CC SUPLIES AND REAGENT - MLS 111 - CC - LABORATORY PRELIM
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
What are the two most popularly used laboratory balances?
Analytic and electronic balances.
What is an analytic balance used for?
The preparation of a primary standard.
What is an electronic balance?
A single pan balance that uses an electromagnetic force to counterbalance the weighed sample's mass.
What is the purpose of a pH meter?
To express the degree of acidity or alkalinity of a solution.
What is a centrifuge used for?
To separate phases of different mass and densities using centrifugal force.
What is the "Principle of balance" for a centrifuge?
Tubes and carriers must be of equal weight, shape, and size, and be placed in opposing positions in the centrifuge head.
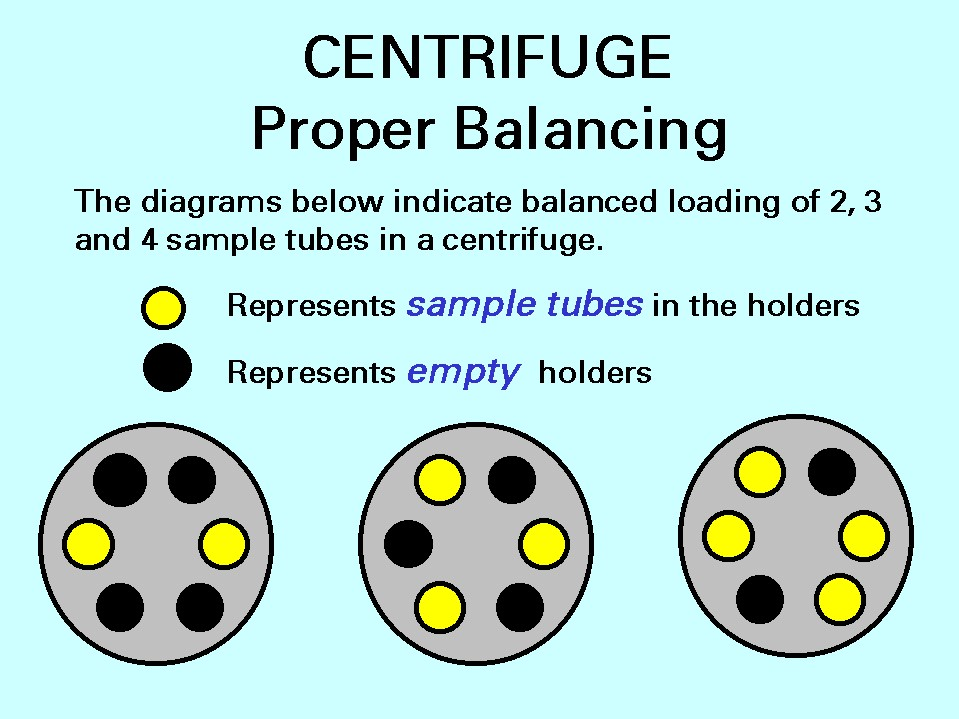
What is a Clinical centrifuge used for?
Urinalysis or serum separation. It has a speed capacity of 0-3,000 rpm and holds tubes from 5-50 mL.

What is a Serofuge?
A small centrifuge used in blood banking and serology to spin serological tubes with 2-3 mL sizes

What is a Microcentrifuge used for?
To spin microtubes with a capacity of 0.5-15 mL at high speeds, usually up to 12,000-14,000 rpm.

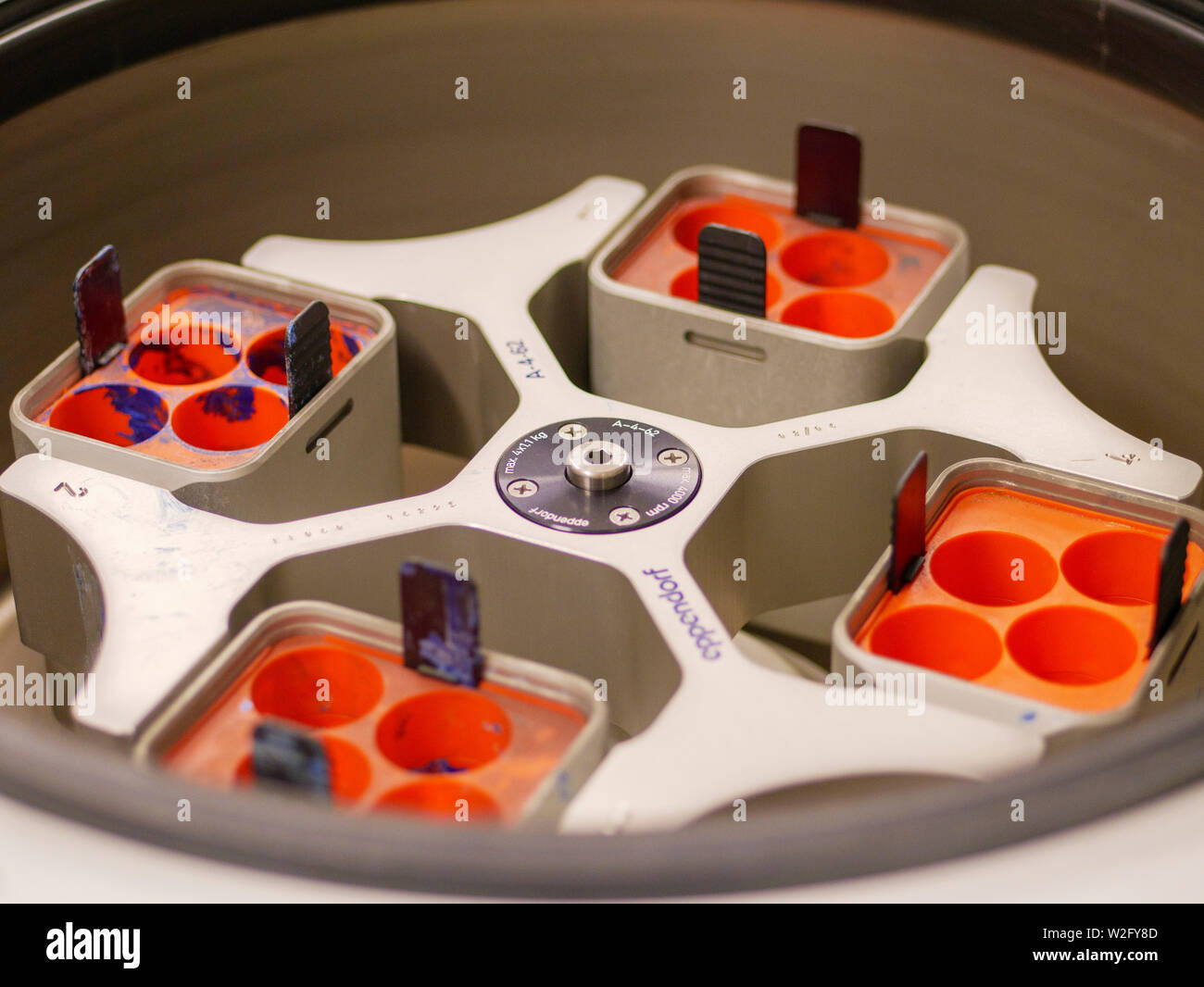
What is a horizontal-head centrifuge?
A centrifuge where the cups holding the tubes are in a vertical position at rest but assume a horizontal position when the centrifuge revolves. It is also known as a swinging bucket centrifuge.

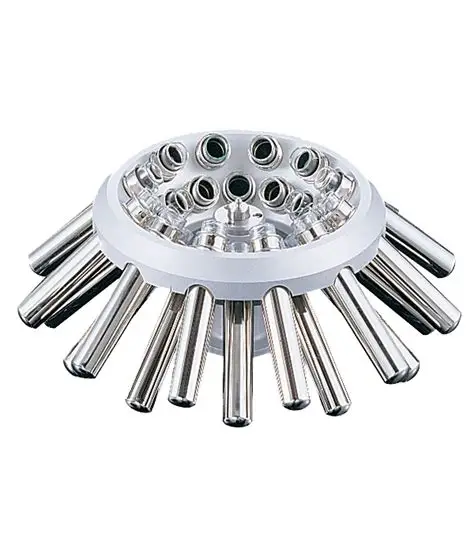
What is a fixed-angle-head centrifuge?
A centrifuge where the cups are held in a rigid position at a fixed angle. This position makes the process more rapid.

What is Borosilicate glass?
It has low alkali content and is resistant to heat, corrosion, and thermal shock.

What is Flint glass (Soda lime glass)?
It is less expensive and less resistant to high temperatures and sudden changes in temperature. It can also release alkali into solutions, causing contamination.

What is a "To Contain" (TC) pipette?
It holds a particular volume but does not dispense that exact volume.
What is a "To Deliver" (TD) pipette?
It is designed to dispense the volume indicated.
What is a Volumetric pipette?
A TD/”no blowout” pipette that measures only one volume and is not graduated. It is more accurate than a serological pipette.

What is a Serological pipette?
A "to deliver" (TD)/"blowout" pipette. Its calibration extends to the tip.
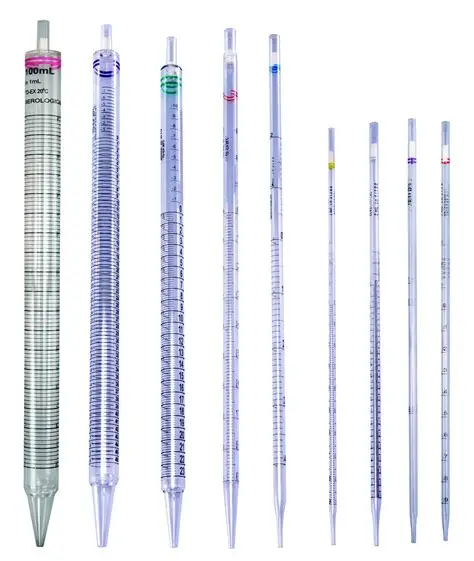
What is a Mohr pipette?
A TD/"no blowout" pipette. The end-calibration line is before the tip.

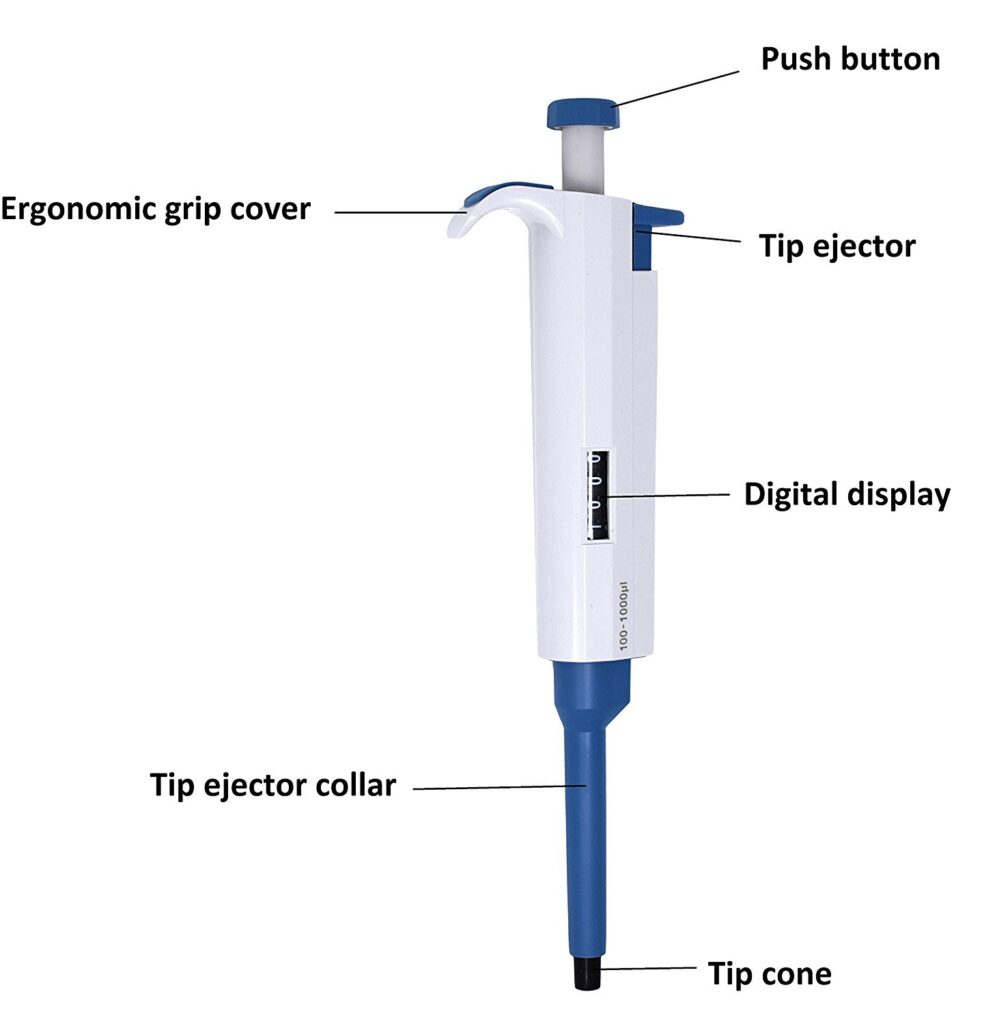
What is a Micropipette?
A pipette that measures a small amount of liquid, less than 1 mL.

What are the grades of chemicals used as reagents?
Analytic Reagent (AR) grade, Ultrapure grade, Chemically Pure (CP) grade, United States Pharmacopeia (USP) and National Formulary (NF) grade, and Technical or Commercial grade.
What is a primary standard?
A highly purified chemical that can be measured directly to produce a substance of an exact known concentration or purity.
What is Type I Reagent Water used for?
Procedures requiring maximum water purity, such as flame photometry, AAS, blood gases and pH, enzyme studies, and trace metal studies. It should be used immediately after production.
What is a buffer?
Weak acids or bases and their related salts that minimize changes in the hydrogen ion concentration.
When selecting a pipette, what is the best practice for volume capacity?
Always use a pipette with a volume capacity closer to the intended amount to be measured.
What are two safety rules to follow when pipetting?
Avoid using chipped pipettes and do not use mouth pipetting.
What personal protective equipment (PPE) should be worn?
Complete PPE
What is the correct aspiration angle for a pipette?
Vertical
What is the correct dispensing angle for a pipette?
20 to 45 degrees
What is the correct aspiration depth?
Just below the fluid.
Referring to a micropipette, name three factors that can lead to incorrect volumes.
A leaky or poorly sealed tip, reusing the pipette tip, or using contaminated pipettes.
What is another factor that can cause an incorrect volume?
Failing to dispense against the inside wall of the vessel.
What can bubbles in a pipette lead to?
An incorrect total volume of fluid.
Why might a micropipette need to be calibrated?
Lack of calibration can affect the volume of liquid.
How do you correctly read the meniscus?
Read the meniscus at eye level, not above or below.
What is the purpose of the first stop on a micropipette?
To aspirate or "suck up" the sample.
What is the purpose of the second stop on a micropipette?
To dispense or "deliver" the liquid.
What is the effect of pressing the first stop to aspirate a specimen?
No effect on volume and reading.
What is the effect of pressing the first stop to dispense a specimen?
Leads to a low volume of specimen and a falsely low reading.
What is the effect of pressing the second stop to aspirate a specimen?
Results in a higher volume of specimen, leading to a falsely high reading.
What is the effect of pressing the second stop to dispense a specimen?
No effect on volume and reading.
If a micropipette tip is leaky, what is the effect on a reading?
Volume of reagent is decreased, leading to a falsely high reading.