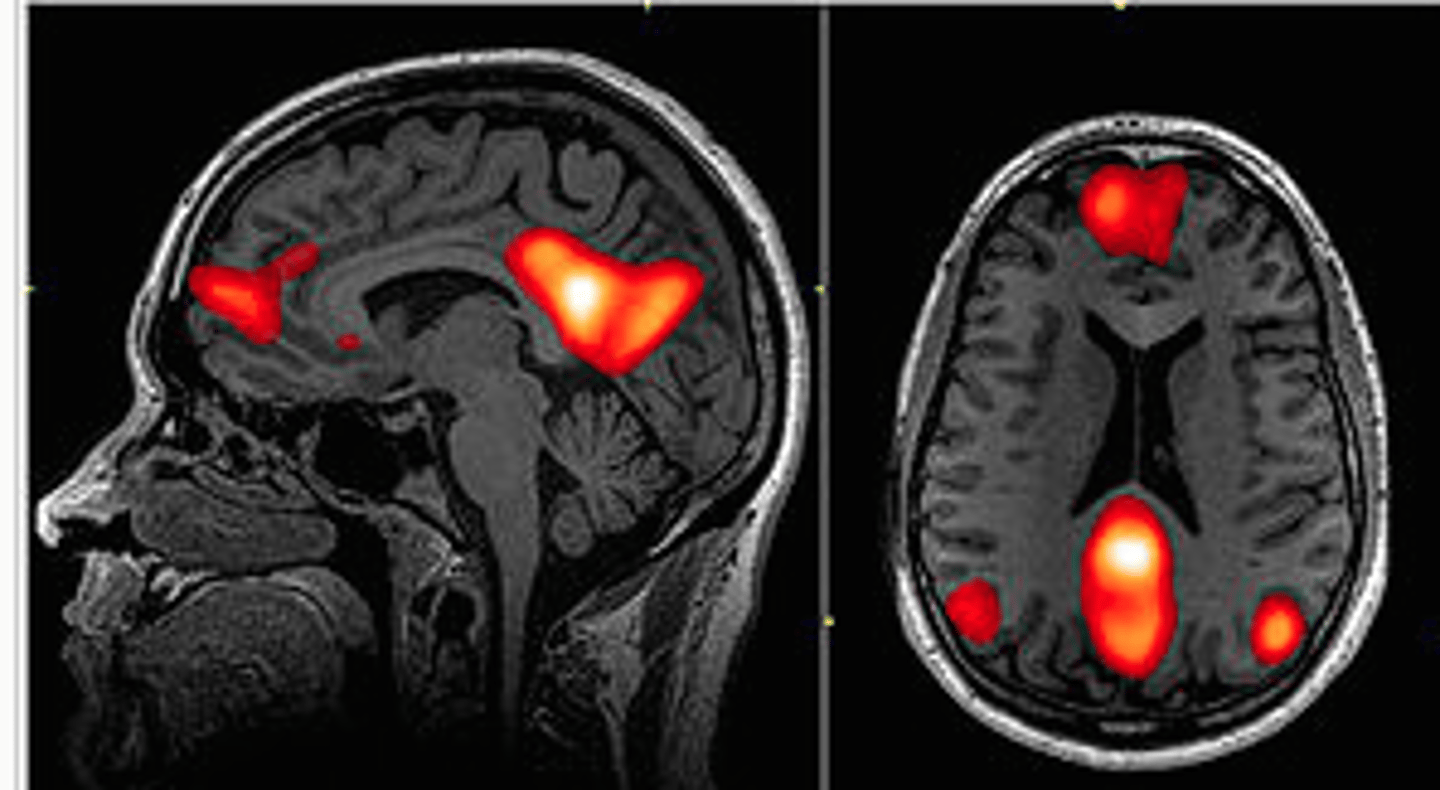
default mode network
brain areas active when participant is in resting state, not focused on particular task
can also be active in goal-oriented tasks like self-referencing, recognition of emotions, ruminating about past, worrying about future
posterior cingulate ctx and precuneus, mFC, temporopatietal junction
AD -> deteriorating connectivity of DMN
meditators show reduced DMN activity
structure of neuron
soma
dendrite
axon
terminal button
neurotransmitter
synapse
mechanisms of neural growth
neurogenesis (hippo, olfactory bulb, amygdala)
development of new synapses
dendritic branching/arborization
neuroplasticity
brain can change in response to both behavioral activity and thoughts alone
psych disorders can inc/dec activity in specific brain circuits > plasticity leads to disorder more