2.2 HUMANISTIC PERSPECTIVE
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
HUMANISTIC PERSPECTIVE
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
HUMANISTIC approach to personality
Abraham Maslow and Carl Rogers
Abraham Maslow & Carl Rogers their theories
emphasize human strengths & aspiration, conscious free will, and the fulfillment of human potential.
present optimistic image of human nature and describe us as active, creative beings concerned with growth & self-actualization.
Maslow
research on creative, independent, self-sufficient, fulfilled adults.
people are born with set of instinctive needs that enable us to grow, develop, and fulfill our potential
The Hierarchy of Needs
needs that activate and direct human behavior.
physiological (lowest scale)
safety
belongingness and love,
esteem,
self-actualization (highest scale)
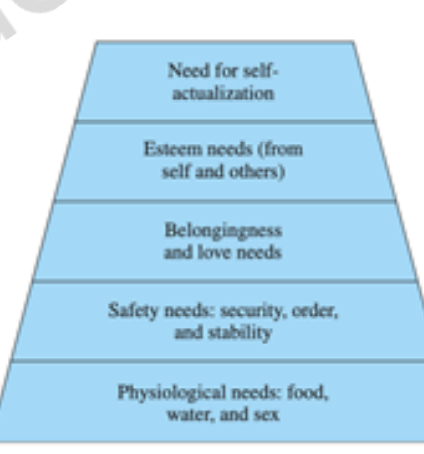
Lower needs must be at least partially satisfied before higher needs become influential.
Conditions for Achieving Self-Actualization
We must be free of constraints imposed by society and by ourselves.
We must not be distracted by the lower-order needs.
We must be secure in our self-image and in our relationships with other people, and we must be able to love and be loved in return.
We must have a realistic knowledge of our strengths and weaknesses, virtues and vices.
Maslow called lower needs deficit, or deficiency, needs
failure to satisfy them produces a deficit or lack in the individual.
Physiological Needs
Basic survival (food, water, air, sleep)
Safety Needs
Feeling secure (shelter, job, health, stability).
Love & Belonging
Social connections (friends, family, relationships).
Esteem Needs
Feeling respected (self-confidence, achievements, recognition)
Self-Actualization
Personal growth (creativity, fulfilling potential, meaning in life).
Short Example for Notes:
Anna was homeless and focused on finding food 🍞 (Physiological). Then, she got a job 💼 and an apartment 🏠 (Safety). Later, she made friends ❤ (Love & Belonging). After some time, she gained confidence through her work 🏆 (Esteem). Finally, she started a charity to help others 🌍 (Self-Actualization)
Key Exam Tip:
Basic needs (1-2) = Survival.
Psychological needs (3-4) = Social & Self-worth.
Growth need (5) = Reaching full potential.
Metamotivation
drive beyond basic needs, focusing on personal growth, self-fulfillment, and achieving one's highest potential.
It is what motivates self-actualized people in Maslow's hierarchy of needs (beyond the basic and psychological levels).
Key Aspects of Metamotivation:
✅ Found in people who have already satisfied their basic needs (food, safety, love, esteem).
✅ Driven by growth, creativity, and purpose, not survival.
✅ Linked to self-actualization (e.g., personal development, helping others).
✅ Opposite of deficiency motivation (D-motivation), which focuses on lacking needs.
✅ Leads to peak experiences (moments of intense happiness and fulfillment).
Short Example for Notes: metamotivation
"Marie has everything she needs—food, safety, love, and respect.
Instead of focusing on money, she spends her time teaching poor children for free, feeling deeply fulfilled.
This is metamotivation because she seeks growth and purpose, not just survival.
Metamotivation & D-Motivation
Metamotivation = Growth & Fulfillment 🌱
D-Motivation = Basic Needs & Deficiencies ❌
Carl Roger
person-centered therapy = improved personality is centred within the person
insisted current feelings and emotions have a greater impact on personality.
personality was only understood by subjective experiences.
Roger term: “fully functioning person”
actualize the self
the inborn tendency to actualize, to develop our abilities and potentials to the fullest
Roger term: Self-insight
✅ Self-Insight = Awareness of one’s true thoughts, feelings, and behaviors.
✅ Essential for personal growth and self-actualization.
✅ People with high self-insight understand their strengths, weaknesses, emotions, and motivations.
✅ Therapy Goal: Rogers believed that client-centered therapy helps people gain self-insight by reducing incongruence between their real self and ideal self.
Example of Rogers self-insight
"Emma used to believe she was always happy, but through therapy, she gained self-insight and realized she was actually suppressing sadness. This awareness helped her grow emotionally and become more authentic.
Actualizing Tendency CARL ROGER
encompasses all of our physiological and psychological needs
serves as motivation to maintain the organism, providing for sustenance and survival.
Organismic Valuing Process
governing process throughout the life span
Positive experiences = promote actualization & are evaluated as good and desirable; we assign them a positive value.
Negative experiences = perceived as hindering actualization & are undesirable, earn a negative value.
self-concept CARL ROGER
involves distinguishing what is directly & immediately a part of the self from the people, objects, and events that are external to the self.
our image of what we are, what we should be, and what we would like to be
Positive Regard
when self emerges infants develop a learned need
includes acceptance, love, and approval from other people, most notably from the mother during infancy.
crucial to personality development
Freud´s version of superego
Unconditional positive regard
Approval granted regardless of a person’s behavior.
In Rogers’s person-centered therapy, the therapist offers the client unconditional positive regard.
Positive self-regard
The condition under which we grant ourselves acceptance and approval.
Conditions of Worth
evolve from positive regard leading to positive self-regard.
Conditional positive regard
when parents not always react depending on a child´s behaviour→ the child understand that sometimes they are prized, and sometimes they are not
incongruence ROGER
a mismatch or inconsistency between a person’s self-concept and their actual experiences or behavior.
is when your real self (how you truly feel or act) does not match your ideal self (how you think you should be), or when your self-image doesn’t align with reality.
due to: We learn to evaluate experiences, and to accept or reject them in terms of whether they bring positive regard from others.
Characteristics of Fully Functioning Persons ROGER
Awareness of all experience; open to positive as well as negative feelings
Freshness of appreciation for all experiences
Trust in one’s own behavior and feelings
Freedom of choice, without inhibitions
Creativity and spontaneity
Continual need to grow, to strive to maximize one’s potential in a state of actualizing