2.1 - Cell Structure and Function
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
How do ribosomes reflect the common ancestry of all known life?
Through their presence in all organisms, their fundamentally similar structure and function in protein synthesis, and the high degree of conservation of their ribosomal RNA (rRNA) sequences
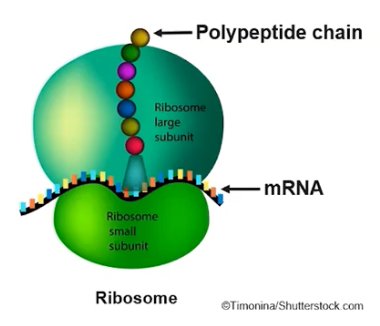
What is the structure and function of ribosomes?
Consist of two subunits that are not membrane-enclosed
Has a small subunit and a large subunit that come together
Ribosomes are made of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and proteins
Ribosomes synthesize protein according to mRNA sequences
Ribosomes make proteins for the cell according to the messenger RNA sequences
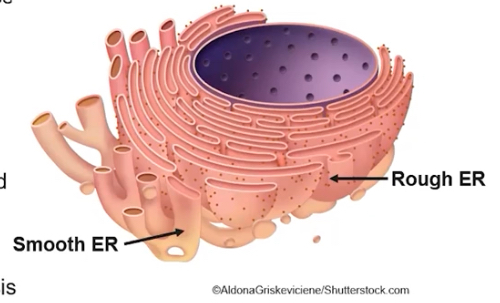
What is the structure and function of the ER (in three ways)?
Provides mechanical support
Plays a role in intracellular transport
Rough ER carries out protein synthesis on ribosomes that are bound to its membrane
What is the structure and function of the rough ER?
Has ribosomes attached to its membrane
Compartmentalizes(organizes) the cell
Associated with packaging the newly synthesized proteins made by attached ribosomes for possible export from the cell
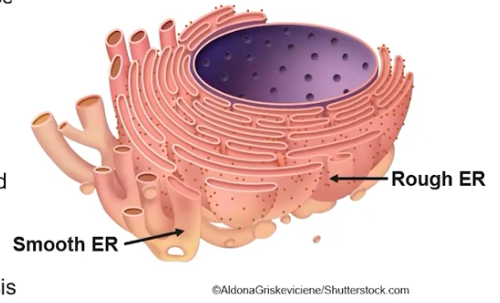
What is the structure and function of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum?
Does not have ribosomes attached
Functions include detoxification and lipid synthesis
What is detoxification in the smooth ER?
The process by which the body removes poisonous or harmful substances, or neutralizes their toxic properties
What is lipid synthesis in the smooth ER?
The set of metabolic processes, also known as lipogenesis, by which cells create complex lipids from simpler precursors, primarily converting carbohydrates into fatty acids
What do structural differences between the rough ER and smooth ER lead to?
Functional differences
What is the structure and function of the Golgi complex?
Series of flattened membrane-bound sacs(Cisternae) found in eukaryotic cells
Involved in the correct folding and chemical modification of newly synthesized proteins and packaging for protein trafficking
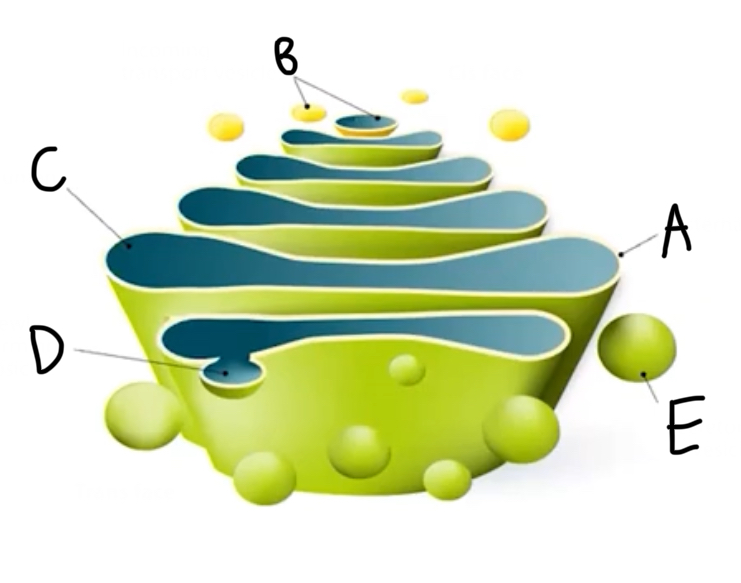
A: Cisternae
B: Incoming transport vesicles
C: Lumen
D: Newly forming vesicle
E: Secretory vesicle
What are vesicles in the Golgi complex?
Small, membrane-bound sacs that transport cellular products to, from, and within the organelle
What are incoming transport vesicles in the Golgi complex?
Membrane-bound bubbles that bud off from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and deliver proteins, lipids, and other molecules to the cis face of the Golgi complex for further processing and modification
What is lumen in the Golgi complex?
The internal, enclosed space within the Golgi apparatus’s flattened sacs (Cisternae)
What are secretory vesicles in the Golgi complex?
Membrane-bound sacs that bud off from the trans Golgi network to transport and release proteins, hormones, neurotransmitters, and other molecules from the cell
What is the structure and function of the mitochondria?
Has a double membrane
Outer membrane is smooth and inner membrane is highly convoluted, forming folds called cristae
Capture energy from macromolecules
Functions in production of ATP energy that eukaryotic cells can use for cell work
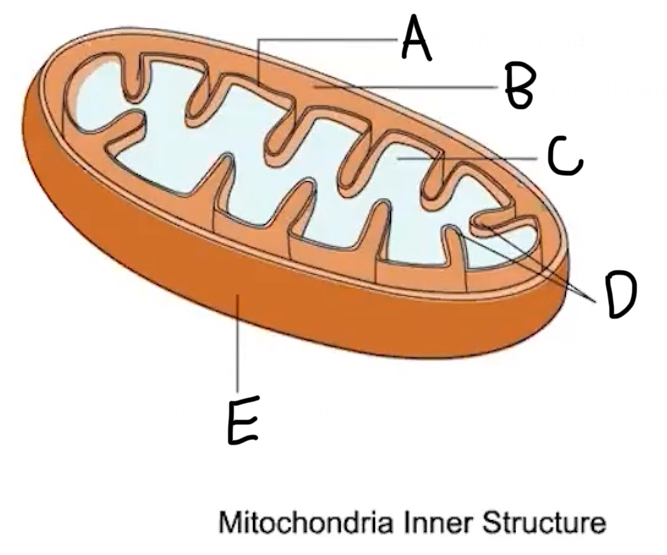
A: Inner membrane
B: intermembrane space
C: Matrix
D: Cristae
E: Outer membrane
Where do the Krebs cycle (citric acid cycle) reactions take place in the cell?
E: Outer membrane
Matrix of the mitochondria
Where in the mitochondria do electron transport and ATP synthesis occur?
Inner mitochondrial membrane
What results from folding of the inner membrane of the mitochondria?
Increases surface area, allowing more ATP to be made
What does the double membrane in the mitochronia provide?
Provides compartments for different metabolic reactions
What is the structure and function of the lysosome?
Membrane-enclosed sacs found in some eukaryotic cells that contain hydrolytic enzymes
Hydrolytic enzymes can be used to digest a variety of materials such as damaged cell parts or macromolecules
How can lysosomes contribute to cell function in three ways?
Intracellular digestion
Recycling of organic materials
Programmed cell death (apoptosis)
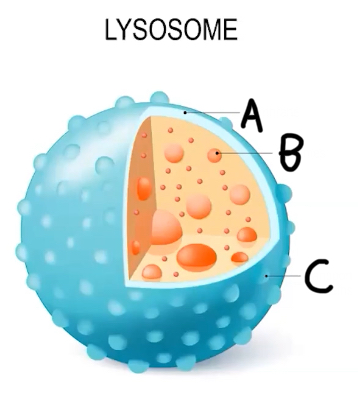
A: Membrane
B: Enzymes
C: Transport proteins
What is the structure and function of the vacuole?
Membrane-bound sacs found in eukaryotic cells
Play variety of roles ranging from storage of water and other macromolecules to the release of waste from a cell
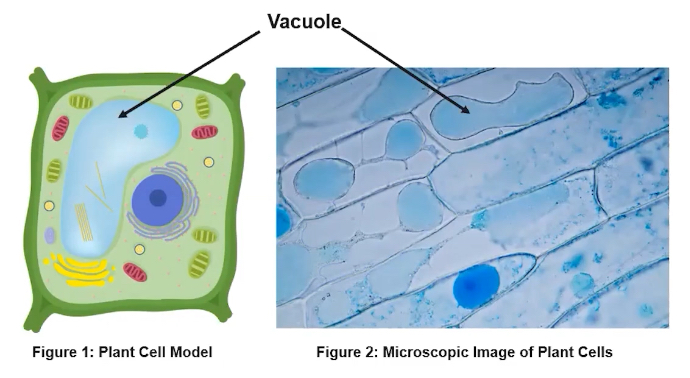
How do vacuoles aid plants?
Aid in retention of water for turgor pressure
What is turgor pressure?
Internal cellular force, usually caused by water pushing up against the plasma membrane and cell wall
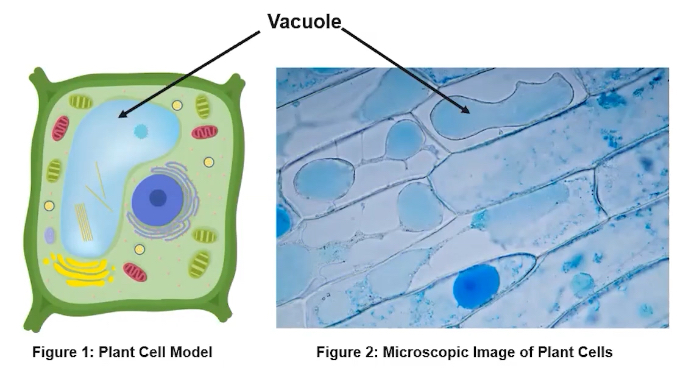
Would Vacuole A or Vacuole B have more turgor pressure?
B, because in A you can see the membrane of the vacuole; it’s not pushing up against its plasma membrane and cell wall; can’t see membrane of vacuole in cell B because it is more filled with fluid and pushing up against its membrane and cell wall; therefore, B would have more turgor pressure
What is the structure and function of the chloroplast?
Found in eukaryotic cells such as photosynthetic algae and plants
Double outer membrane
Specialized from capturing energy from the sun and producing sugar for the organism
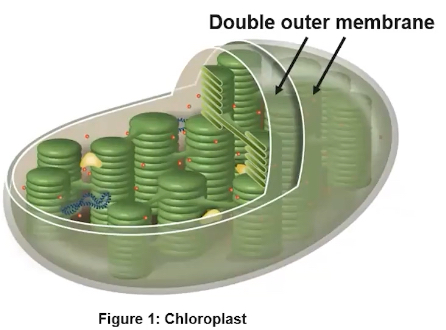
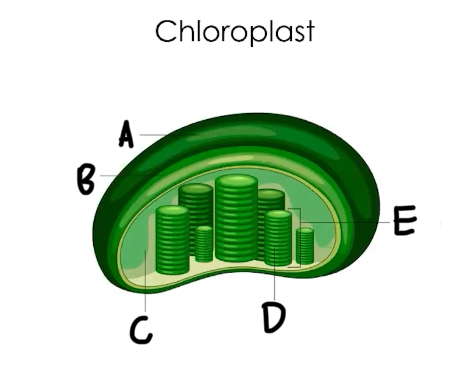
A: Outer membrane
B: Inner membrane
C: Stroma
D: Thylakoid
E: Granum
What is the thylakoid in the chloroplast of the cell?
Highly folded membrane compartments that are organized in stacks called grana
What do the membranes of the chloroplast contain?
Membranes contain chlorophyll pigments that comprise the photosystems
What is the stroma of the chloroplast of the cell?
Fluid between the inner chloroplast membrane and outside thylakoids
What kind of reaction occurs in the stroma of the chloroplast?
Carbon fixation (Calvin-Benson cycle) reaction
Where can electron transport proteins be found in the chloroplast?
Between the photosystems, embedded in the thylakoid membrane
Where do light-dependent reactions occur in the cell?
The chloroplast
How does the folding of the internal membranes of chloroplasts affect light-dependent reactions?
Increases the surface area and efficiency
What is the structure and function of the genome?
Chromosomes made of nucleotide sequences that form a double helix
Primary function is to store genetic information to guide protein production and other cellular functions
What is the structure and function of the nucleus?
Contains and protects the cell’s DNA (chromatin) and is the control center for gene expression and cell growth
What is the structure and function of the ER (endoplasmic reticulum)?
Network of membrane tubes within the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells
What is the difference between a prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell?
Euka has a nucleus while euka doesn’t
Euka: larger and more complex
Pro: divide through binary fission (simpler form of asexual reproduction) while eukas divide by a more complex process called mitosis
Location of DNA: in eukas, most of the DNA is in the nucleus which is bounded by a double membrane
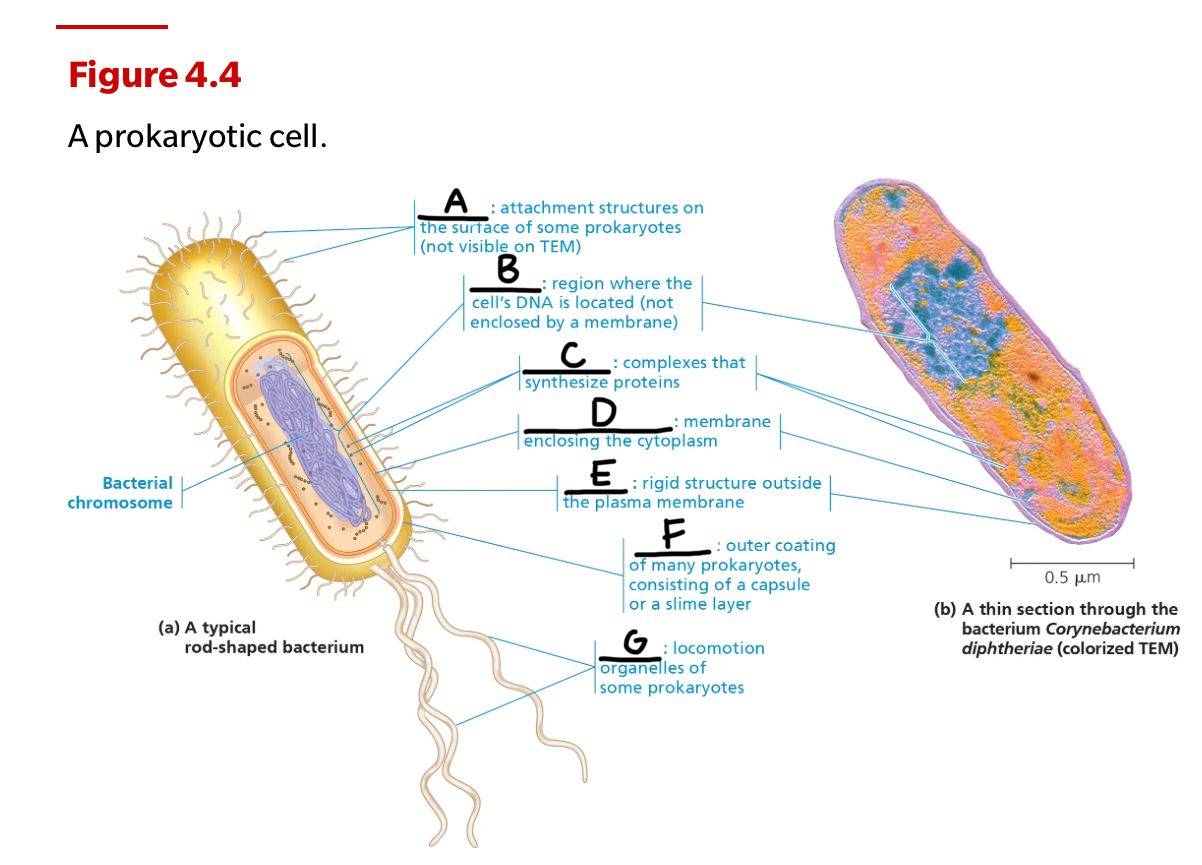
A: Fimbraie
B: Nucleoid
C: Ribosomes
D: Plasma membrane
E: Cell wall
F: Glycocalyx
G: Flagella
What do all living cells contain, and what does it reflect?
A genome and ribosomes, and it reflects the common ancestry of all known life
What is synthesis?
The process by which living organisms, or cells within them, create more complex organic compounds from simpler precursors through chemical reactions, often aided by enzymes
What do ribosomes synthesize and what does it originate from?
Synthesizes protein according to mRNA sequence and the instructions that are encoded in that mRNA sequence originate from the genome of the cell
The ribosomes that are found in both cell types are not __________________ structures.
Membrane-closed
Correct answer: B
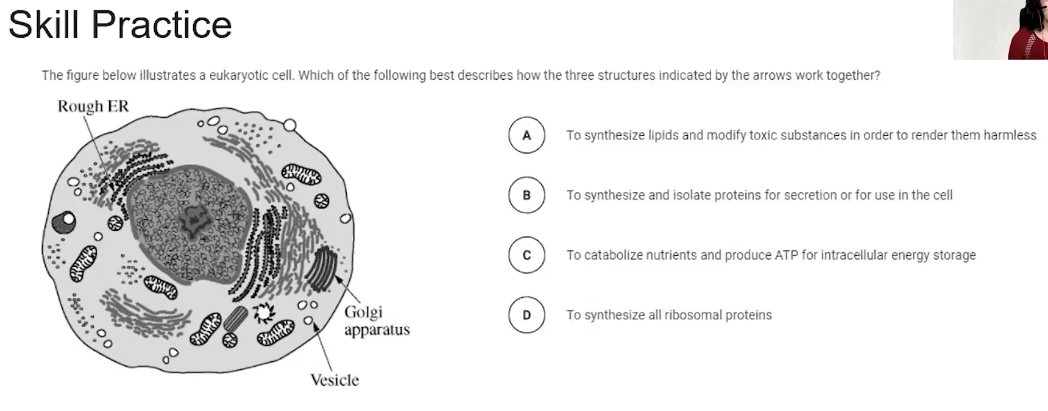
How do subcellular components and organelles interact and contribute to the function of the cell?
Through direct contact via membrane contact sites (MCSs) and vesicular trafficking, allowing for the exchange of molecules p, the division and shaping of compartments, and the coordination of metabolic processes
What are the structural features of a cell that allow organisms to capture, store, and use energy?
The organelles mitochronia (in all eukaryotes) and chloroplasts (in plants and algae)
Correct answer: B
What are all cells bound by?
Selective barrier called the plasma membrane
What is cytosol in a cell, and what is its structure and function?
Jelly-like fluid portion of the cytoplasm, distinct from the organelles within it
Primarily composed of water, ions, small molecules, and water-soluble proteins
Serves as the medium for many metabolic processes, such as glycolysis, and for the transport and signaling of molecules within the cell
What do all cells always have?
Chromosomes and ribosomes
What does the plasma membrane of the cell serve as?
A selective barrier that allows passage of enough oxygen, nutrients, and wastes to service the entire cell
For each square _________ of membrane, only a limited amount of a particular substance can cross per _______, so the ratio of surface area to volume is critical.
Micrometer, second
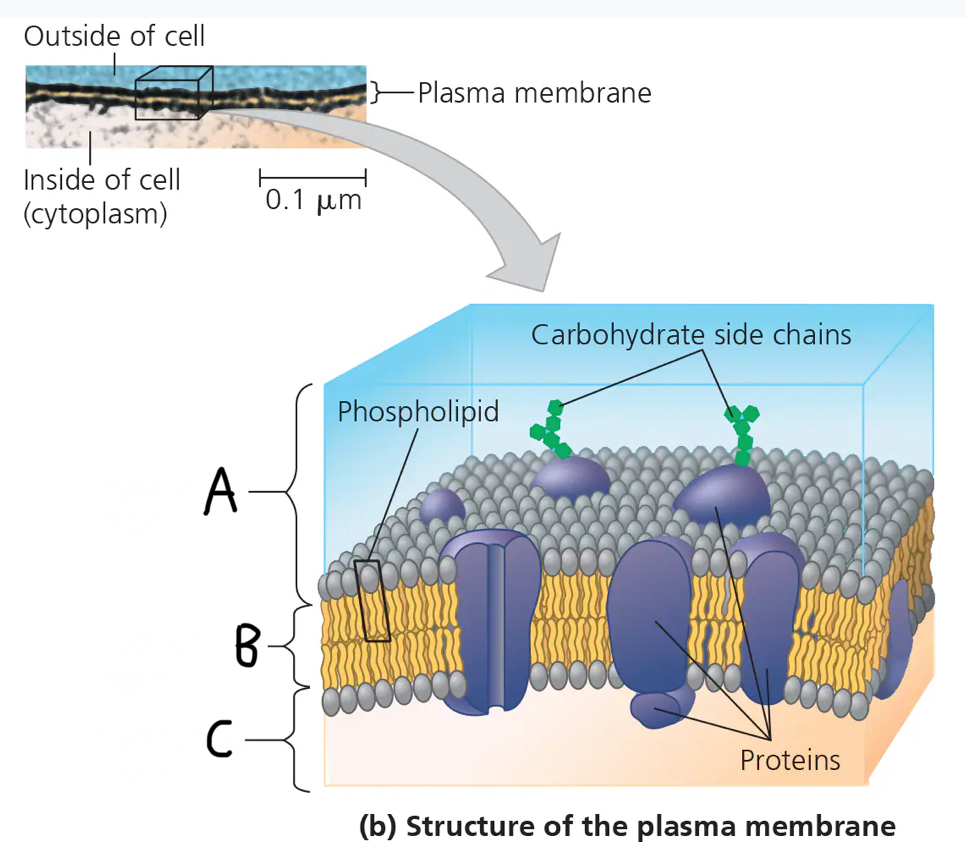
A: Hydrophilic region
B: Hydrophobic region
Hydrophilic region
What formula do you use to calculate the volume of a sphere?
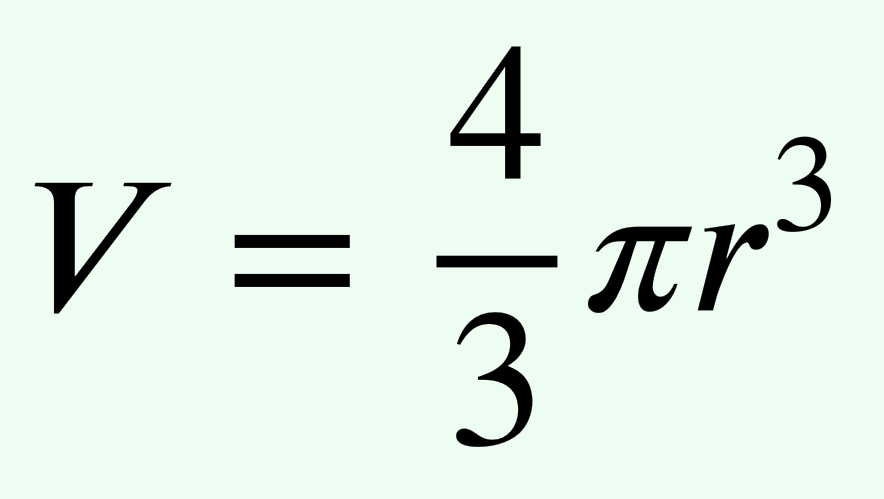
What formula do you use to calculate the surface area of a sphere?
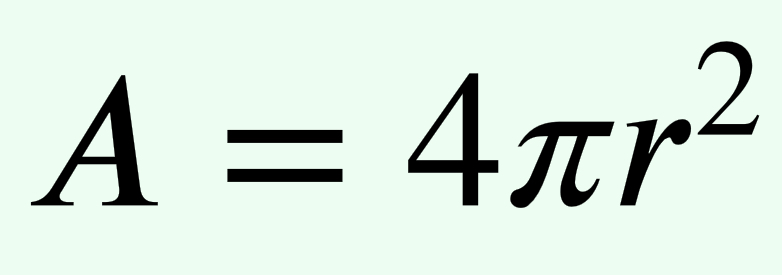
What is microvilli?
Long, thin, projections from a cell’s surface
What is the basic fabric of most biological membranes?
Double layer of phospholipids and other lipids