RADT 1065 Unit 4 The X-ray tube
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
X-ray tube
-where electrical energy is converted into heat and x-rays
-the most important part of an x-ray machine
vacuum, source of electrons, acceleration of electrons, and deceleration of electrons
what are the 4 requirements of x-ray production?
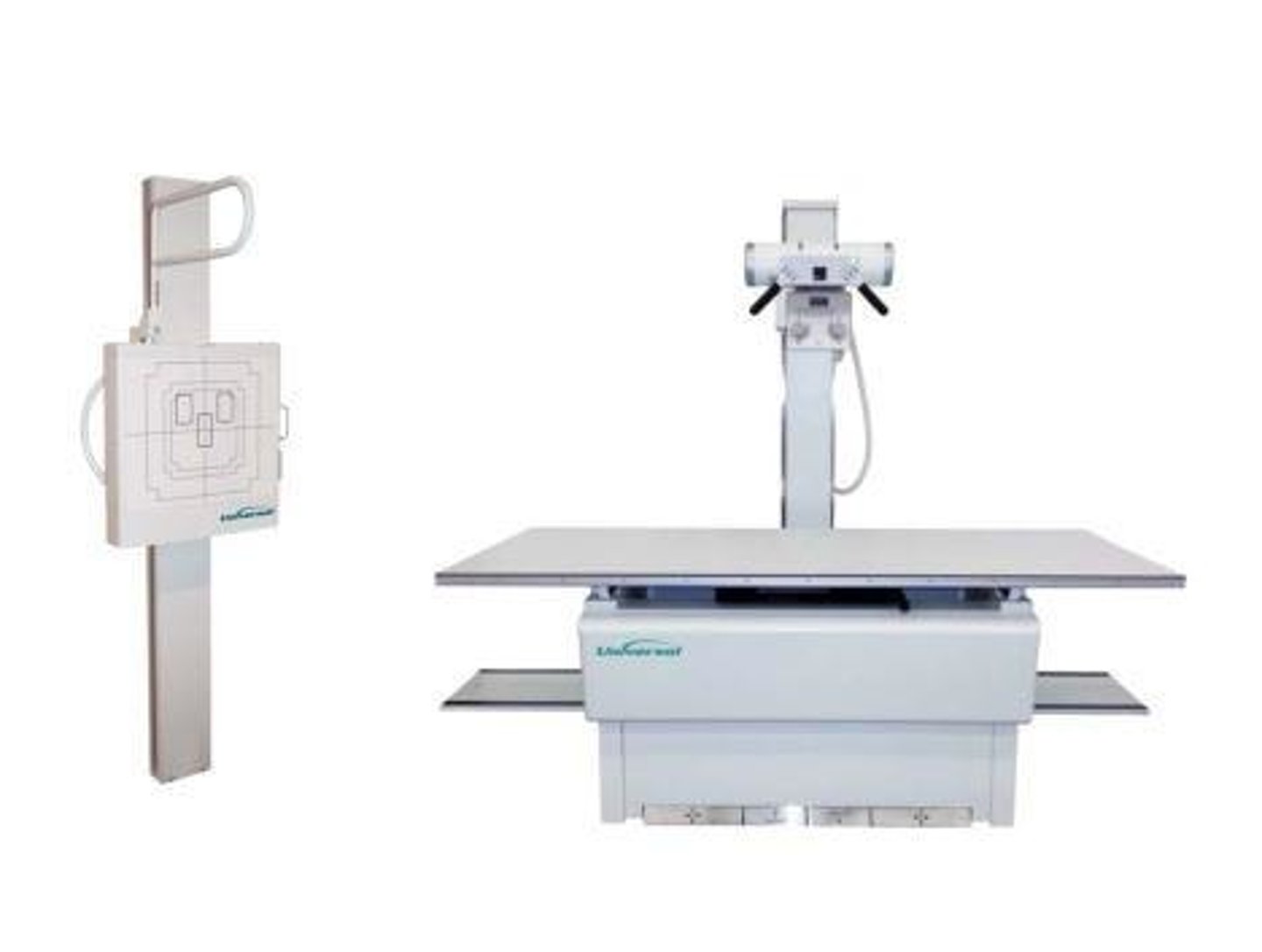
ceiling support
-most common type of tube support
-2 sets of rails for longitudinal and transverse movement
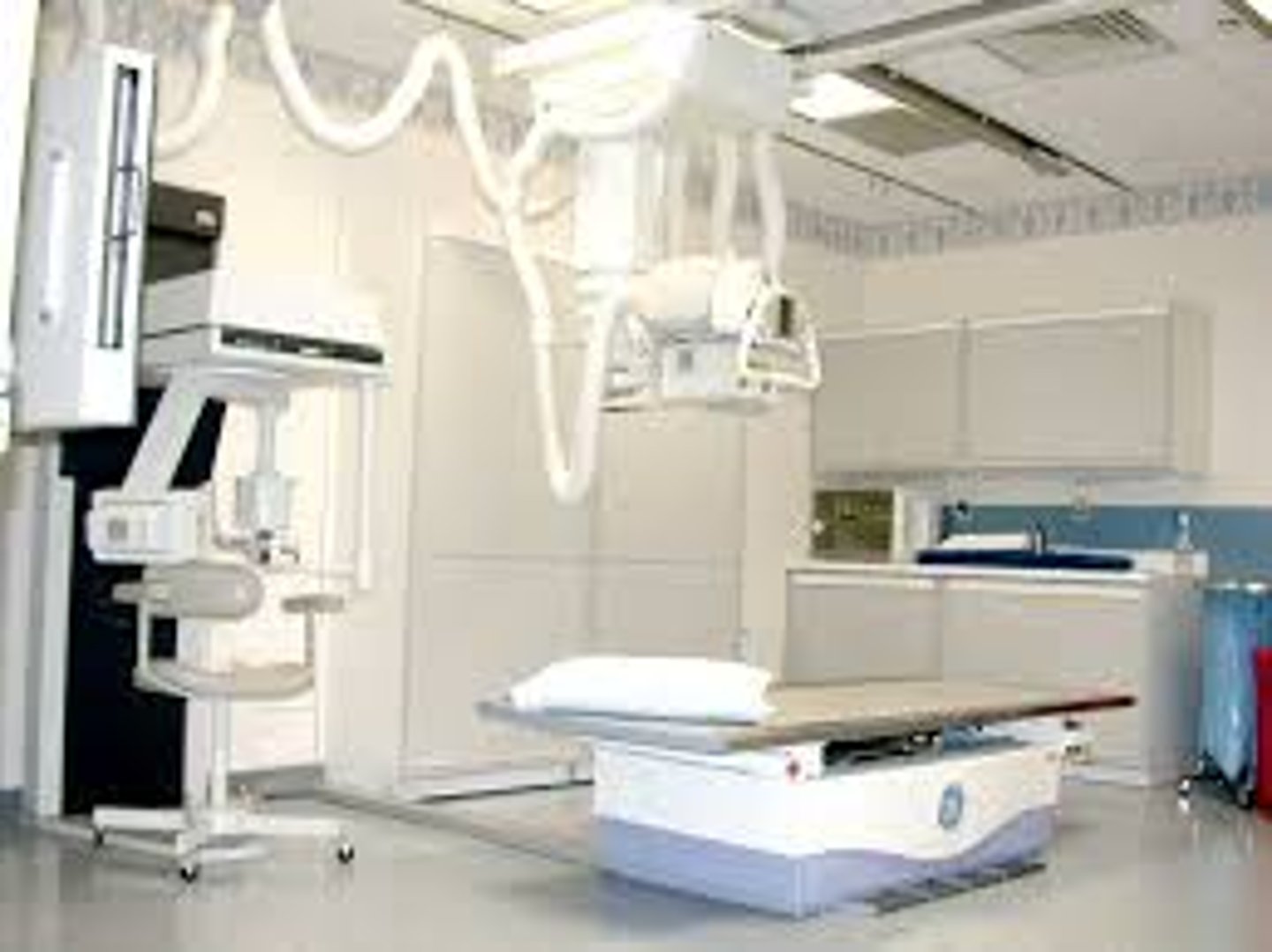
floor to ceiling support

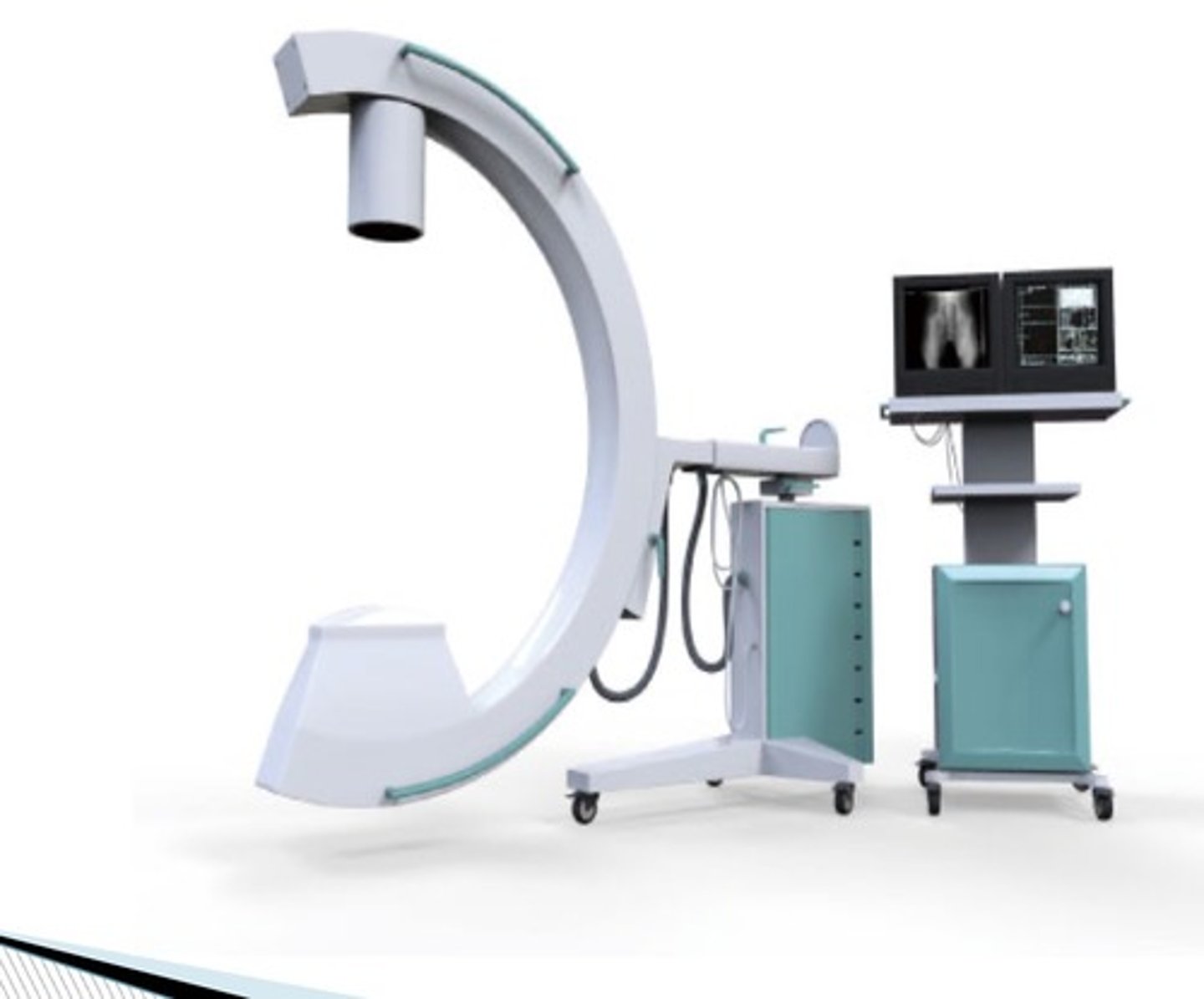
C-arm support
-used in interventional radiology
-used in OR during surgery and fluoroscopy
isotropically (all direction)
how do x-rays emit?
protective housing
-limits the x ray bam
-directs the x-rays to one direction
insulation against shock and heat cushion
what is the purpose of oil in an X-ray tube?
Leakage radiation
-any photons that escape from the protective housing
-less than 1 mGya/ hr at 1 m
mGya
the intensity of X-rays
electric shock and excessive exposure
what does the X-ray tubes protective housing reduce?
Glass envelope
-maintains the vacuum of the X-ray tube
-made of pyrex and can withstand heat
partially, gas
The Crookes tube was partially _________ and contained _______.
Drawbacks of the glass tube
-over time the tungsten coats vaporize from the heat and allows electrons to diverge
-the tube will fail eventually
Metal envelope
-improvement over the glass tube
-tungsten will not collect = constant electric potential
-longer life and less likely to fail
window
the thin area of the envelope where useful x ray beam leaves the tube
cold cathode tube
-crookes tube
-no thermionic emission
-partially evacuated
-relied on ionization of gases within the tube to create x rays
hot cathode tube
-coolidge tube
-total vacuum
-Improved efficiency
-heated filament= thermionic emission
thermionic emission
emitting electrons with heat
cathode (-) and anode (+)
what are the 2 major internal components of the X-ray tube?
cathode
-the negative side of the tube
-acceleration
anode
-the positive side of the tube
-deceleration
electrostatic repulsion
-unlike charges attract and like charges repel
the focusing cup is even more negative than the electrons
If all of the negative electrons are repelled from one another, how do we get the together?
space charge
the focusing cup is so negative, it forces the electrons to attract and form an electron cloud
Space Charge Effect
-once apace charge is generated, electrostatic repulsion makes it difficult to produce more electrons from the filament
saturation current
-tube current rises with increasing tube voltage to a maximum value
-all available electrons have been used, and no increase of kVp can increase number of electrons used for x-ray production
-the only way to increase electrons is to increase mA
3 functions of the anode
1. electrical conductor
2. mechanical support
3. thermal dissipater
stationary anode
-lower exposure
-dental X-ray tubes
-immobile
rotating/conventional anode
-high intensity system
-faster rotation= more heat dissipation
-3400 rpm
strator magnets
spins rotor and anode through electromagnetic induction
target
Area of the anode struck by the electrons from the cathode
tungsten and rhenium
what is the anode made of?
to withstand rotation speeds (all tungsten would be too heavy), and expansion/contraction from heat
why is rhenium added to the anode?
high atomic number, good thermal conductivity, high melting point
why is the anode made of tungsten?
induction motor
-current passes through starter magnets, causing rotor to spin, causing anode to spin
-this is used because in order to maintain a vacuum, no mechanical connect is possible
Rotoring
-anode side: strator receives current, turns rotor
-cathode side: filament receives current, space charge is created
Exposure
once kVp is applied, electrons will travel from cathode to anode at a very high speed. The electrons will hit the target at focal spot.
focal spot
where x-rays are emitted
dual focus focal spot
has a small focal spot that corresponds with the small filament, and a large focal spot that corresponds with the large filament
small focal spot
lower heat capacity, lower technique is used
large focal spot
higher heat capacity
line focus principle
-By angling the target 15-20 degrees, the effective area of the target much smaller than the actual area of electron interaction
-Effective focal spot is always smaller than the actual focal spot
Anode heel affect
x-ray photons on anode side of the tube are attenuated by the anode heel, and are therefore weaker than the cathode side photons
off focus radiation
when electrons bounce off the focal spot and photons are created. this leads to unfocused x-rays, high dose, and reduces contrast
tube failure
almost always related to heat
heat dissipation
radiation, conduction, and convection
radiographic rating chart
shows which radiographic techniques are safe for tube operation
anode cooling chart
chart than shows how long it takes the anode to cool completely
housing cooling chart
Graph showing the cooling rate of an x-ray tube housing