Ch. 42 RHS Slides
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
Extraoral radiographs are useful in
evaluating large areas of the skull and jaws but are not recommended for detection of subtle changes, like caries or early periodontal changes
what type of x-ray is cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) (intra/extraoral?)
extraoral
Panoramic imaging allows the dentist to ________on a single image
view the entire dentition and related structures
Panoramic imaging allows the dentist to view the entire dentition and related structures in how many images
one single image
panoramic images were not recommended for________
diagnosing dental caries or periodontal disease or lesions because of the overlapping of posterior contact areas
full-featured digital panoramic units with a special ___-arm
C
Can panarox do bitewing? good or bad?
yes and its fine but better to use bitewing paralleling
Panoramic digital images produced with these machines can show____________
small interproximal carious lesions
patient receives less radiation exposure on panorex compared with the full-mouth survey. (true or false)
True
Two types of panoramic machines
Film-based imaging
Direct digital imaging
The main difference between direct digital panoramic imaging and film-based panoramic imaging is the __________
image receptor
does direct digital use senor array or film? is the image produced right away or does it have to develop?
Digital units use a sensor array rather than film, and the image is produced immediately on the computer monitor rather than on film after processing
True or False- In panoramic imaging, both the film/sensor and the tubehead rotate around the patient
True
Focal trough is an __________
imaginary three-dimensional curved zone in which structures appear clear on a panoramic radiograph
the vertical angulation of the panoramic tubehead is or is not adjustable
is not
for pano each head positioner consists of a _________________
chin rest, a notched bite-block, a forehead rest, and lateral head supports or guides
what can be adjusted in pano- mA, kVp, time
only mA and kVp. exposure time cannot be changed for panorex
what are ghost images
If all metallic or radiodense objects are not removed before exposure, a “ghost” image results
Do you use thyroid collar and lead apron when taking panorex
no thyroid collar yes lead apron
what happens if a patient’s lips arent closed on the bite-block during exposure of a panoramic film.
dark radiolucent shadow that obscures the anterior teeth
during panorex the tongue must be in contact with _______ during exposure of a panoramic film. what happens if not?
the palate; a dark radiolucent shadow that obscures the apices of the maxillary teeth
the positioning of the patients chin is also called
positioning of the Frankfort plane
If the Frankfort plane is incorrect and the patient’s chin is positioned too high or is tipped upward:
Hard palate and the floor of nasal cavity will appear superimposed over the roots of the maxillary teeth
Detail in the maxillary incisor region will be lost
Maxillary incisors will appear blurred and magnified
A “reverse smile line” will be apparent on the radiograph
If the Frankfort plane is incorrect and the patient’s chin is positioned too low or is tipped downward:
The mandibular incisors will appear blurred
Detail in the anterior apical regions will be lost
The condyles will not be visible
An “exaggerated smile line” will be apparent on the radiograph
If the patient’s anterior teeth are positioned too far back on the bite-block or posterior to the focal trough, the anterior teeth appear___________
“fat” and out of focus on the radiograph
If the patient’s anterior teeth are not positioned in the groove on the bite-block and are too far forward or anterior to the focal trough, the teeth appear________
“skinny” and out of focus
If the patient is not standing or sitting with a straight spine, the cervical spine appears ______________
as a radiopacity in the center of the film and obscures diagnostic information
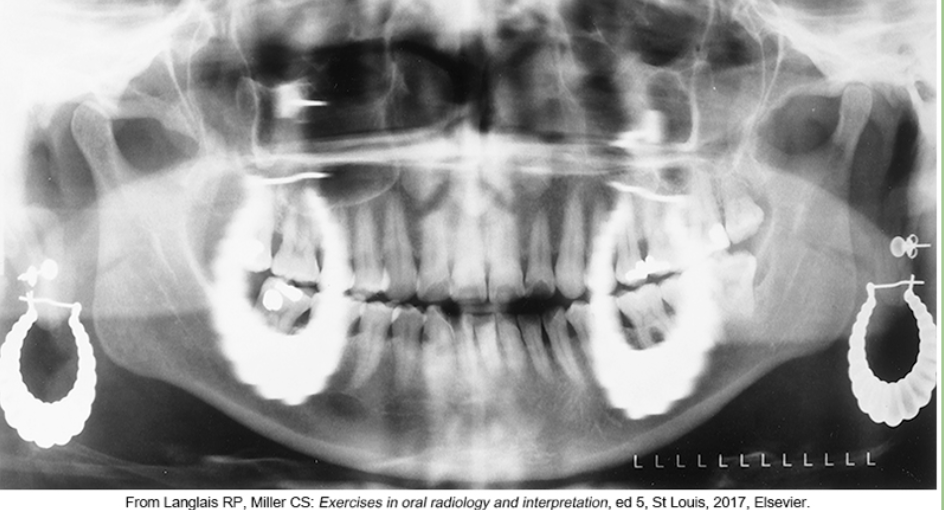
whats the problem
wearing earrings
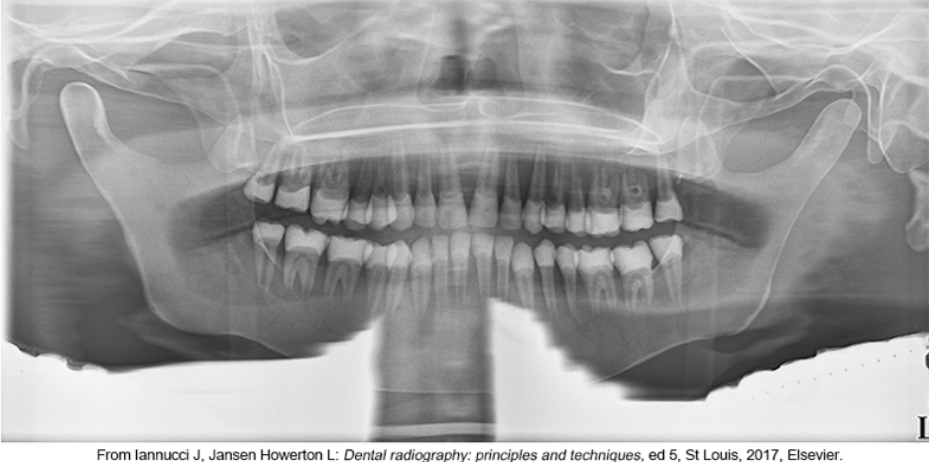
what is the problem
thyroid collar
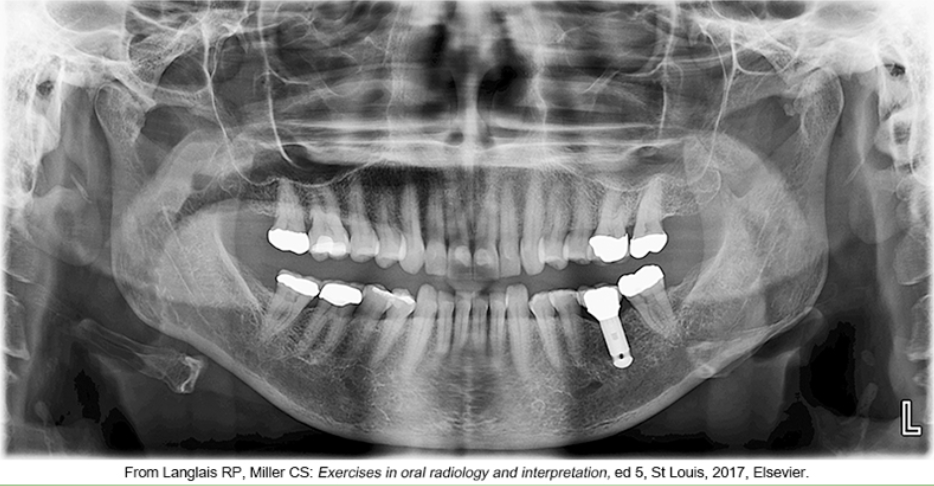
whats the problem
lips arent closed and tongue isnt on palate
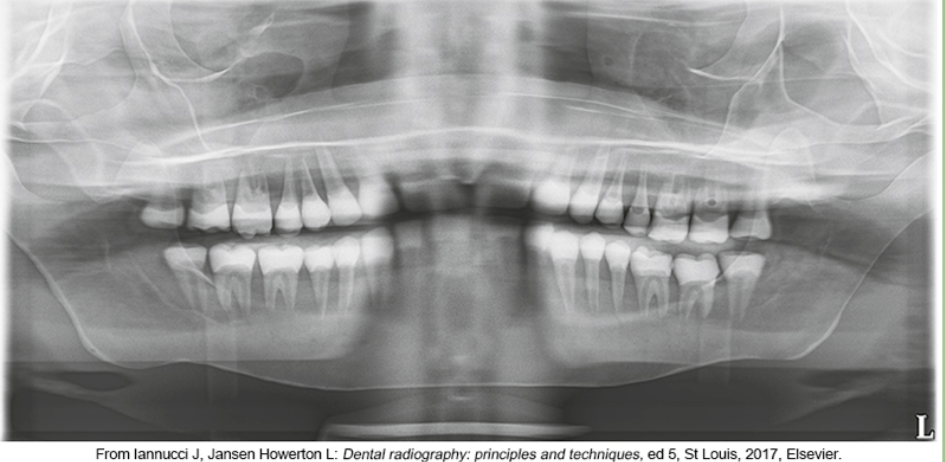
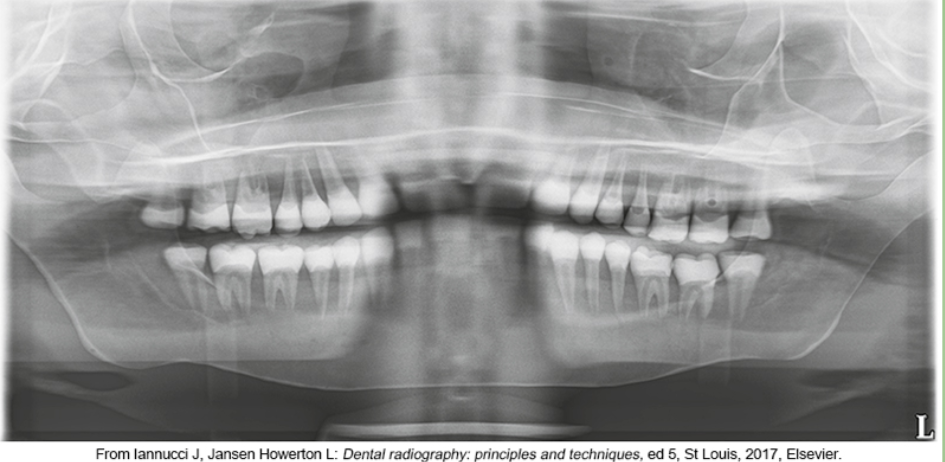
whats the problem
chin too high
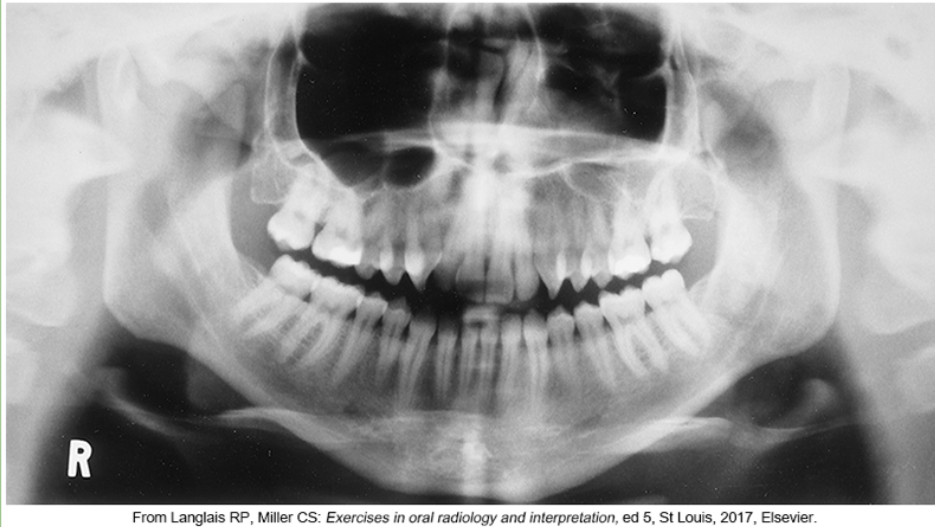
whats the problem
chin too low
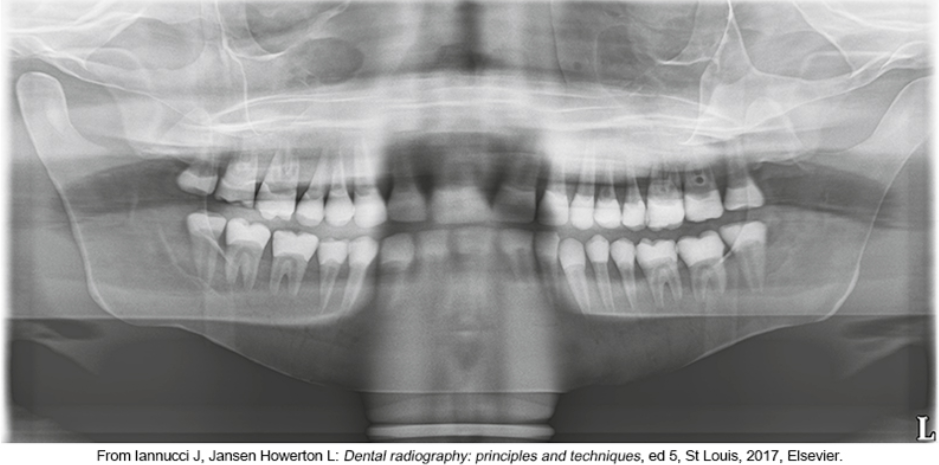
whats the problem
patient’s anterior teeth are positioned too far back on the bite-block
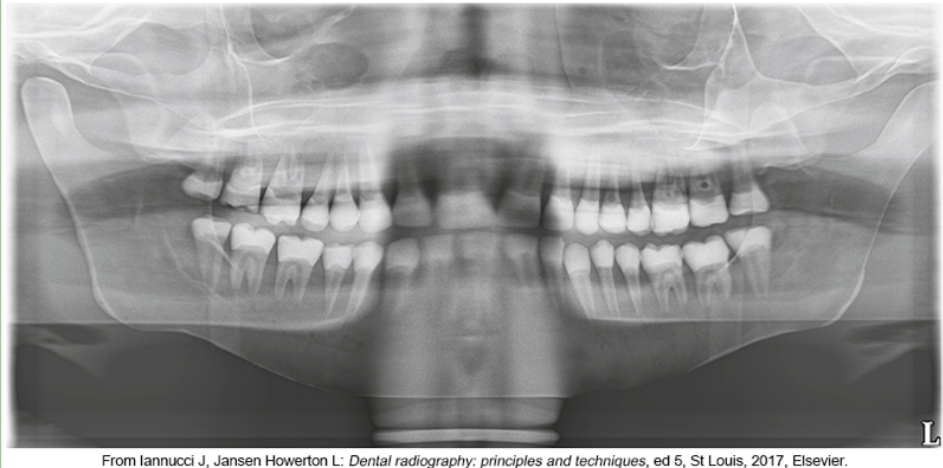
whats the problem
patient’s anterior teeth are not positioned in the groove on the bite-block and are too far back wider teeth
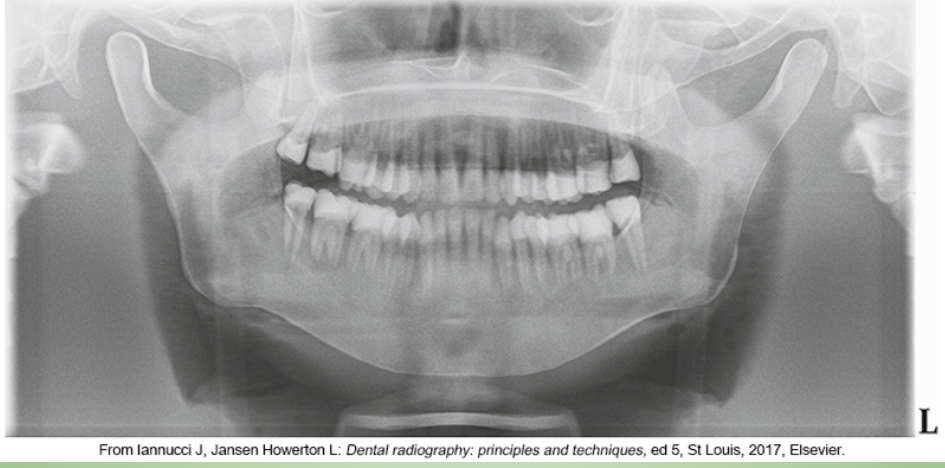
whats the problem
patient’s anterior teeth are not positioned in the groove on the bite-block and are too far forward or anterior to the focal trough- skinny
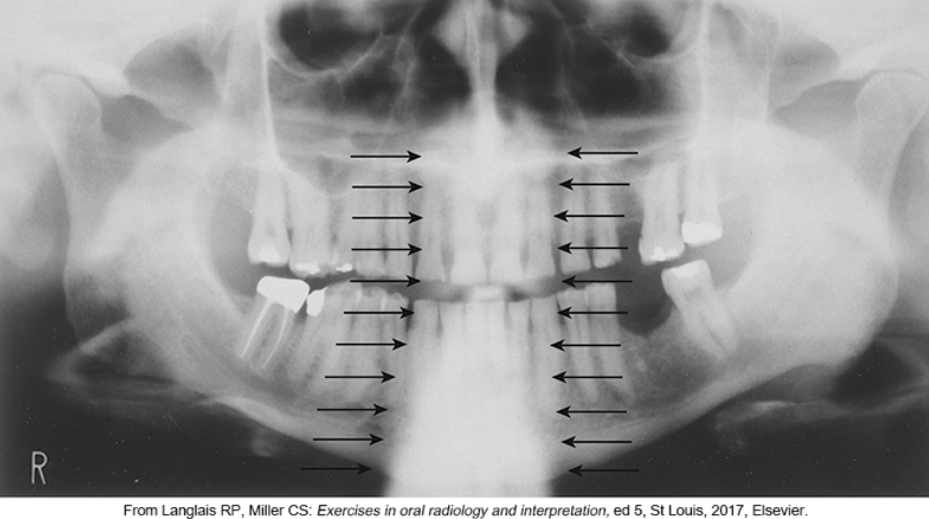
whats the problem
patient is not standing or sitting with a straight spine
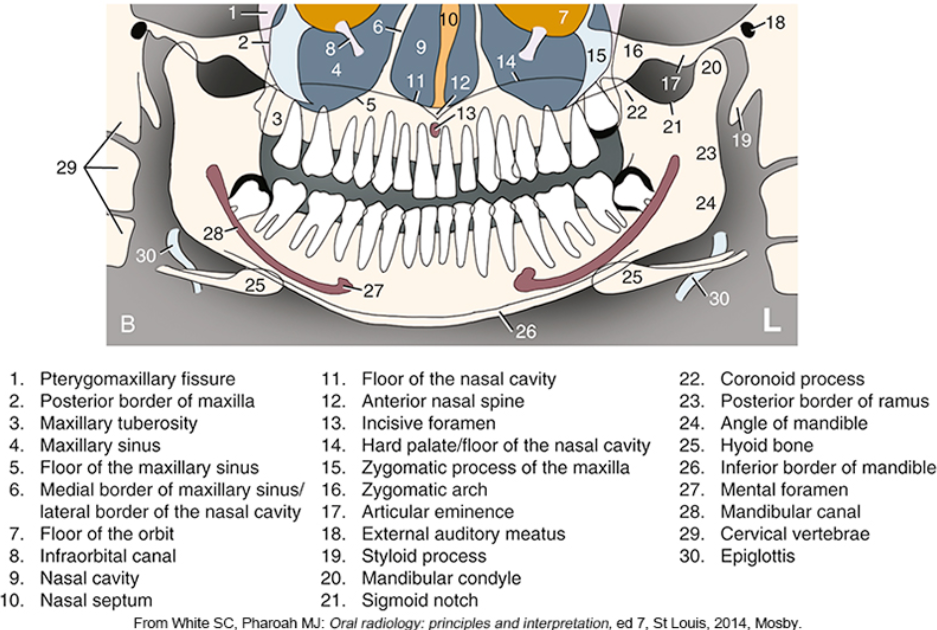
what is #2
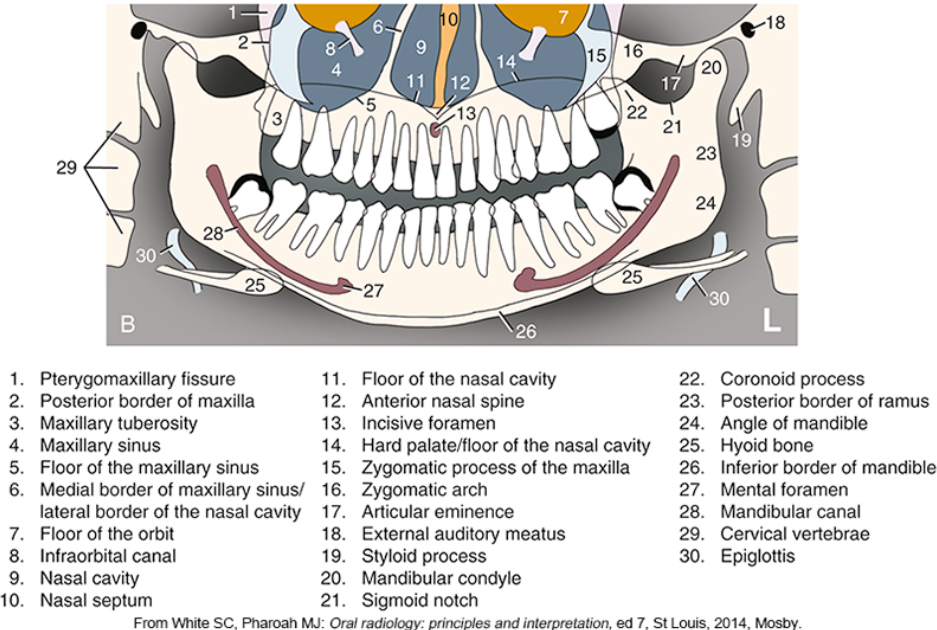
what is #3
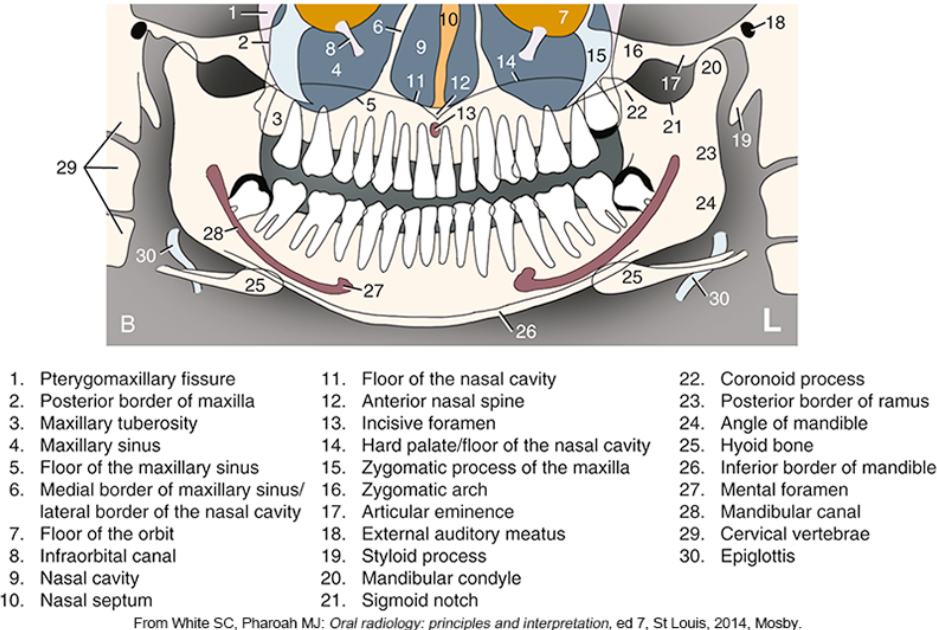
what is #4
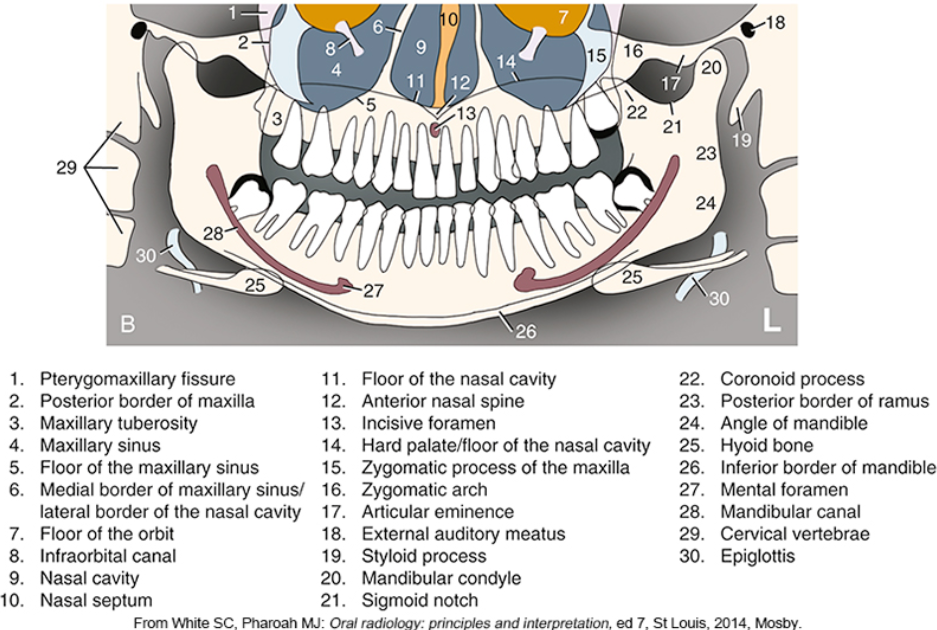
what is #5
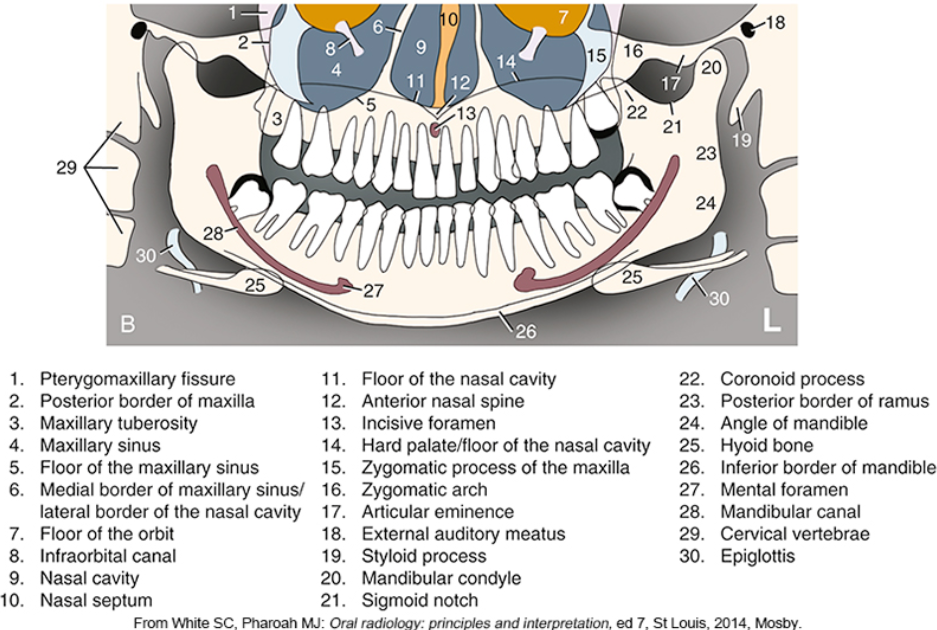
what is #6
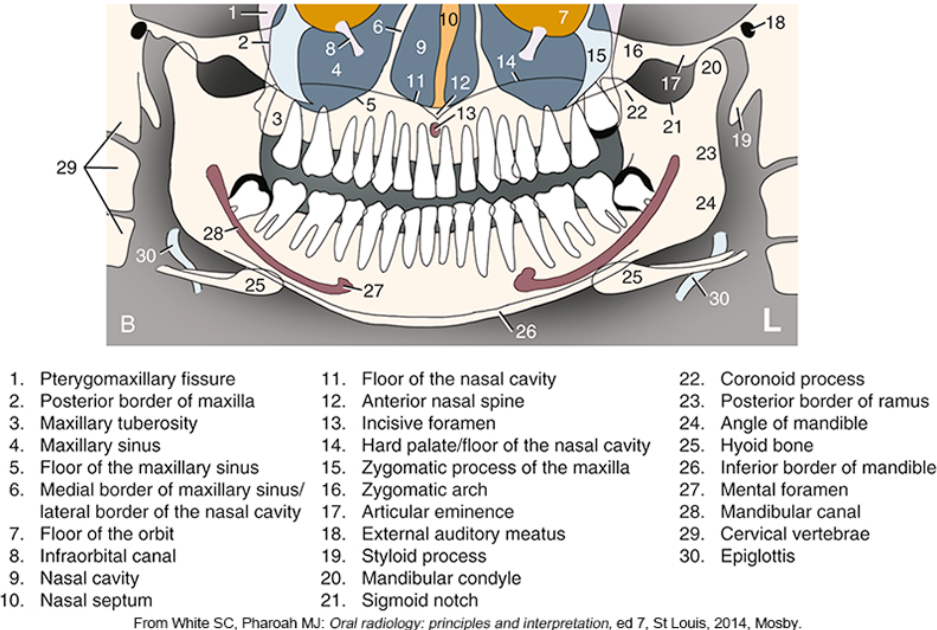
what is #9
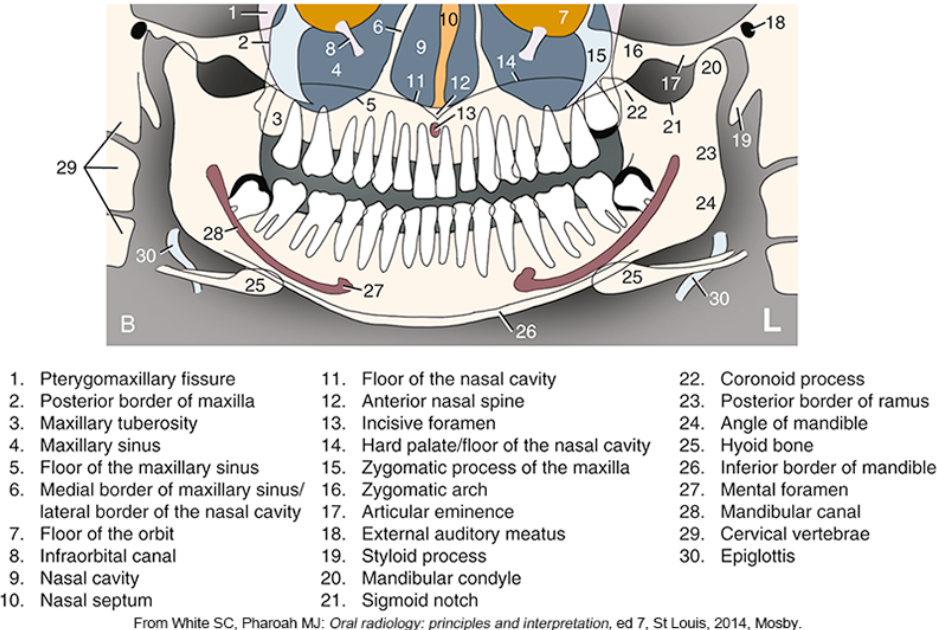
what is #10
what is #11
what is #12
what is #13
what is #14
what is #15
what is #16
what is #18
what is #20
what is #22
what is #23
what is #24
what is #25
what is #26
what is #27
what is #28
During a cone beam CT examination, the arm rotates around the patient’s head in a _____________
complete 360-degree rotation
While doing CT cone beam, it takes anywhere from _______ (how many) two-dimensional (2D) images that the software collects
200 to 600
CBCT gives a 2D or 3D or 1D image
3D
what does CBCTThe proper placement of implants
The proper placement of implants
The extraction of impacted teeth
Determining the exact location of the mandibular nerve prior to surgery
The most common skull radiographs used in dentistry include:
Lateral cephalometric projection
Posteroanterior projection
Temporomandibular joint projection
best x-ray for oral surgery
skull radiorgraphy
Lateral Cephalometric Projection used for
evaluate facial growth and development, trauma, disease, and developmental abnormalities
Lateral Cephalometric Projection showsPosteroanterior Projection
shows the bones of the face and skull as well as the soft tissue profile
Posteroanterior Projection used to
evaluate facial growth and development, trauma, disease, and developmental abnormalities
Posteroanterior Projection shows
This projection shows the frontal and ethmoid sinuses, the orbits, and the nasal cavities