lower extremity attachments, actions, nerve supply
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
gluteal and posterior thigh regions
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
proximal attachment - gluteus maximus muscle
ilium posterior to posterior gluteal line; dorsal sacrum and coccyx; sacrotuberous ligament
distal attachment - gluteus maximus muscle
illotibital (and gluteal tuberosity)
nerve supply - gluteus maximus muscle
inferior gluteal nerve
actions - gluteus maximus
extends hip joint (especially from flexed position)
aids in lateral/external rotation of thigh (interchangeable)
stabilizes thigh, rising from sitting position
proximal attachment - gluteus medius muscle
external ilium between anterior and posterior gluteal lines
distal attachment - gluteus medius muscle
(lateral side of) greater trochanter
nerve supply - gluteus medius
superior gluteal nerve (innervation)
action - gluteus medius muscle
abduction hip joint
medial/internal motion of thigh
keeps upright when walking
proximal attachment - gluteus minimus muscle
external ilium between anterior and inferior gluteal lines
distal attachment - gluteus minimus muscle
(anterior surface of) greater trochanter
nerve supply - gluteus minimus
superior gluteal nerve
action - gluteus minimus
abduct hip joint
medial/internal rotation of thigh
proximal attachment - tensor fascia latae
anterior superior iliac spine
distal attachment - tensor fascia latae
illotibial tract (IT band)
nerve supply - tensor fascia lata
superior gluteal n.
actions - tensor fascia latae
abduct hip joint
medial/internal rotation
creates extra tension, helps contract and flex
proximal attachment- piriformis muscle
anterior surface of sacrum; sacrotuberous ligament
distal attachment - piriformis muscle
(superior border) greater trochanter
nerve supply - piriformis
nerve to piriformis
action - piriformis muscle
lateral/external rotation of thigh
abduction flexed thigh
proximal attachment - obturator internus muscle
internal surface of obturator foramen and membrane
distal attachment - obturator internus
trochanteric fossa on femur
nerve innervation- obturator internus
nerve to obturator
action - obturator internus
lateral/external rotation of hip
abduct flexed thigh
proximal attachment - inferior gemellus
ischial tuberosity
distal attachment - inferior gemellus
trochanteric fossa on femur
nerve innervation - inferior gemellus
nerve to quadratus
action -inferior gemellus
Lateral/external rotation of hip
abduct flexed thigh
triceps coaxe - distal attachment
gemelli muscles attach to tendon of obturator internus
proximal attachment - quadratus femurs
ischial tuberosity (lateral surface)
distal attachment - quadratus femoris
intertrochanteric cers (quadrate tubercle)
nerve innervation - quadratus femoris
nerve to quadratus femoris
actions - quadratus femoris
lateral/external rotation of thigh
deep hip rotator
nerves of gluteal region
superior gluteal
inferior gluteal
pudendal
nerve to quadratus femoris
posterior femoral cutaneous
sciatic
super and inferior gluteal arteries
derive from internal iliac artery
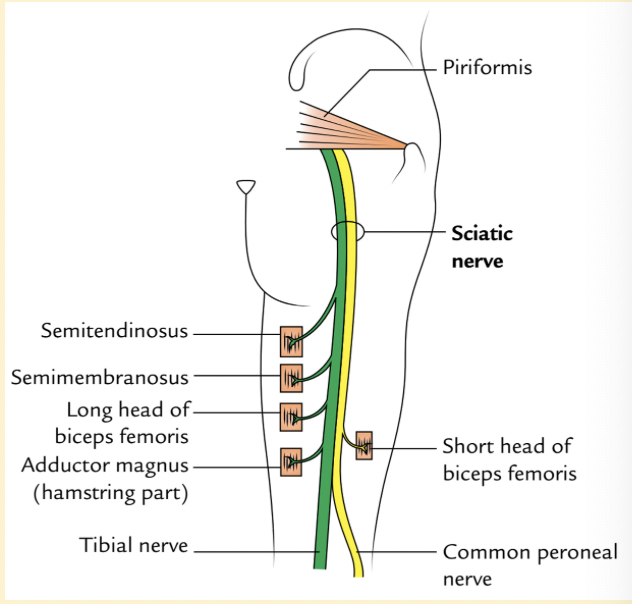
semitendinosus muscle - proximal attachment
ischial tuberosity
distal attachment - semiteninosus muscle
supero-medial(upper front) surface tibia (part of pes anserinus)
nerve supply - semitendinosus muscle
tibial division of sciatic nerve
actions - semitendinosus
extends hip joint when trunk bent forward (controls forward flexion of trunk @ hip joint-eccentrically)
flex knee joint, with semi flexion —> medial rotation present
affixed foot on ground —→ lateral rotate the hip (stationary tibia)
muscle insertion - Pes anserinus (‘such good tendon’)
‘goose foot’ shape at muscle insertion site, on superior medial tibia
sartorius muscle (anterior compartment)
gracilis muscle (medial compartment)
semitendinosus muscle (posterior)
proximal attachment - semimembranosus muscle
ischial tuberosity
distal attachment - semimembranosus
posterior surface of medial tibial condyle
nerve supply - semimebranosus muscle
tibial division of the sciatic nerve
actions - semimembranosus
extends hip joint when trunk bent forward (controls forward flexion of trunk @ hip joint-eccentrically)
flex knee joint, with semi flexion —> medial rotation present
affixed foot on ground —→ lateral rotate the hip (stationary tibia)
proximal attachment - long head of biceps femoris
ischial tuberosity
distal attachment - long head biceps femoris
lateral side of fibular head
nerve supply - long head biceps femoris
tibial division of the sciatic nerve
action - long head biceps femoris
extends hip joint when trunk bent forward (controls forward flexion of trunk @ hip joint-eccentrically)
flex knee joint, with semi flexion —> lateral rotation at knee present
proximal attachment - biceps femoris short head
lower half of the linea aspera; lateral supracondylar ridge
distal attachment - biceps femoris short head
lateral side of fibular head
nerve supply - short head of biceps femoris
common fibular division of the sciatic nerve
actions - short head of biceps femoris
flex knee joint, semi-flexion —> lateral rotation at knee
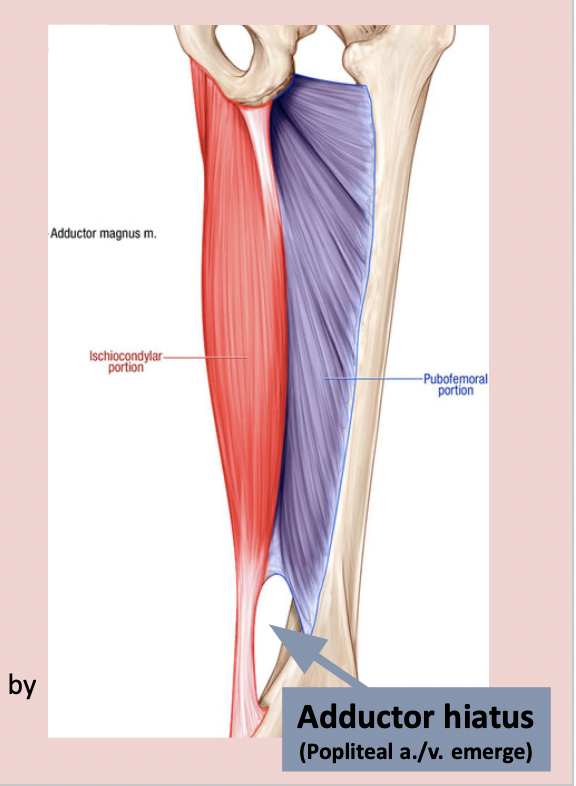
proximal attachment - ischiocondylar portion of adductor Magnus muscle
ischial tuberosity
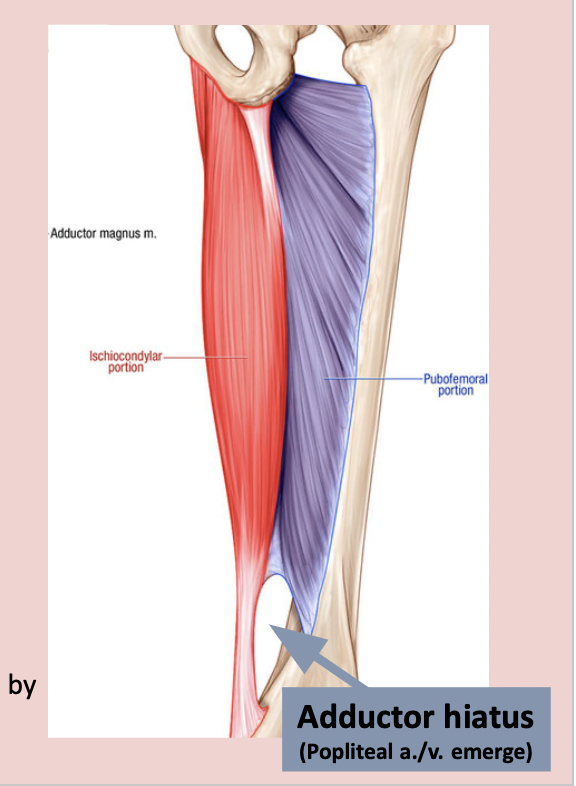
distal attachment - ischiocondylar portion of adductor magnus
adductor tubercle (femur)
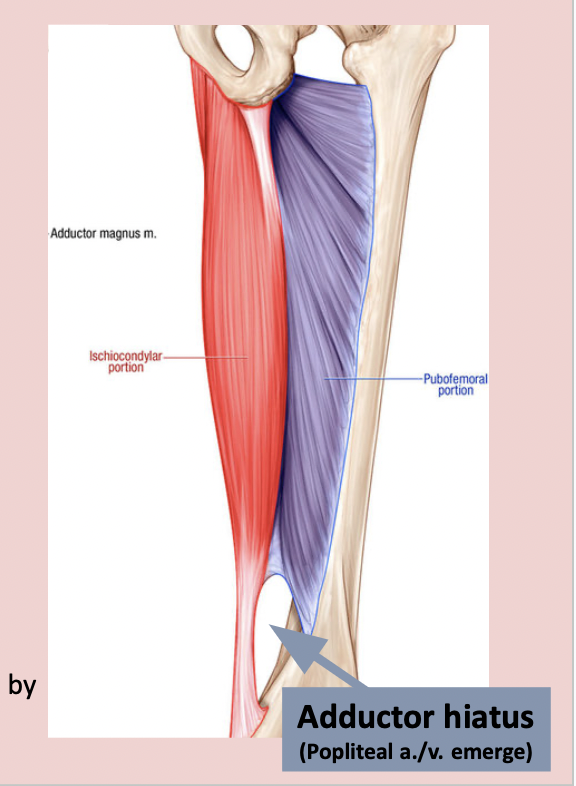
nerve supply - ischiocondylar portion of adductor magnus
tibial division of sciatic nerve
adductor component is innervated by obturator nerve of medial thigh
action - ischiocondylar portion of adductor magnus
extend hip joint
‘hamstring’ attachments
(Other than BFSH) extends from posteroinferior pelvis to posterior knee (ST & SM medial “hamstrings”; BFLH lateral “hamstring”)
actions of ‘hamstring’
hip extension when trunk is flexed position (in lengthened state)
knee flexion
pelvic tilt (anterior-posterior)
swing phase of walking —> deceleration forward motion of tibia
nerve innervation - posterior thigh
sciatic nerve - emerges from piriformis muscle