4.2.3.4 The Phillips Curve
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Phillips curve
shows that in the short-run there is an inverse relationship between improving inflation and improving unemployment
demand pull and cost-push inflation
What causes the inverse relationship in the Phillips curve?
demand-pull inflation
excess demand in economy => businesses need more workers => unemployment drops and wages rise => spending and average price levels rise
cost-push inflation
unemployment falls => more workers in trade union => more power to demand higher wages => workers spend more => average price level rises
short term given the lack of trade union power now
Demand pull infaltion tends to have a bigger effect in the ______________________________
stagflation
both inflation and unemployment are high
policy makers may use the Phillips curve to support higher interest rates, which can bring in revenue for the gov.
Why might policymakers be tempted to ‘exploit’ the Phillips curve?
short-run tradeoff between unemployment and inflation
movement along the SRPC represents the:
conflict between managing inflation and unemployment
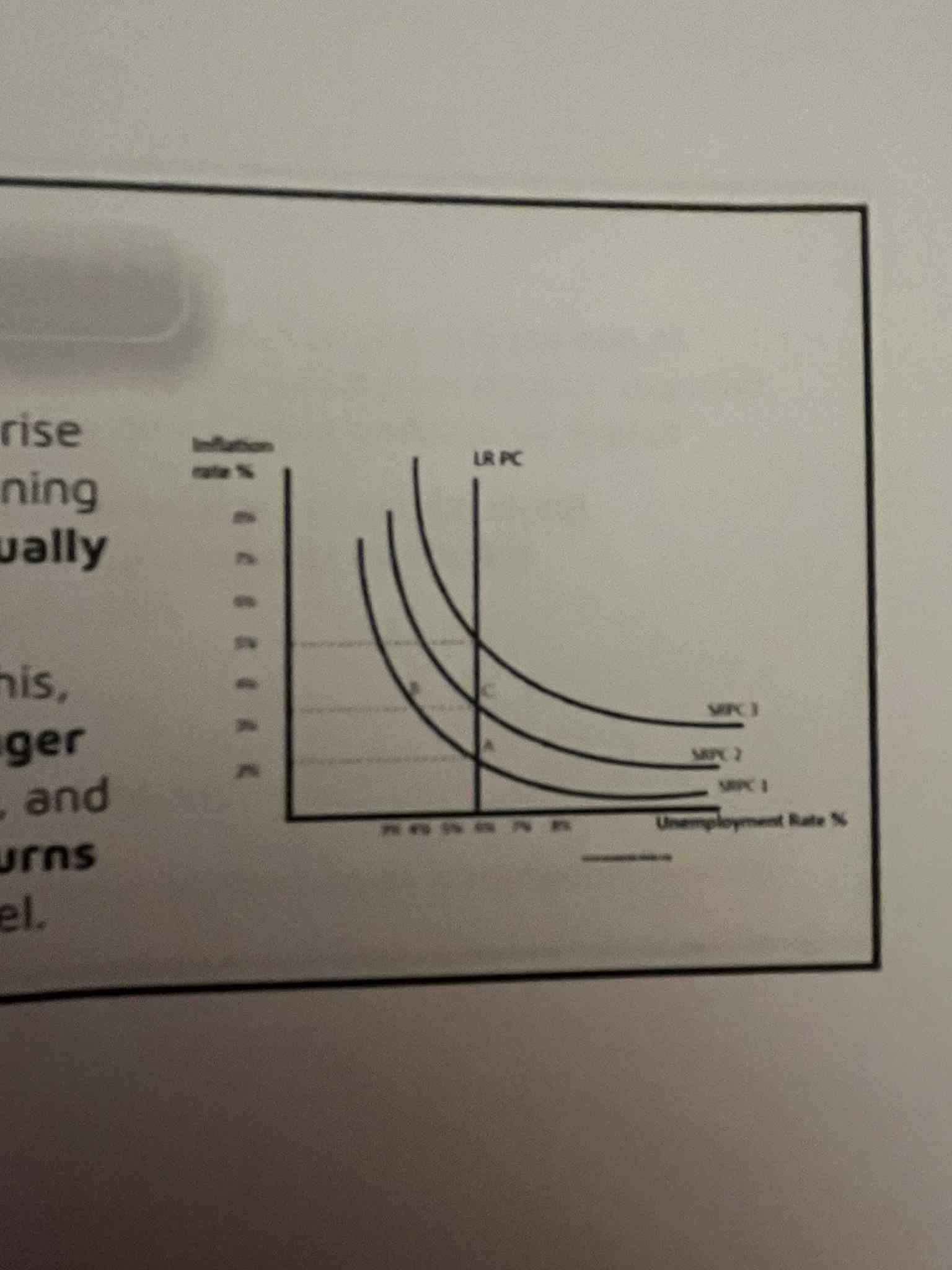
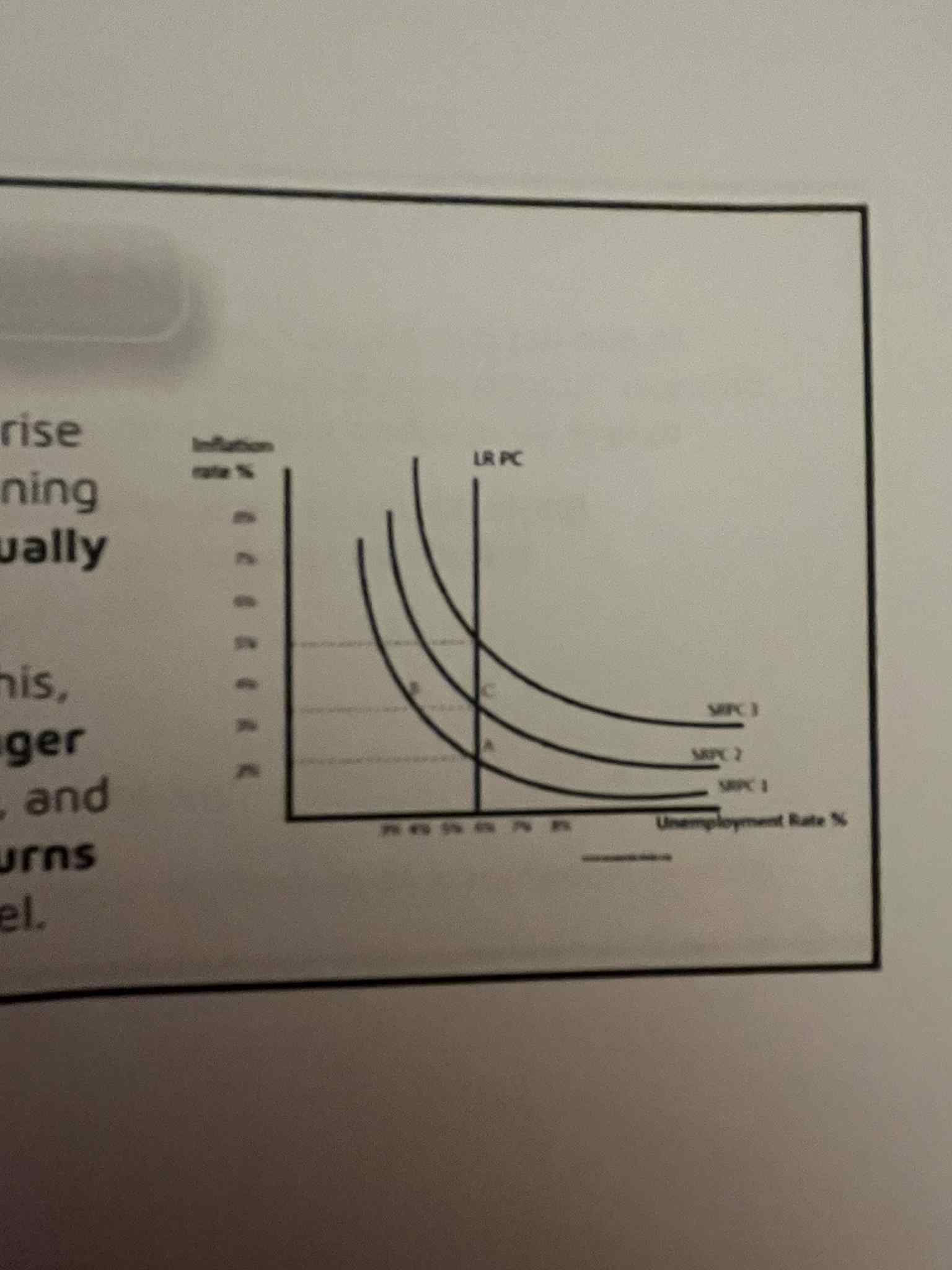
the short-run Phillips curve illustrates the
Milton Friedman
Free market economist
argued that the link of the Phillip’s curve was not that simple and that in the long-run there was no conflict between inflation and unemployment
long-run Phillip’s curve
drawn as a vertical line at the natural rate of unemployment (Un)
natural rate of unemployment
the rate when all those wanting to work at the prevailing real wage rate have found employment and there is no involuntary unemployment
level of unemployment that we can’t go below, thus trying would cause bigger issues
the NRU suggests there is a…
unemployment, increases, spending, tradeoff, higher nominal wages, willing, more, inflation, stay the same, no longer, previous
As ___________ decreases, AD _______ as spending rises(_____). Higher AD means workers demand _______ ________ _____, making them _______ to do ____ hours as they feel their real wages have risen. But wage rise causes _________ meaning their real wages actually ____ ___ ____. Once they realise this, workers __ _______ supply more labour, and unemployment returns to ________ levels.
new normal, decrease, NRU, rising
In the LR Phillips curve, the higher inflation rate becomes the ___ _______(shifting the whole Phillips curve). If we keep trying to ________ unemployment below the ___, inflation will just keep ______
AD, income, positive output gap, real, left, inflation, no change, unemployment
We show workers’ increased willingness to work on a graph via higher __ as people offer more work, increasing their ______, causing a ______ ______ ___, As people realise they are not earning any more in ___ terms, SRAS shifts ____ leaving higher _________ and __ ________ in _______________ and output
institutional factors, e.g. level of welfare, availability of job info., occupational or geographical mobility, labour market regulations/flexibility, hysteresis
Milton Friedman suggested that the NRU is determined by:
reducing unemployment benefits, reducing workers’ rights, reducing restrictions on firm’s appointments, giving retraining opportunities
Through supply-side policies, the gov. ought to be able to reduce NRU for instance, by…
rate of unemployment is independent of the rate of inflation
The Long run Phillips curve, in efffect, says that the …
spending, full employment, inflation, consumption, natural rate
The argument behind the LR Phillips curve assumes that we start at a point where inflation is 0 and unemployment is at it s natural level.
In an attempt to bring down unemployment, the gov. increases ____________.
This increases AD and lowers the unemployment rate. With the economy close to ____ ____________, workers have more power to demand higher wages, so ___________ rises.
The higher price level brings ______________(in real terms) back down and firms respond, returning unemployment ot its ___________ ____
equilibrium, demand, temporary, SRAS, normal capacity, higher,
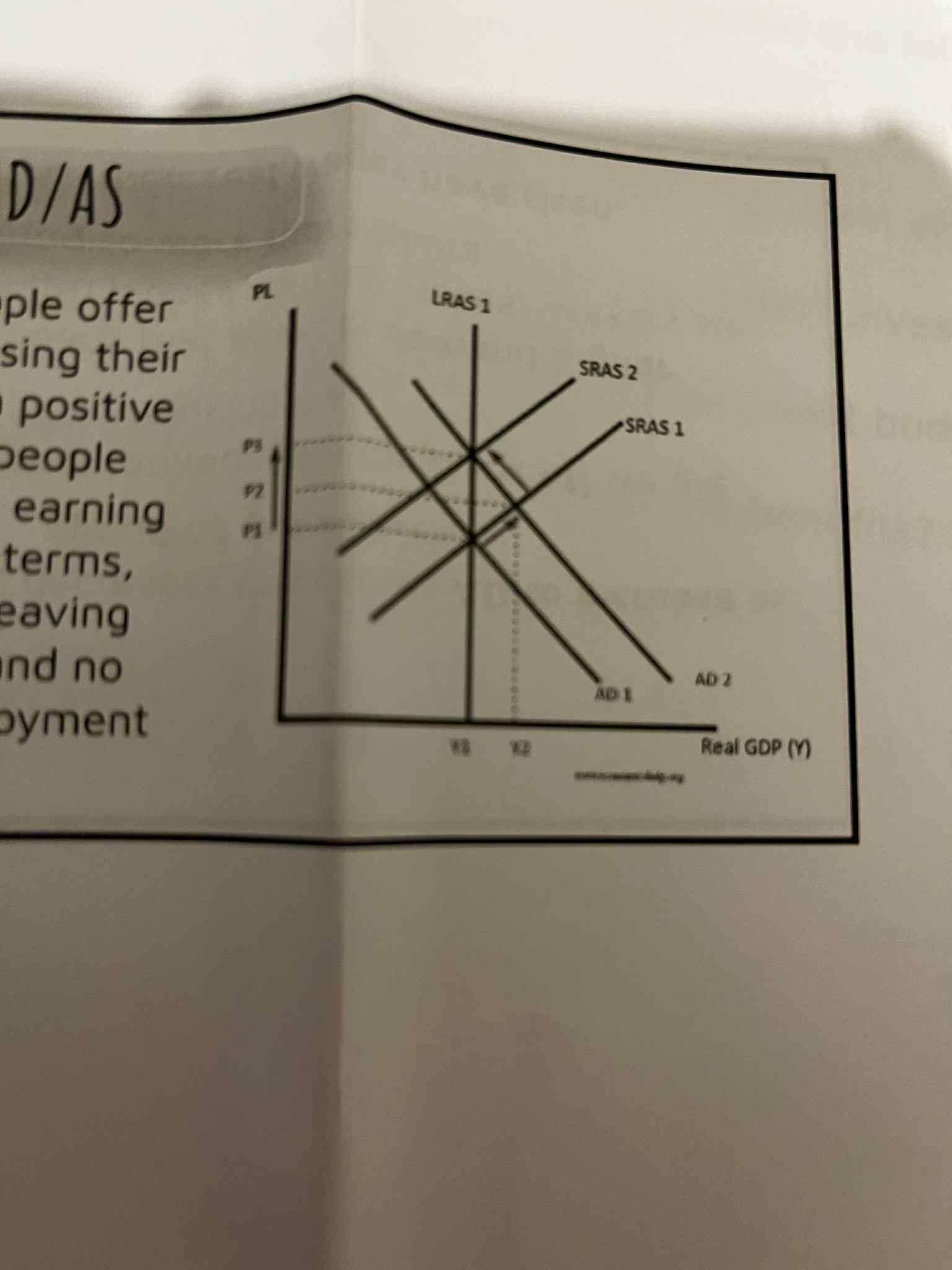
We can see the same process of the argument of the LR Phillips curve in terms of AD and AS.
Starting from an __________ at point A, the boost to _______, shifts the AD curve leading to a _________ new equilibrium at B.
This increase in wage costs however moves _____ to the left which return output to the ________ ________ level but the price level is now ________ than previously this new equilibrium is at point C
conflict, long run, lower, NRU, attractive, unemployment
Supply-side economists conclude that there is no inherent ________, at least in the ____ ___, between the goals of low unemployment and low inflation.
The challenge is to create a set of policies that _____ the ___, by making work more _______ and ___________ less attractive and encouraging economic growth through enterprise