Cell structure
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/26
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
1
New cards
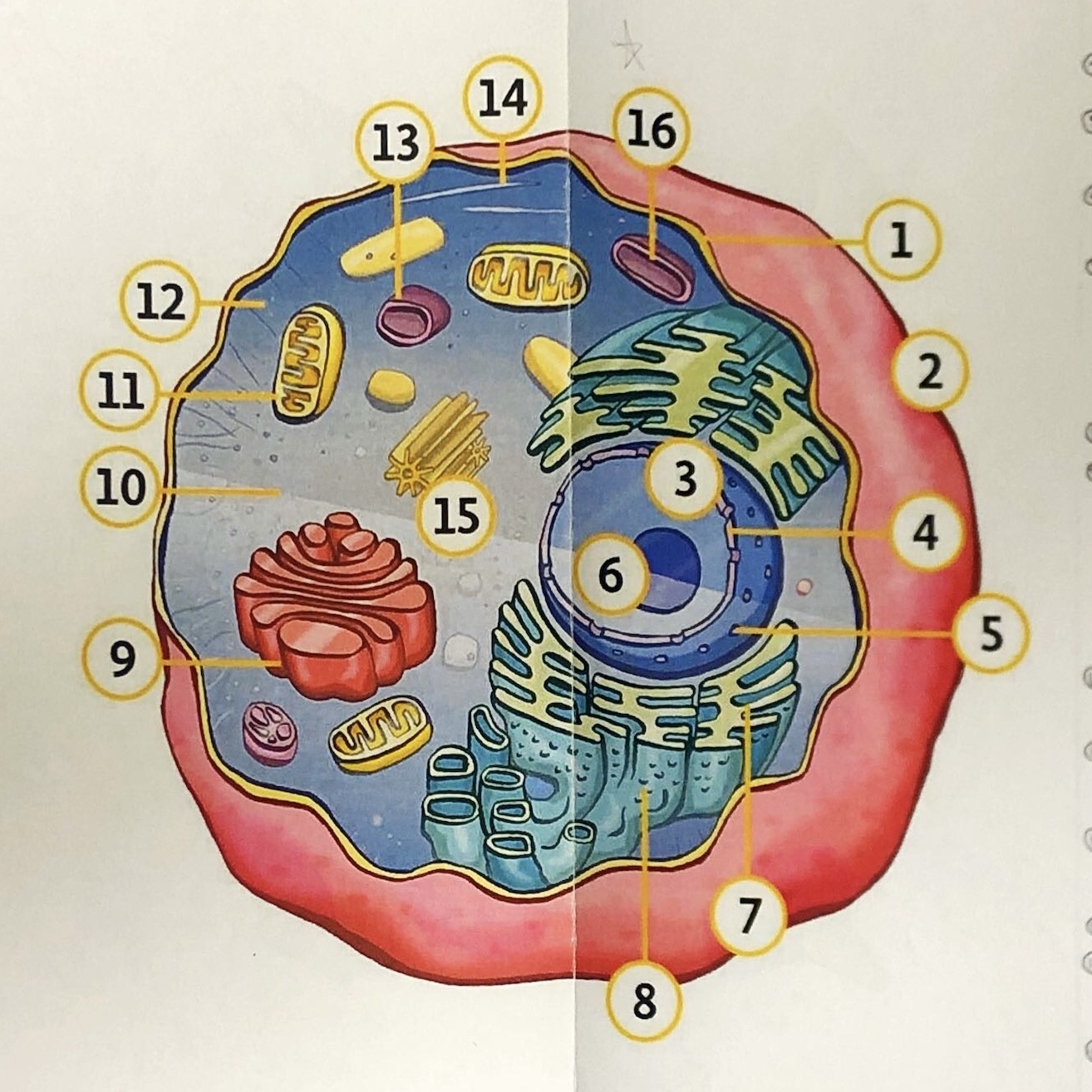
State all the components of an animal cell
1. cell membrane
2. extra cellular space
3. nucleus
4. nuclear pore
5. nuclear envelope/ membrane
6. nucleolus
7. endoplasmic reticulum
8. ribosomes
9. golgi apparatus/ body
10. cytoplasm
11. mitochondrion
12/14. cytoskeleton
13. temporary vacuole
15. centrioles
16. lysosomes
2. extra cellular space
3. nucleus
4. nuclear pore
5. nuclear envelope/ membrane
6. nucleolus
7. endoplasmic reticulum
8. ribosomes
9. golgi apparatus/ body
10. cytoplasm
11. mitochondrion
12/14. cytoskeleton
13. temporary vacuole
15. centrioles
16. lysosomes
2
New cards
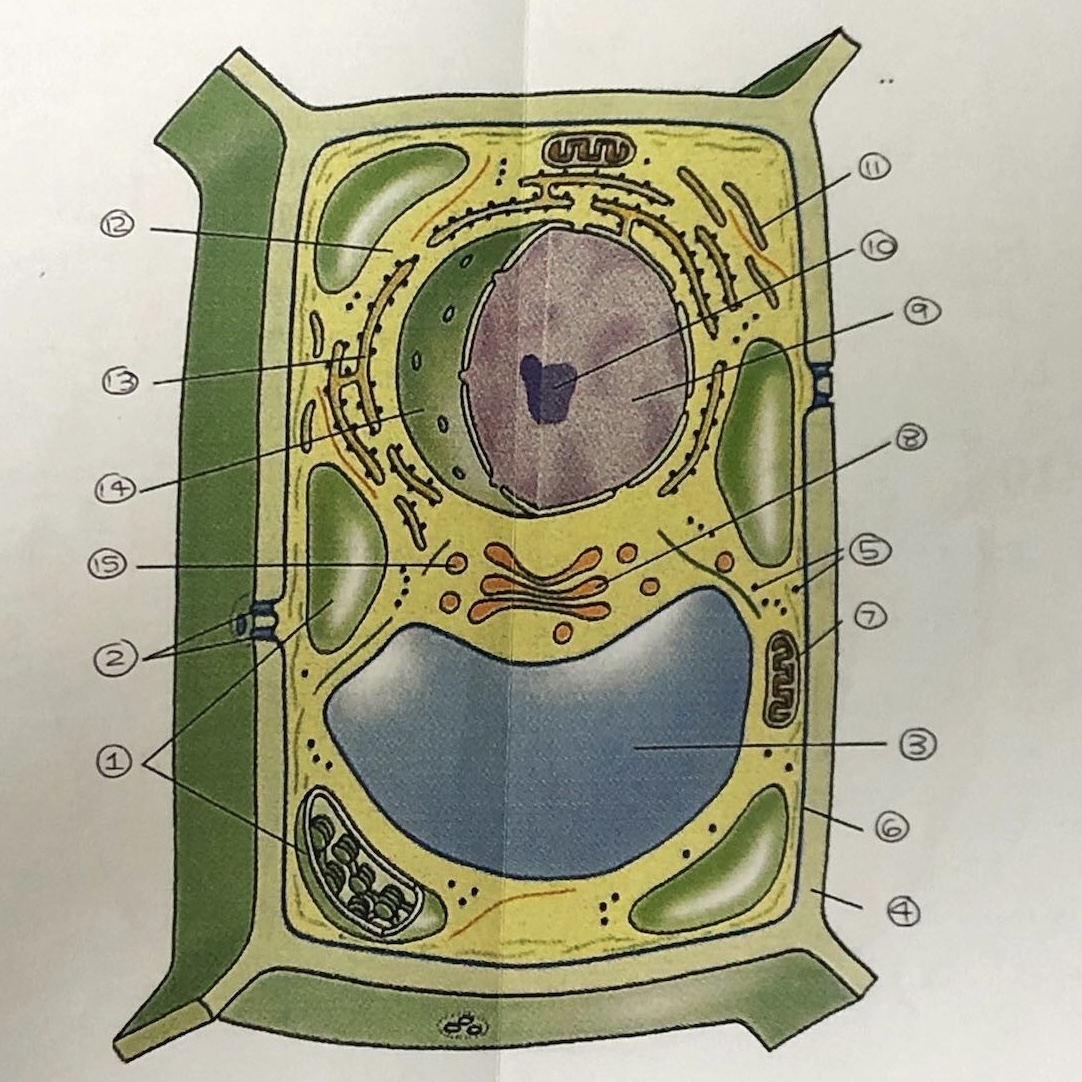
State all the components of a plant cell
1. chloroplasts
2. plasmodesmata
3. vacuole
4. cellulose cell wall
5. ribosomes
6. cell membrane
7. mitochondrion
8. golgi body
9. nucleus
10. nucleolus
11. smooth E.R
12. cytoplasm
13. rough E.R
14. nuclear membrane
15. vesicles
2. plasmodesmata
3. vacuole
4. cellulose cell wall
5. ribosomes
6. cell membrane
7. mitochondrion
8. golgi body
9. nucleus
10. nucleolus
11. smooth E.R
12. cytoplasm
13. rough E.R
14. nuclear membrane
15. vesicles
3
New cards
State the structure and function of the nucleus
1. It is double membraned (enveloped)
2. Contains nuclear pores which control exit of mRNA
3. It contains nucleolus- the site of ribosome production
2. Contains nuclear pores which control exit of mRNA
3. It contains nucleolus- the site of ribosome production
4
New cards
State the structure and function of the endoplasmic reticulum
1. It is a series of membrane bound compartments
2. Smooth E.R- lipid and carbohydrate synthesis
3. Rough E.R- does protein sysnthesis
2. Smooth E.R- lipid and carbohydrate synthesis
3. Rough E.R- does protein sysnthesis
5
New cards
State the structure of the Golgi apparatus
1. A series of fluid filled, flattened and curved sacs
2. Processes and packages proteins and lipids
3. Produces lysosomes
2. Processes and packages proteins and lipids
3. Produces lysosomes
6
New cards
State the structure and function of the mitochondria
1. They are oval shaped and double membraned
2. It is the site of aerobic respiration
2. It is the site of aerobic respiration
7
New cards
State the structure and function of lysosomes
1. They are vesicles containing digestive enzymes bound by a single membrane
8
New cards
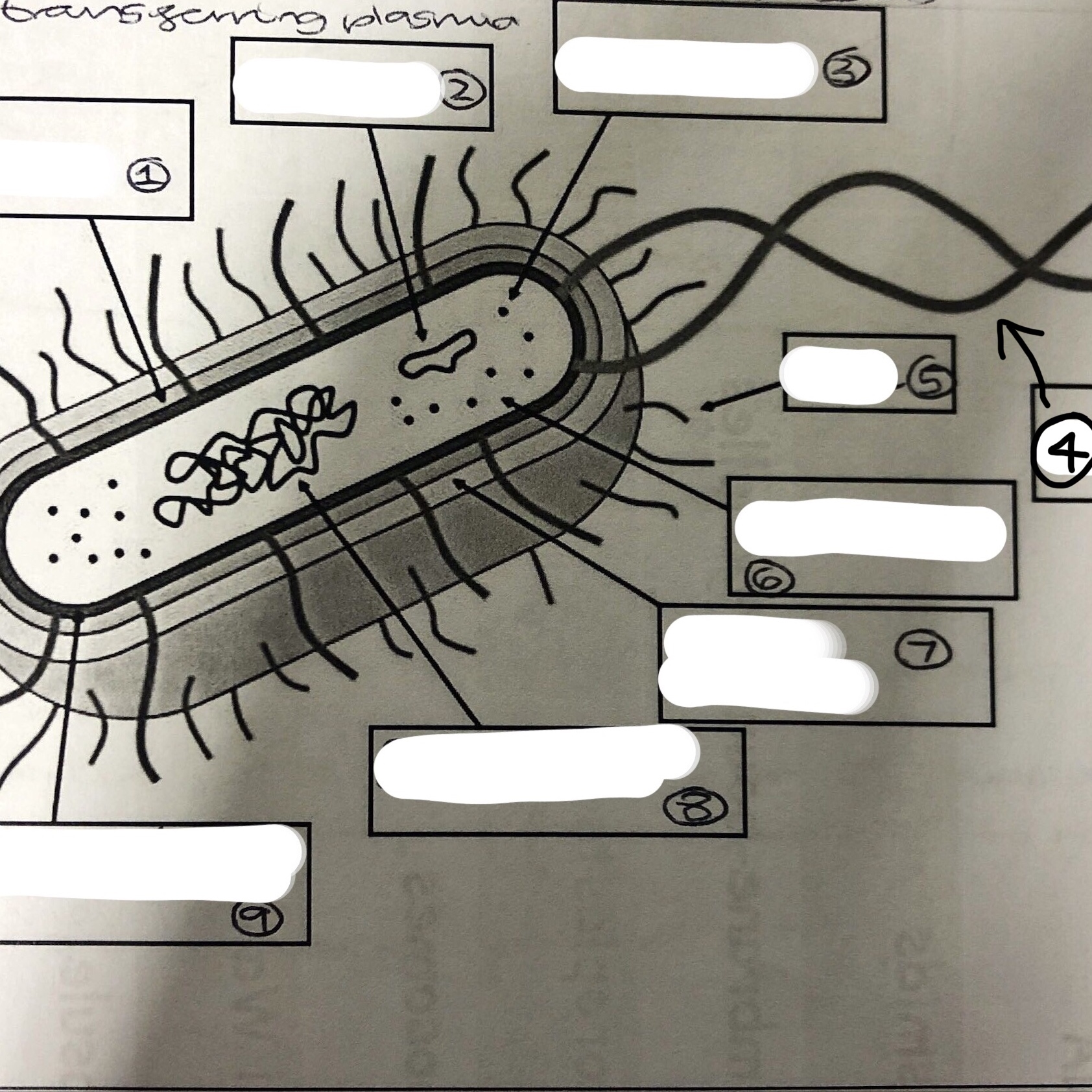
State all the components of a prokaryotic cell
1. cell wall
2. plasmid
3. ribosomes
4. flagella
5. pilli
6. cytoplasm
7. slime capsule
8. circular DNA chromosome
9. plasma, cell membrane
2. plasmid
3. ribosomes
4. flagella
5. pilli
6. cytoplasm
7. slime capsule
8. circular DNA chromosome
9. plasma, cell membrane
9
New cards
What is the cell wall of a prokaryote made of
Murein
10
New cards
State the function of the slime capsule
It provides a protective layer and prevents the cell from drying out
11
New cards
Describe the structure of viruses
They are non-living structures that consist of nucleic acid enclosed in a capsid
12
New cards
Describe a light microscope
Wavelength- 400-800nm
Imagery- direct
Resolution- 200nm
Radiation- light
Image- 2D/3D
Focused- lens
Magnification- x1000
Imagery- direct
Resolution- 200nm
Radiation- light
Image- 2D/3D
Focused- lens
Magnification- x1000
13
New cards
Describe a scanning EM
Wavelength- 0.2nm
Imagery- indirect
Resolution- 0.1nm
Radiation- electron beams
Image- 3D
Focused- magnets
Magnification- x100000
Imagery- indirect
Resolution- 0.1nm
Radiation- electron beams
Image- 3D
Focused- magnets
Magnification- x100000
14
New cards
Describe a transmission EM
Wavelength- 0.2nm
Imagery- indirect
Resolution- 0.1nm
Radiation- electron beams
Image- 3D
Focused- magnets
Magnification- x1,000,000,000
Imagery- indirect
Resolution- 0.1nm
Radiation- electron beams
Image- 3D
Focused- magnets
Magnification- x1,000,000,000
15
New cards
State the advantages and disadvantages of a light microscope
A- cheap, portable, easy to use, living things, colour
D- lower mag and res
D- lower mag and res
16
New cards
State the advantages and disadvantages of a TEM and SEM
A- high mag and res,
D- expensive, long preparation, dead samples used, damages the specimen
D- expensive, long preparation, dead samples used, damages the specimen
17
New cards
Describe and explain the solution used in cell fractionation
1. It is cold- to reduce enzyme activity
2. Isotonic- stops the cells shrinking or bursting
3. Buffered- pH is stable
2. Isotonic- stops the cells shrinking or bursting
3. Buffered- pH is stable
18
New cards
Describe the process of cell fractionation
1. Tissue is cut up and kept in a cold, buffered solution
2. The tissue is further broken up in a homogeniser
3. The tissue is further broken up in a ultra centrifuge at a low speed for 10 minutes (to separate nuclei)
4. It is then spun at medium speed (to seperate mitochondria)
5. Finally it is spun at a high speed (lysosomes)
2. The tissue is further broken up in a homogeniser
3. The tissue is further broken up in a ultra centrifuge at a low speed for 10 minutes (to separate nuclei)
4. It is then spun at medium speed (to seperate mitochondria)
5. Finally it is spun at a high speed (lysosomes)
19
New cards
State the 3 main phases of the cell cycle
Interphase, mitosis and cytokinesis
20
New cards
State the steps involved in interphase
G1- cells grow and organelles replicate
S- DNA is replicated
G2- cells grow more
S- DNA is replicated
G2- cells grow more
21
New cards
State the steps involved in mitosis
Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
22
New cards
Define cytokinesis
When the cell splits in two to form 2 daughter cells
23
New cards
Describe interphase
1. Normal cell function occurs
2. Chromosomes are unwound at the chromatin
2. Chromosomes are unwound at the chromatin
24
New cards
Describe prophase
1. Spindle fibres form- extend from centrioles and the centrioles migrate to poles of cells
2. Chromosomes condense
3. Nuclear envelope breaks down
2. Chromosomes condense
3. Nuclear envelope breaks down
25
New cards
Describe metaphase
1. Chromosomes align at the equator of the cell
26
New cards
Describe anaphase
1. Sister chromatids are separated by spindle fibres and pulled to opposite poles of the cell
27
New cards
Describe telophase
1. Chromosomes reach opposite poles and are enveloped by new nuclear membranes
2. Chromosomes unravel
3. Spindle fibres disintegrate
2. Chromosomes unravel
3. Spindle fibres disintegrate