Level 2—WelComs Review + Comquest Management + Microbiology + HY Drugs
1/1455
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
1456 Terms
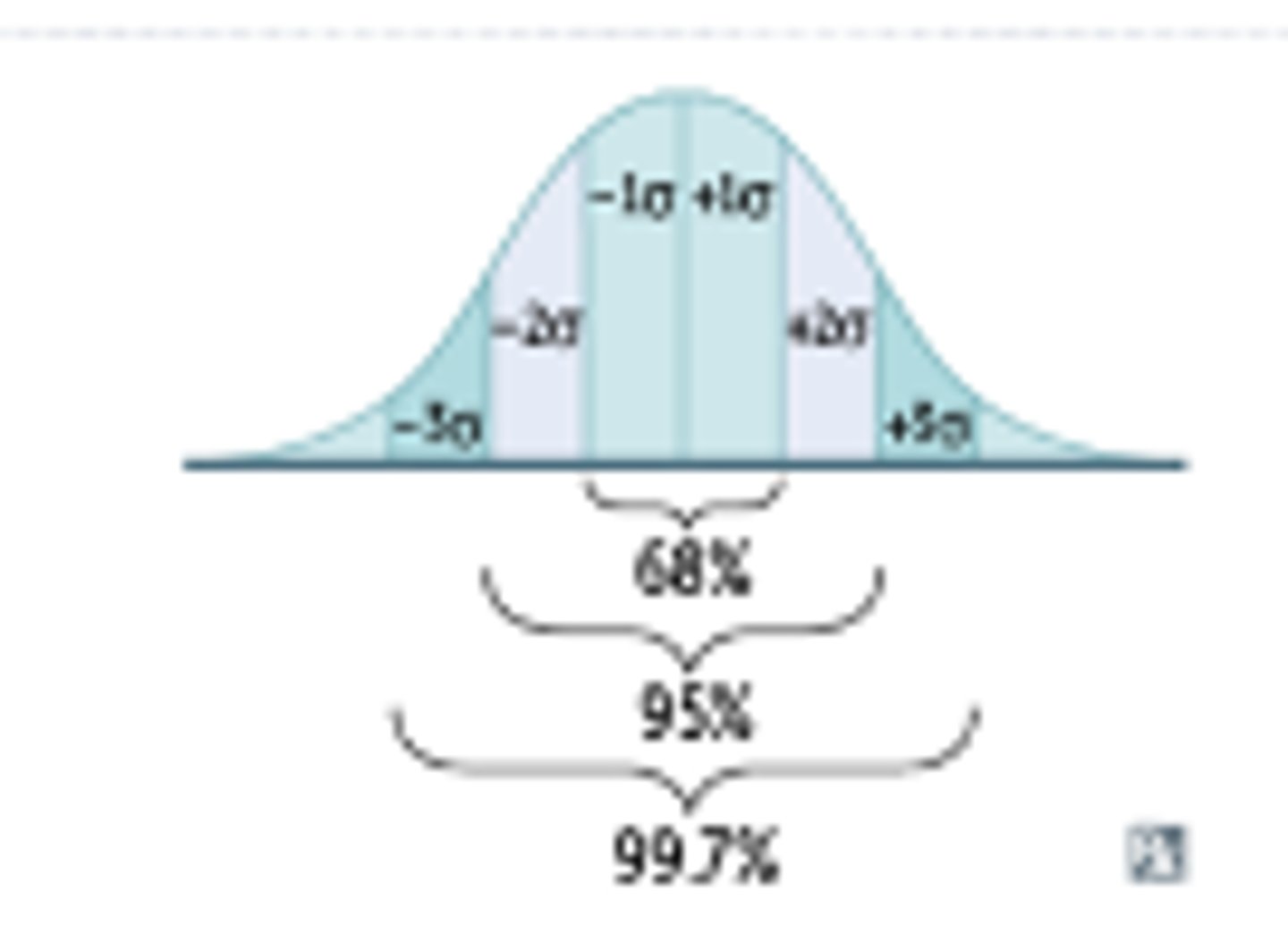
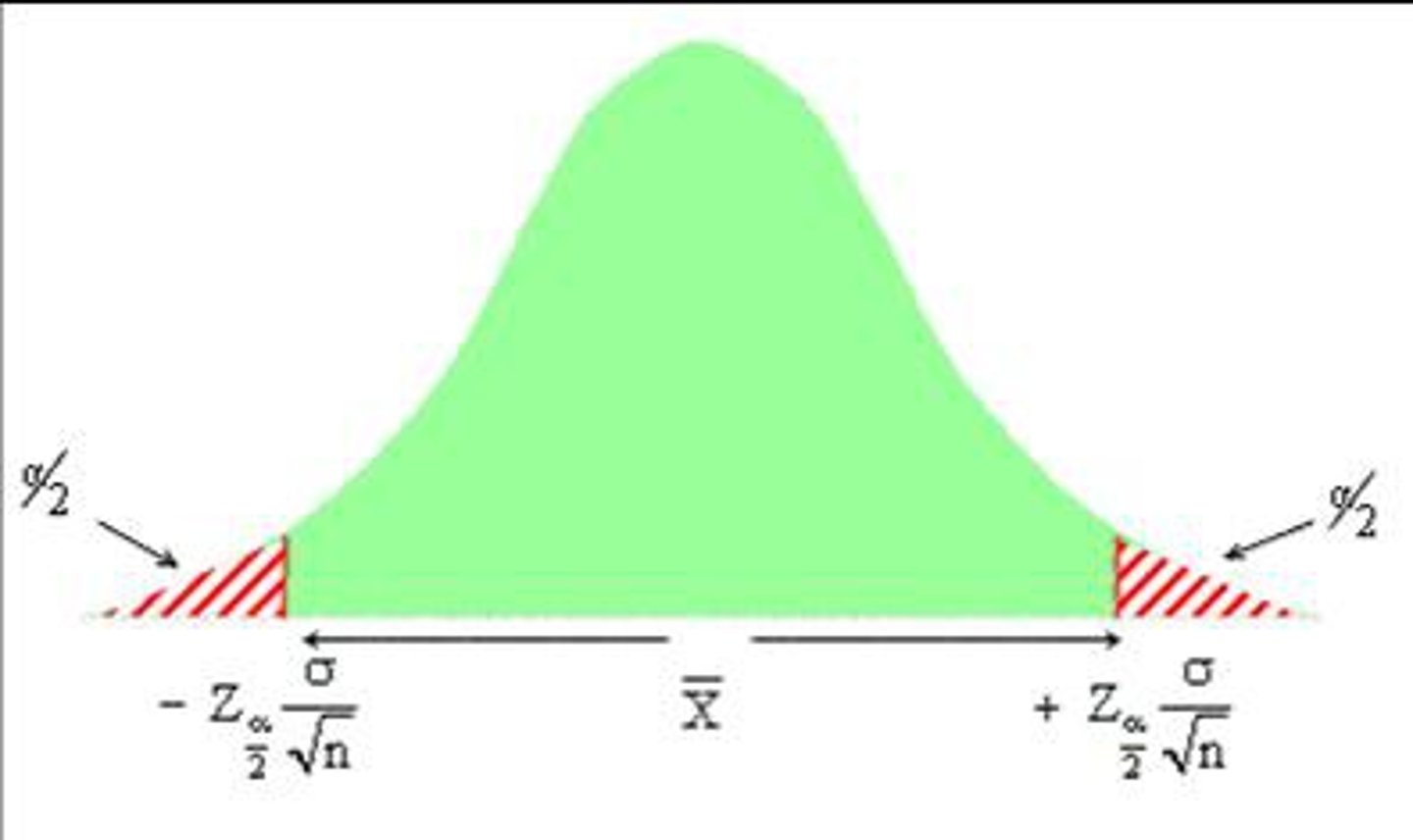
95% Confidence Interval
- Interval ⦸ include 1
- Null value of 1 should ⦸ be included in the confidence interval to denote a statistical significance at 95%/ p < 0.05
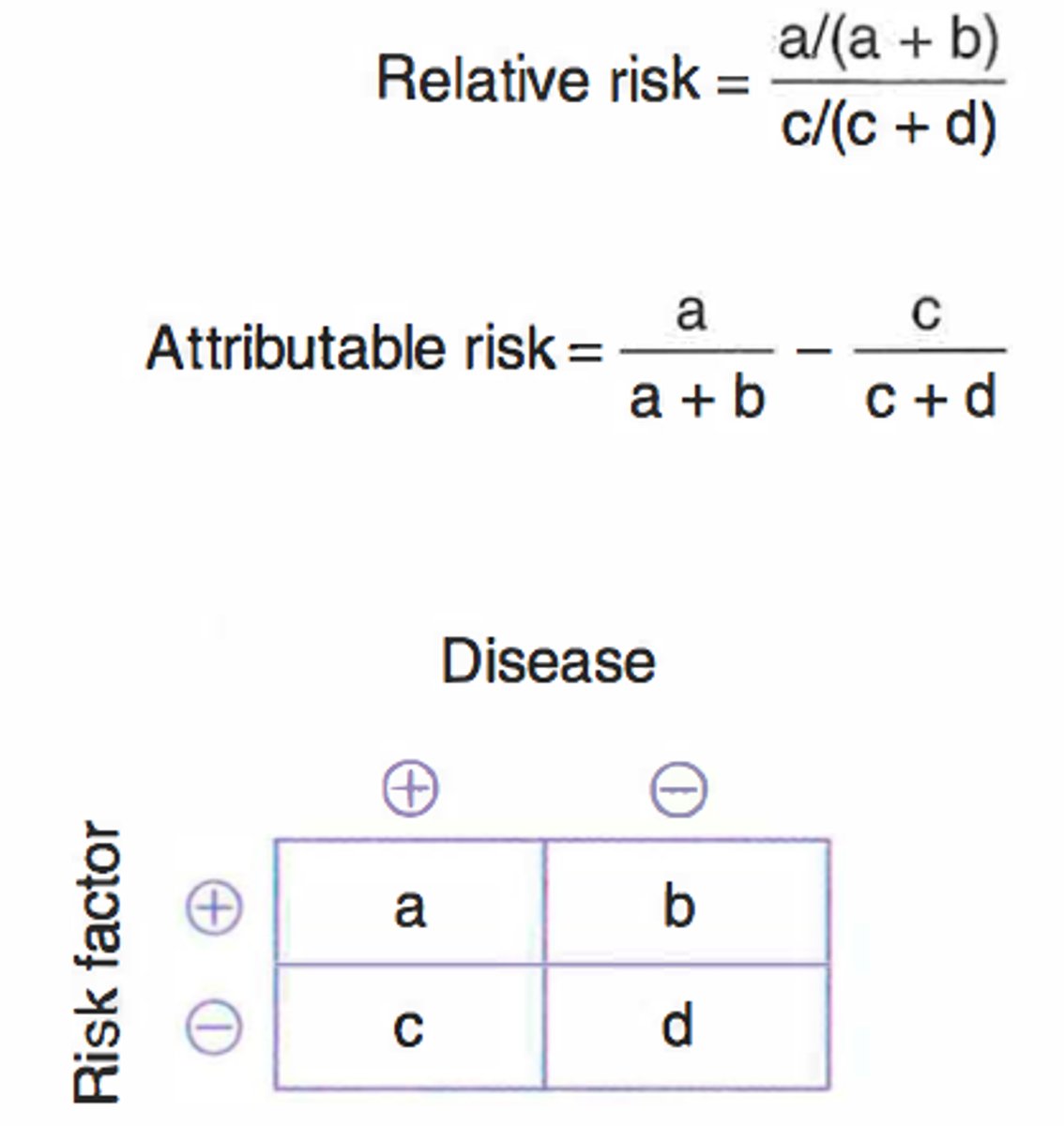
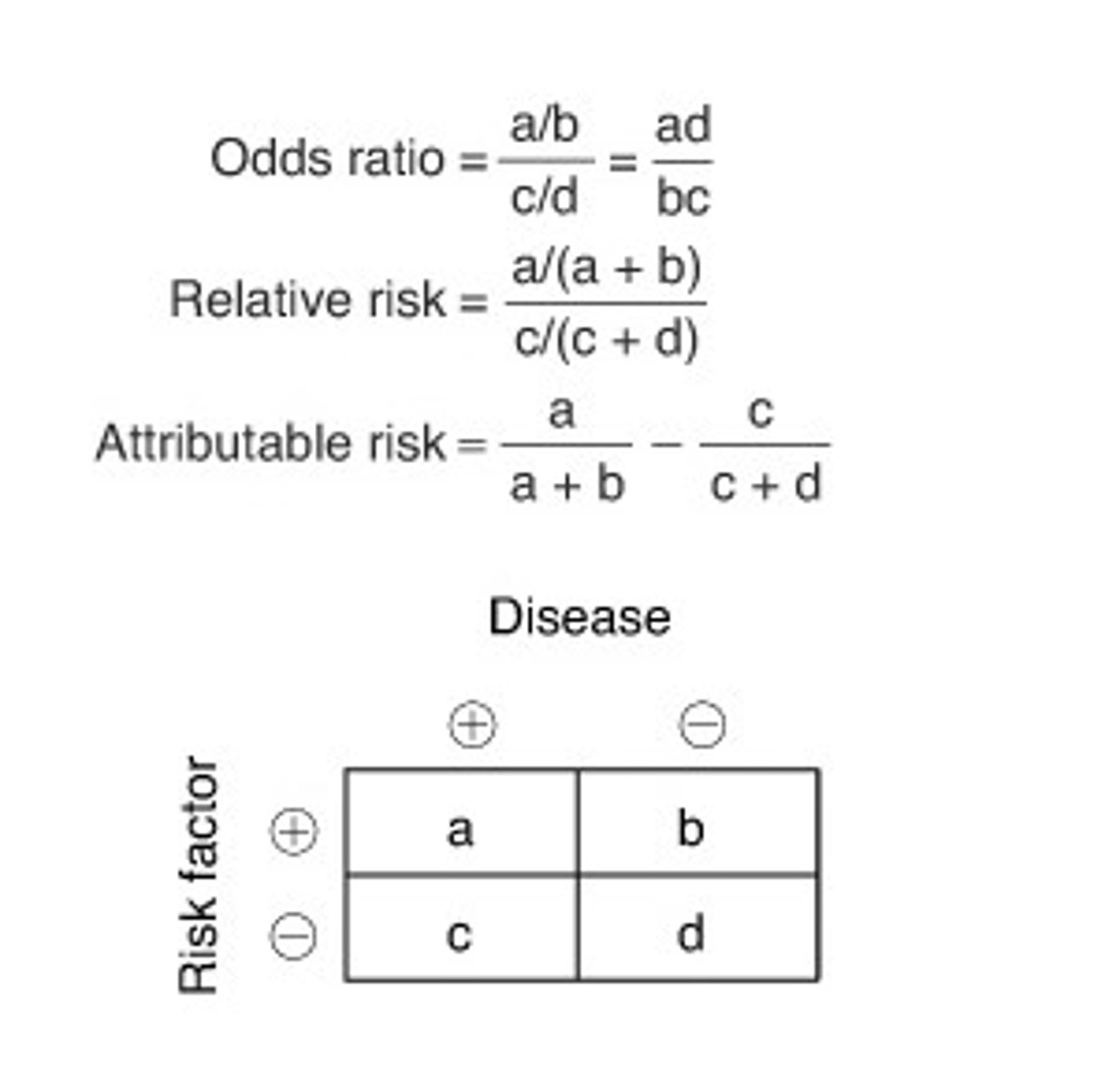
Attributable Risk
- Difference between the incidence rates in exposed and unexposed groups
Case Fatality Rate
- Proportion of deaths within a designated population of cases over the course of the disease
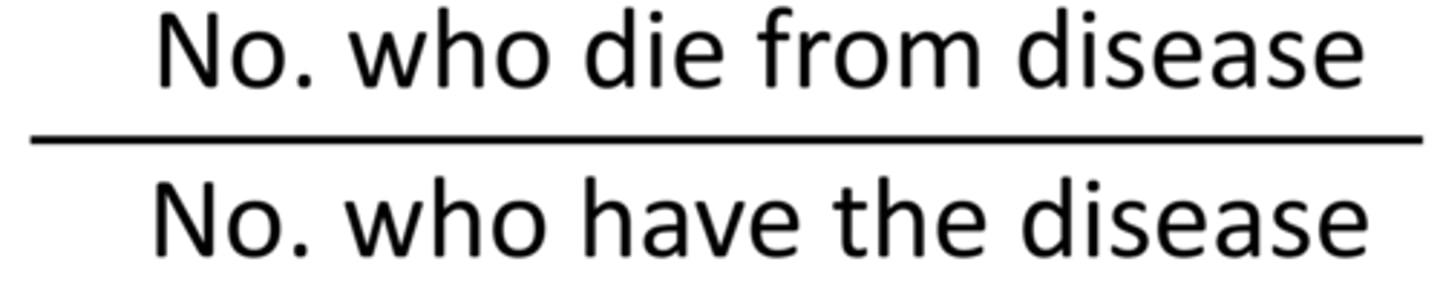
Chi-square test
- For categorical variables
- Test for differences in proportions as well as an association between 2 variables
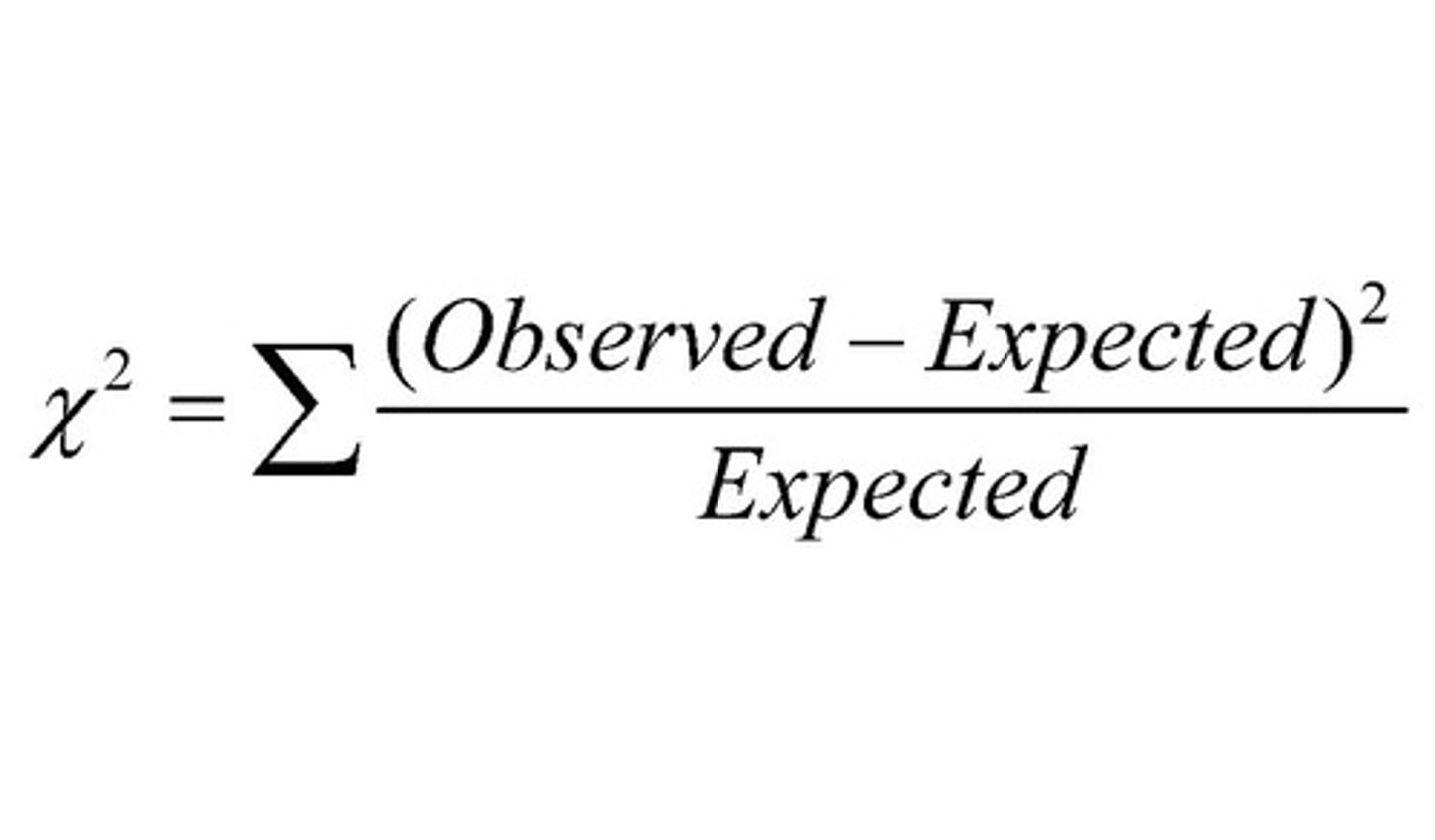
Confounding variable
- 3rd variable that may affect outcome
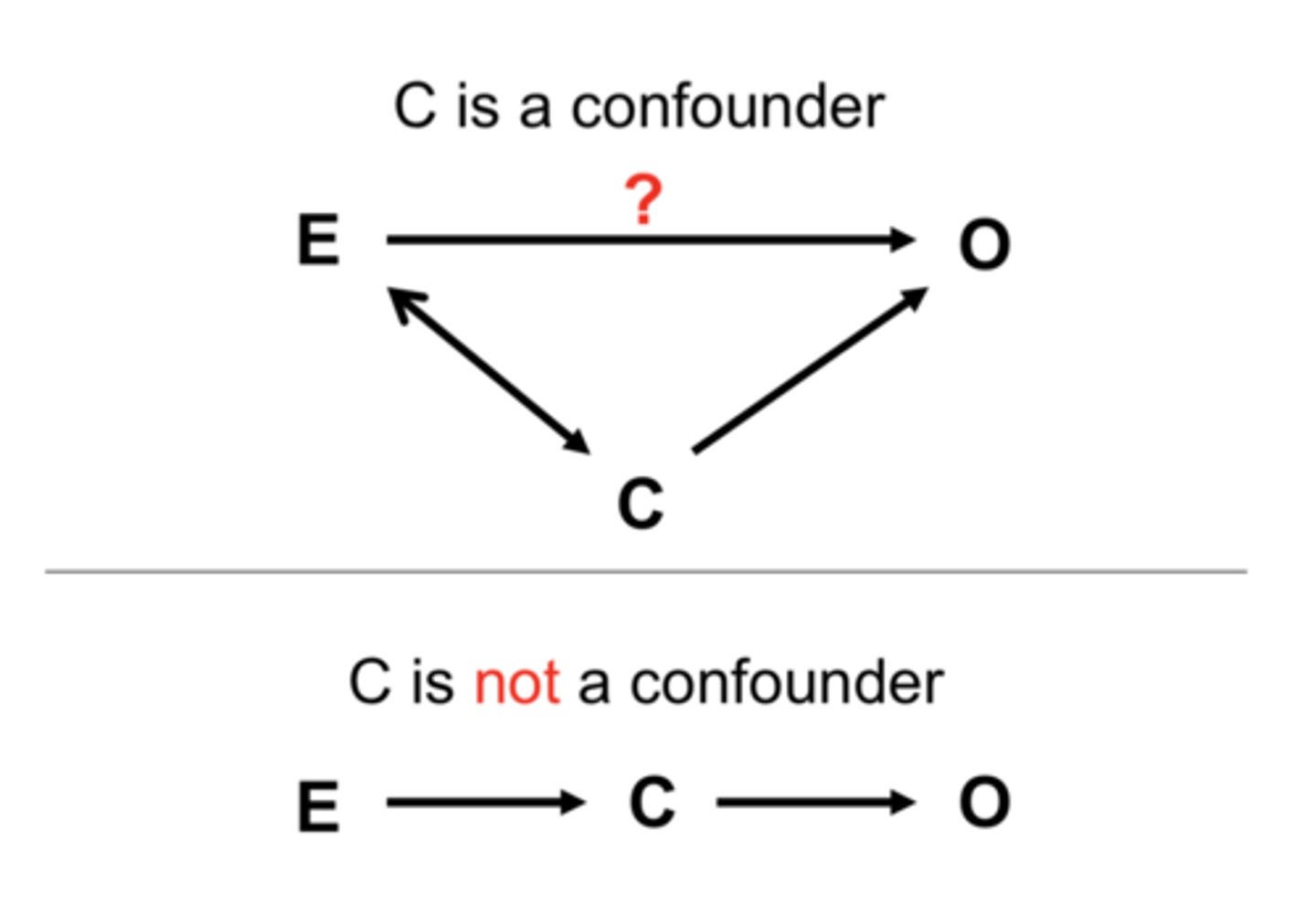
Incidence Rate
- Number of new cases per population at risk in a given time period
- IR = # new cases/ total time that disease free individuals in cohort are observed over time
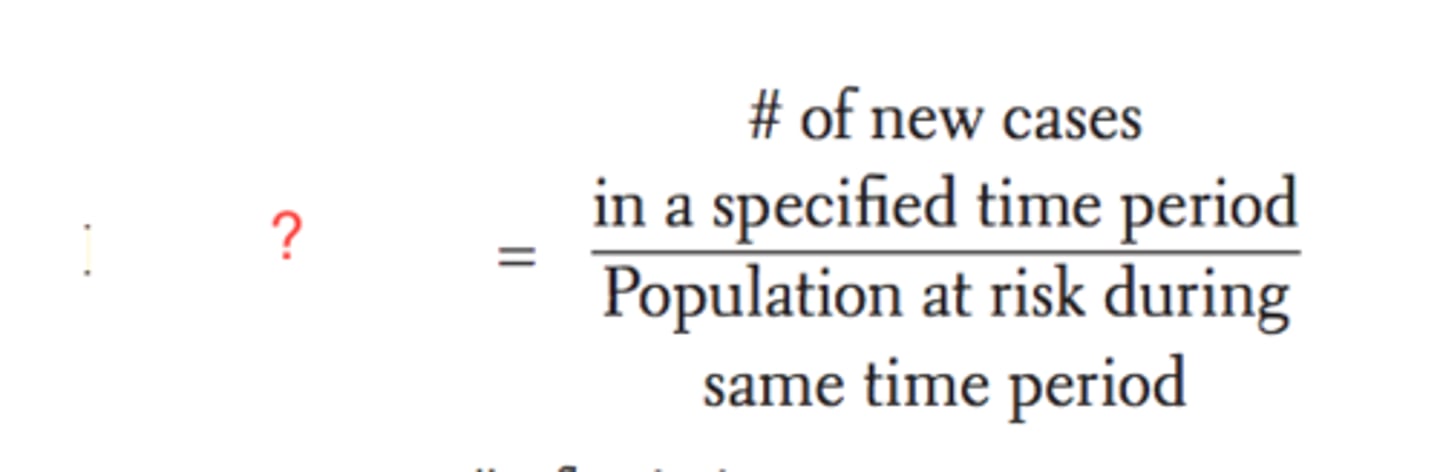
Mortality Rate for patient procedures
What variable to adjust for facility to facility?
Risk
High risk patients have a higher mortality rate
Multiplicative Rule of Probability
- Find the probability of 2 or more events occurring together
E.g. If a patient has 2 siblings and a 1/4 chance that a sibling is a suitable stem cell transplant donor, what is the probability that either sibling will be a match?
1-[1-(1/4) * 1-(1/4)]
1-[3/4*3/4]
1-[0.5625]
0.4375 = 43.75%
![<p>- Find the probability of 2 or more events occurring together</p><p>E.g. If a patient has 2 siblings and a 1/4 chance that a sibling is a suitable stem cell transplant donor, what is the probability that either sibling will be a match?</p><p>1-[1-(1/4) * 1-(1/4)]</p><p>1-[3/4*3/4]</p><p>1-[0.5625]</p><p>0.4375 = 43.75%</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/ee6ef6ac-c86f-41cf-968f-e695564331a7.jpg)
Null Hypothesis
- Equal effect or no difference between effects of an exposure or treatment
Ordinal Variable
- Scale of measurement that uses labels to classify cases (measurements) into ordered classes or categories
- Implies that the classes must be put into an order such that each case in one class is considered greater or less than every case in another class
e.g. Cancer Staging, Education Level, SES
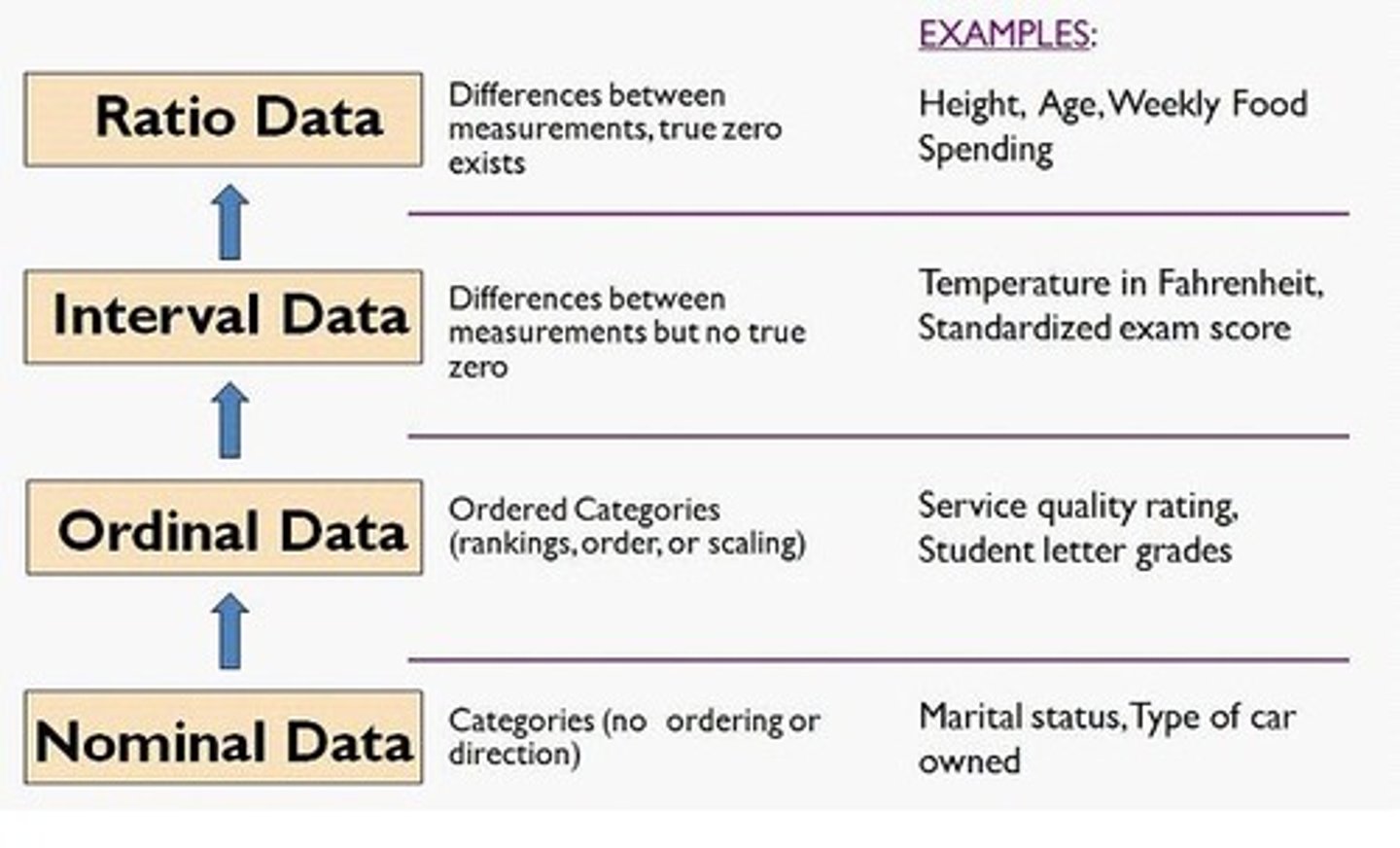
Continuous Variable
- variables that can assume any real number value
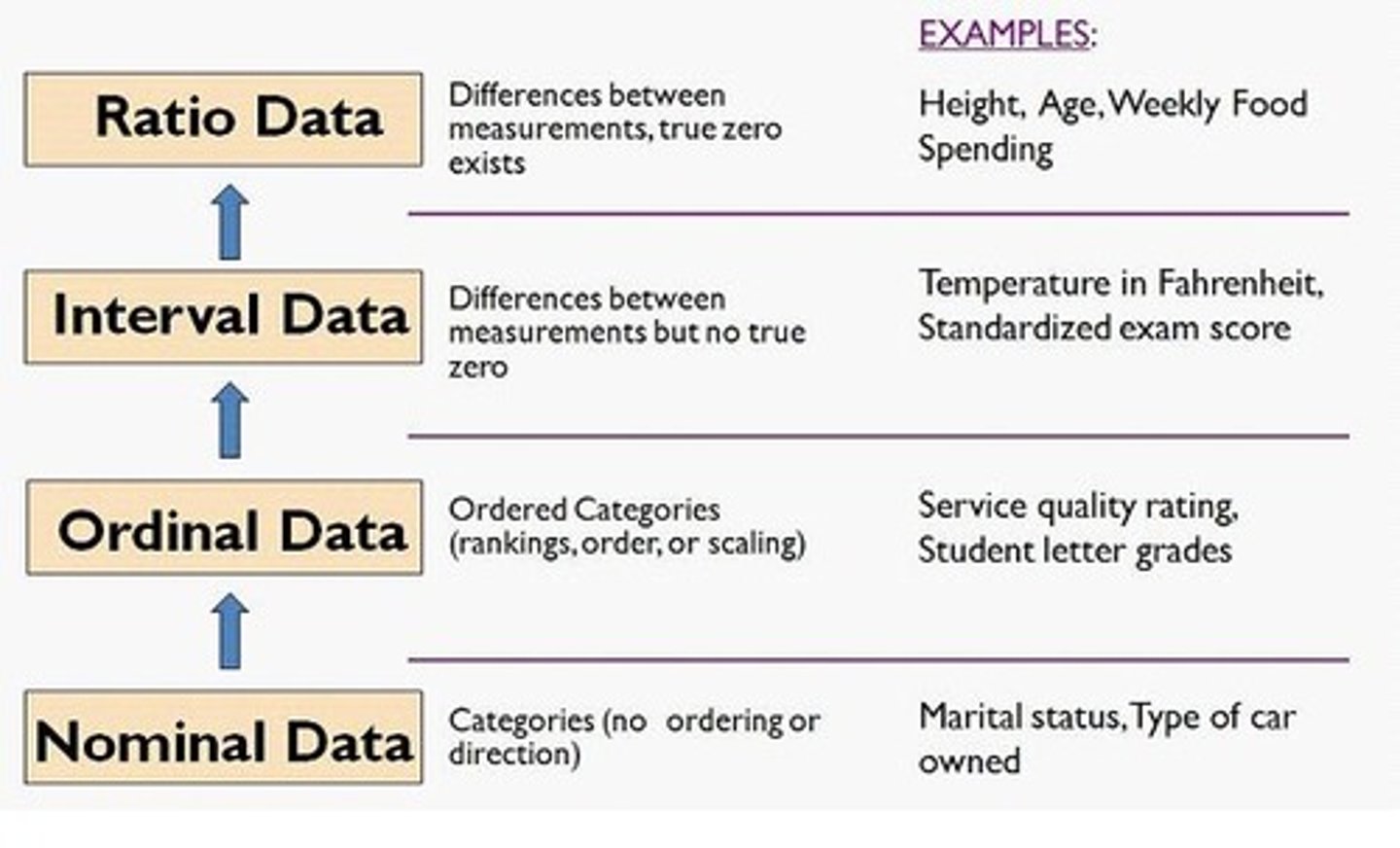
Nominal Variable
- describes a name, label or category without natural order
e.g. gender, eye color, blood type
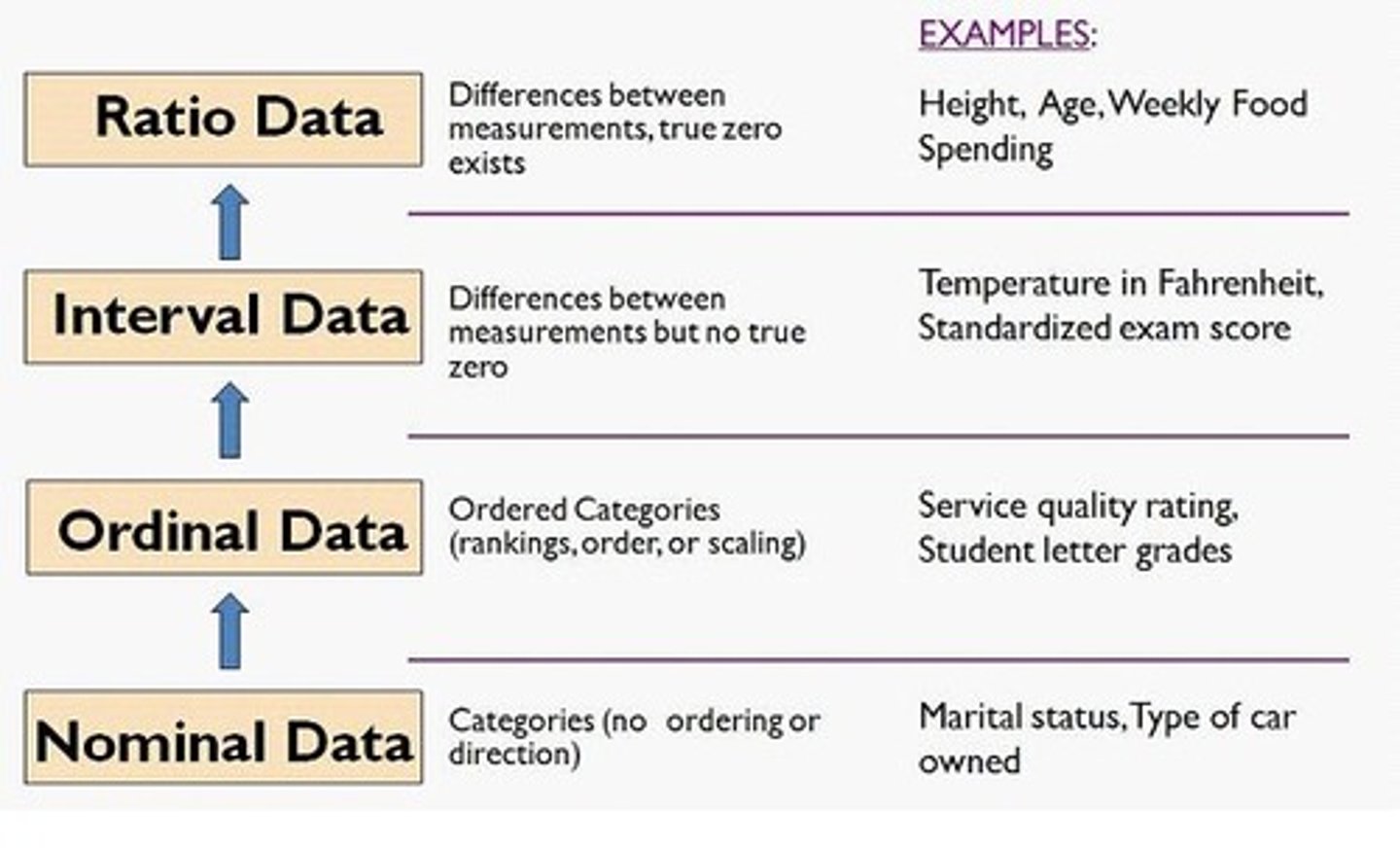
Interval Variable
- quantitative variable with meaningful and equally spaced intervals between its values
- ⦸ true zero point
Paired T-test
- For continuous variable
- The same group is sampled at two different times
- Test that looks at before and after results on each patient
- Calculates whether the means of two groups differ from one another
- Useful for detecting changes that might otherwise be obscured by variation within subjects because each subject is his or her own control
- Analyzed by evaluating the differences themselves

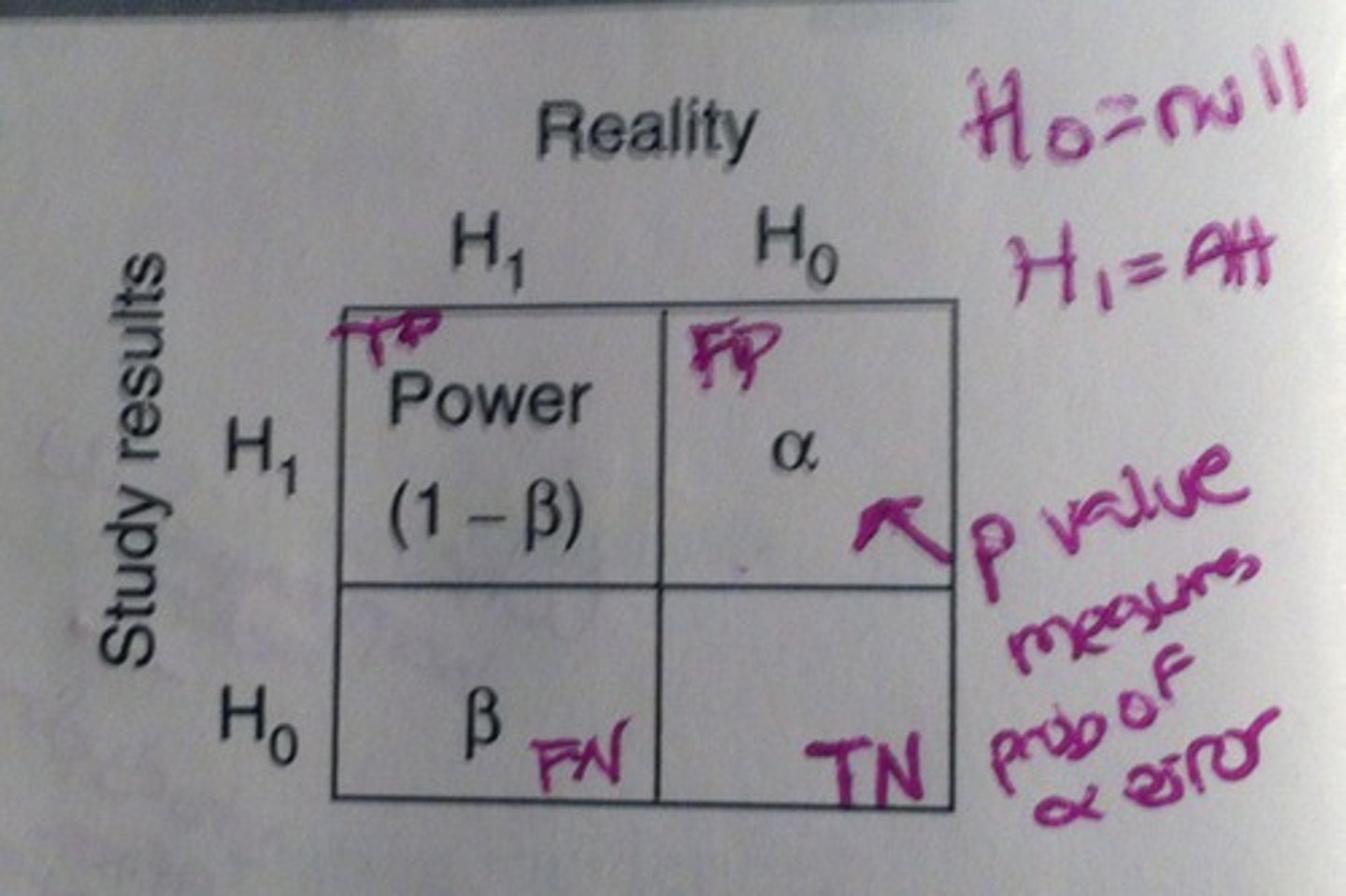
Power
= 1 - Beta
- The probability of correctly rejecting the null hypothesis
i.e., the ability to detect a difference between two groups when there truly is a difference
- Positively correlates with the sample size and the magnitude of the association of interest
- small sample size = inadequate power to be statistically significant
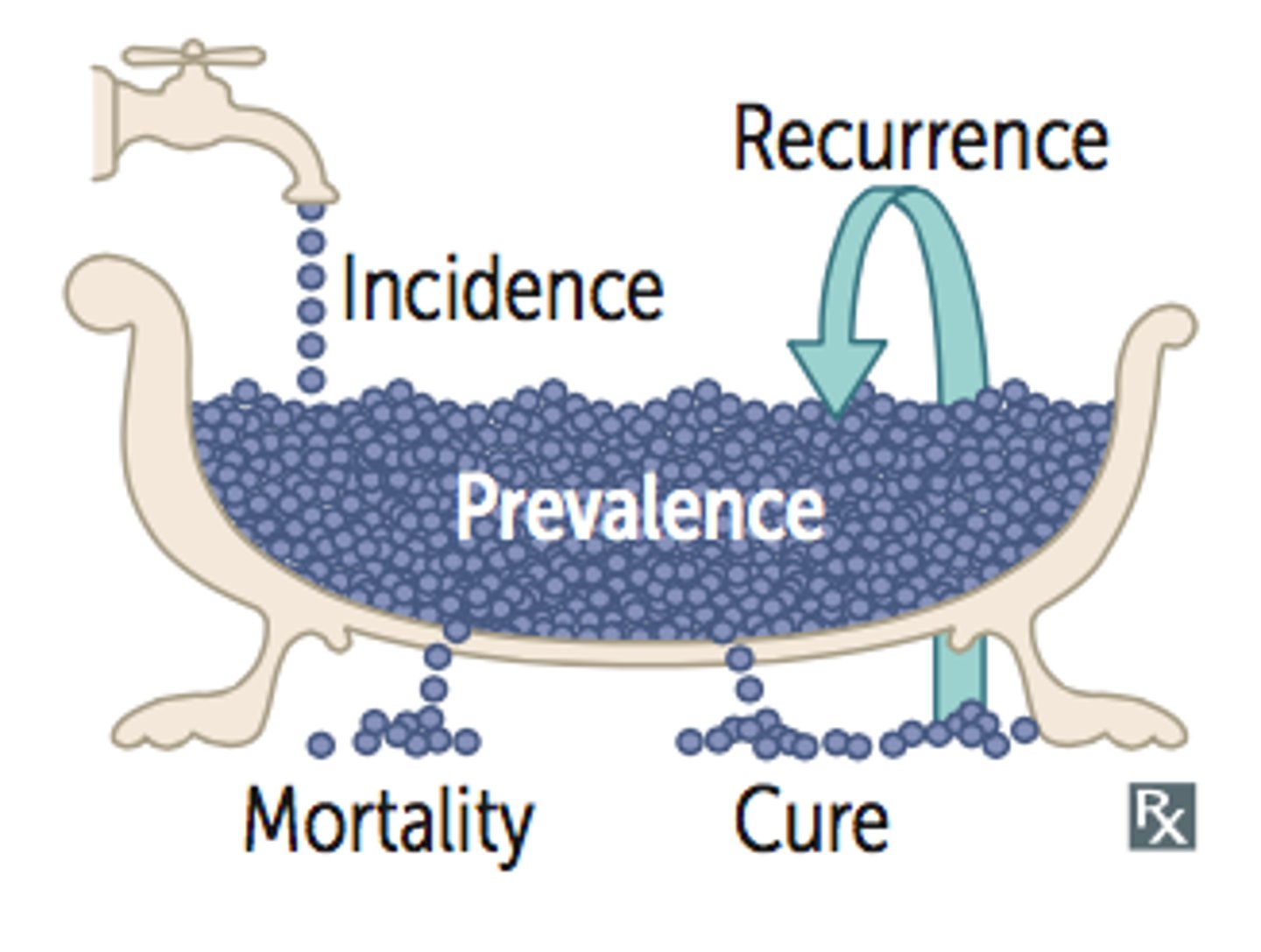
Prevalence
- Proportion of a particular population found to be affected by a medical condition
P-value
- Alpha = 0.05
- If results are statistically significant that means
- 5% likelihood or less that the results are due to chance
If < 0.05 = reject null hypothesis
Recall Bias
- Subjects in one group (experienced the illness) are more likely to remember the events than those in the other (did not experience the illness)
Relative Risk
- Incidence among exposed over the incidence among unexposed
- Ratio of the probability of the event occurring in an exposed group vs. the probability of the event occurring in an unexposed group
(A/A+B)/(C/C+D)
RR = 1 = ⦸ association
RR > 1 = exposure correlates to ↑ disease occurrence
RR < 1 = exposure correlates to ↓ disease occurrence
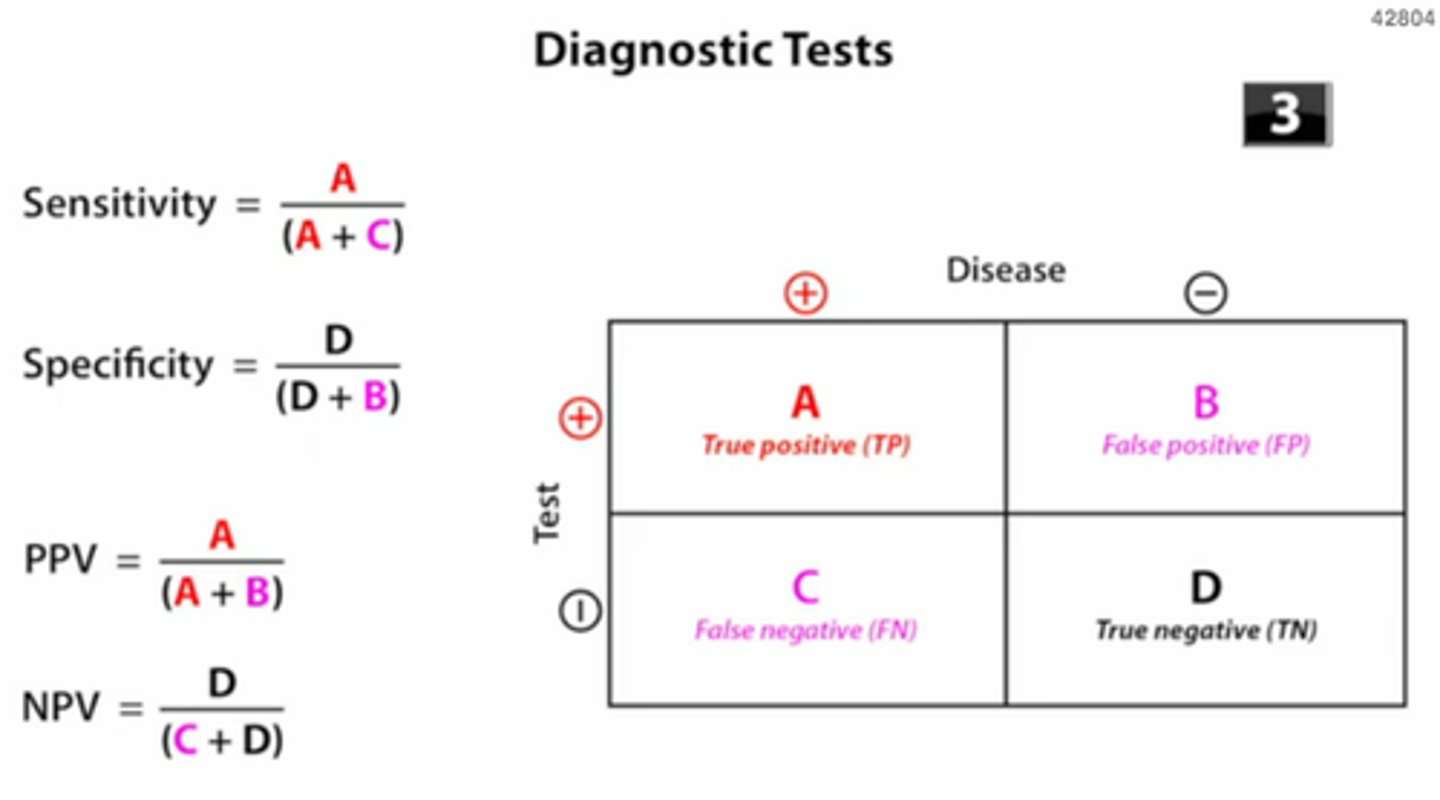
Sensitivity
- True positive rate of a test = ↓ false negative rate
- Reflects how well the test identifies patients w/ disease
- Proportion of patients with the disease who have a positive test
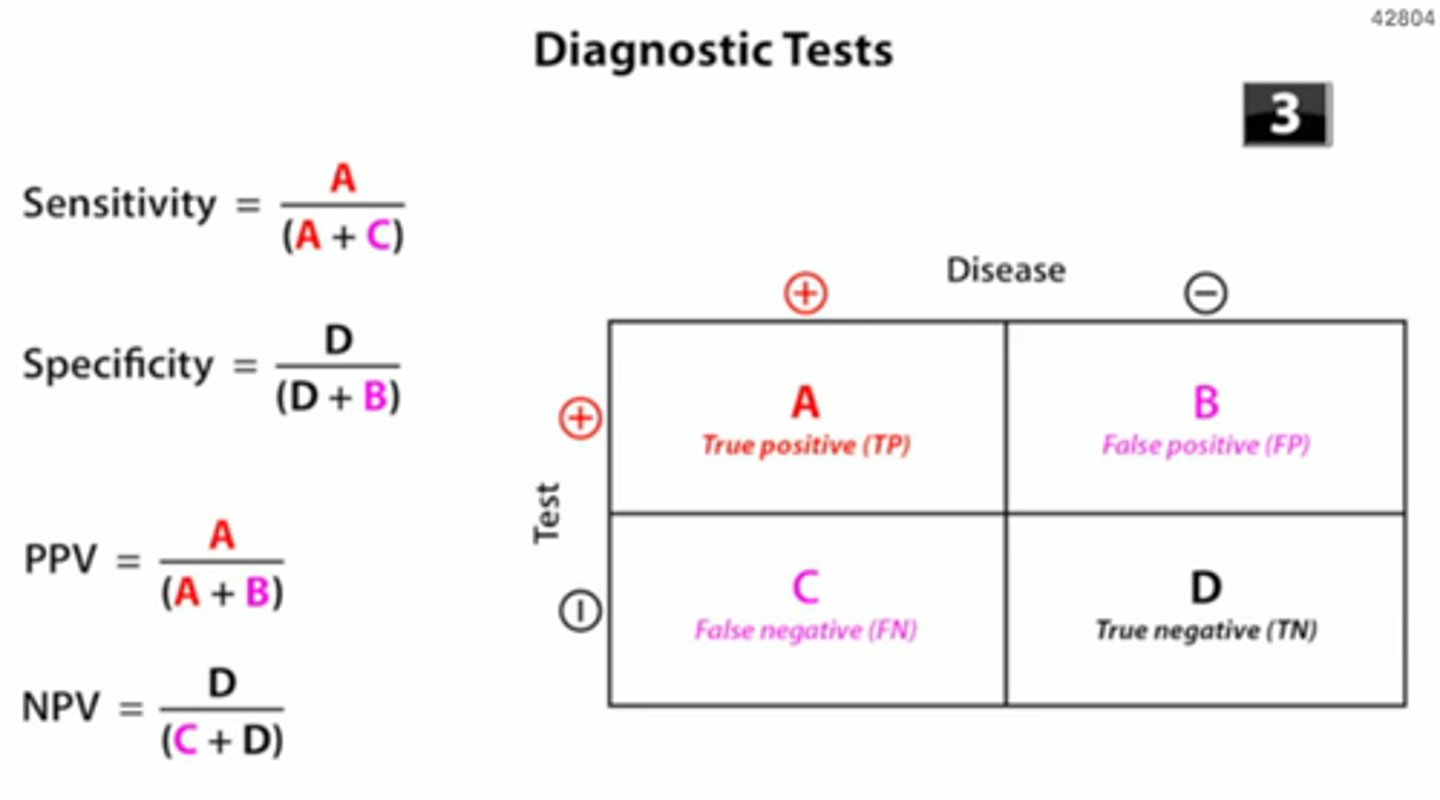
Specificity
- True negative rate of the test = ↓ false positive rate
- How well the rest correctly identifies patients w/out disease
- Proportion of patients without disease who have a negative test
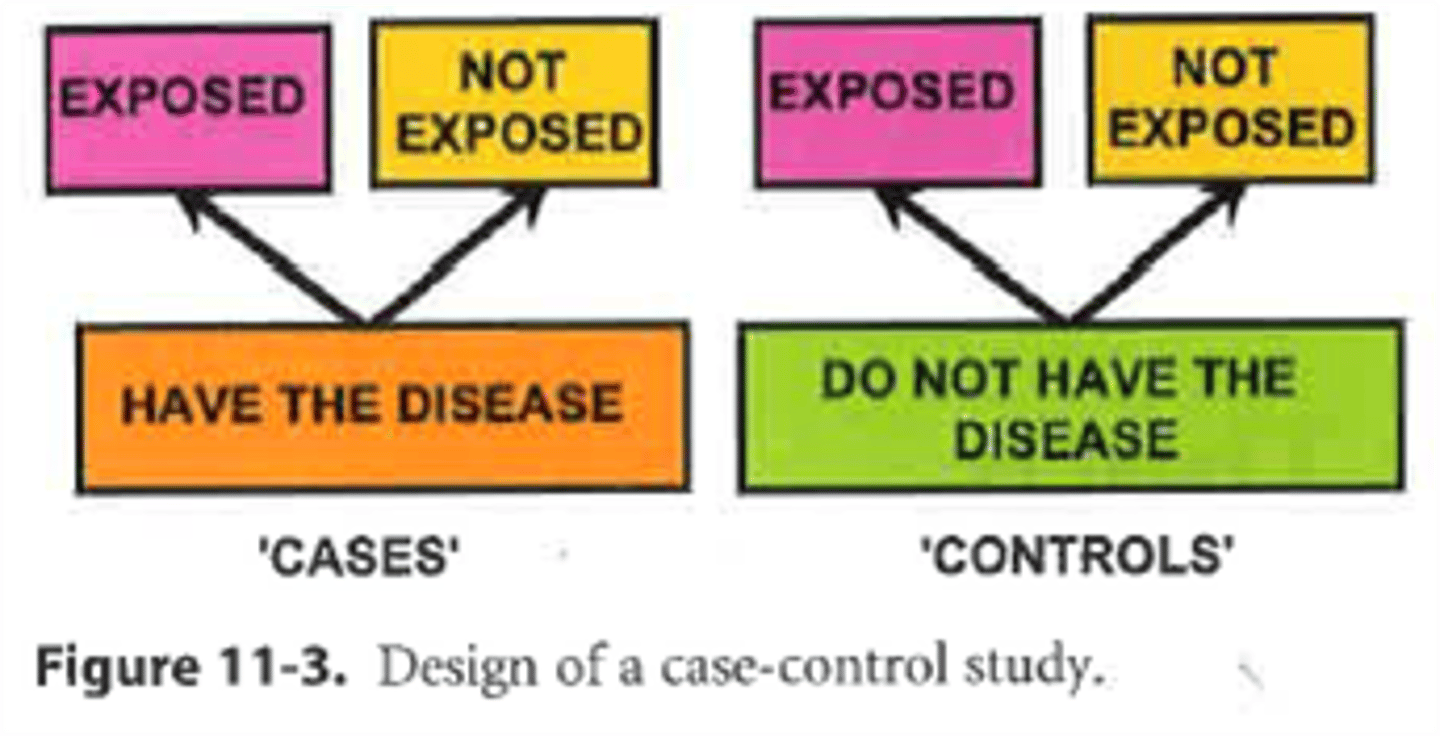
Case Control Study
- Observational
- Goal—identify factors that may contribute to a condition by comparing subject who have that condition
- two existing groups and outcome are identified and compared on the basis of some supposed causal attribute
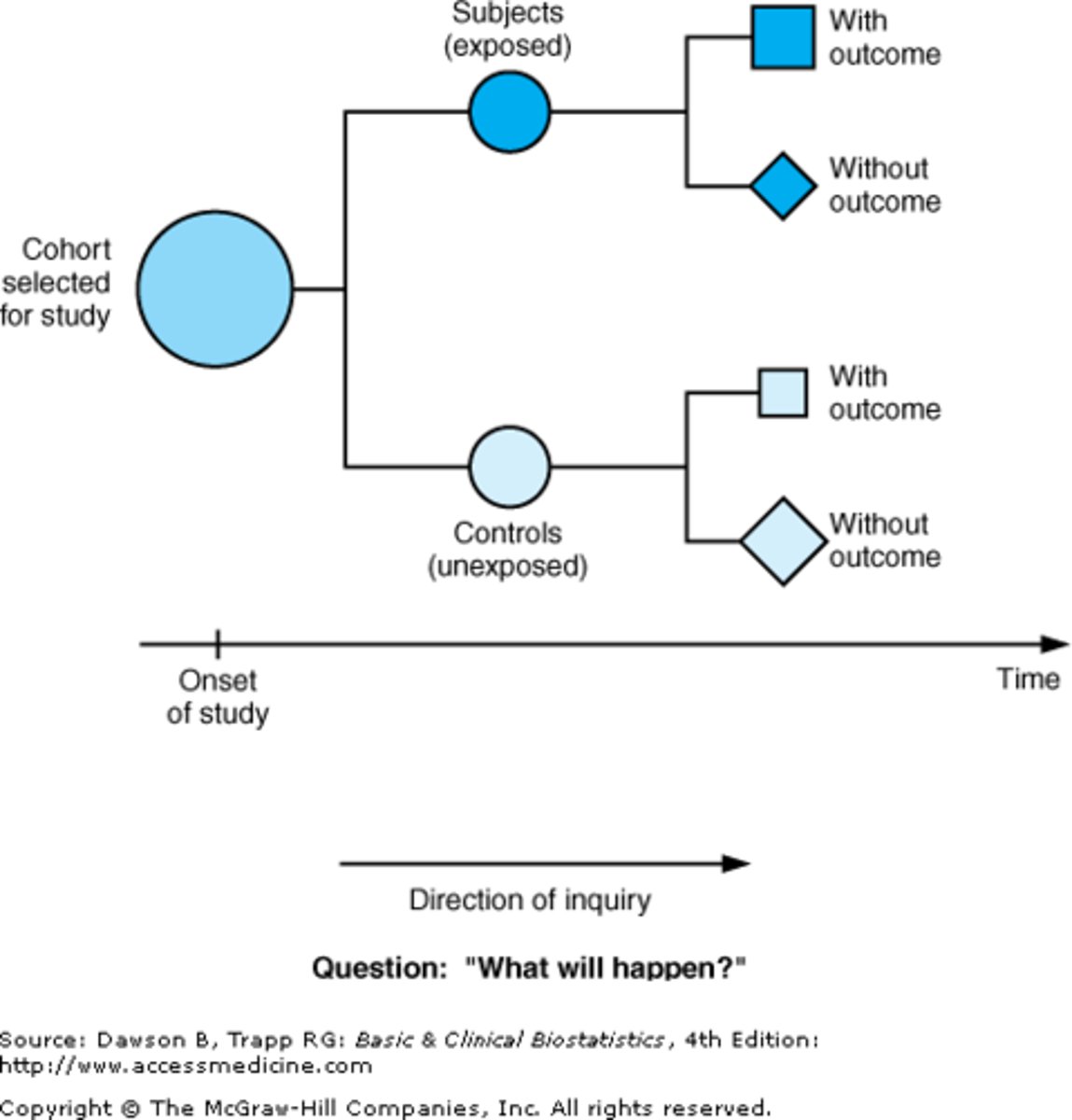
Cohort Study
- Longitudinal study that samples a cohort performing a cross section analysis at intervals through time
- a group of people who share a defining characteristic
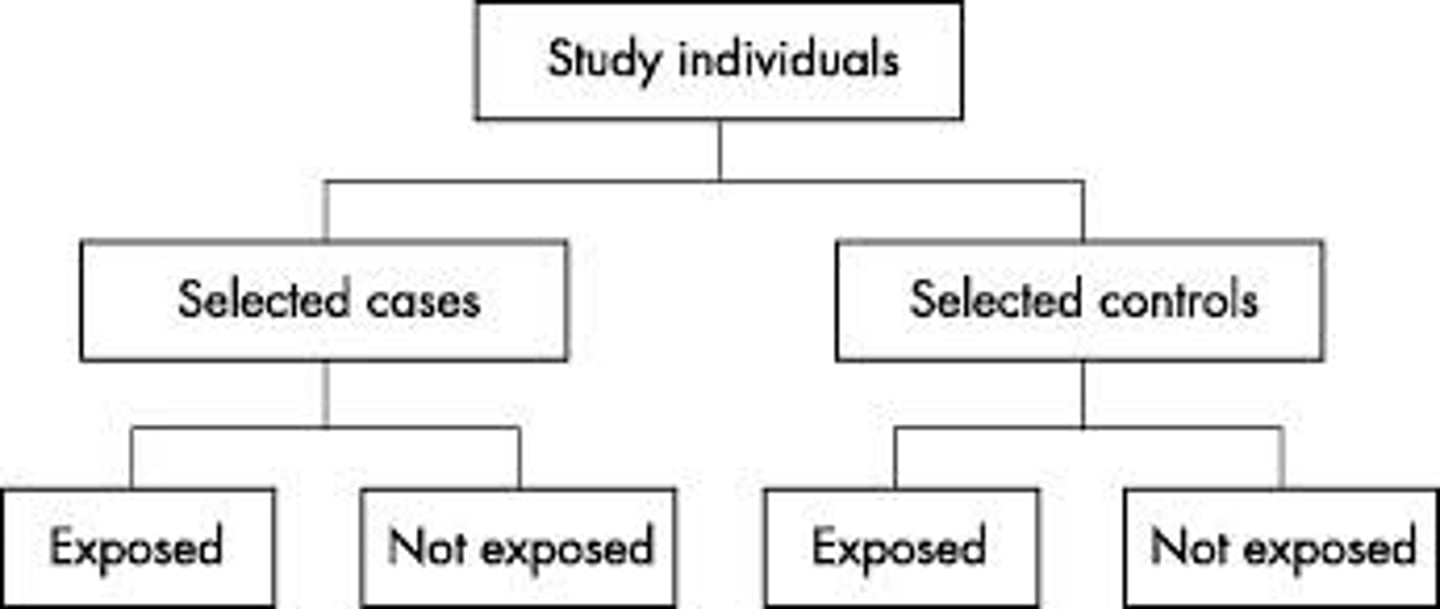
Cross-Sectional Study
- Observation
- Measures prevalence of a health outcome in a population at a single point in time
- analyzes data from a population or a representative subset at a specific point in time
Experimental Study
- Created a procedure is carried out to support refute or validate a hypothesis
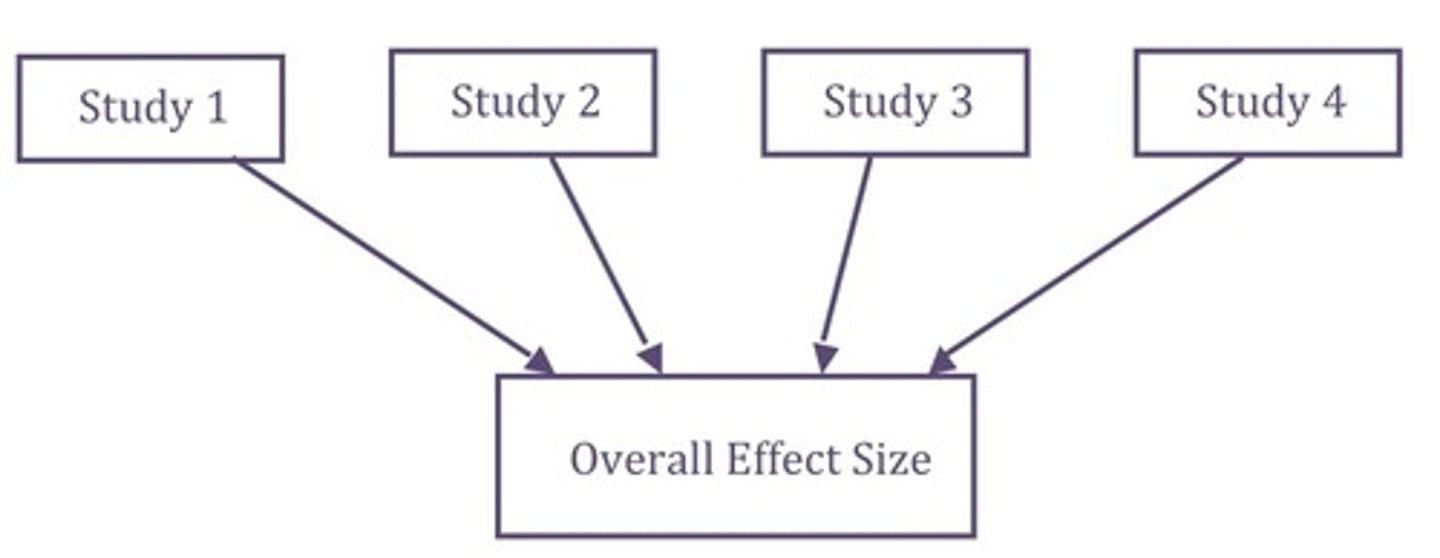
Meta-Analysis
- Explores knowledge about aggregating studies to asses several point estimates from separate studies
Prospective Cohort Study
- Follow similar groups of individuals who differ by a certain factor
T-test
- for continuous variable
e.g. BMI

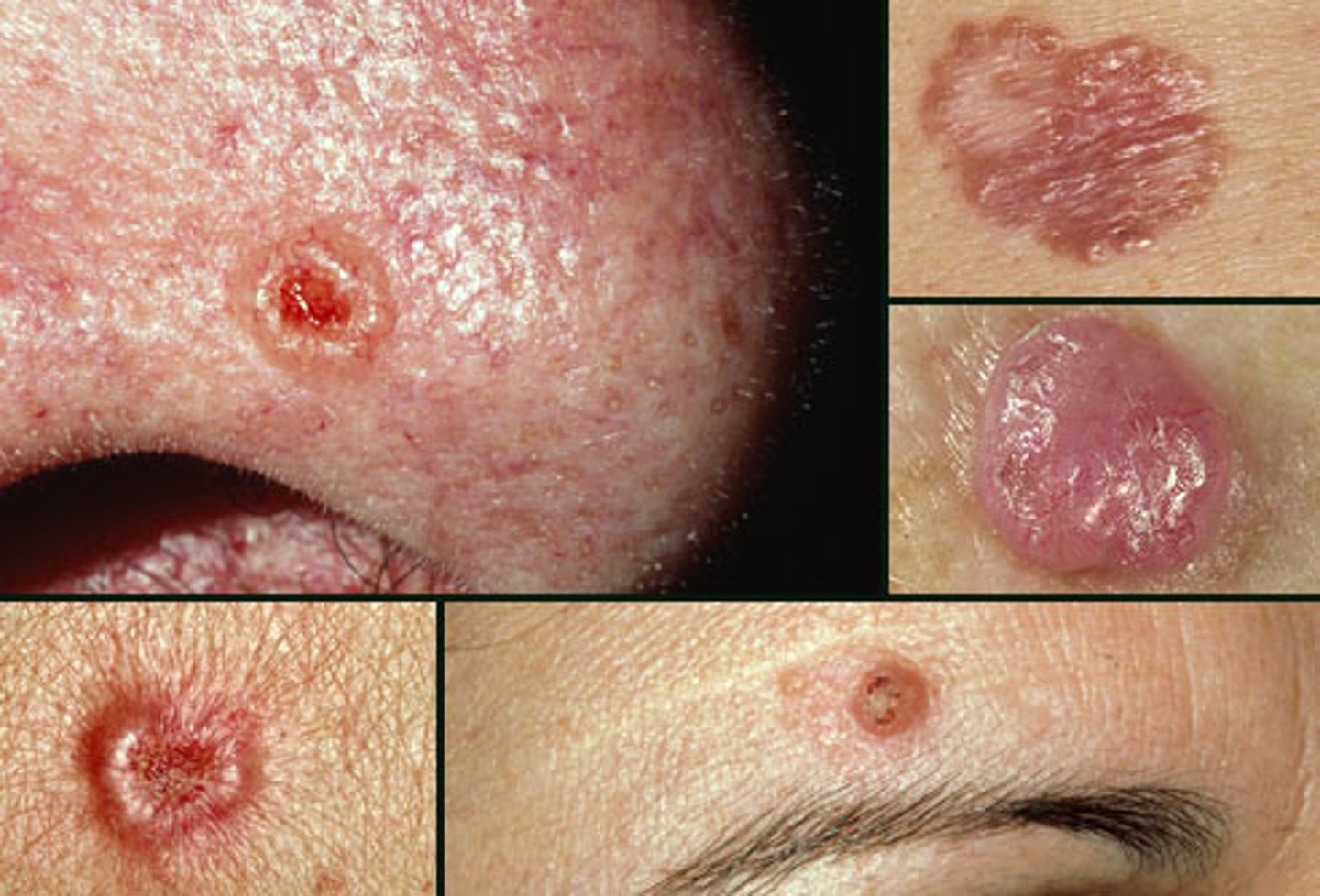
Basal Cell Carcinoma
PX
- Waxy/pearly, translucent
- Telangiectatic vessels
- Blue basaloid cells in dermis
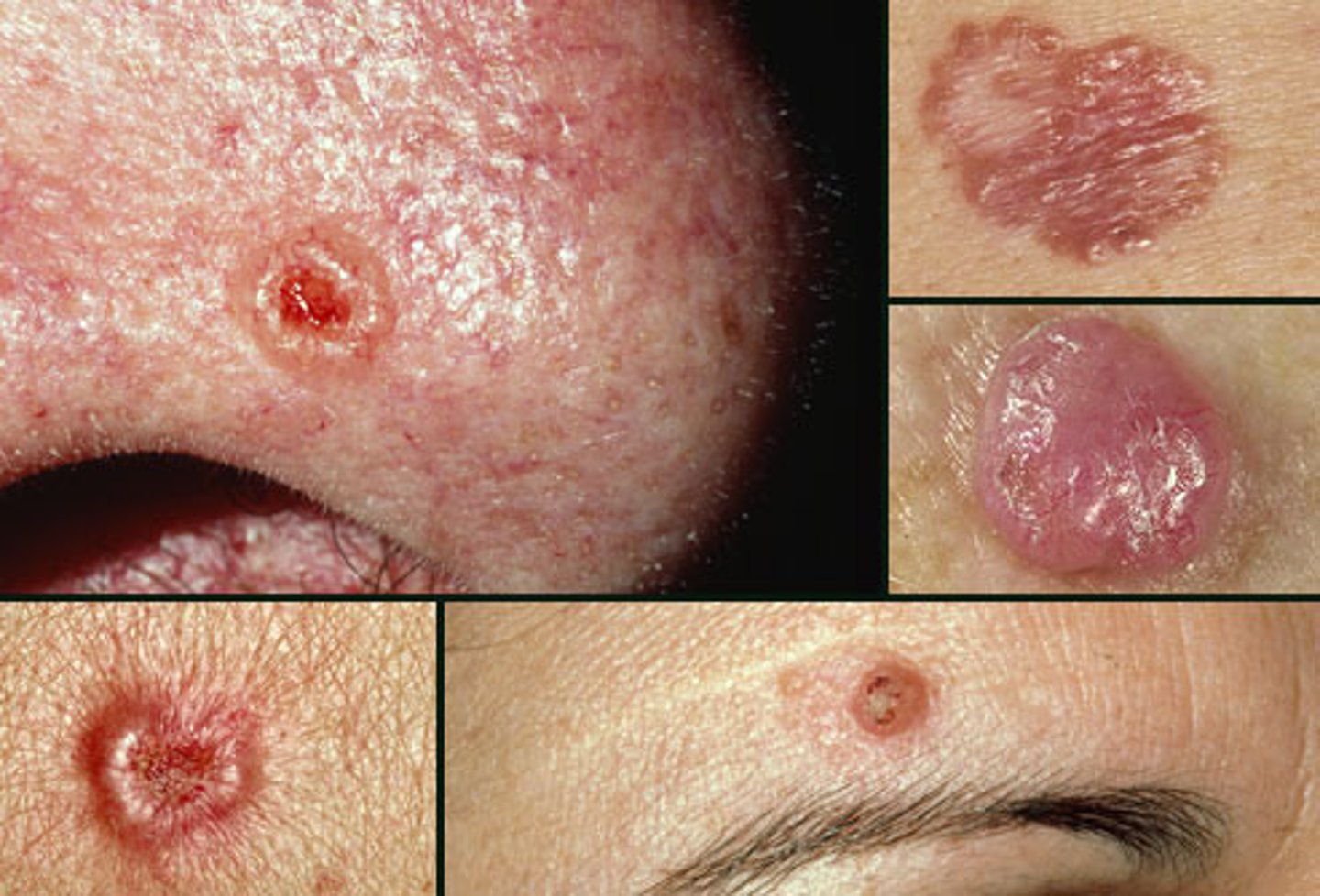
Basal Cell Carcinoma
MX
Mohs micrographic surgery
- Tumor removal followed by immediate frozen section histopathology examination of margins until clear
- Minimizes tissue loss
- 98% cure rate
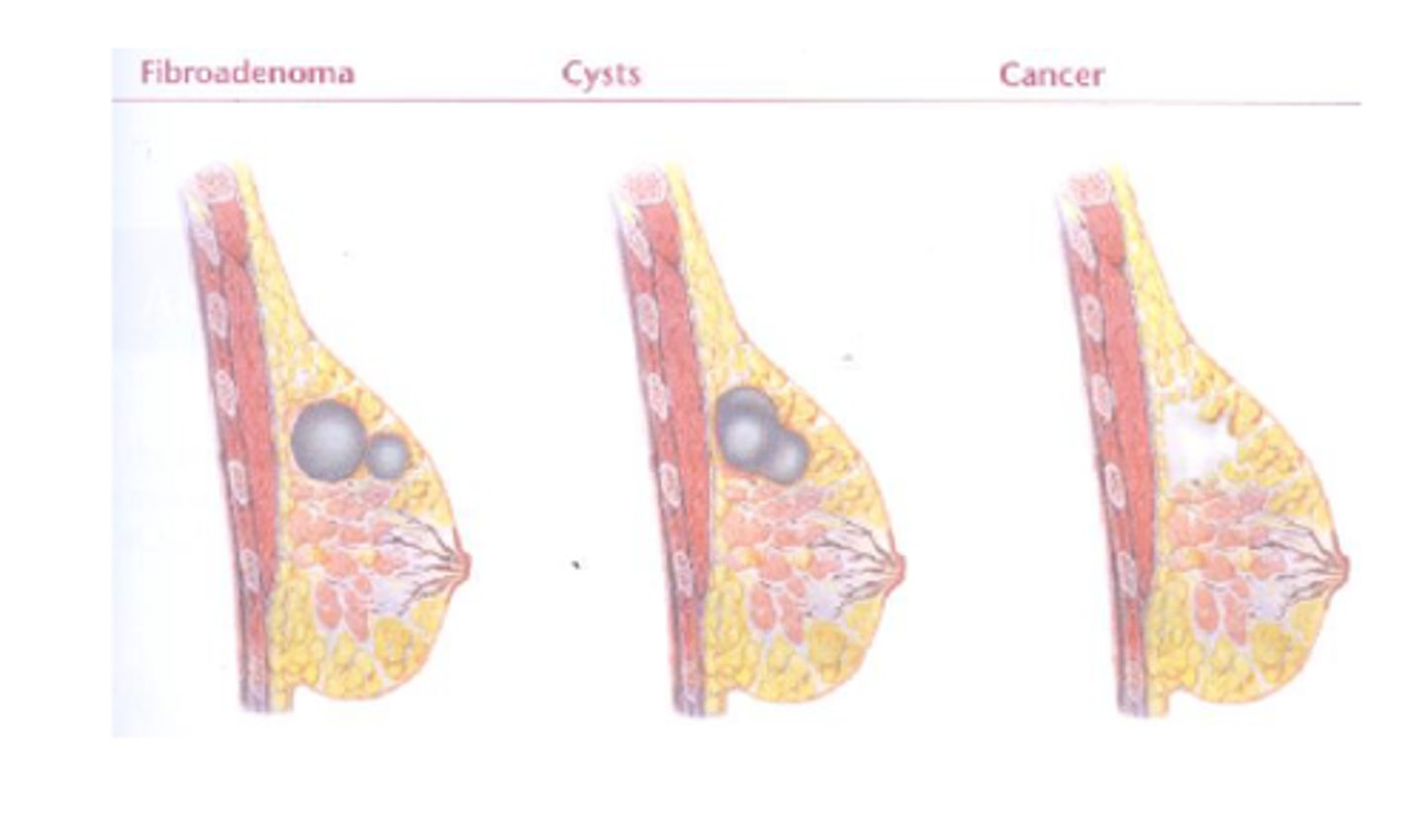
Fibroadenoma
PX
- benign, solid breast tumor
- < 30 y.o. woman
- well-circumscribed, mobile, rubbery
- painless
- may get bigger with pregnancy or menstrual cycle
Fibroadenoma
DX
U/S—Circumscribed, homogenous, oval-shaped, hyperechoic mass
Biopsy—Encapsulated, fibrous tissue
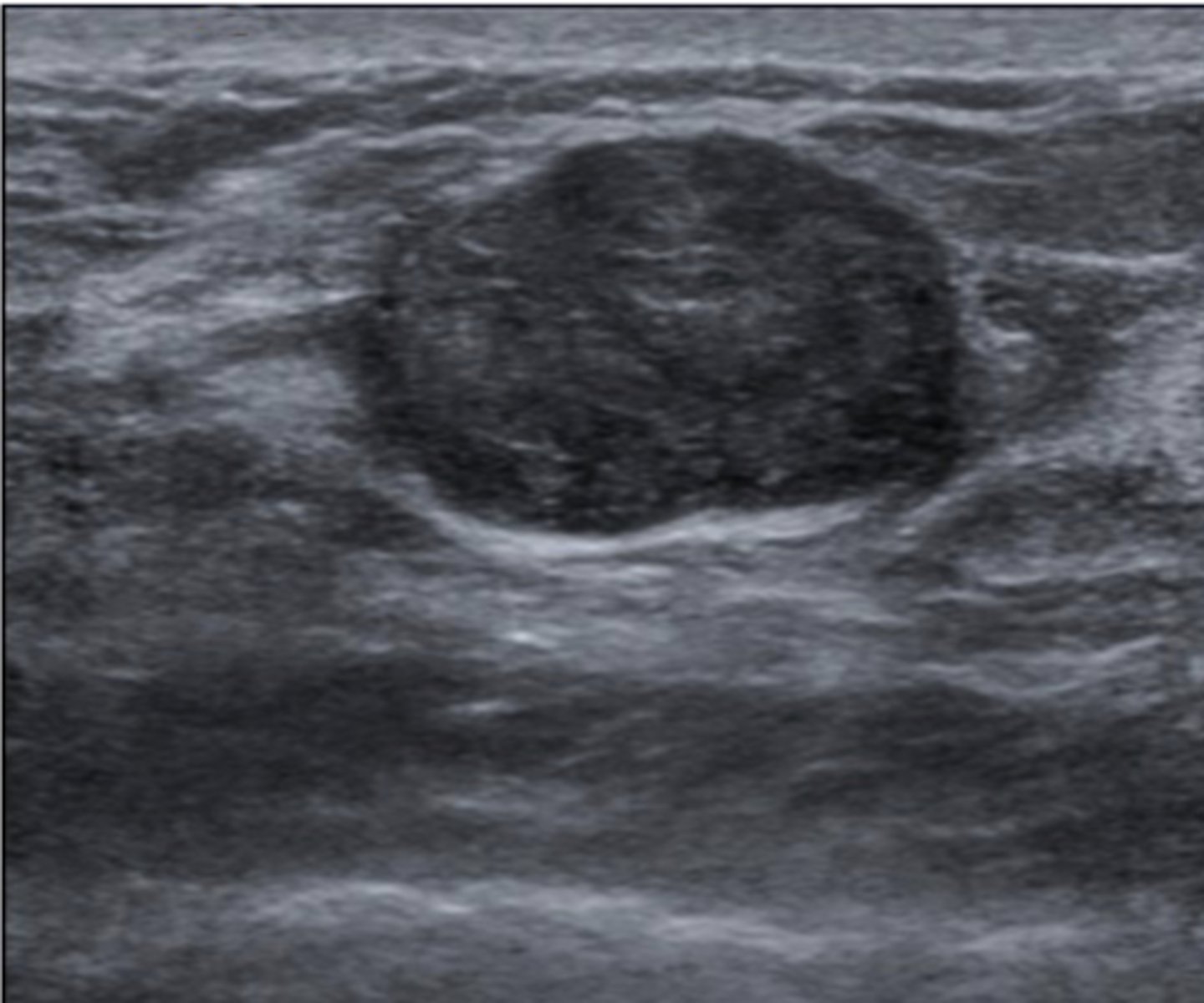
Fibroadenoma
MX
Observation
- 10% resolve spontaneously
Chemotherapy induced Alopecia
MX
Reassurance
- will resolve with end of chemotherapy
- hair may grow back a different color or texture
Colon Cancer
PX
- Hematochezia—blood in stool
- Iron deficiency anemia w/ fatigue— ↓ HgB, Hematocrit
- Tenesmus—persistent, uncomfortable feeling of needing to have a bowel movement
- Fecal Urgency
- ⦸ stool or gas beyond hepatic flexure
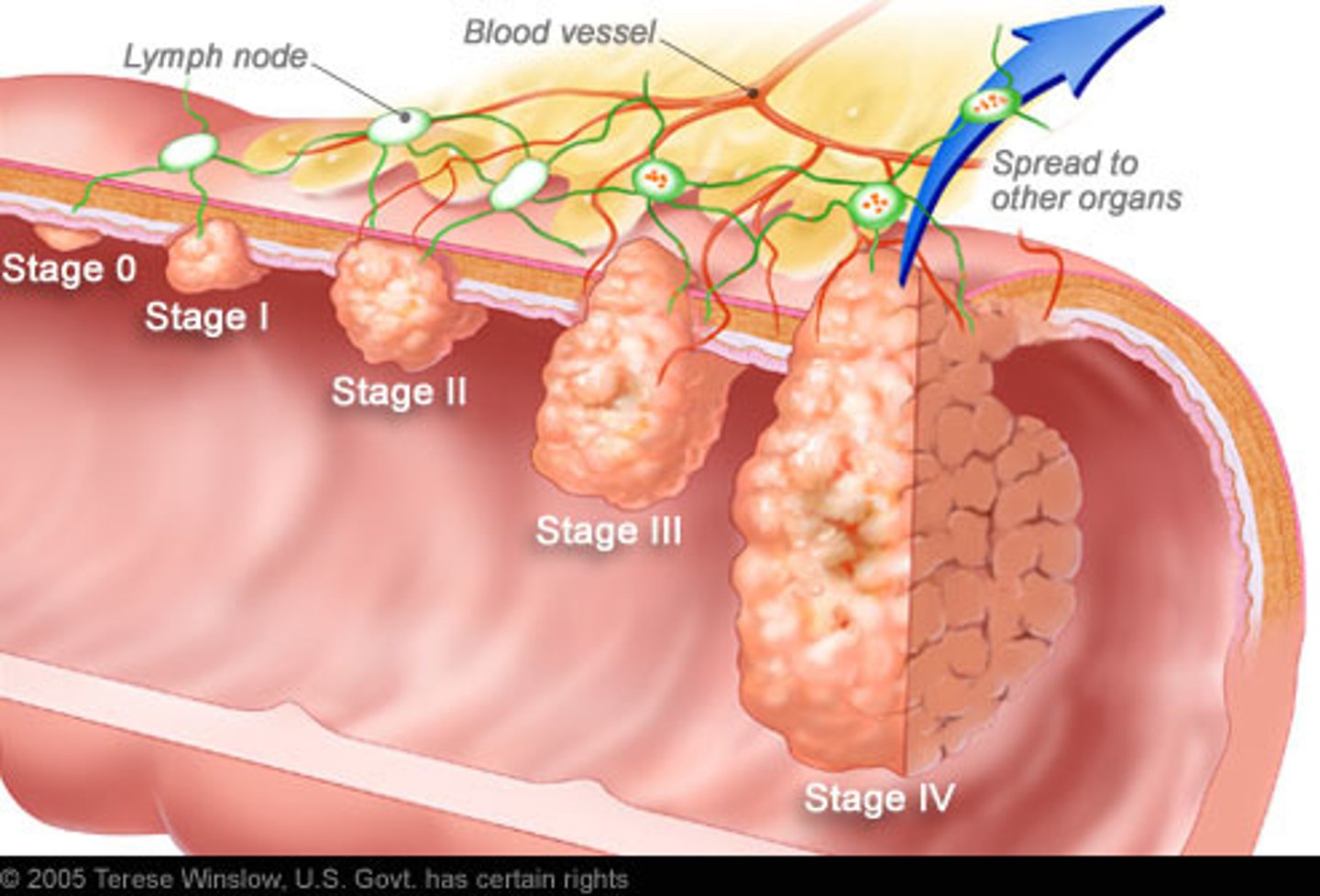
Colon Cancer
DX
Colonoscopy—Gold standard
- Apple-core appearance
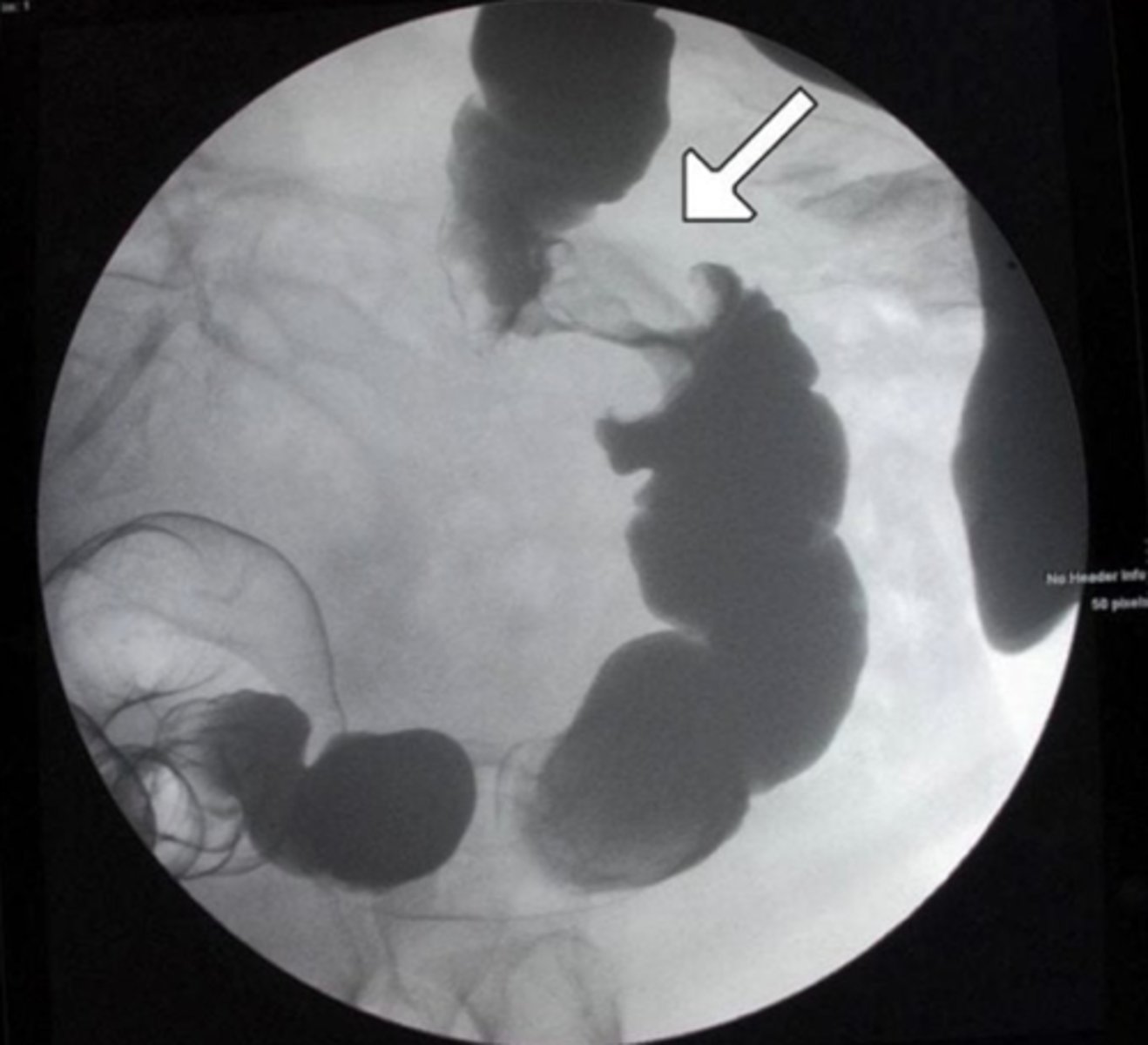
Endometrial Adenocarcinoma
PX
- Post menopausal bleeding
Biopsy
- ↑ nuclear-to-cytoplasmic ratio
- irregularity in size & shape of the nuclei
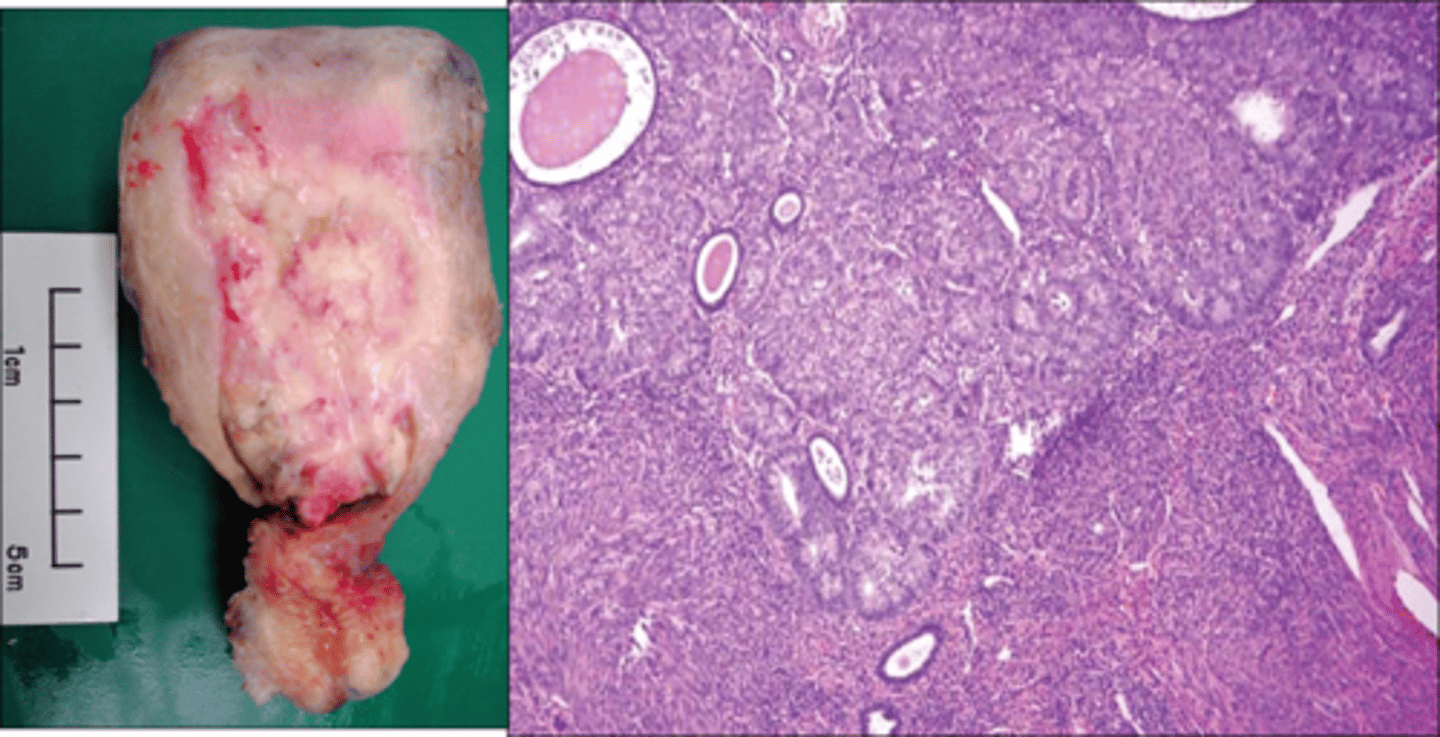
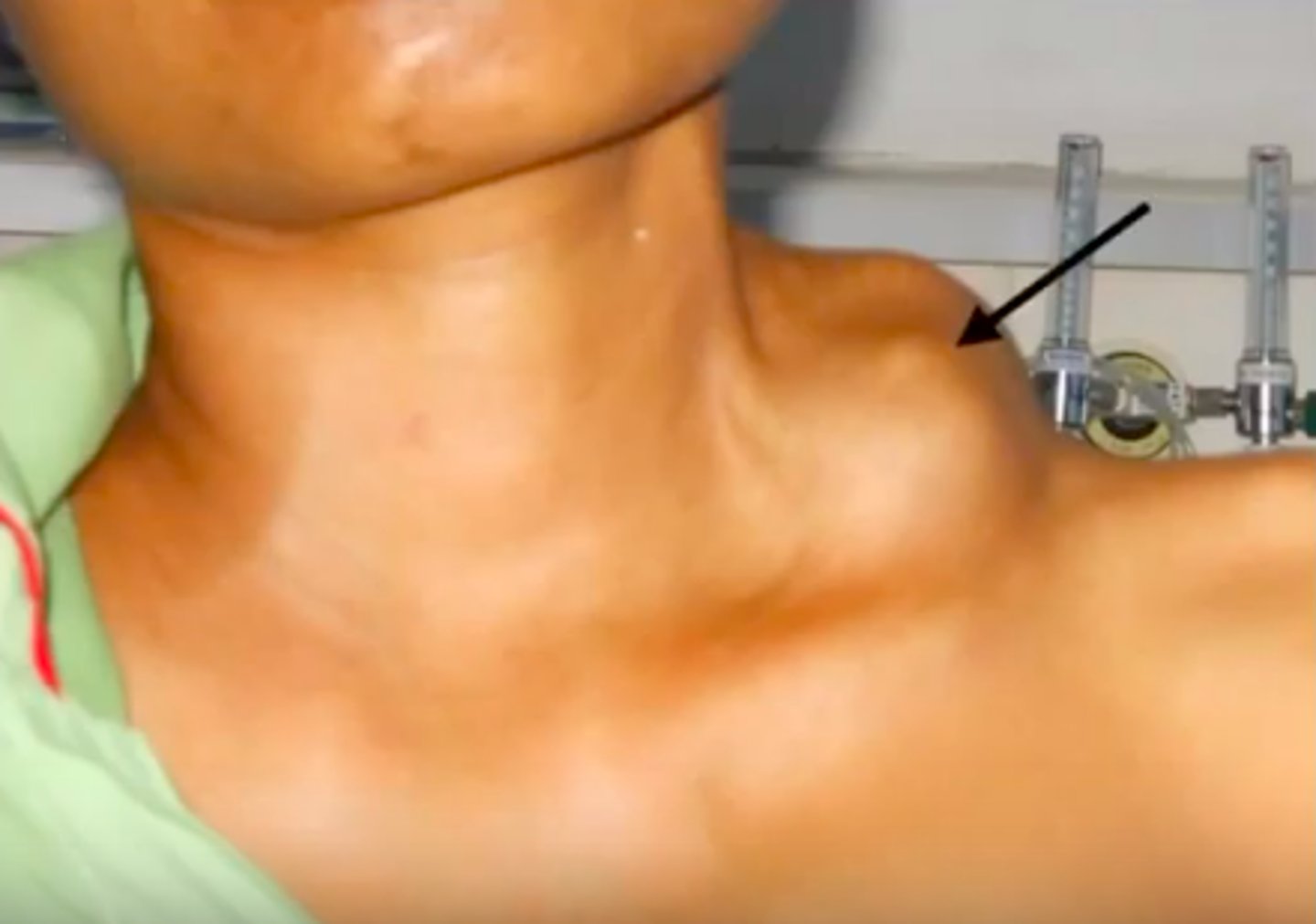
Gastric Cancer
PX
- Virchow's node—supraclavicular lymphadenopathy
- Night sweats
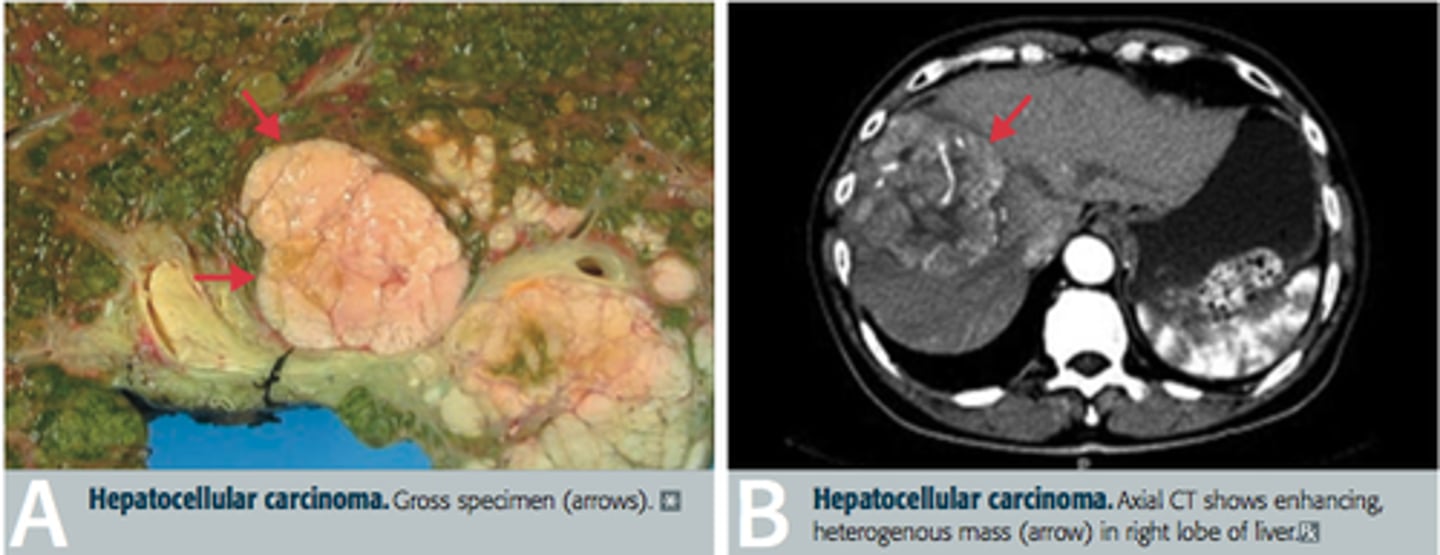
Hepatocellular Carcinoma
PX
- Malaise
- Weight loss
- Anorexia
- Abdominal discomfort
Laryngeal Cancer
Risk Factors
- Adv. Age
- Male gender
- Occupation exposure—Nickel
- Alcohol abuse
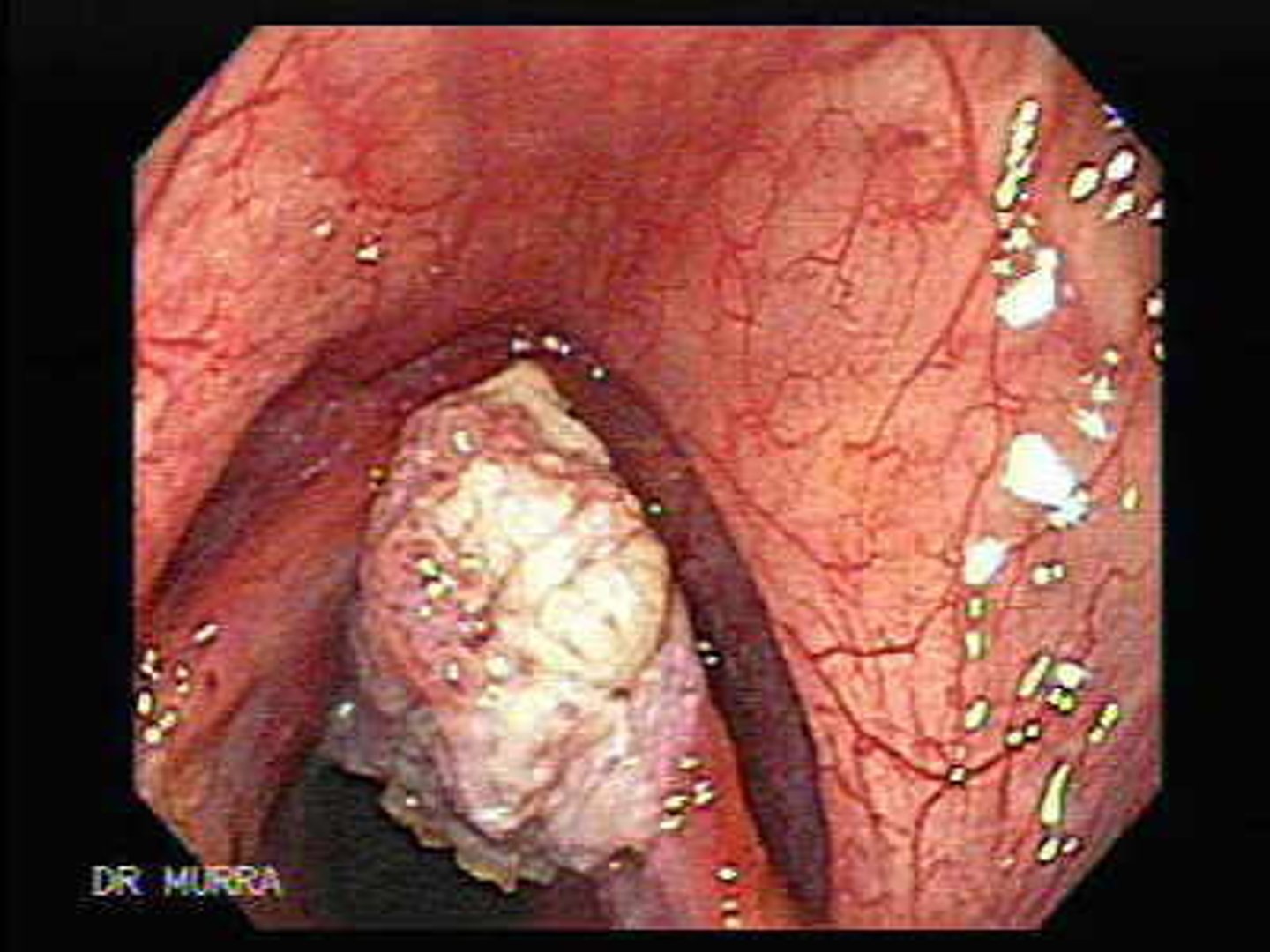
Laryngeal Cancer
PX
- Hoarseness
- Odynophagia, Dysphagia
- ↓ tongue mobility
- Otalgia—ear pain
- Airway obstruction
- Cranial neuropathies
- Trismus
- Fistulas
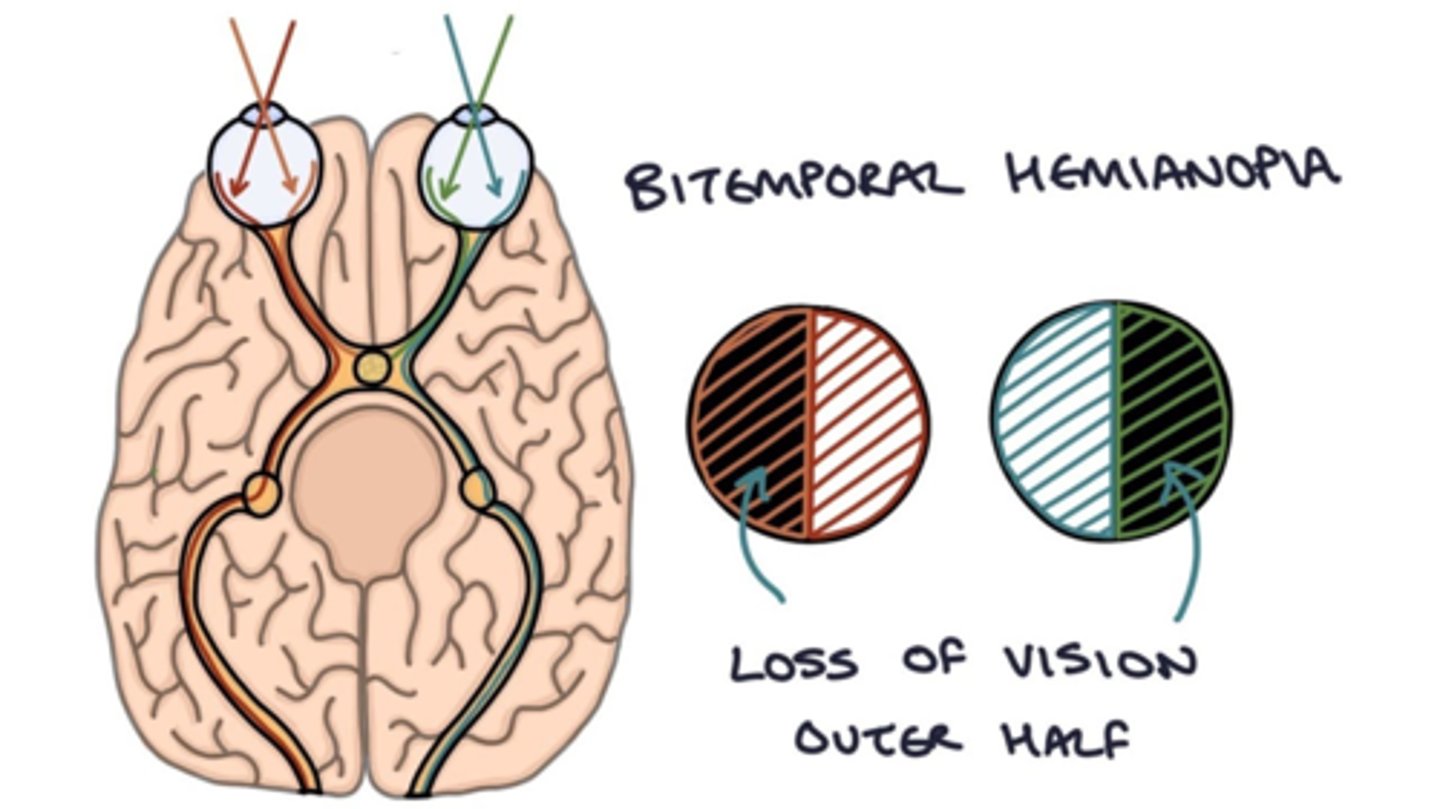
Pituitary Tumor
PX
- Bitemporal hemianopia
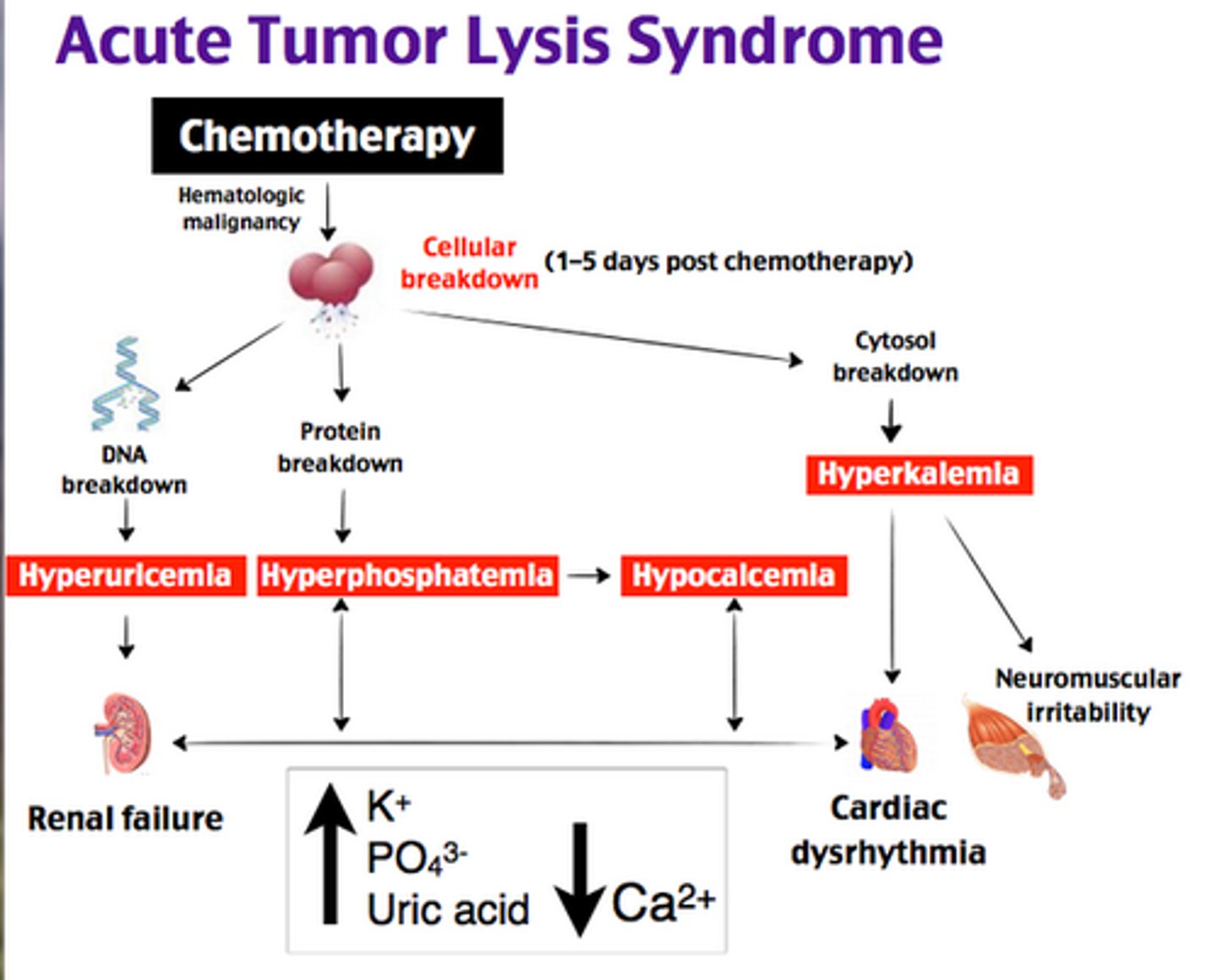
Tumor Lysis Syndrome
← Acute tubular obstruction
- ↓ urine output
- ↑↑ uric acid
- Lympho or myeloproliferative disorders
- oliguric Renal failure
- acute Urate nephropathy
Symptomatic Bradycardia
MX
IV Atropine
Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema
- Pulmonary edema related congestive heart failure
- Decompensation occurs over days to weeks
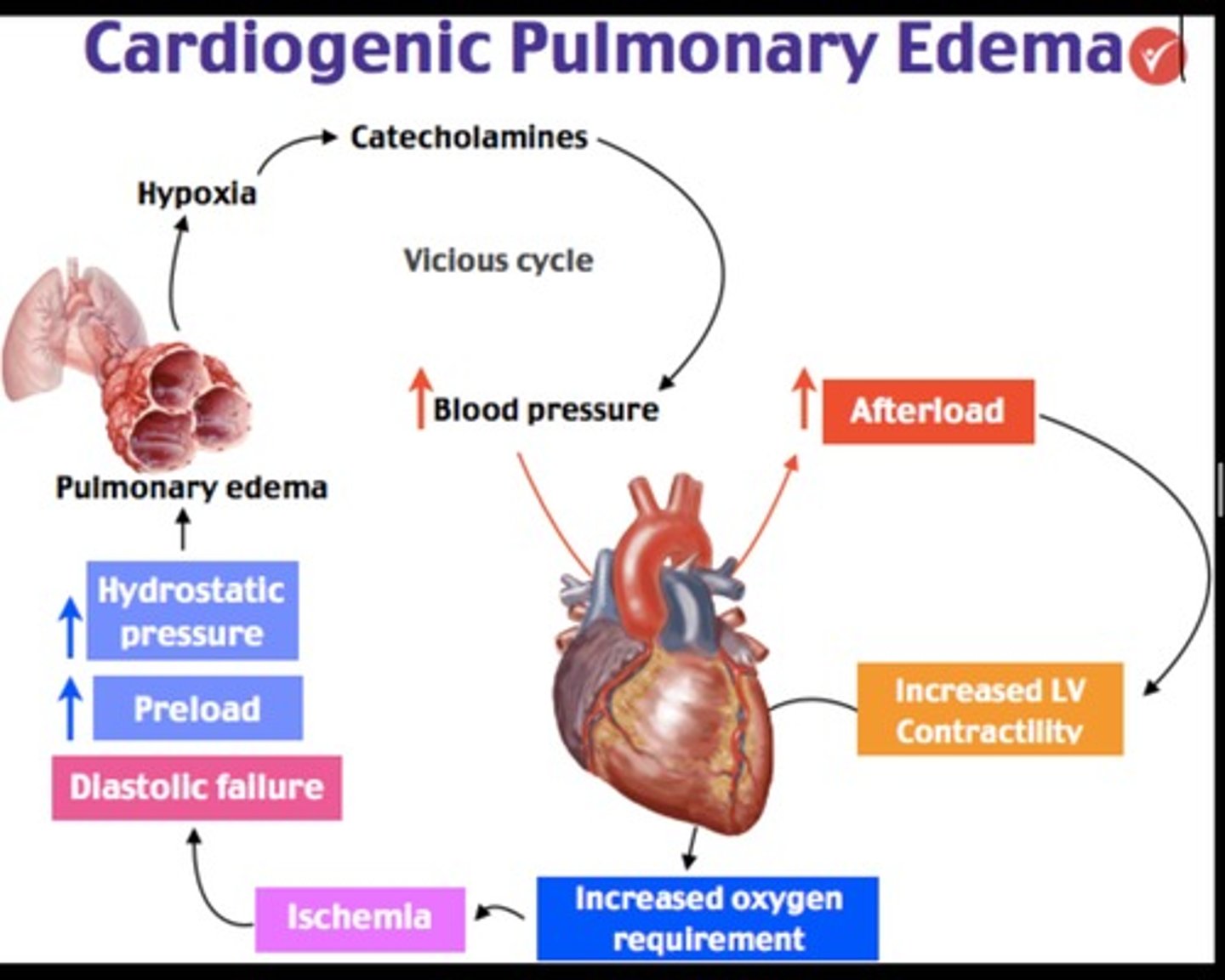
Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema
PX
Left-sided Heart Failure
- ↑ BP
- Rales
- JVD
- S3 gallop
- Back up of blood into the lungs
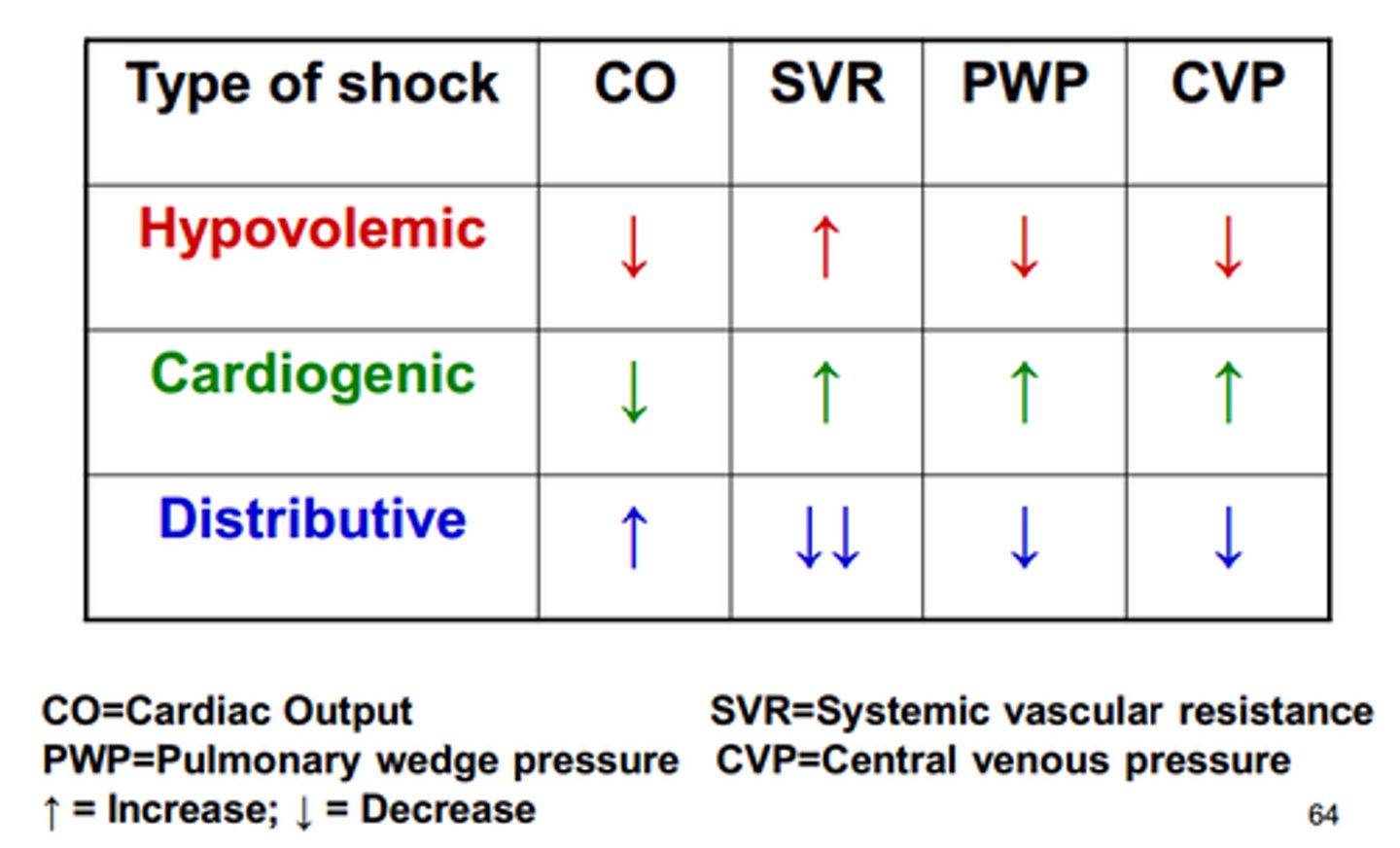
Cardiogenic Shock
- Heart ⦸ sustain adequate perfusion to the body's organs
- BP < 90 mmHg, often present
- Semi-conscious
- Cool, clammy
Cardiovascular Disease
MX
some Risk Factors + ⦸ diabetes or high cholesterol
Lifestyle changes
Claudication
Risk Factors
Smoking
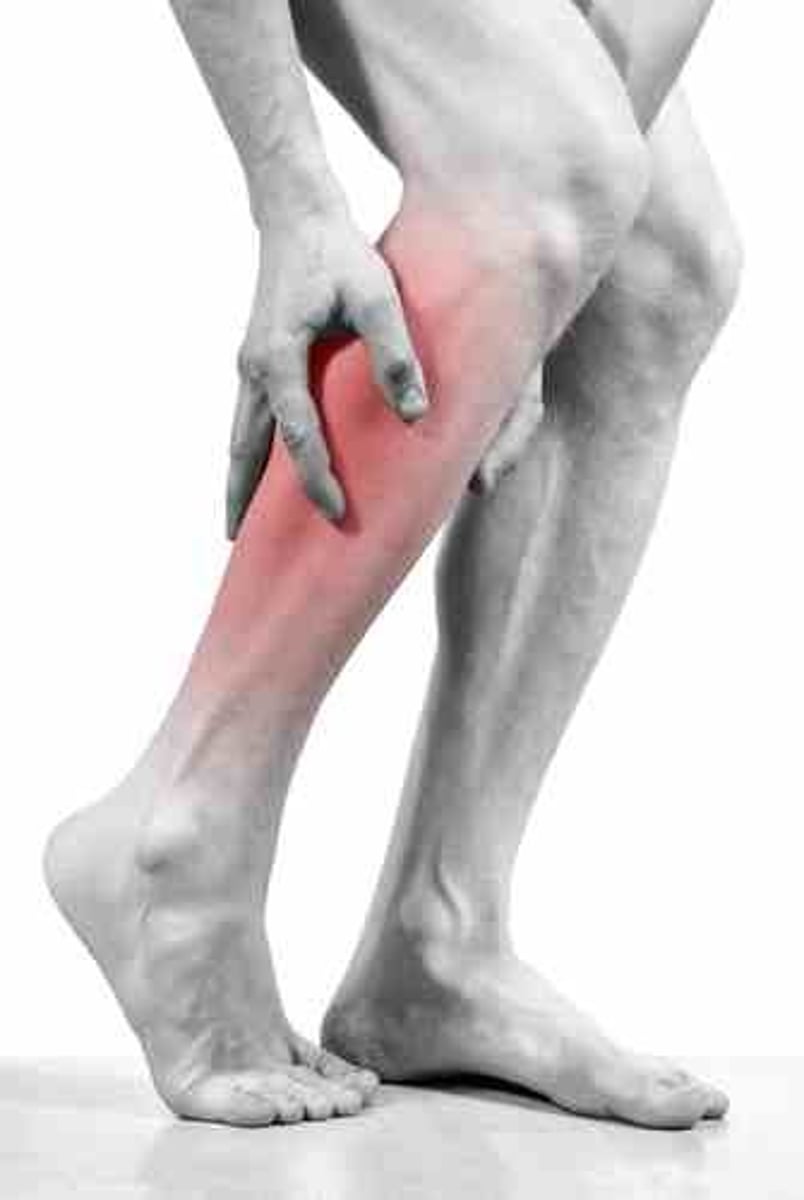
Claudication
PX
← peripheral artery disease—↓ peripheral pulses ↓ hair growth on extremity
- Leg pain ← ↓ blood supply
- Worse with use
- Better with rest
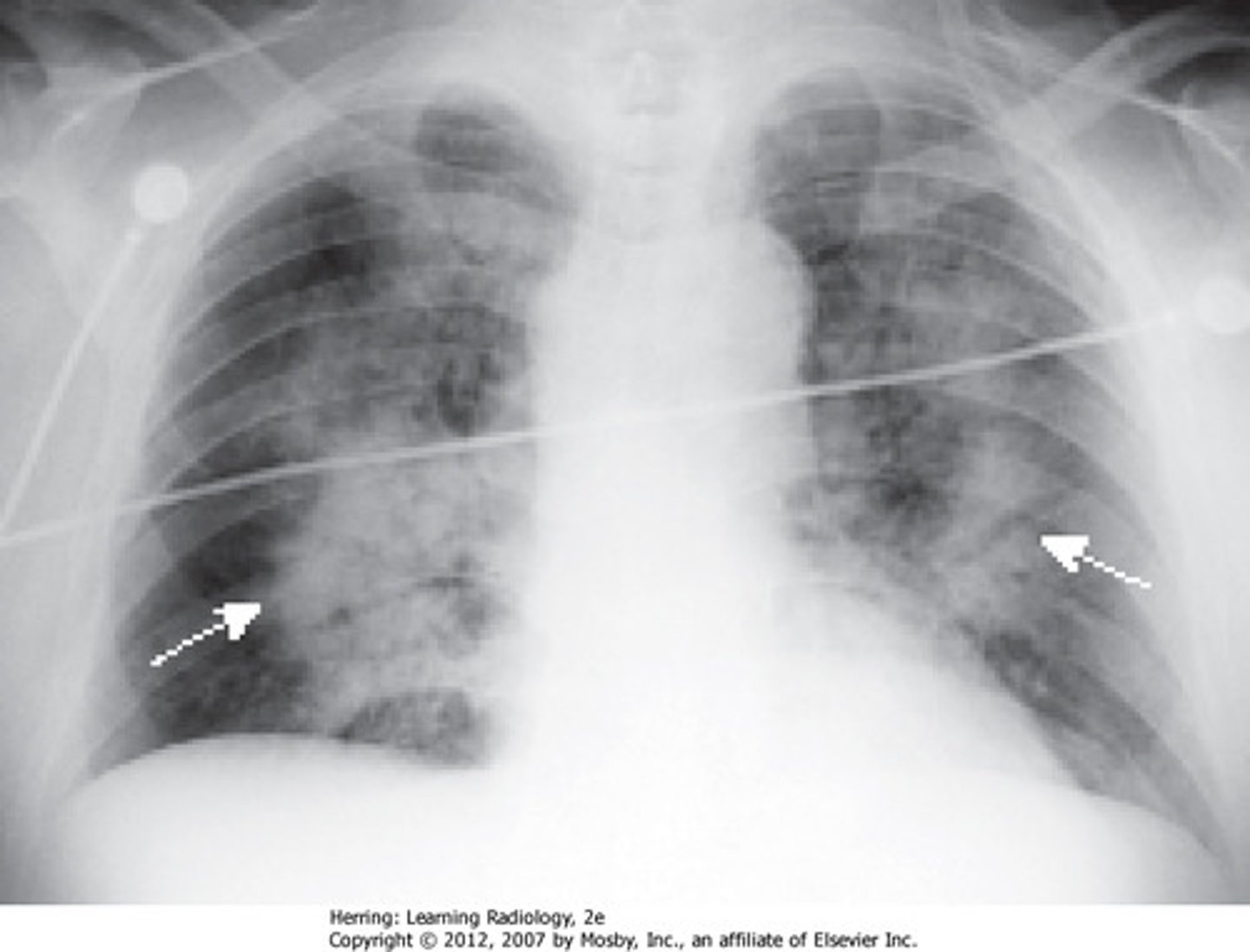
Congestive Heart Failure (CHF)
CXR
- bilateral Pleural effusions
- enlarged heart
- pulmonary vascular markings
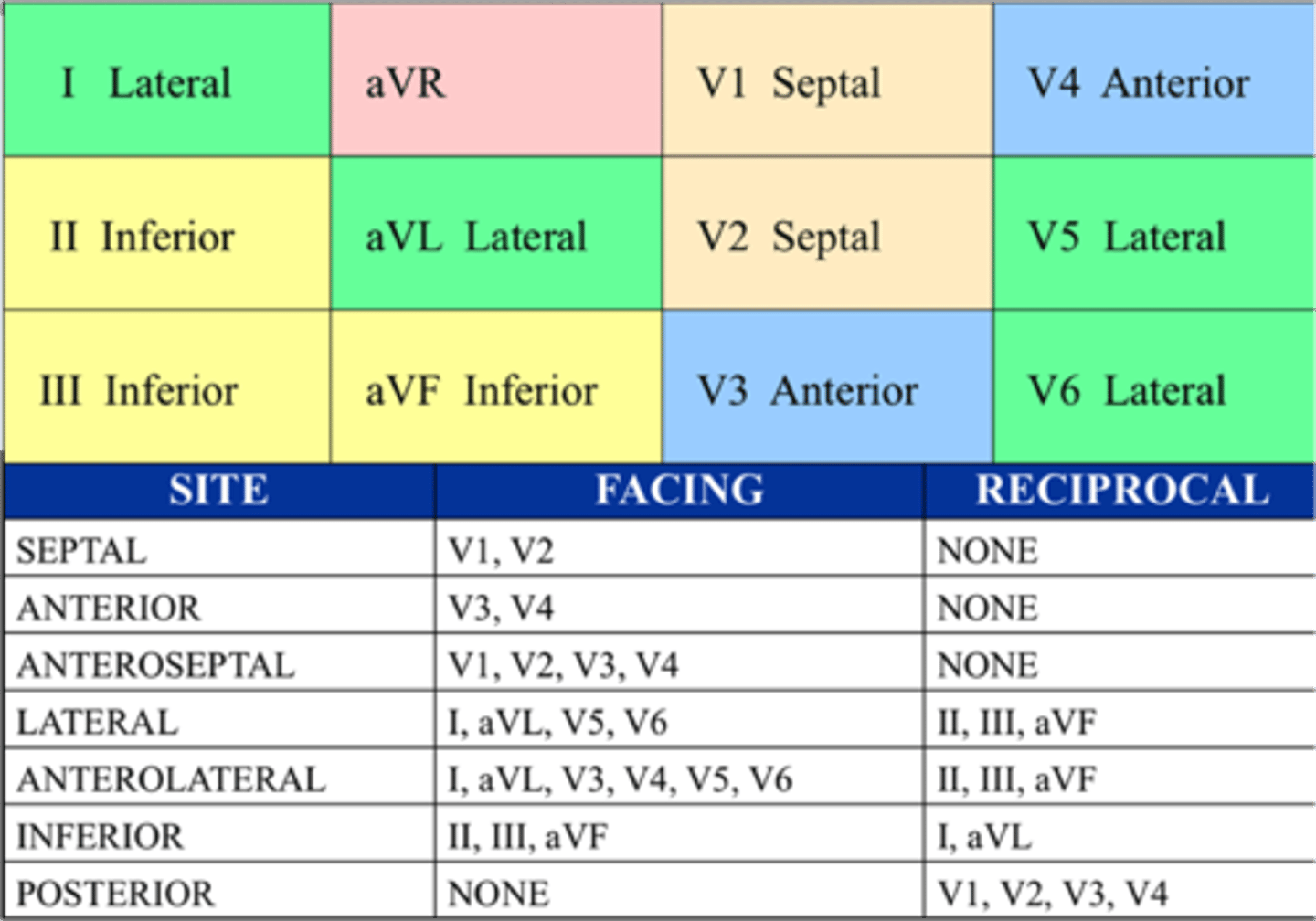
EKG
Anteroseptal Leads
V1—V4
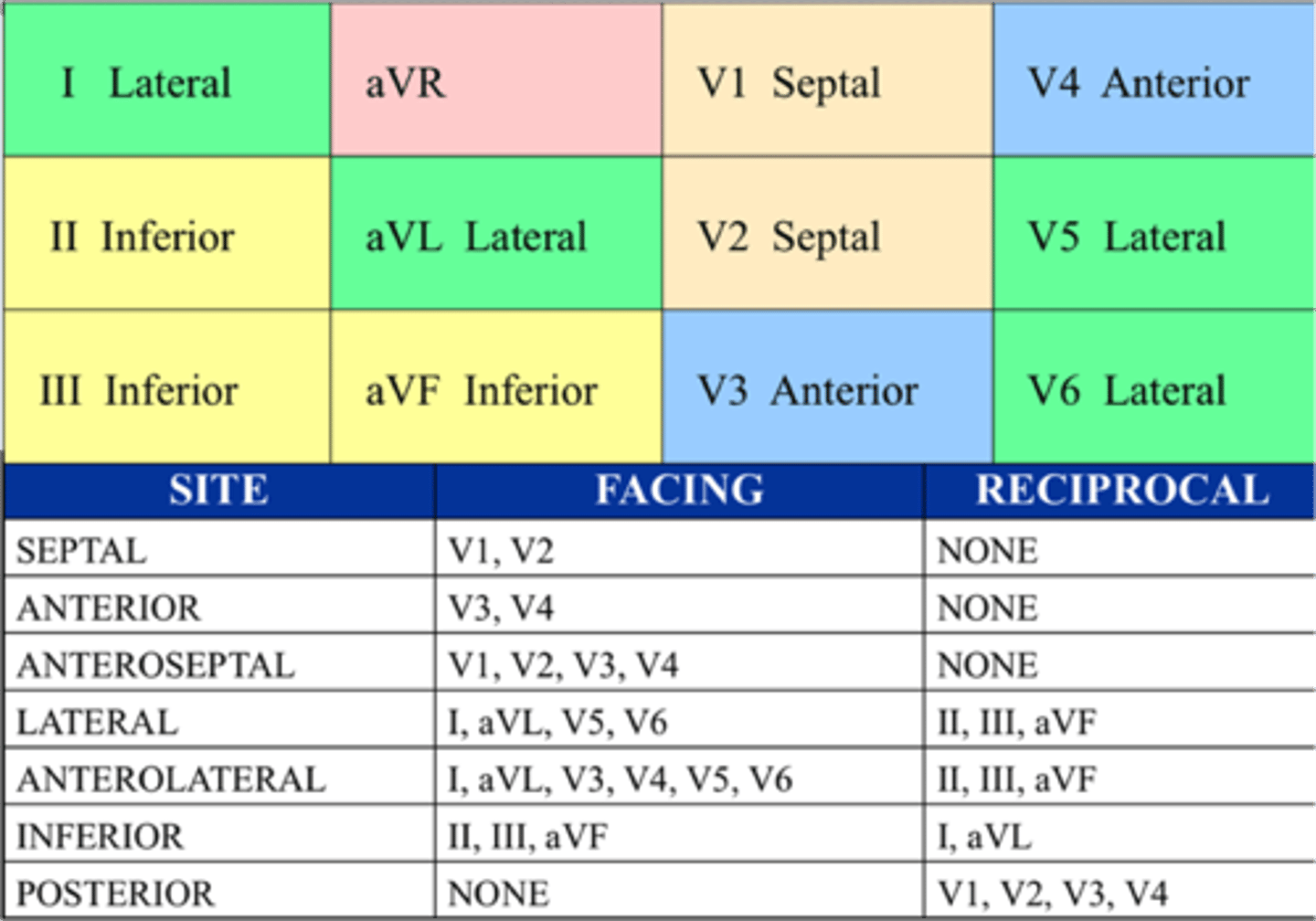
EKG
Inferior Leads
II, III, aVF
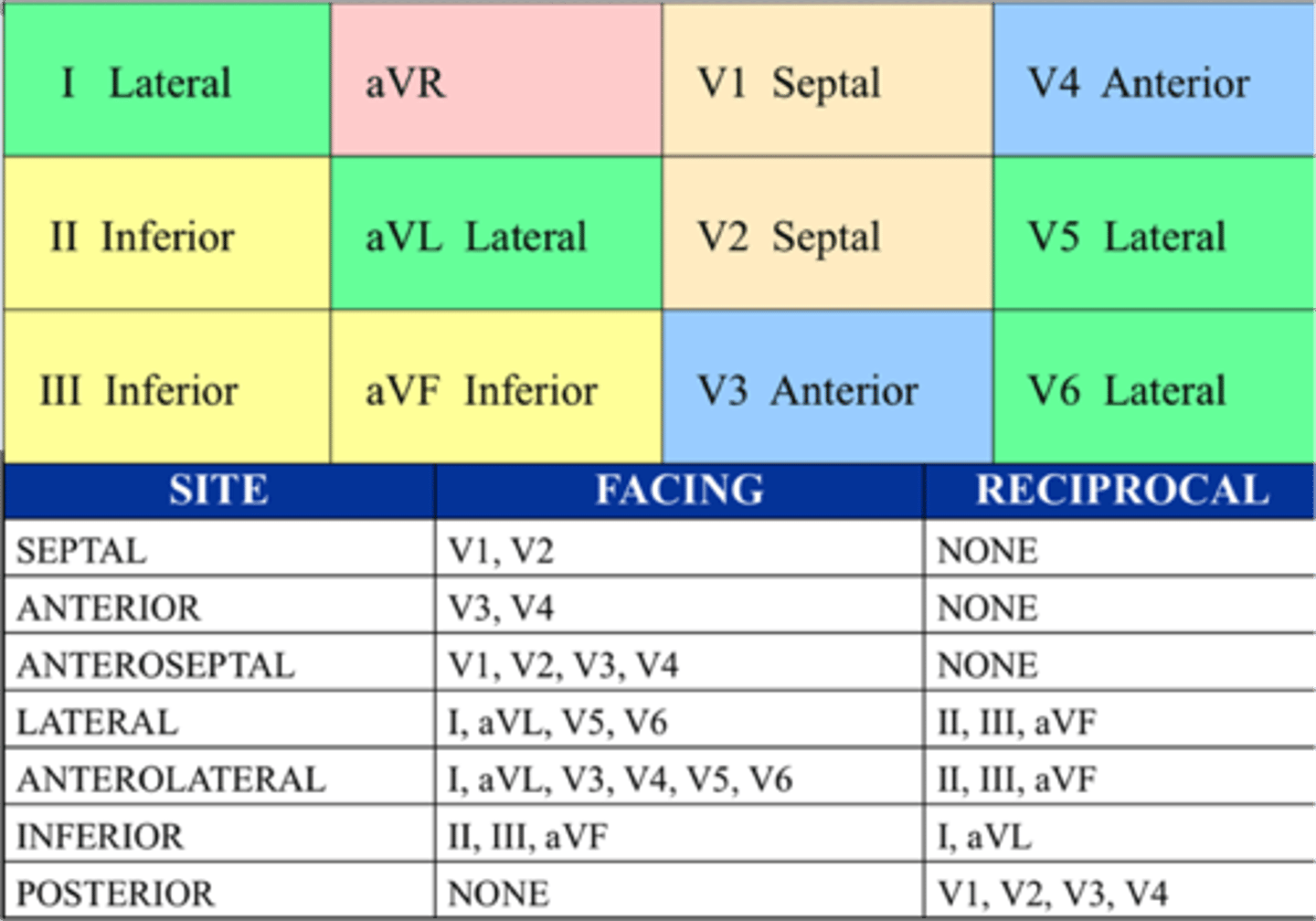
EKG
Lateral Leads
I, aVL, V5, V6
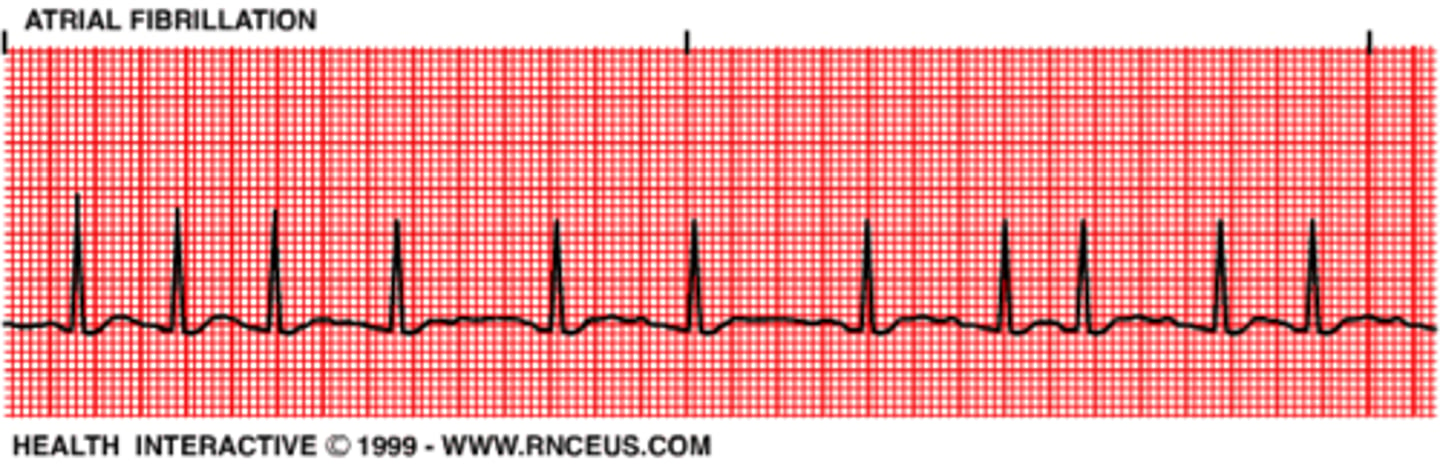
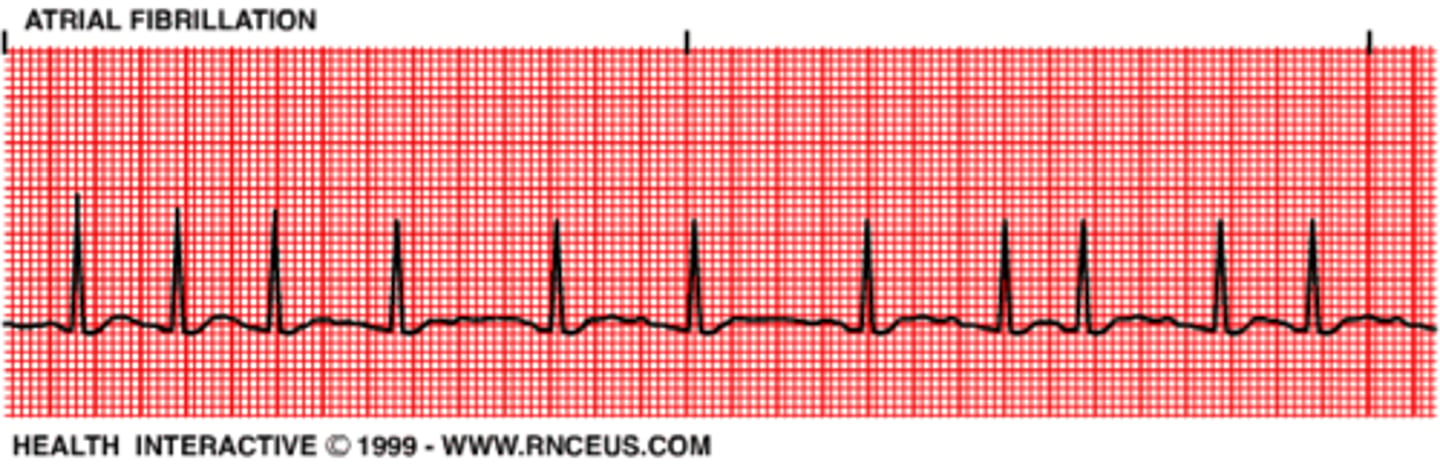
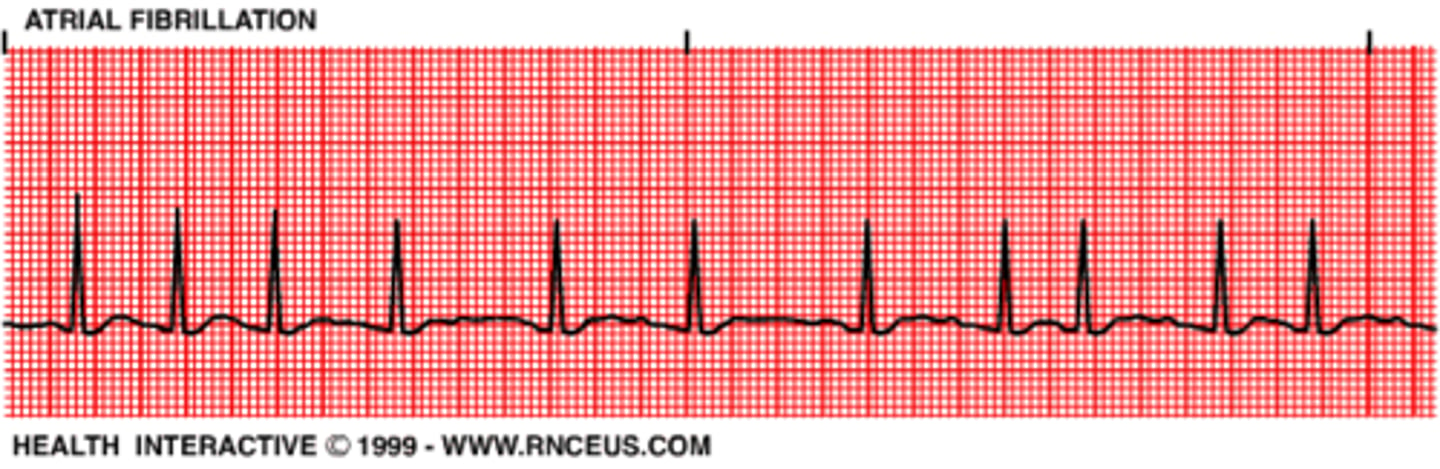
Atrial Fibrillation
EKG
- ⦸ p waves
- Disorganized, rapid, irregular atrial activation
- loss of atrial contraction
- Irregularly, irregular ventricular rate
Atrial Fibrillation
PX
- Palpitations
- shortness of breath
- dyspnea
- exertional syncope
Atrial Fibrillation
MX
If hemodynamically unstable
- Cardioversion
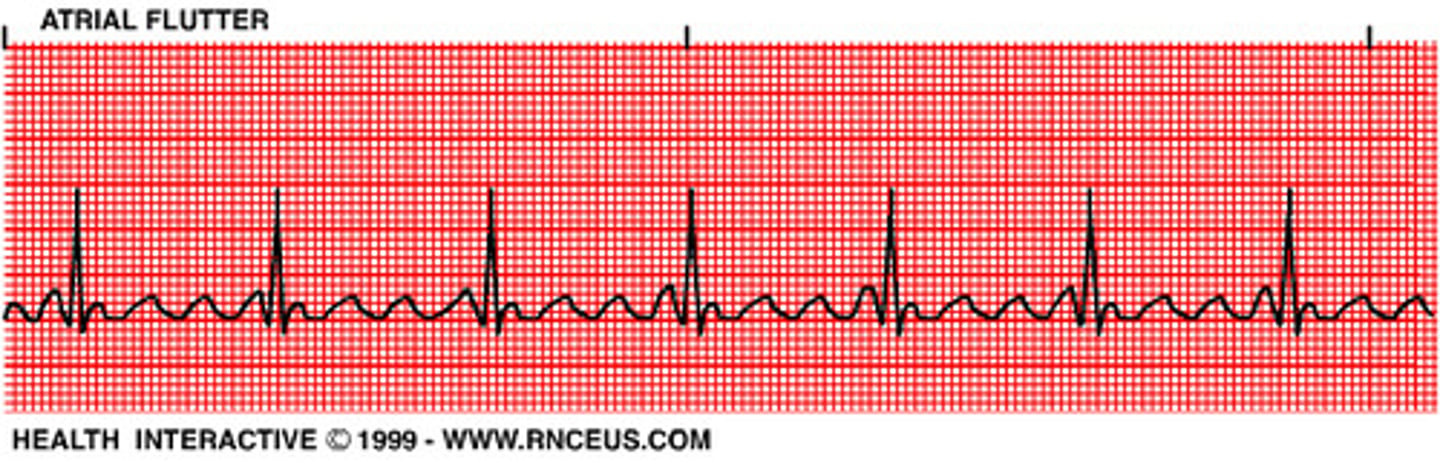
Atrial Flutter
EKG
- Small, very fast p waves
- 'sawtooth' pattern
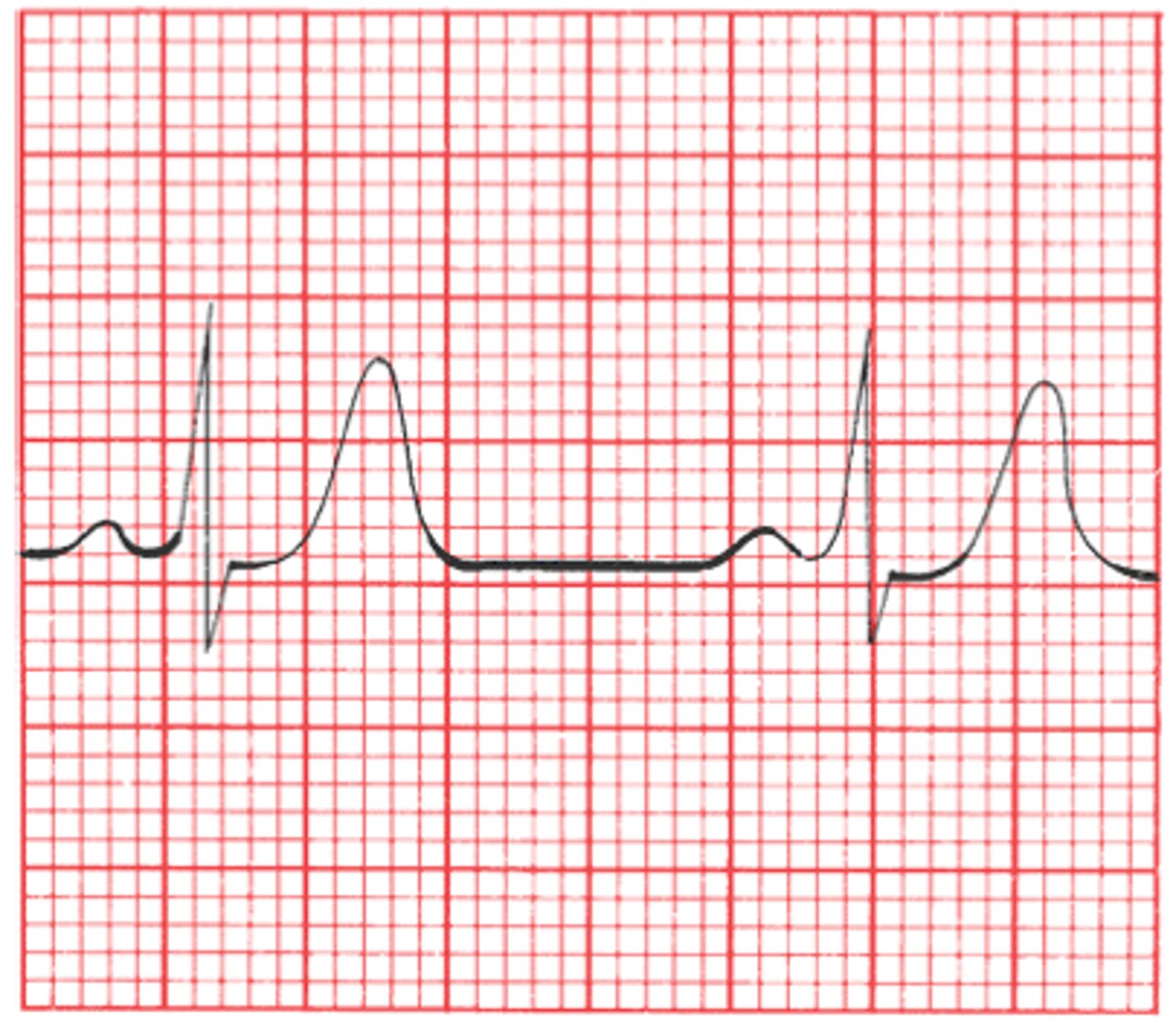
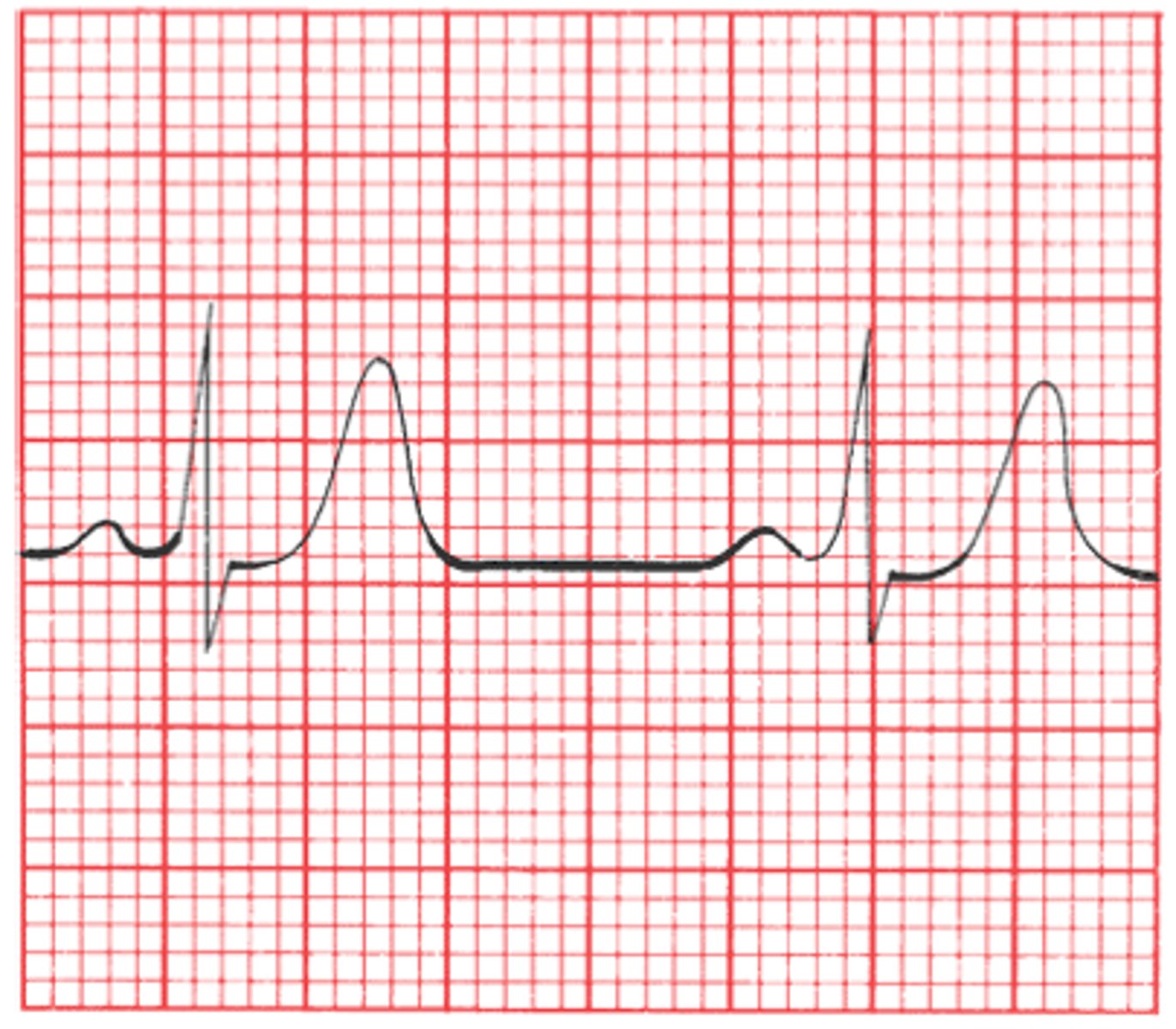
Hyperkalemia
EKG
- peaked T-waves
> 5.5. mEq/L
Hyperkalemia
Complications
Arrhythmia
- Bradycardia, Sinus Arrest, Ventricular fibrillation, Ventricular Tachycardia
- Asystole
Hyperkalemia
MX
Calcium gluconate—shifts K+ intracellular
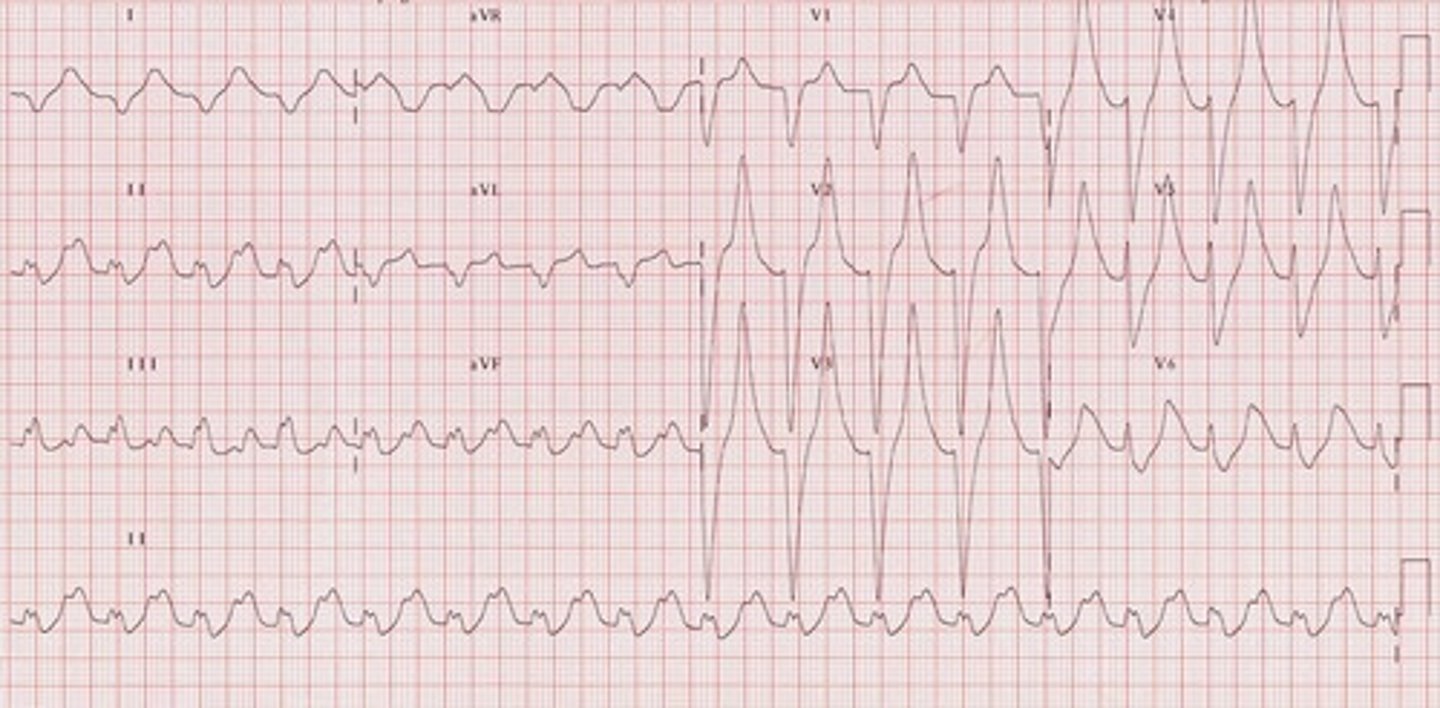
Hyperkalemia
PX
- > 5.5. mEq/L
- Muscle weakness, paralysis
- Impaired NMJ transmission
← missed hemodialysis sessions
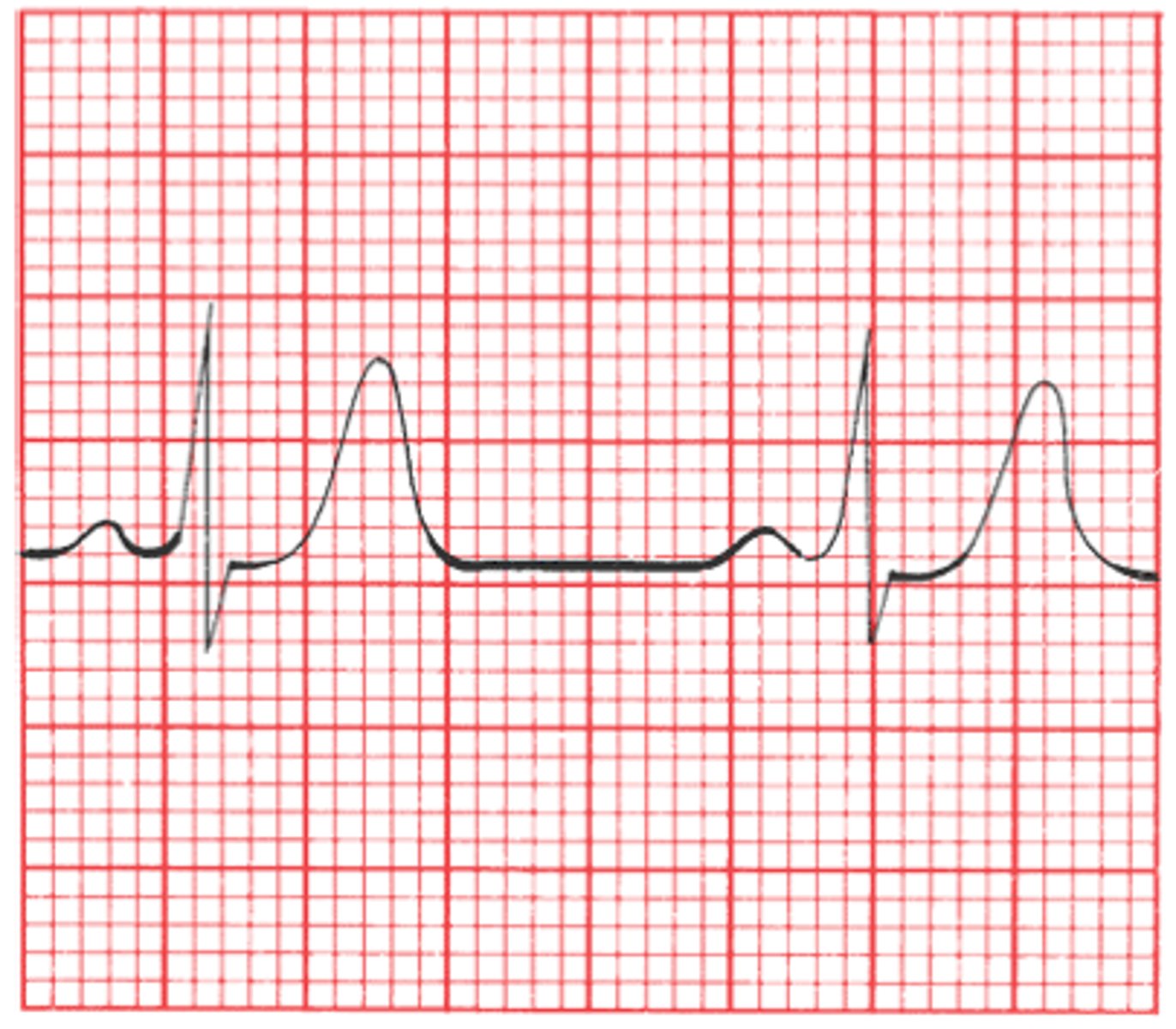
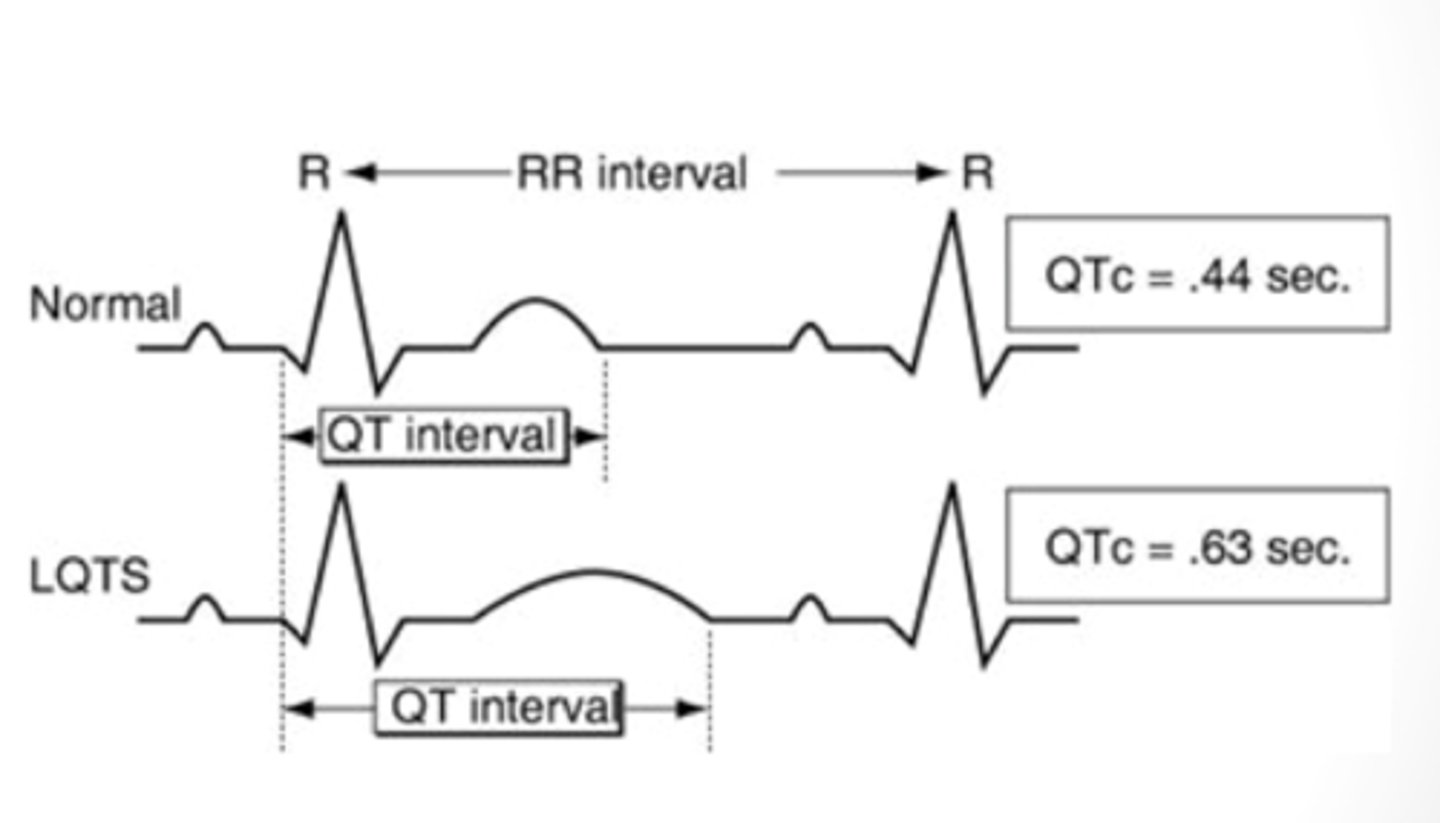
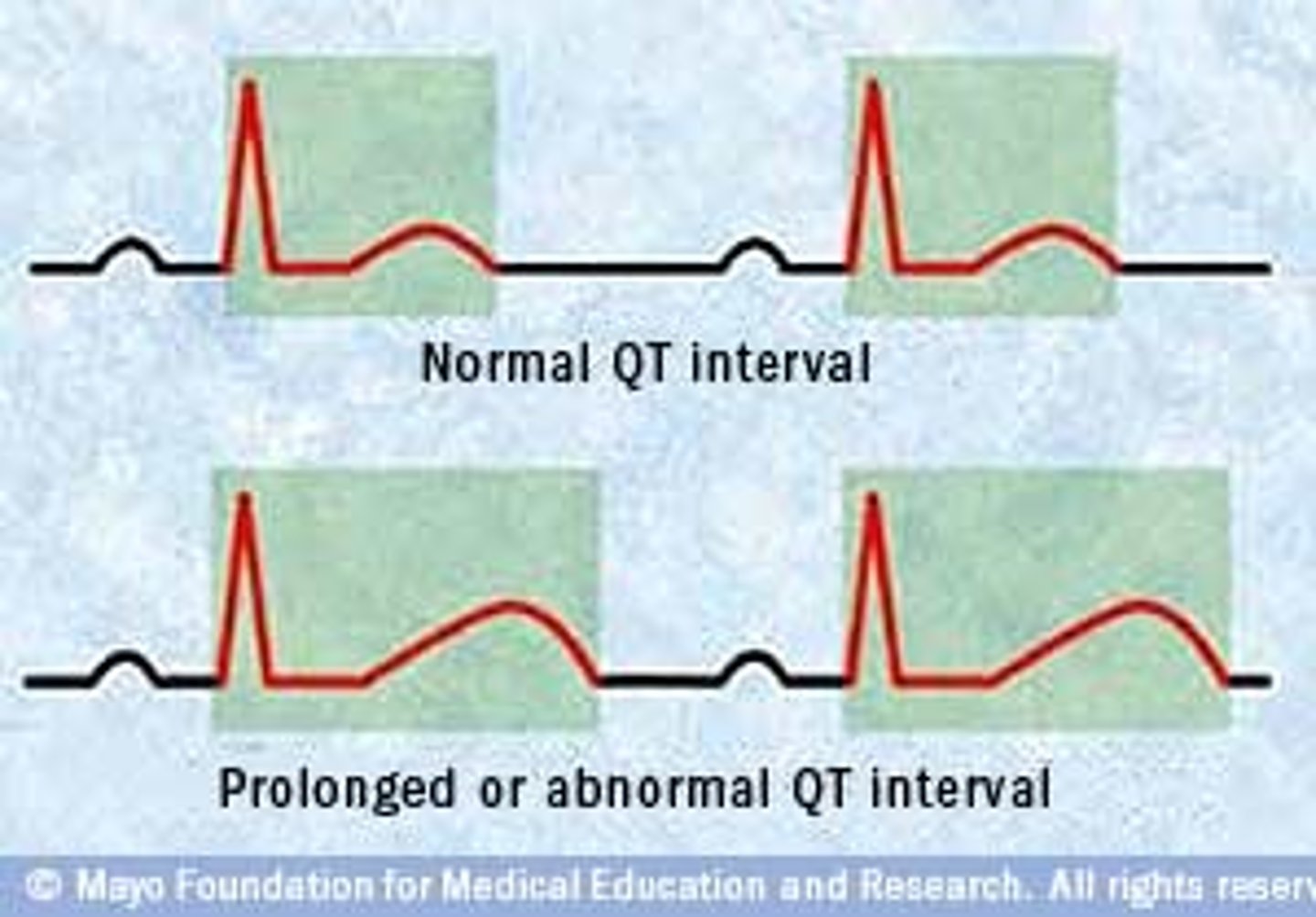
Long QT Syndrome
EKG
↑ QT-interval
- Lead II or V5/V6
Long QT Syndrome
Complications
- Torsades de Pointes
Ventricular Tachycardia
EKG
regular, wide complex tachycardia
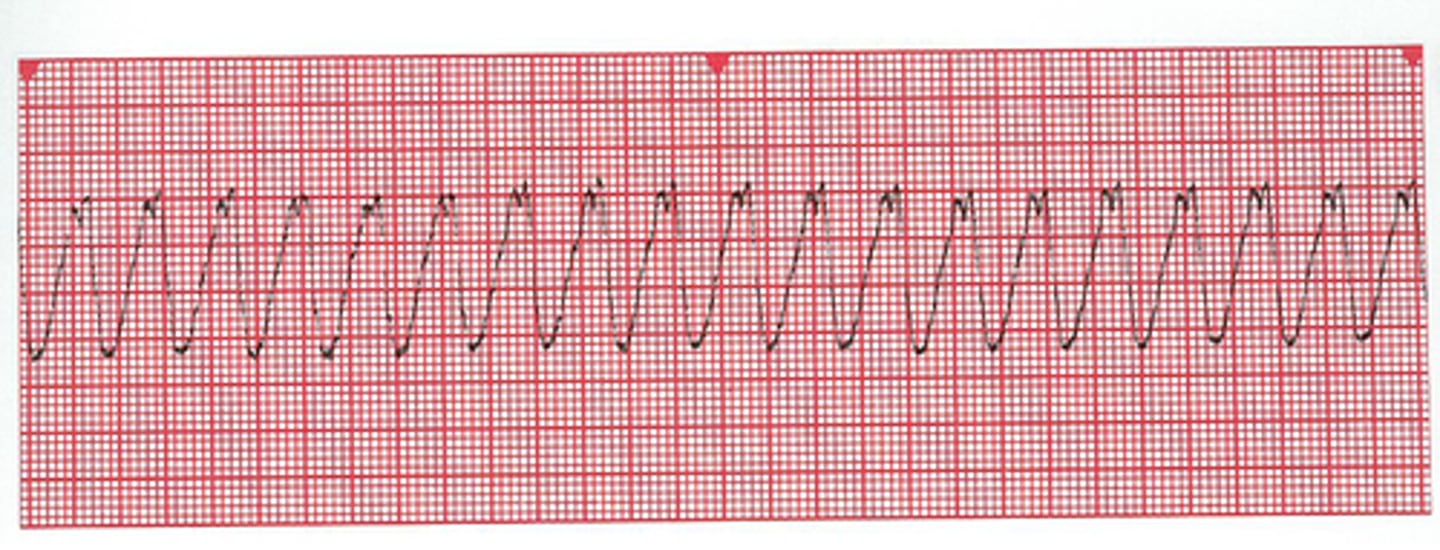
Ventricular Tachycardia
PX
- Hypotension
- Chest pain
- shortness of Breath
Ventricular Tachycardia
TX
If hemodynamically unstable
- Cardioversion
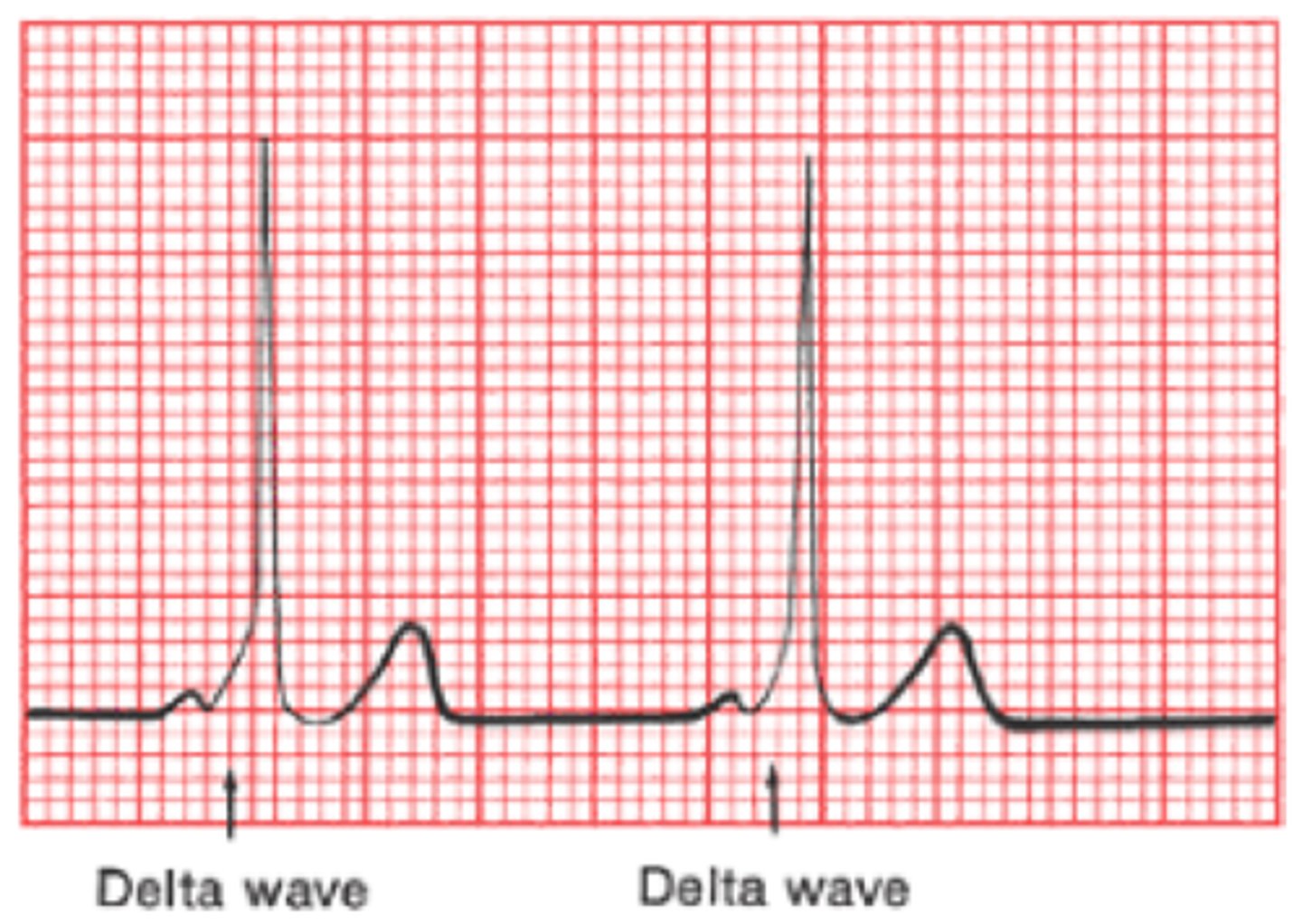
Wolff-Parkinson White Syndrome
EKG
- Delta wave—slurred initial portion of the QRS
- Represent AV node conduction via accessory pathway—bundle of Kent
- Palpitations secondary to AV re-entrant tachycardia
Aortic Regurgitation
Heart Sound
- Diastolic
- @ left sternal border
- mid-diastolic rumble
Louder—sitting & leaning forward

Aortic Regurgitation
PX
- de Musset sign—head bobbing
- wide pulse pressure, > 60 mmHg
- left ventricular hypertrophy

Aortic Stenosis
Heart Sound
- Systolic
- @ R 2nd ICS
- Radiates → carotids
Aortic Stenosis
PX
ECG—Aortic root dilation
- Syncope
- Angina
- Heart failure
- Older pts. w/ Bicuspid aortic valve
Mitral Regurgitation
EKG
- Systolic
- @ apex
- holosystolic murmur
- Radiates → Left Axilla
- diastolic rumble
- Opening snap
- loud S1
Louder—squatting
Rheumatic Heart Disease
Tricuspid Valve Regurgitation
- Pts. who inject drugs
- Immunocompromised
- Congenital Heart disease
- instrumentation in right heart
Mitral Stenosis
Heart Sound
- Diastolic
- @ Apex
- mid-diastolic rumble
- Opening snap
- low-pitched
- loud S1
Louder—squatting
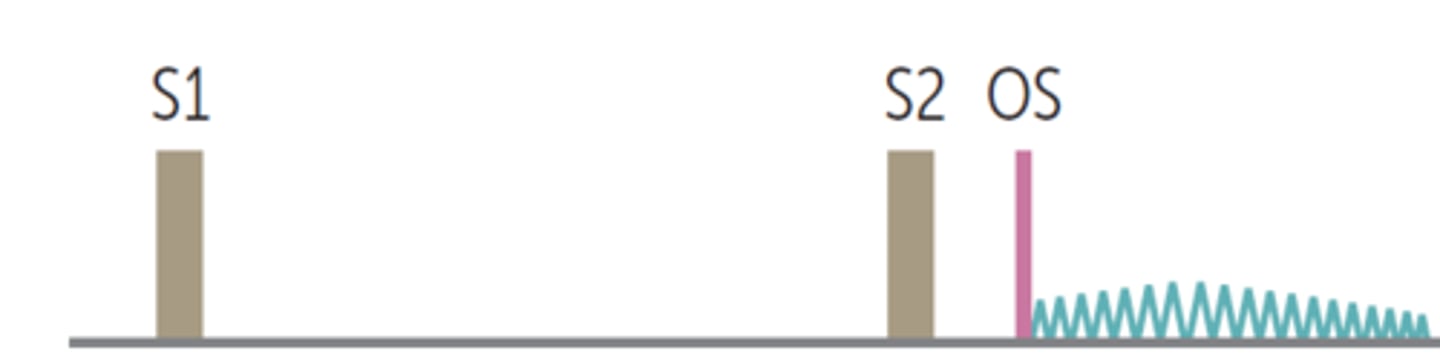
Mitral Valve Prolapse
Heart Sound
- late systolic murmur
- mid-systolic click
- @ apex
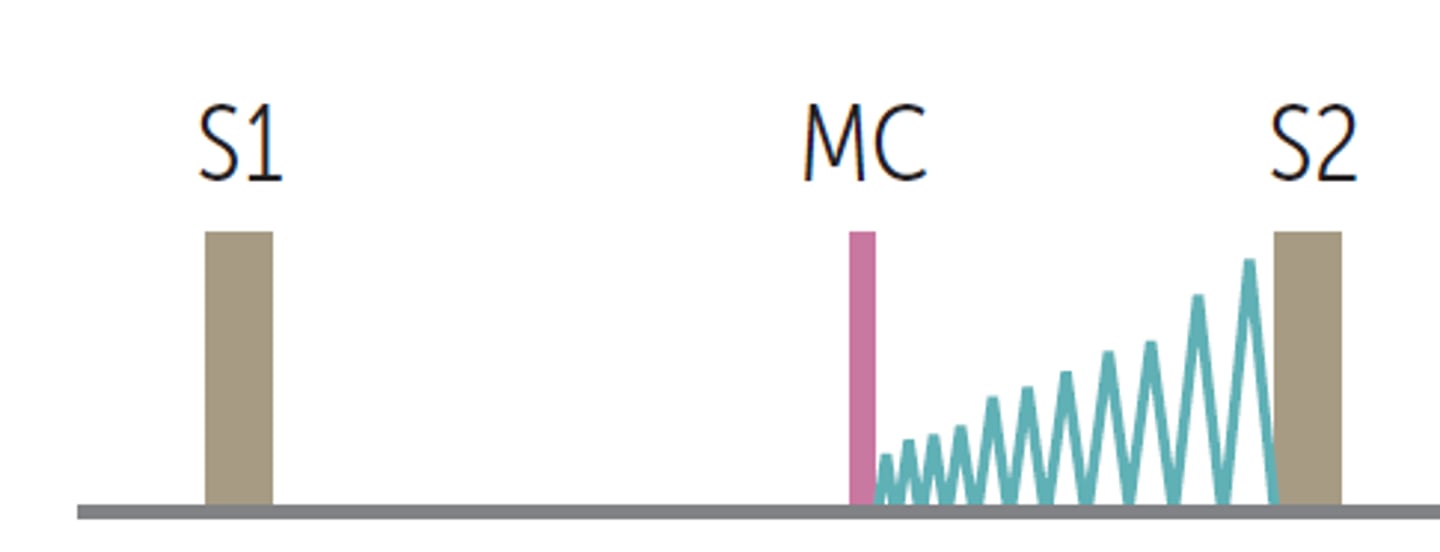
Hypertensive Emergency
Has signs of end organ damage
- rales, edema, JVD = heart failure
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
- Hyperdynamic point of maximal impulse
- Athlete
- Syncope from inadequate increase of cardiac output
- Systolic murmur
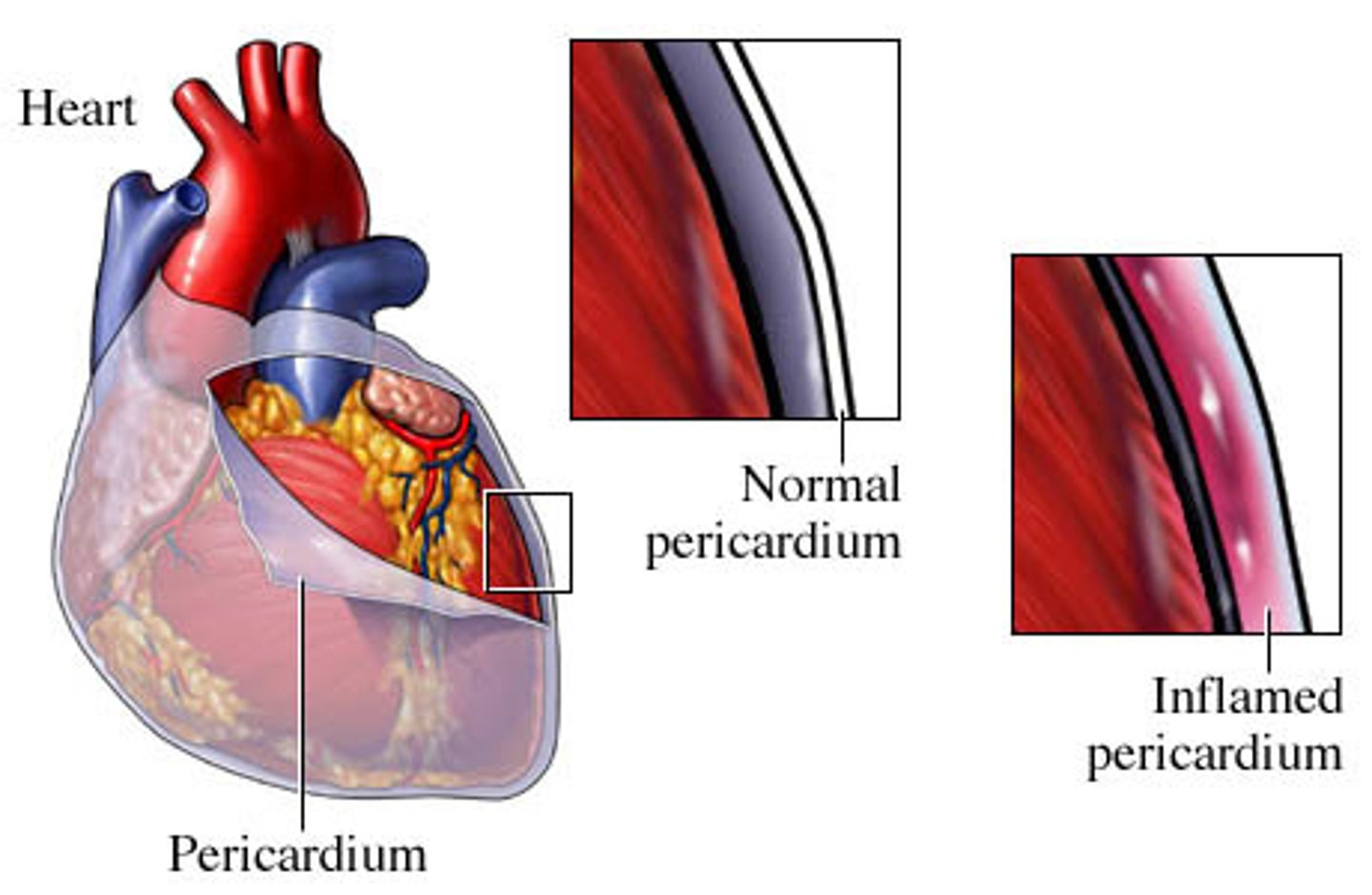
Pericarditis
- better w/ leaning forward
- friction rub on auscultation
Acute Respiratory Arrest
MX
Intubation
Support Ventilation
Apnea, Cyanosis
Breast Milk
Vitamin Supplementation
- Vitamin D
- All exclusively breastfed neonates should receive 400 IU/day of vitamin D beginning within days after birth
Because
- ↓ vitamin D content of breast milk
- Inconsistent & unpredictable cutaneous vitamin D synthesis from sun exposure
- ↑ rate of rickets among exclusively breastfed newborns
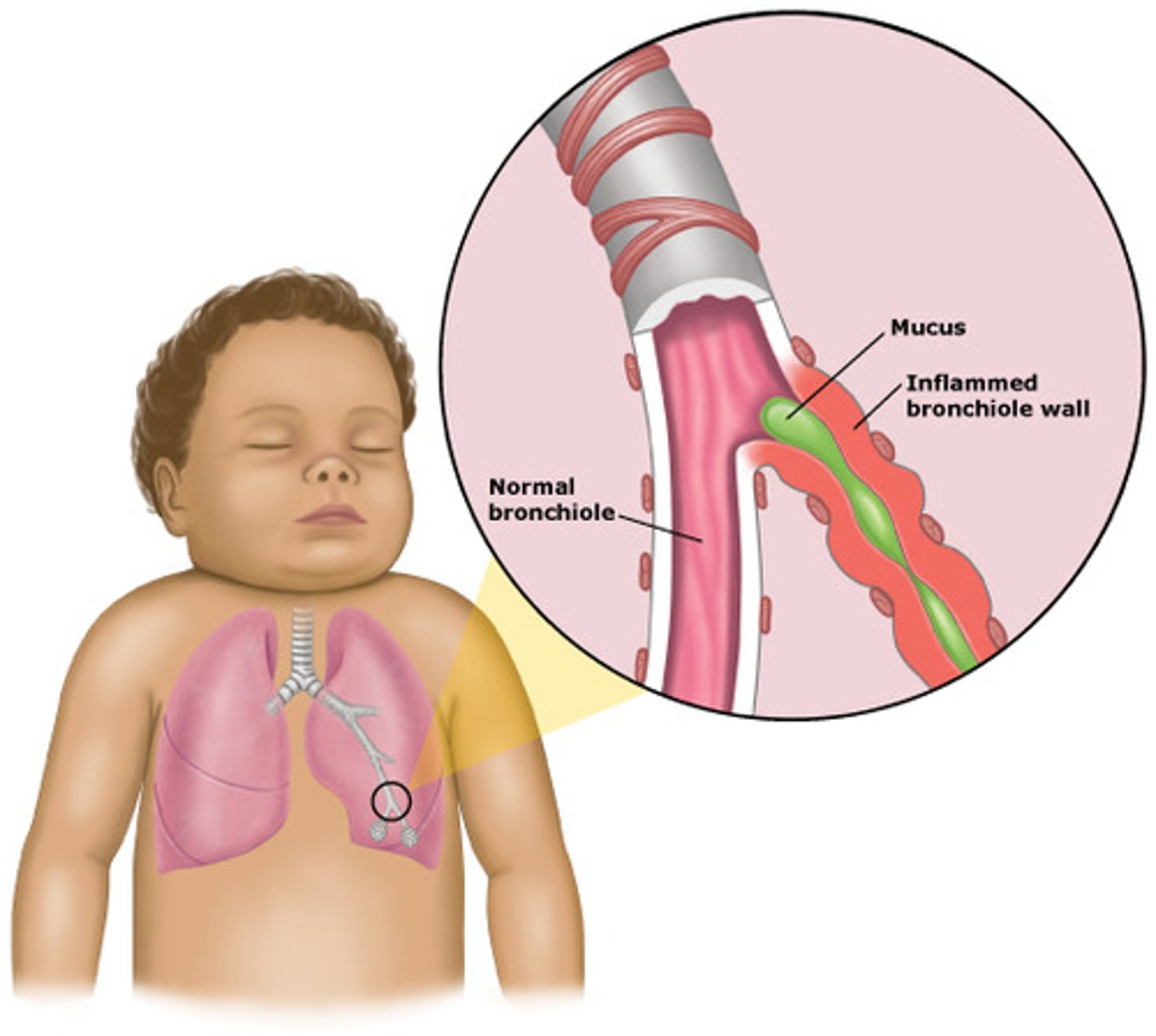
Bronchiolitis
PX
- very young infants
- self-resolves
- Sudden onset
- Low grade fever
- Wheezing
- Coryza, Nasal congestion
- Prolonged respiration
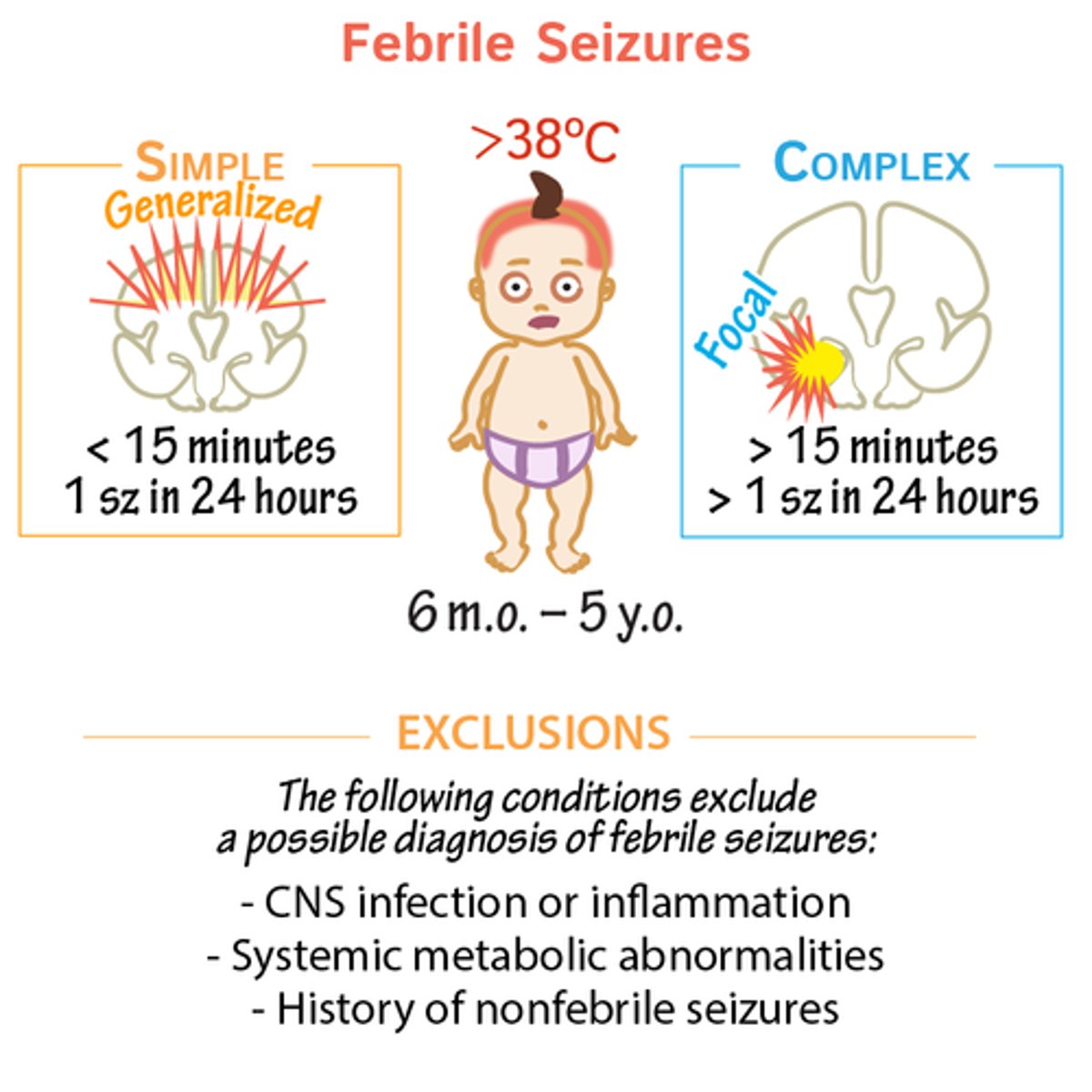
Febrile Seizure
- Child
- Uncomplicated, acute 3-minutes tonic-Clonic seizure
MX
- provide seizure educations
Ear anomaly/deformity
Associated anomalies
- Renal Anomolies—Renal U/S
- CHARGE syndrome
- Branchio-oto-renal syndrome
Down Syndrome
Sports Screening
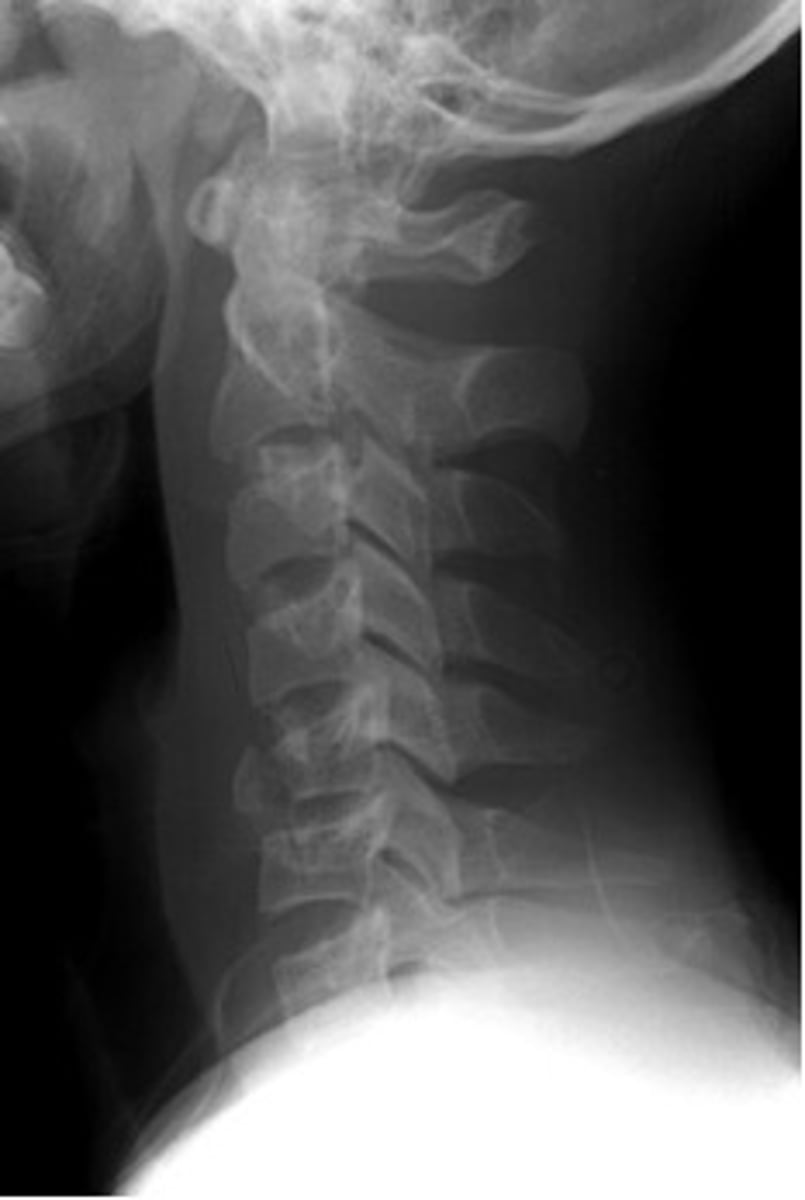
Cervical spine X-ray
- ↑ risk of ligament laxity & atlantoaxial instability
- ↑ risk of cervical spinal injury
Marfan Syndrome
CV defect
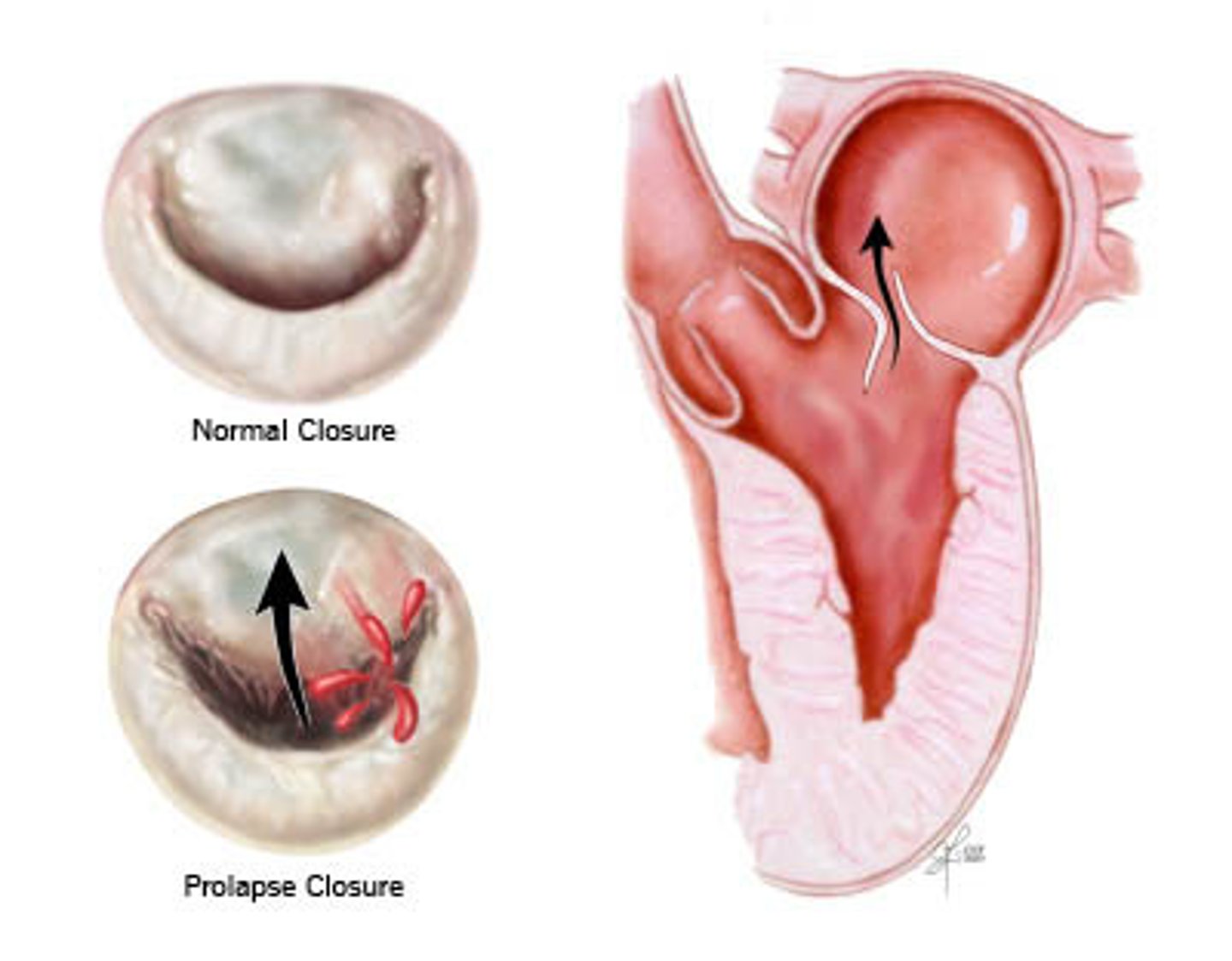
Mitral Valve Prolapse
- mid systolic click
- shortness of breath
- palpitations
Tay-Sachs, Gaucher Disease
Assc. Ethnicity
Ashkenazi Jewish
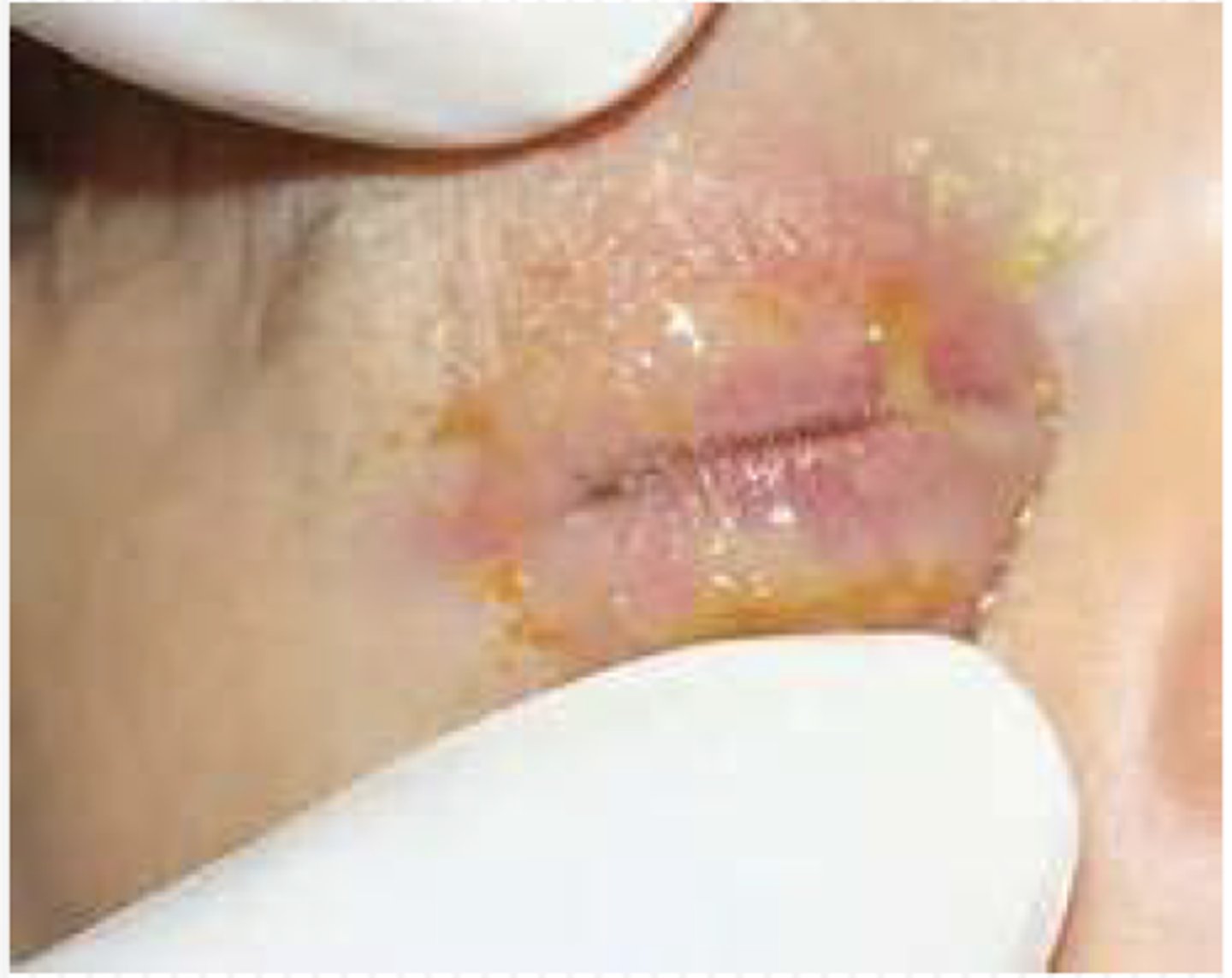
Neonatal Chlamydia Trachomatis
PX
- Conjunctivitis
- Pneumonia
Neonatal Chlamydia Trachomatis
TX
oral Erythromycin
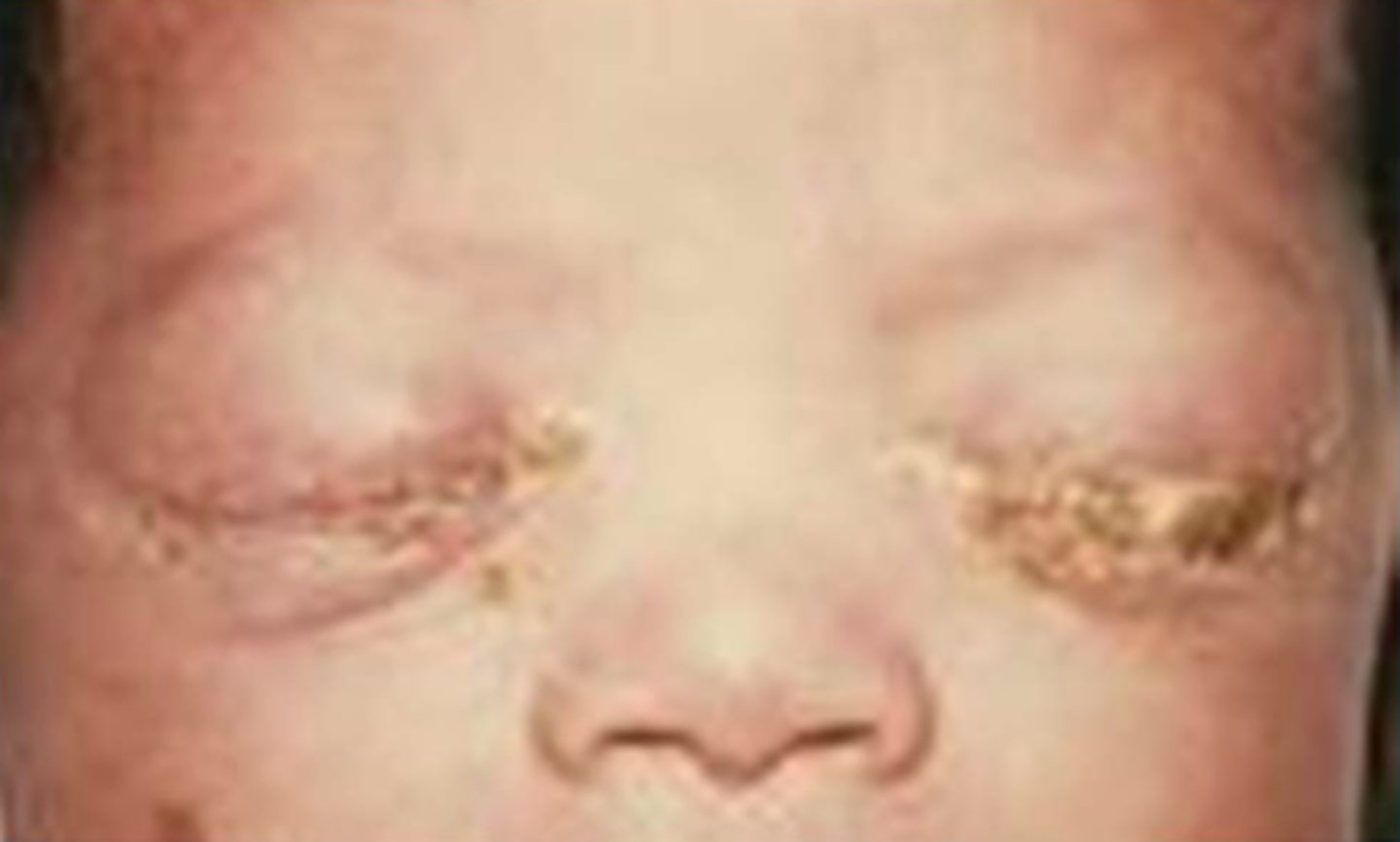
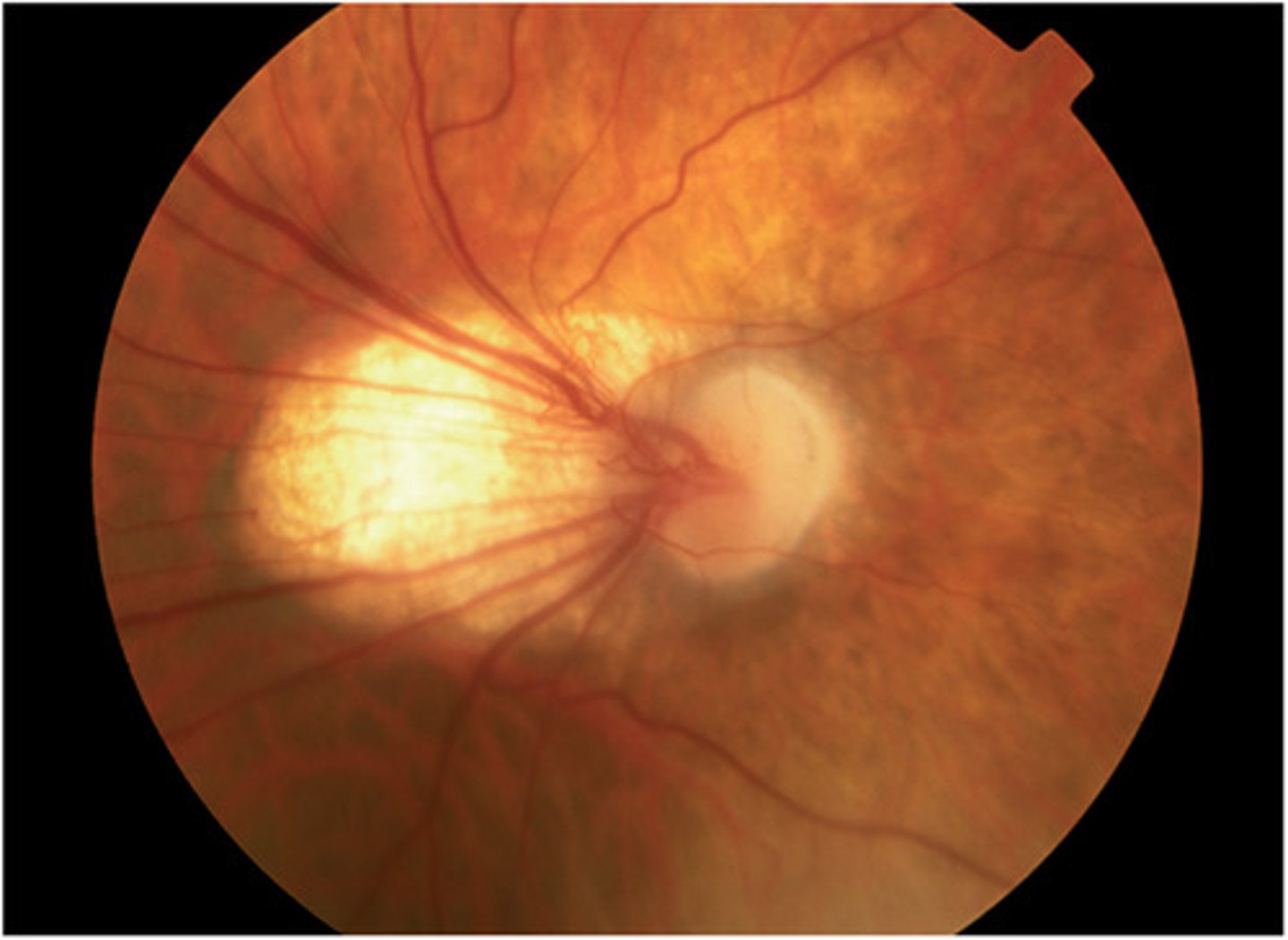
Retinopathy of Prematurity
- Incomplete vascularized premature retina
← initial injury to developing retinal vessels & ↓ insulin-like growth factor 1
- Highest incidence infants of the lowest gestation age
- Can be controlled by regulation of the baby's O2 saturation level
Ophthalmoscopy
- ridge of fibrovascular proliferation
- abnormal blood vessels
- fibrous tissue
Physician Abandonment
When a physician:
- terminates a relationship with a patient without giving timely notice
- Ceases to provide care for a patient who requires ongoing medical attention
- Does not provide medical records to a patient's new physician
- Most states consider 30 days adequate notice of termination to allow patients time to establish care with a new provider
Accepting Gifts from Patients
- Should be sensitive to potential motives behind the gift giving and should declining gifts that are inappropriately large
Autonomy
- Ability of a person to make his or her own decisions
- Respecting a competent patient's right to make their own decisions
Child Abuse
- Crossed 2 major percentiles in weight = indicates failure to thrive is secondary to inorganic causes
- Poor hygiene
- Bottle caries
- Abuse—symmetric healing scars on both feet
Call Child Protective Services (CPS)
Comparative Negligence
- where a patient's own fault is considered in a medical malpractice claim, reducing the compensation they receive by their percentage of responsibility
Consensus facit legem
"consent makes the law"
- emphasizes that a mutual agreement or "meeting of the minds" between parties forms a binding agreement, a principle fundamental to contracts and other agreements.
- For consent to be legally valid, it must be given freely and without coercion, fraud, misrepresentation, or mistake
Contributory Negligence
- a legal defense where the patient's own actions or inactions are alleged to have contributed to their injury or the medical negligence itself
e.g. not following discharge instructions
Distributive Justice
- Fair, equitable, appropriate distribution of benefits and burdens determined by norms that structure the terms of social cooperation
Double Effect
- Principle by which an act may be chosen, even if it has both helpful and harmful effects as long as the act is good or neutral, the agent intends only the good effect
- The bad effect is not the means to the good effect
Emergency Medical Treatment & Active Labor Act (EMTALA)
- Prevents hospitals from transferring patients with emergency conditions to other facilities to avoid financial losses
- Guarantee access to emergency services in specific circumstances
- If your hospital lacks the care a patient needs, in order to transfer them to another facility with the needed resource speak directly with the physician at the facility you would like to transfer them to
E.g. Behavioral Unit, Labor & Delivery