Ocular Motilities #13: Cerebellar Syndrome
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Lateropulsion in the Cerebellum
ipsipulsion (hypermetric towards, hypometric away from lesion)
The most common type of cerebellar stroke
Superior cerebellar artery (SCA)
-due to gravity
Least common type of cerebellar stroke
anterior inferior cerebellar artery (AICA)
SCA stroke presentation
AICA stroke syndrome
Bell's Palsy and hearing loss (CN 7 and 8)
Posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA) is _________ most likely to stroke
in the middle for
PICA supplies the _______ and is often misdiagnosed as ______
medulla, lateral medullary syndrome
PICA syndrome looks like
dorsolateral medullary (Wallenberg) Syndrome so make a compare and contrast between Wallenberg vs PICA
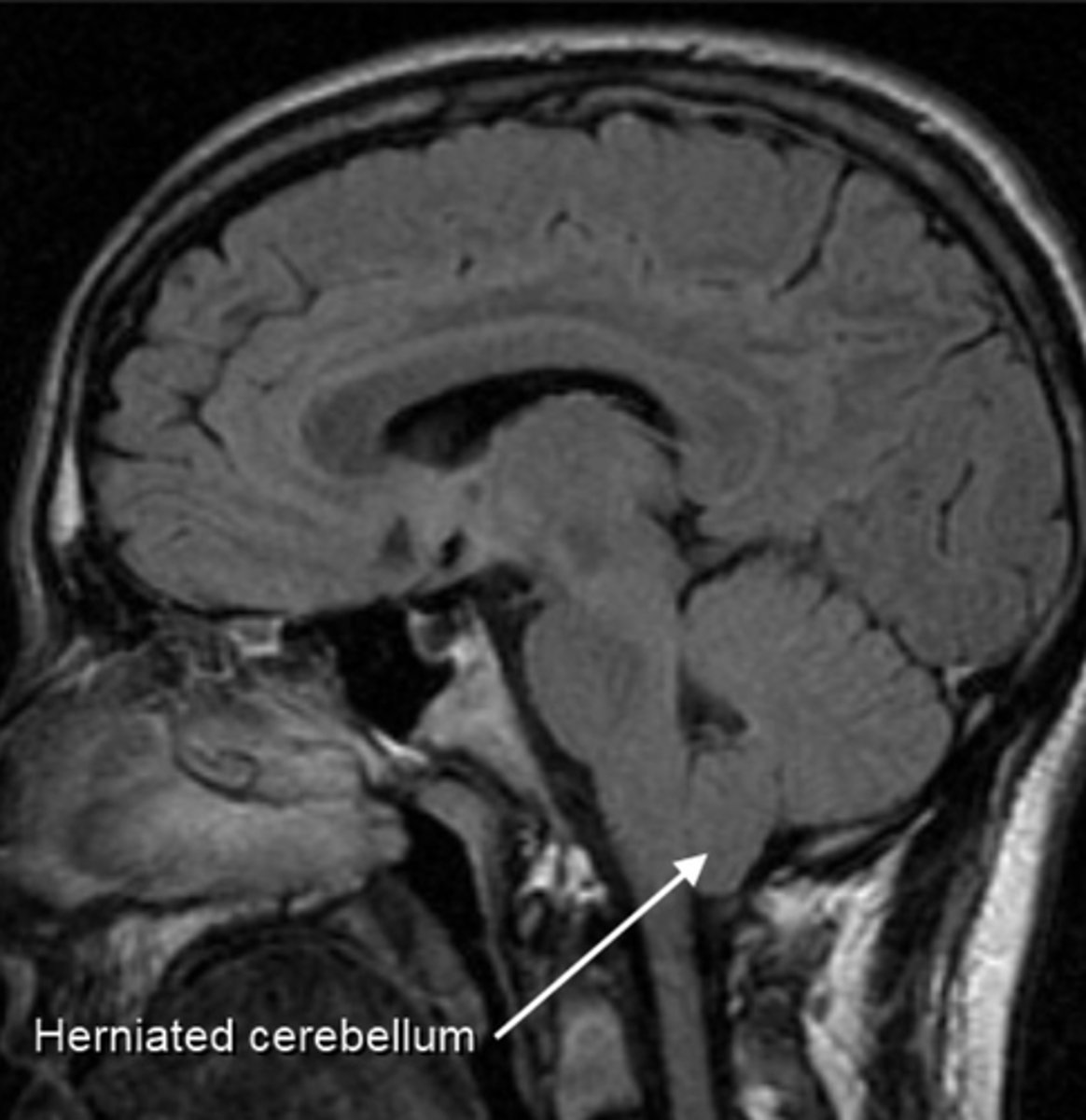
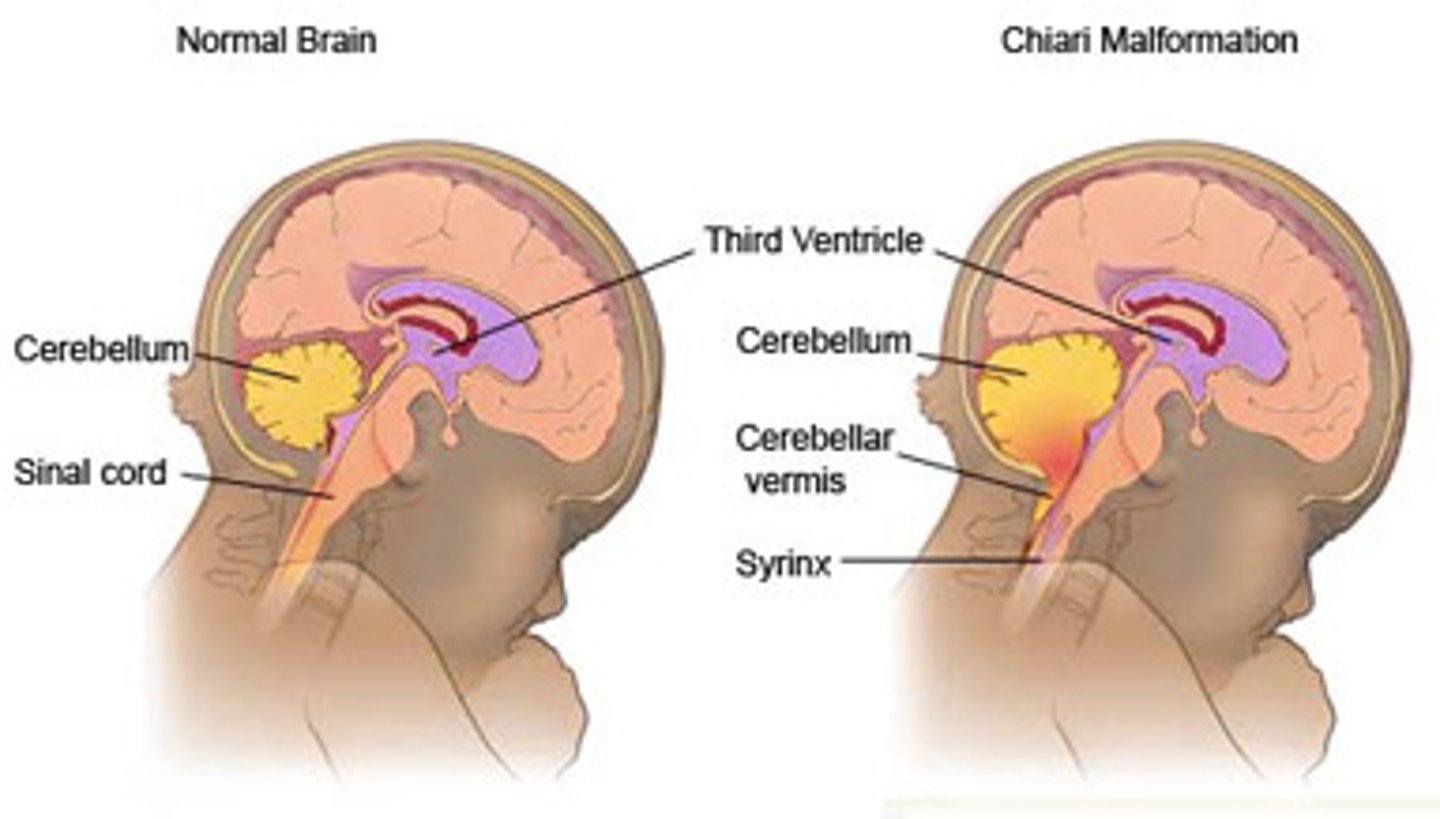
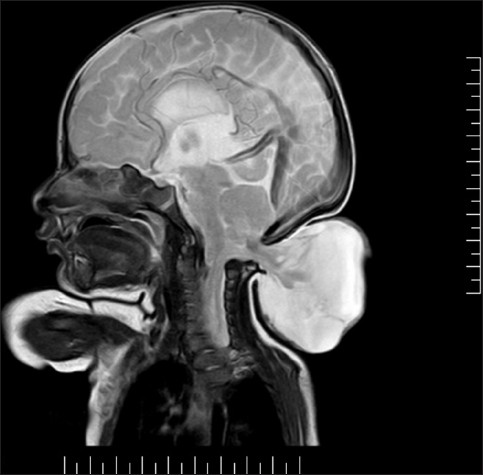
Chiari Malformation
acquired hydrocephalus due to cerebellar tonsils protrude into foramen magnum, pinching the medulla, and blocking CSF flow
Eye movement problems with Chiari
a lot is possible due to high CSF pressure with occlusion of the foramen magnum, but downbeat nystagmus points to the problem often
Type I Chiari
not eligible for surgery, herniation of cerebellar vermis (symptoms occur is usually in adulthood), 2/3 of the cases
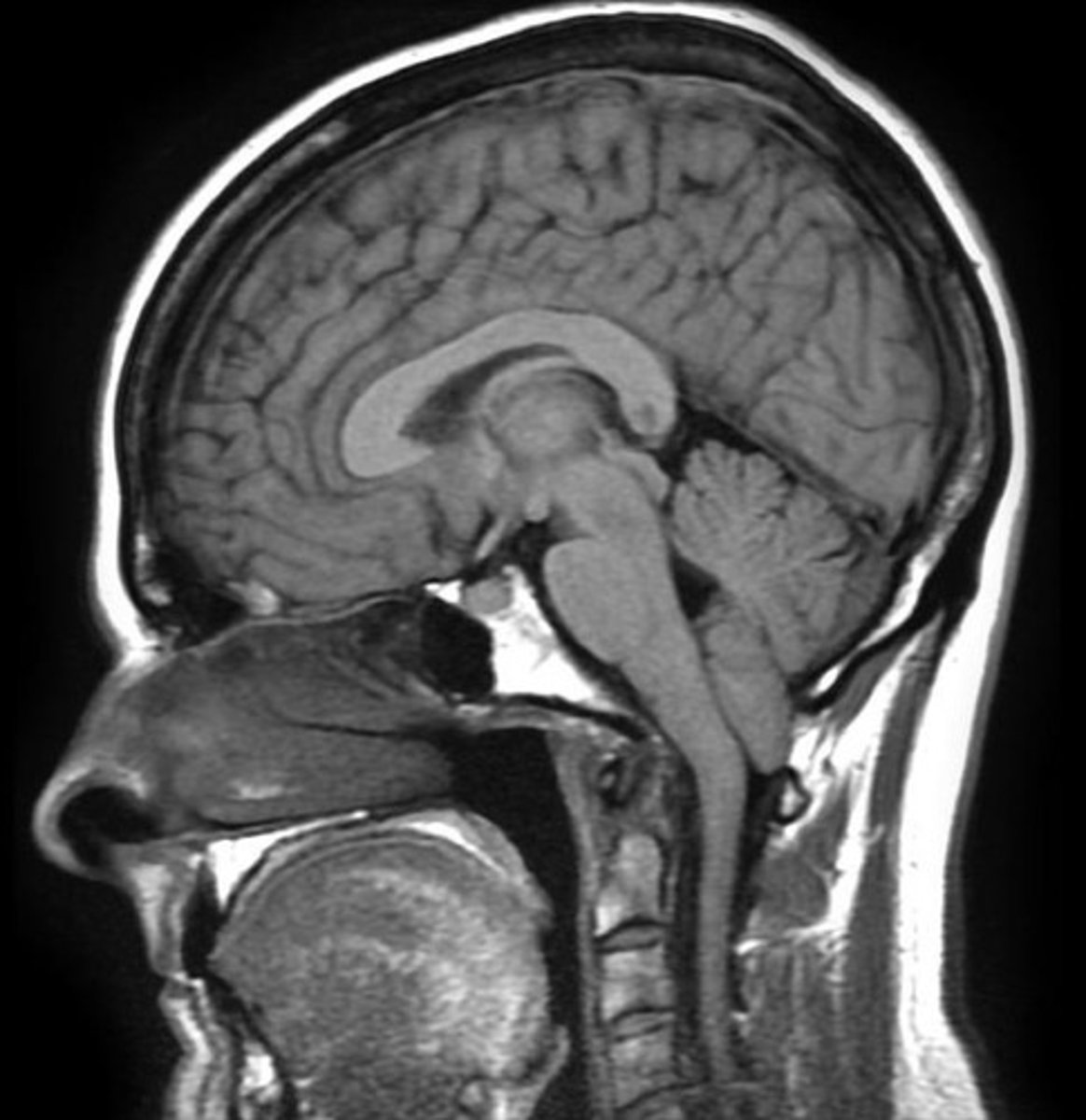
Chiari Type 1 is _______ onset and most symptoms are positional, particularly when the patient is __________
adult, reclined
Type II Chiari (Arnold-Chiari)
less common but can qualify for surgery!
-childhood onset, more severe symptoms
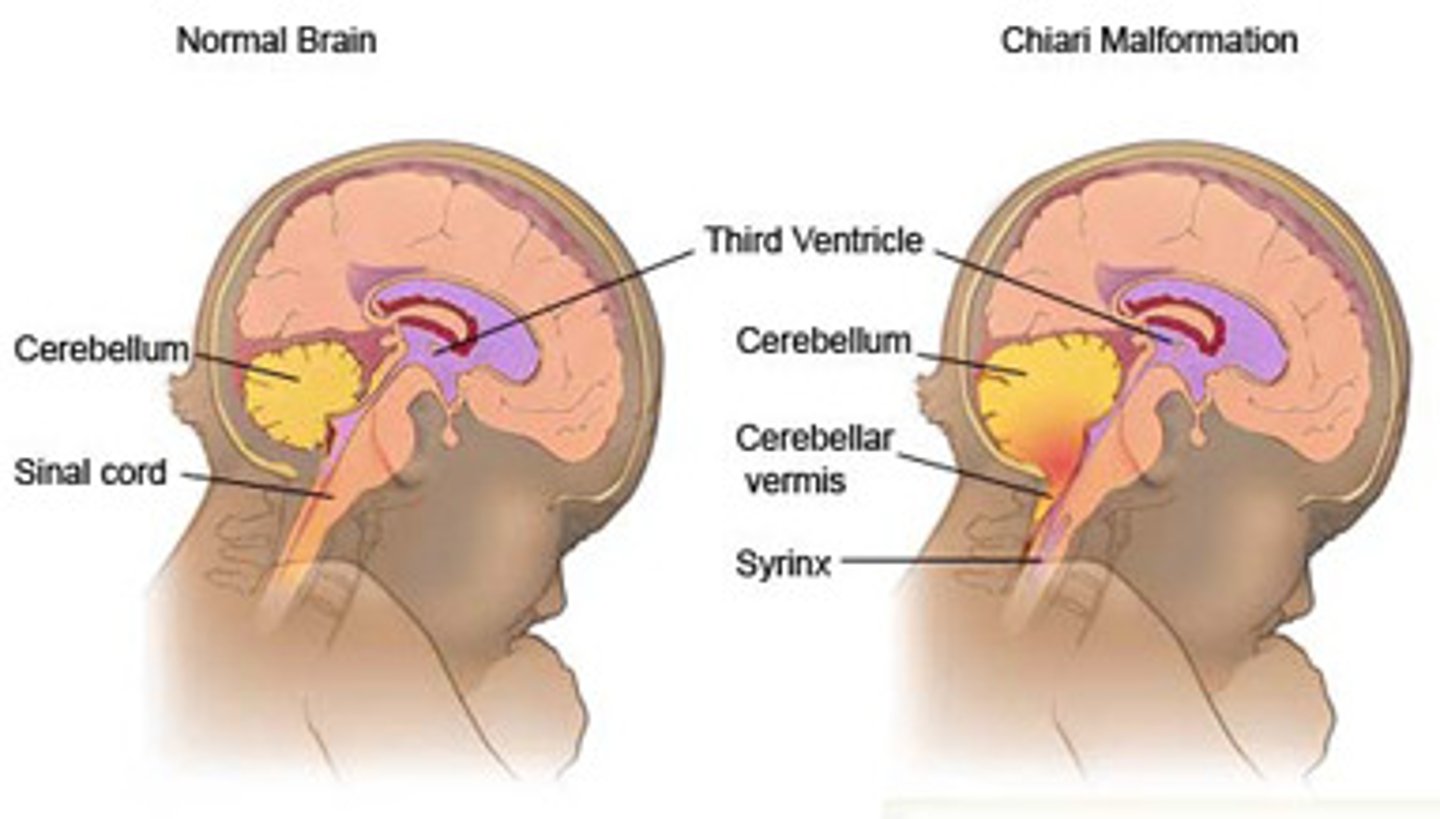
Type III Chiari
terrible birth defect where cerebellum herniates outside the skull, called a myelomeningocele
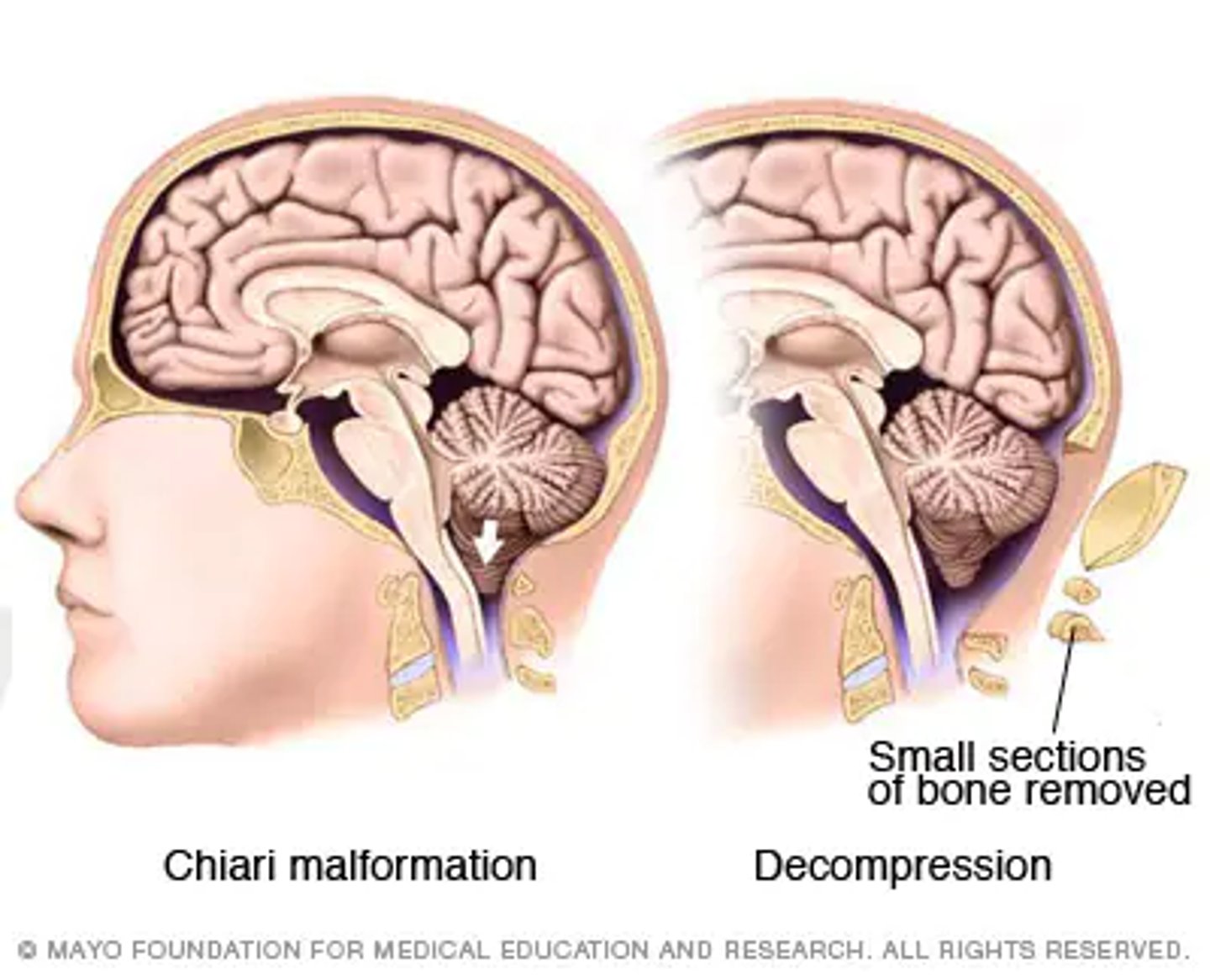
How to do surgery on chiari
Craniectomy, takes care of the syrinxes but leaves a soft spot that needs protection with helmets
Chiari Type 0
IIH, treat like Type 1 and give Diamox or loop diuretic -____-
Dandy-Walker Malformation
congenital brain malformation in which there is enlargement of the 4th ventricle, also results from absence of the corpus collosum and most or all of the cerebellar vermis
Dandy-Walker signs
hydrocephalus, slow/clumsy motor development, speech-language problems, EOM striated muscle motor issues
***Dandy-Walker can happen when mothers take ________ while pregnant
Warfarin
Walker-Warburg Syndrome
Causes micro OR megalo opthalmos, cerebellar malformation, hydrocephalus, coloboma, retinal dysplasia, congenital cataract, enlarged 4th ventricle
What kind of cataract is seen with Walker-Warburg?
It's not a PSC despite being congenital; persistent fetal vasculature from hyaloid turning fibrotic and obstructing vasculature
How to treat Walker-Warburg
Pars plana vitrectomy and cataract sx
*****A lesion of the flocculus / paraflocculus in the cerebellum impairs what two things?
fixation and smooth pursuits
-impaired smooth pursuits in all directions
-impaired eye-head tracking with VOR cancellation
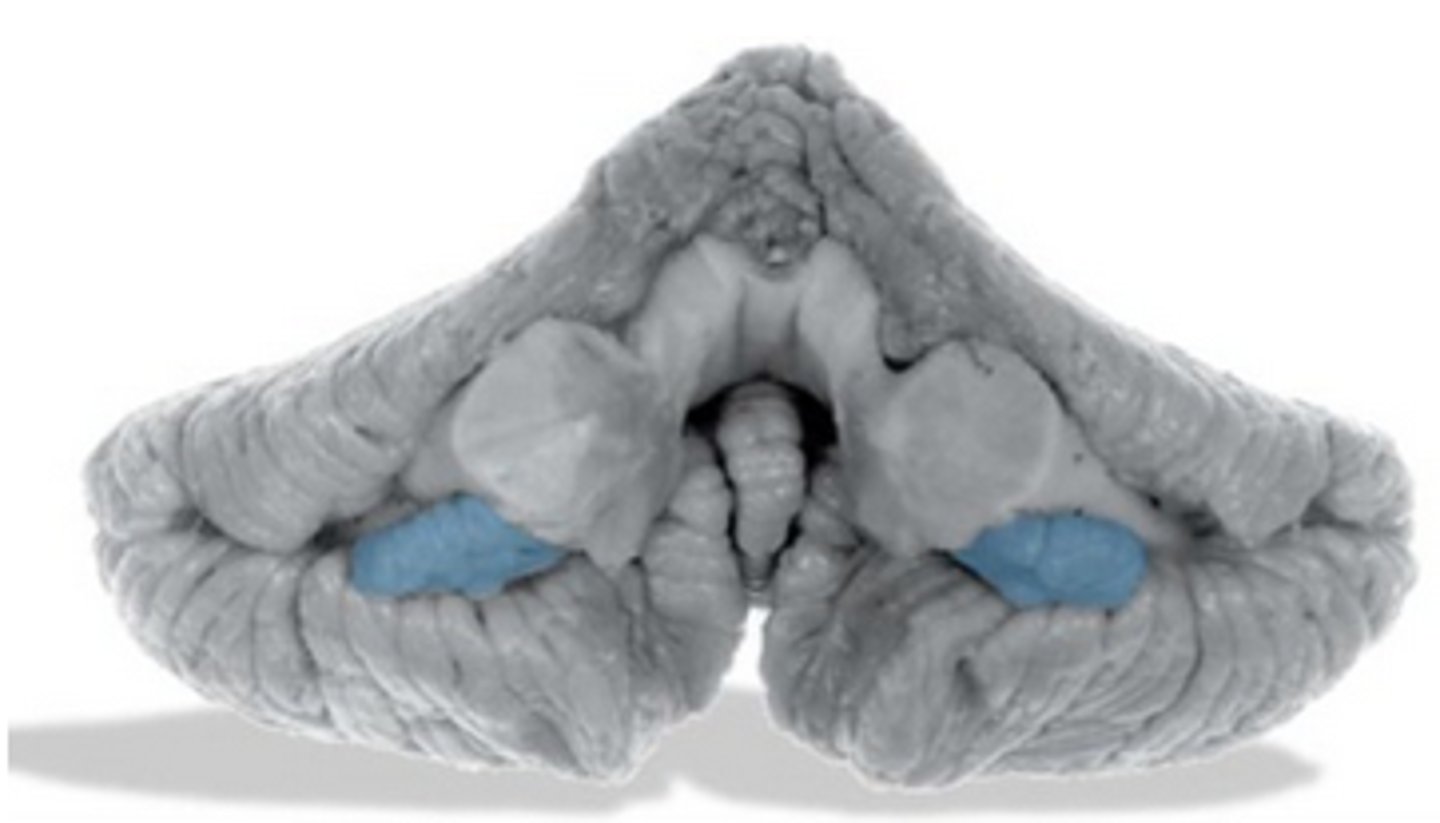
****A lesion of the nodulus and uvula of the cerebellum cause what kind of nystagmus?
PAN
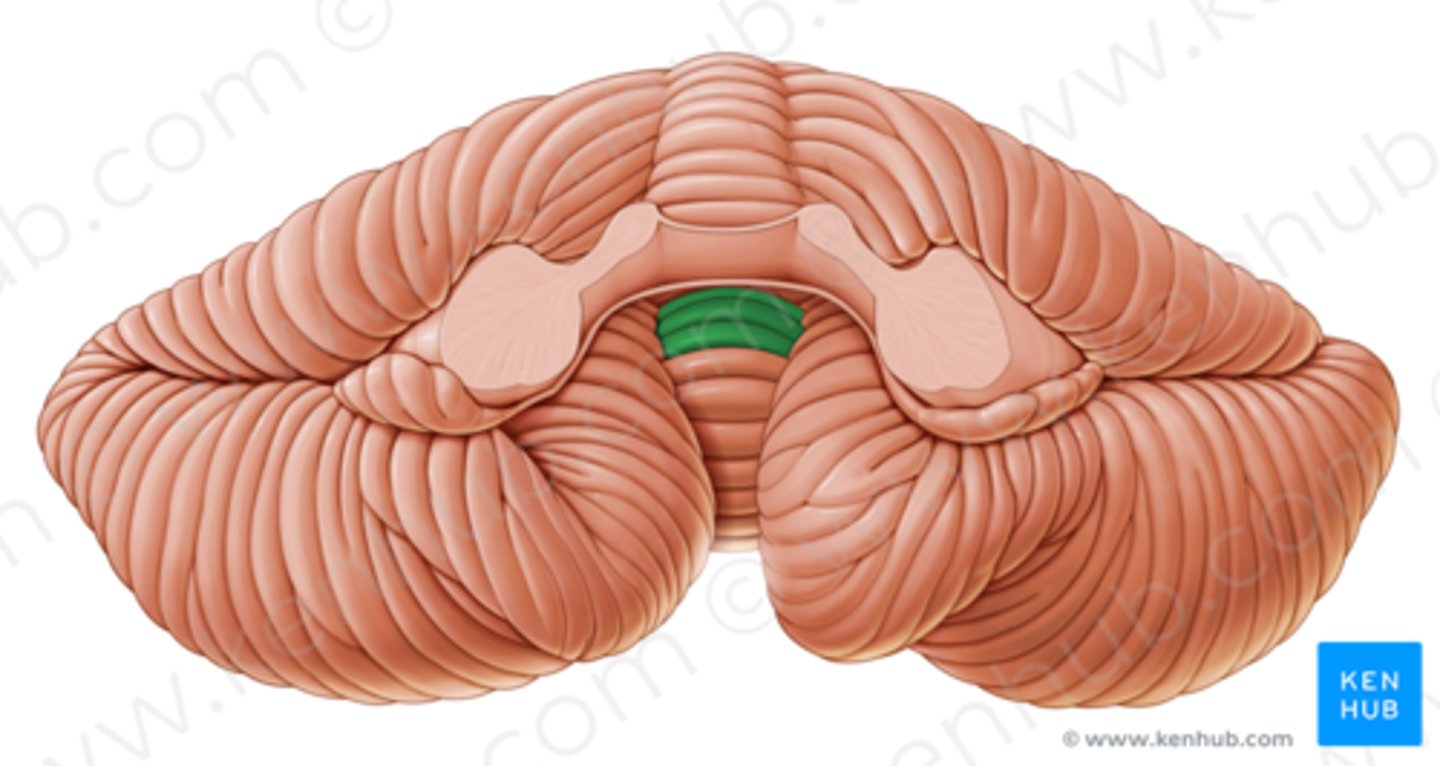
****A lesion of the dorsal vermis of the cerebellum causes what 4 eye movement issues?
saccadic undershooting
saccadic ipsipulsion
eso deviation
longer pursuit latency
-ipsilateral hypometria and mild contralateral hypermetria of saccades
-gaze is tonically deviated away from the lesion
-smooth pursuits are impaired for targets moving towards the side of the lesion
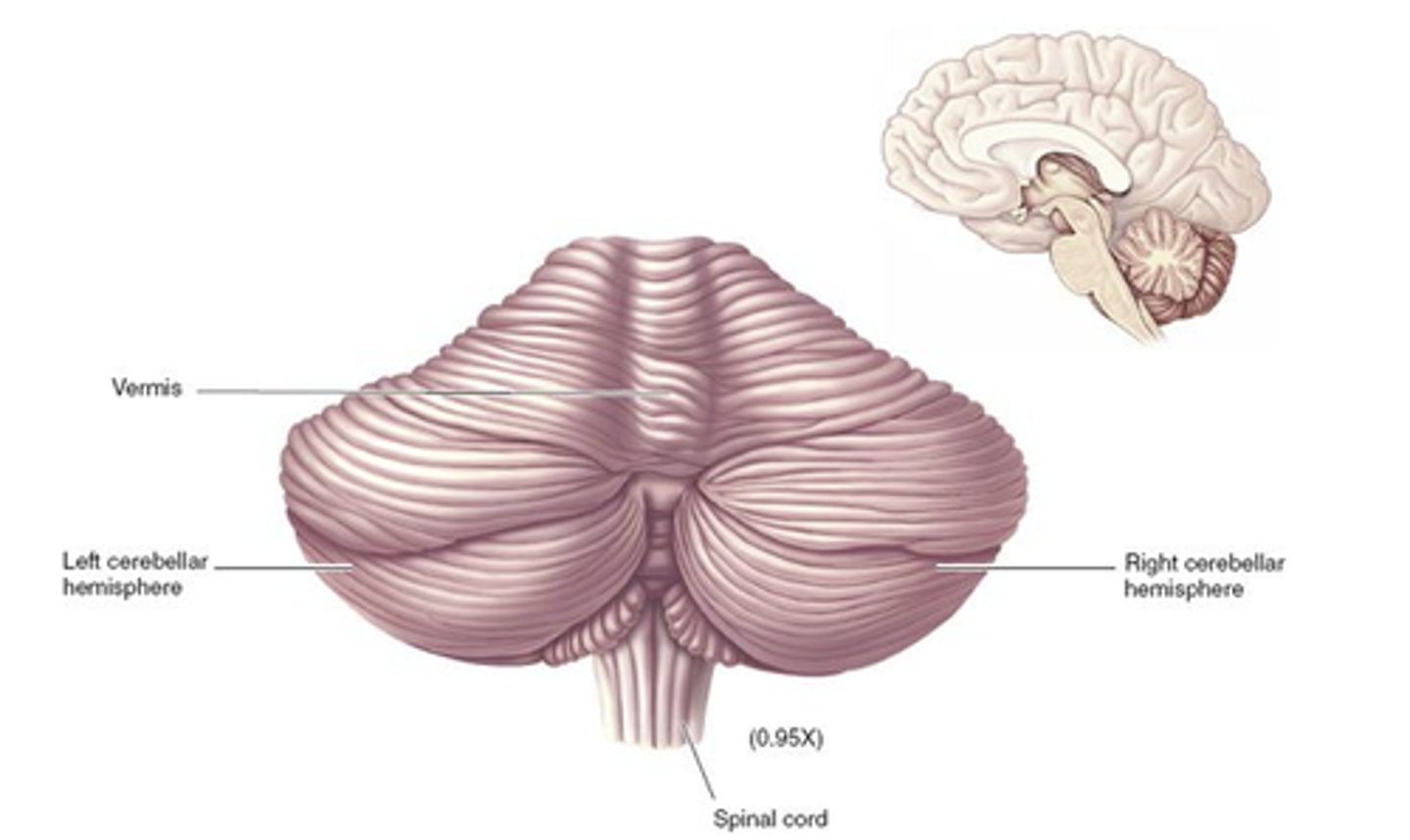
****A LESION of the fastigial nuclei of the cerebellum generally cause (hyper or hypo?) metria
hypermetria / overshooting
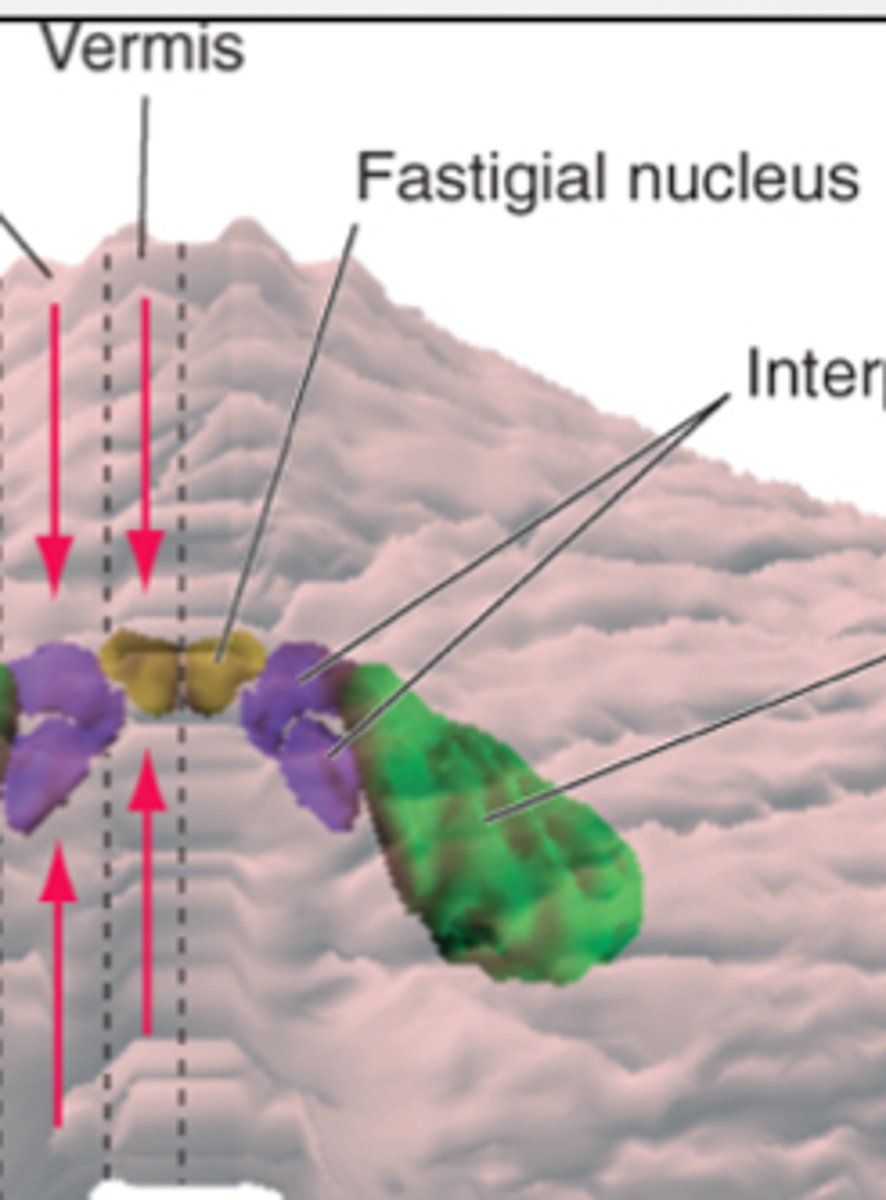
***REVIEW: What binocular vision problem do these lesions cause?
vermis lesion
fastigial lesion
vermis lesion causes DI
fastigial lesion causes CI
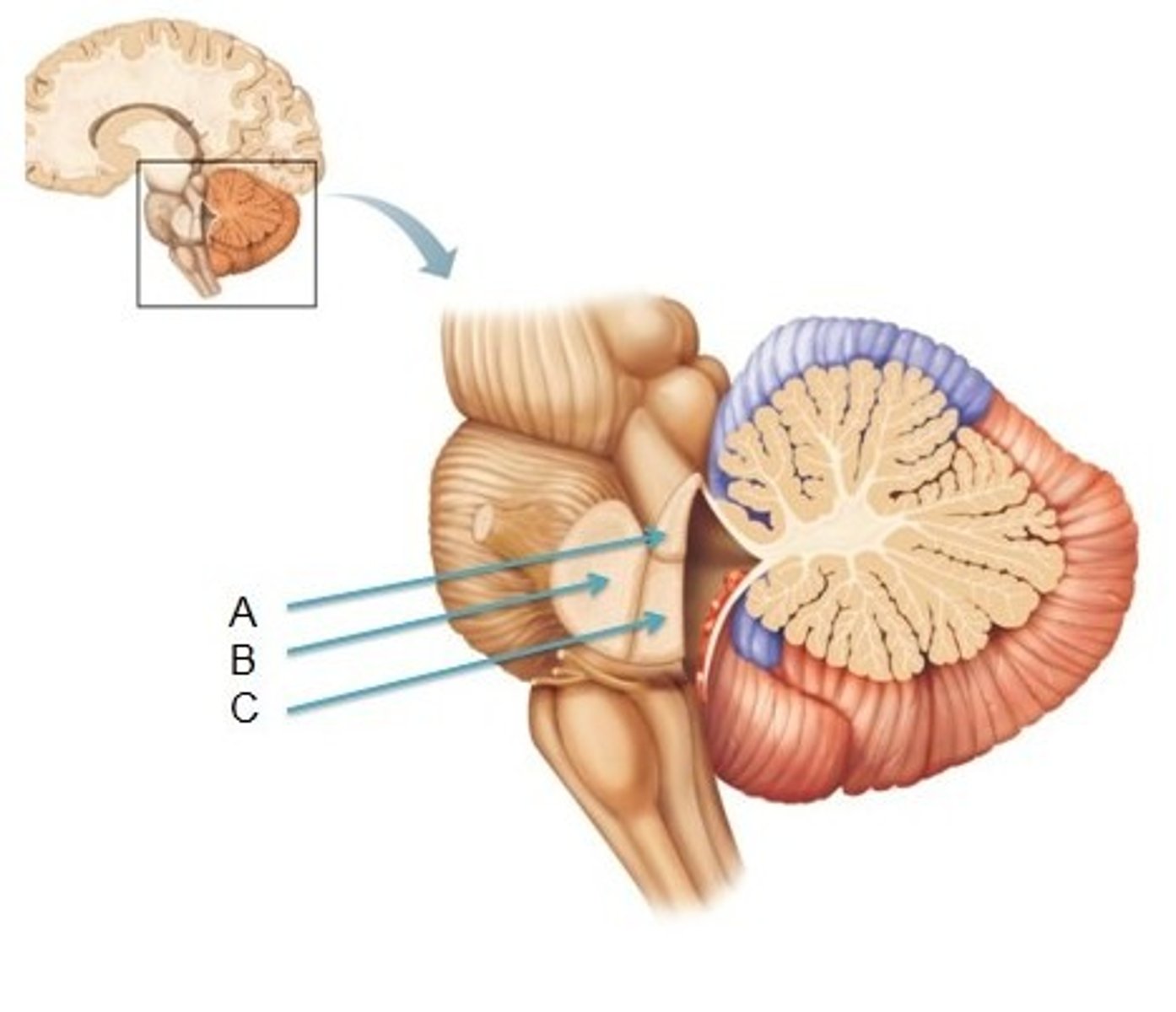
There are 3 fiber bundles for the cerebellar peduncles: inferior, middle, and superior. Which one talks to which part of the brain stem?
inferior peduncle -> medulla
middle peduncle -> pons
superior peduncle -> midbrain
This makes sense given the anatomy. of the brain stem being midbrian pons medulla from top to bottom.
Lateropulsion can happen with dorsolateral medullary syndrome, OR with ____
cerebellum
***Which of the arteries is the most common to receive a cerebellar stroke and why?
Superior cerebellar artery (SCA) due to gravity making it the least likely to retain blood since it's the highest of them all
Which of the arteries is the least common to receive a cerebellar stroke?
Anterior Inferior Cerebellar artery (AICA)
**Superior Cerebellar Artery (SCA) Syndrome signs
Very similar to dorsolateral medulla Wallenberg signs!
-ipsilateral ataxia
-dysarthria
-ipsilateral Horner's
-contralateral Pain and T loss
-vertigo
***Anterior inferior cerebellar artery (AICA) syndrome
-gaze evoked nystagmus
-horizontal gaze palsy
-ipsilateral Bell's palsy (CN7)
-deafness (CN8)
AICA patient video
black lady that looks like her left eye was gouged out, when they jerk her head side to side, she has to refixate with saccades
Compared to AICA and SCA, Posterior inferior cerebellar artery strokes are the ________
middle most common
Put these in order of which is most common to least common:
PICA
AICA
SCA
most common: SCA > PICA > AICA : least common
PICA supplies what part of the brain?
lateral medulla, inferior peduncle of the cerebellum, nodulus, and uvula
PICA strokes are often misdiagnosed as
lateral mediullary syndrome
AICA supplies what part of the brain?
pons
SCA supplies what part of the brain?
midbrain
***Label what part of the brain is supplied by these 3 arteries:
PICA
AICA
SCA
SCA midbrian
AICA pons
PICA medulla
******____________ syndrome looks like dorsolateral medullary (Wallenberg) Syndrome, so if you see lateropulsion on the final exam you will PICK THIS AS YOUR ANSWER NO MATTER WHAT
PICA
Name the 3 congenital abnormalities of the cerebellum
1) chiari malformation
2) Dandy-Walker Malformation
3) Walker-Warburg Syndrome
Chiari Malformation definition
Cerebellar tonsils protrude through the foramen magnum and pinch the medulla / block CSF