Unit 7 - Natural Selection
1/64
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Evolution of a species, via natural selection, involves a change in the species genetic makeup over time.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
Charles Darwin
english naturalist, researched the Glapagos Islands and how birds like finches diversified and gave rise to new species
theory of natural selection through evolution
Evolution
change in genetic makeup of a population over time; descent with modification
Natural Selection
individuals that have certain traits tend to survive and reproduce at higher rates than other individuals because of those traits
Fitness
ability to survive and reproduce measured by reproductive success
“Traits are Heritable”
characteristics can be passed from parents to offspring
Adaptations
inherited characteristics of organisms that enhance their survival and reproduction
“More offspring are produced than can survive”
leads to competition for limited resources which results in differential survival (favorable traits lead to survival and will accumulate in the population)
Artificial Selection
selective breeding of domesticated plants and animals to encourage the occurrence of desirable traits
Population
a group of individual of the same species that live in the same area and interbreed to produce fertile offspring
Gene Pool
a population’s genetic makeup and consists of all copies of every type of allele
Microevolution
small scale genetic changes in a population; change in allele frequencies within a single species or population
Mutations
a change in the DNA sequence of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA and can result in genetic variation
Genetic Drift
chance events that cause a change in allele frequency from one generation to the next and can lead to a loss of genetic variation
Butterfly Effect
when a large population is drastically reduced by a non-selective disaster
Founder Effect
when fewer individuals become isolated from a large population and establish a new small population with a gene poll that differs from the large population and loses genetic diversity
Gene Flow
transfer of alleles into or out of a population due to fertile individuals or gametes
Relative Fitness
number of surviving offspring that an individual produces compared to the number left by others in the population and measures reproductive success
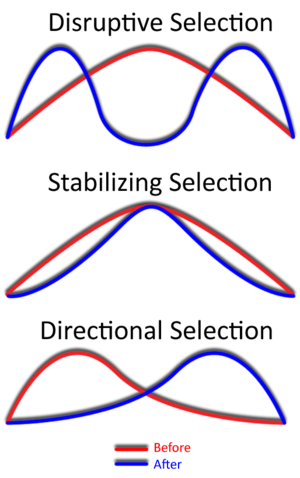
Directional Selection
Natural Selection towards 1 extreme phenotype
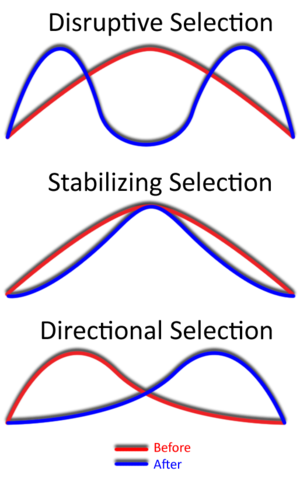
Stabilizing Selection
Natural Selection towards the mean and against the extreme phenotypes
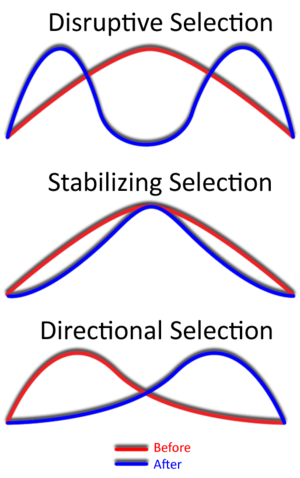
Distriptive Selection
Natural Selection against the mean; both phenotypes extremes have the highest relative fitness
Sexual Selection
type of natural selection that explains why many species have unique/showy traits
Hardy Weinburg Equilibrium
a model used to assess whether natural selection or other factors are causing evolution at a particular locus
p + q = 1
frequency of the dominant allele in a gene population plus frequency of the recessive allele in a population
p² + 2pq + q² = 1
percentage of the homozygous dominant individuals + twice the percentage of the heterozygous individuals + percentage of the homozygous recessive individuals
Fossil Records
remains or traces of past organisms gives a visual of evolutionary change over time and geographical data from where the organism is found
Comparative Morphology
analysis of the structures of living and extinct organisms
Homology
characteristics in related species that have similarities
Embryonic Homology
many species have similar embryonic development
Vestigial Structures
structures that are condensed even through they no longer have a use
ex. human tailbone and appendix
Molecular Homology
many species share similar DNA and amino acid sequences
Homologous Structures
characteristics that are similar in two species because they share a common ancestor
ex. arm bones of many species
Analogous Structures
Structures that are similar but have separate evolutionary origins
ex. wings in birds vs. bats
Biogeography
distribution of animals and plants geographically
ex. species on oceanic islands resemble mainland species but species on the same continent are similar and distinct from species on other continents
Phylogeny
hypothesis of evolutionary history
Systematics
classification of organisms and determining their evolutionary relationship
Taxonomy
naming and classifying species
Phylogenetic Trees
DIagrams that represent the evolutionary history of a group of organisms and show the amount of change over time measured by fossils
Cladograms
show the branching linkage of common ancestors of all species represented by a node
sister taxa are two classes from the same node
basal taxon is a lineage evolved from the root and is unbranched
Synapomorphy
a derived character shared by Claude members
Derived Characteristics
similarily inherited from the most recent common ancestor of an entire group
Ancestral Characteristics
similarily that rose prior to the common ancestor
Monophyletic Group
includes the most recent common ancestor of the group and all of its decendants
Paraphyletic Group
includes that most recent common ancestors of the group, but not all its descendants
Polyphyletic Group
does not include the most recent common ancestor of all members of the group
Speciation
a formation of a new species (a group able to interbreed and produce viable, fertile offspring) results in diversity of life forms
Allopatric Speciation
physical bamer divides population or a small population is sperated from main population and prevents gene flow often caused by natural disasters
Sympatric Speciation
new species evolves while still inhabiting the same geographic region as the ancestral species usually due to the exploitation of a new niche
Prezygotic Barriers
prevent mating or hinder fertilization; five types
Habitat Isolation
species live in different areas or they occupy different habitats within the same area
Temporal Isolation
species breed at different times of the day, year, or season
Behavior Isolation
unique behavioral patterns and rituals seperate species
Mechanical Isolation
reproductive anatomy of one species does not fit with the anatomy of another species
Gametic Isolation
preoteins on the surface of gametes do not allow for the egg and sperm to fuse
Postzygotic Barriers
prevent a hybrid zyogote from developing into a variable, fertile adult
Reduced Hybrid Viability
the genes of different parent species many interact in ways that impair the hybrid’s development or survival
Reduced Hybrid Fertility
a hybrid can develop into a healthy adult, but it is sterile usually results due to differences in number of chromosomes between parents
Hybrid Breakdown
the hybrid of the first generation may be fertile, but when they mate with a parent species or one another, their offspring will be sterile
Macroevolution
large evolutionary pattens
Stasis
no change over long periods of time
Punctuated Equilibrium
when evolution occurs rapidly after a long period of stasis
Gradualism
when evolution occurs slowly over hundreds, thousands, or millions of years
Divergent Evolution
groups with the same common ancestors evolve and accumulate differences resulting in the formation of a new species
Adaptive Radiation
If a new habitat ot niche becomes available, then a new species can diversify rapidly
Convergent Evolution
two different species develop similar traits despite having different ancestors; similar adaptations that have evolved in distantly related organisms due to similar environments
Extinction
termination of a species