Cytoskeleton II: Higher Order Structures and Cellular Functions
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
actin filament dynamics alter cell - and -
shape, movement
- family of monomeric - regulate actin filament dynamics and cell morphology
Rho, GTPases
accessory proteins with - for actin filaments mediate - between filaments to create different structures with varying rigidity or flexibility
two binding sites, cross-linking
contractile stress fibers are - packed parallel bundles complexed by -, found in -
loosely, alpha-actinin, skeletal muscle
non-contractile stress fibers are - packed parallel bundles complexed by -, found in -
tightly, fimbrin, filopodia
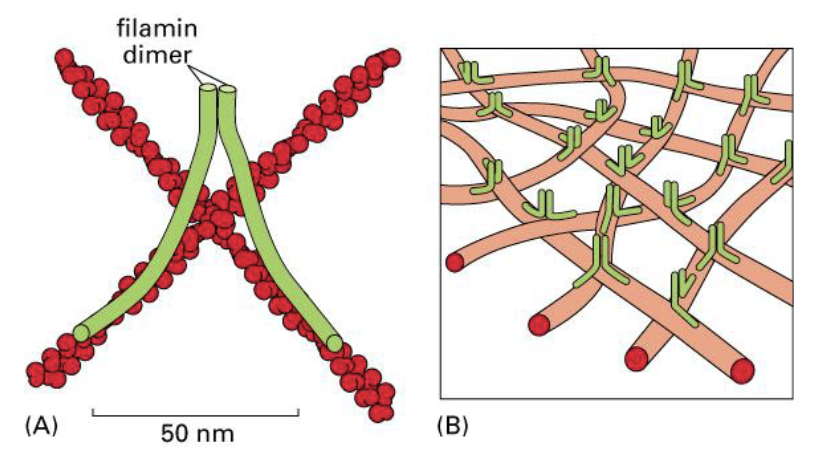
actin gel refers to - actin filaments complexed by -
cris-crossed, filamin dimer
actin gel is a major structure in -, helping stabilize actin web formed in -
cell cortex, lamellipodia
filamin forms a long, - linkage between two criss-crossed actin filaments resulting in a -
wishbone-like, viscous 3D actin gel
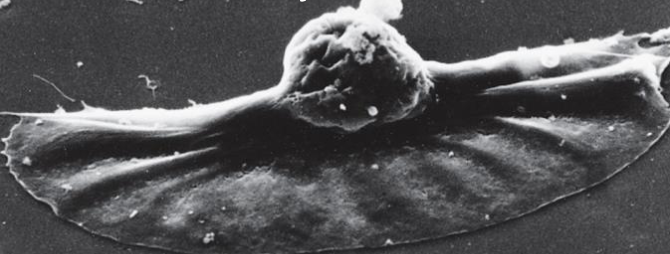
lamellipodia are - of the PM all along one side of the cell
thin, sheet-like protrusions
formation of - is the first step in cell crawling because it extends and leads cell in the -
lamellipodia, direction of movement
Arp 2 and Arp 3 are actin nucleating proteins that structurally resemble -
actin monomers
active Arp2/Arp3 complex nucleates a - by binding and recruiting several actin monomers, once nucleated, polymerization occurs rapidly from the - end
new actin filament, plus
Arp complex usually remains bound to - ends, serving as a protein cap that - actin filaments
minus, stabilizes
Arp complex can also bind - on an actin filament, creating new -
internally, nucleated branches
the actin web, as a whole, can undergo -, in which the overall size of the web does not - much, but growth at the leading edge and disassembly at the trailing edge create - movement
treadmilling, change, unidrectional
at the leading edge of the treadmilling actin web, Arp2/3 nucleates - and creates a branched actin web, causing -
at the trailing edge of the treadmilling actin web, cofilin mediates - and consequent disassembly of - resulting in the - of actin monomers to the leading edge
new actin filaments, membrane protrusion
severing, ADP-bound filaments, recycling
cell crawling is complex, requiring 4 distinct and coordinated movements
extension
adhesion
translocation
de-adhesion
extension/protrusion refers to the actin-web pushing PM - at the leading-edge of the cell to form a protruding -
outwards, lamellipodium
adhesion refers to the cell cortex connecting to the -
extracellular matrix
translocation refers to the cell body being - to catch up to the leading edge, mediated by - powered by -
pulled forward, contractile actin bundles, myosin II
de-adhesion refers to the - of cell cortex from the -
detachment, ECM
MTOC in animal cells and most eukaryotic cells is the -, comprised of
pair of -, each made from 27 short MTs packed into a cylindrical bundle
rings of - that nucleate the minus end to grow new MTs from the centrosome
variety of -
centrosome
centrioles, gamma-tubulin, accessory proteins
centrosome is duplicated during - and form -
S-phase, mitotic spindles
an interphase cell contains a single -, located near the -
cytoplasmic array of - radiate from the centrosome to virtually all regions of the cell
centrosome, nucleus
microtubules
cytosolic microtubule and - contact provide - for the - end of microtubule growth
PM, negative feedback, plus
kinesins are superfamily of proteins that walk along - toward the - end
microtubules, plus
kinesins have neck region between two motor heads to alternately mediate - and - on the microtubule
docked head has -, undocked head has -
docking, undocking
ATP, ADP
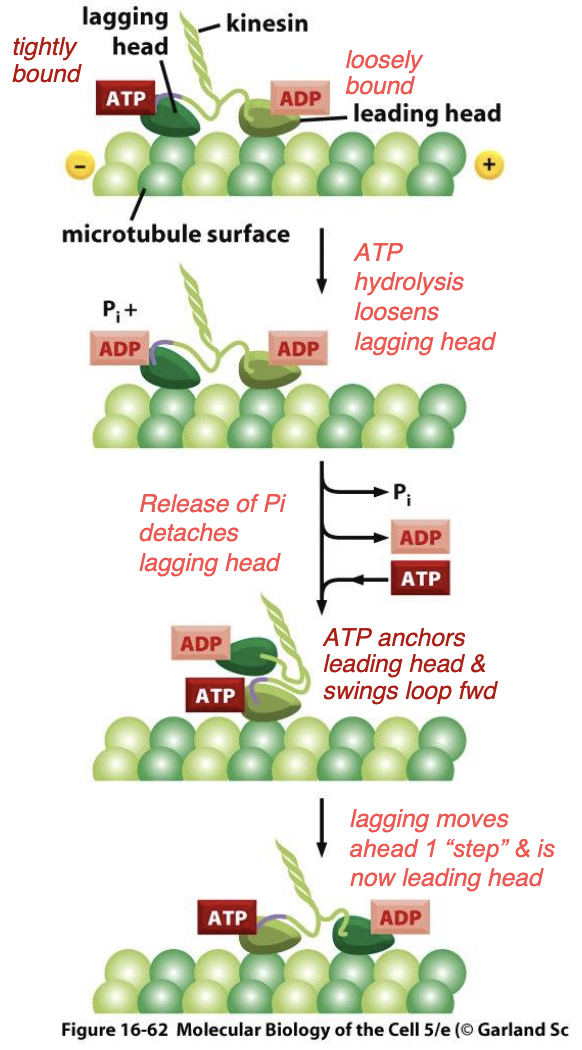
how do kinesins work?
leading head exchanges ADP for ATP, causing it to be - to the microtubules and for it to -
simultaneous - on lagging head + release of - from lagging head allows for it to detach from MT so it can swing forward to be the -
tightly anchored, swing forward, ATP hydrolysis, Pi, leading head
heavy chain tails of kinesin contain a binding site for - or another - and can even carry an entire - along a microtubule
vesicles, microtubule, organelle
dyneins are another family of - proteins that walk towards the - end of microtubules
motor, minus
dyneins are important in - and helps in localization of the -
vesicular trafficking, golgi apparatus
mitosis requires the separation of duplicated chromosomes and division of nuclei, performed by -
the spindle microtubules form from - that migrate to - of the dividing cell
bipolar mitotic microtubule spindles
duplicated chromosomes, opposite poles
cytokinesis is the division of -, performed by the - containing both - and - filaments
contractile ring forms around the - of the cell just beneath the plasma membrane, once contracted, it pulls the membrane - until two daughter cells pinch off
cytoplasm, contractile ring, actin, myosin
equator, inward
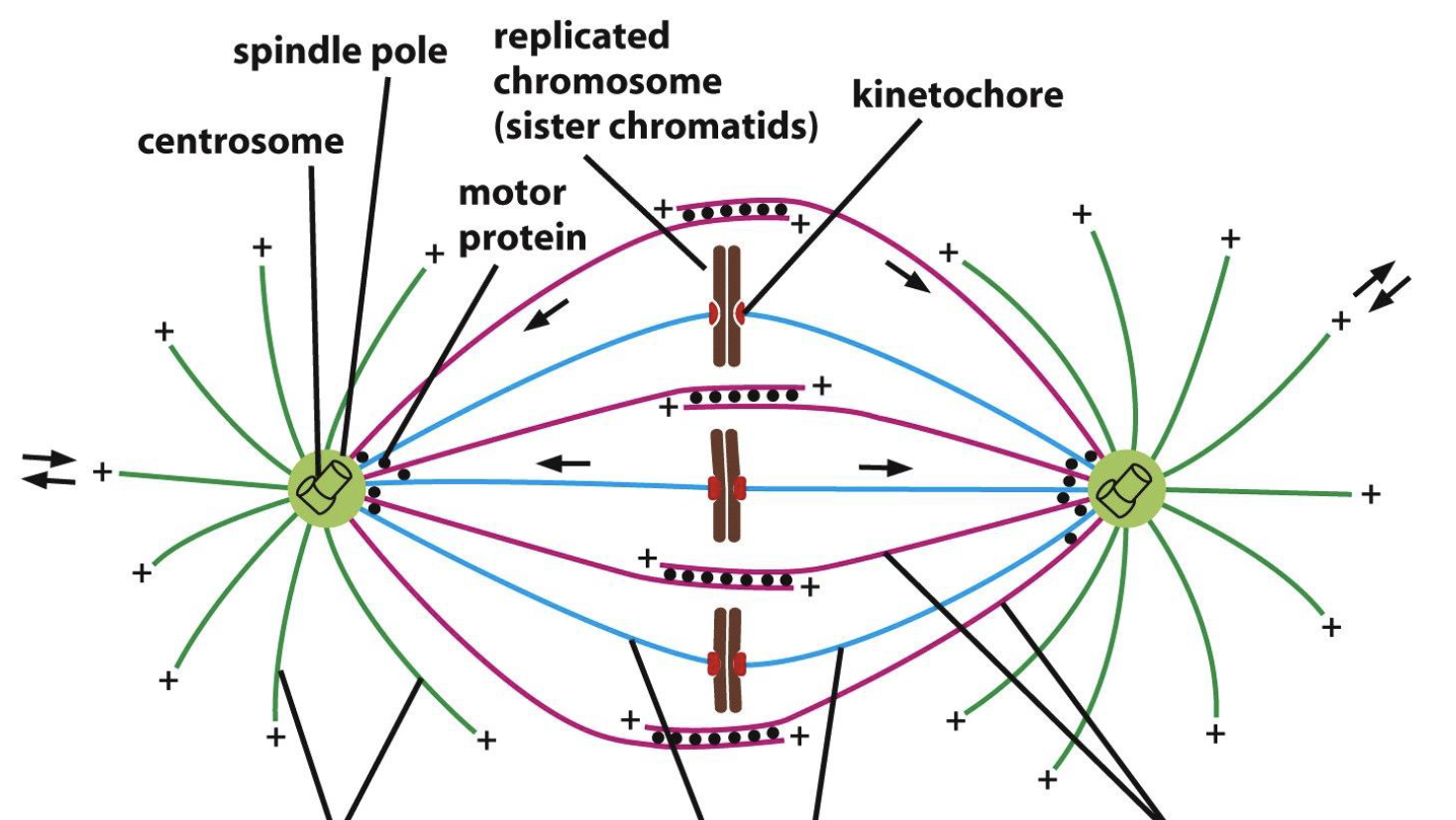
what are the green microtubules?
blue microtubules?
purple microtubules?
astral
kinetochore
interpolar
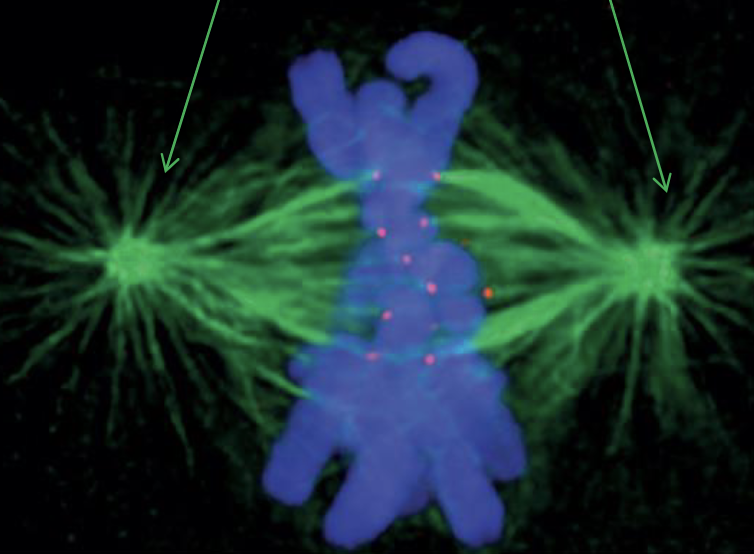
blue? red? green?
blue is the duplicated chromosomes
red is the kinetochores
green is the kinetochore microtubules
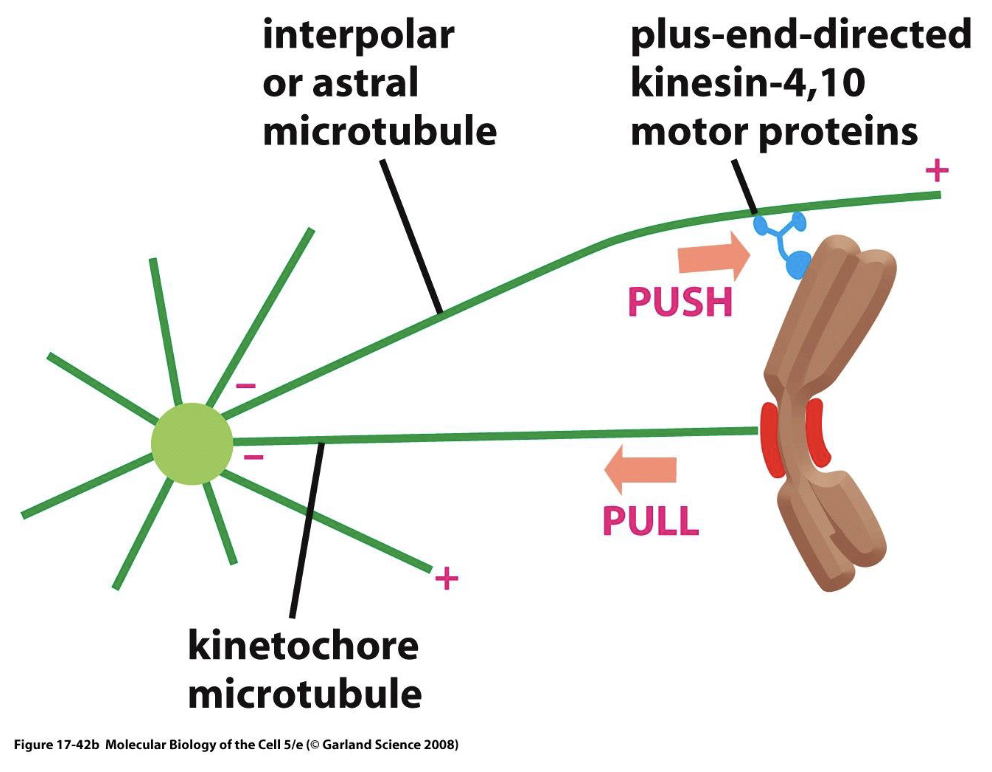
alignment of chromosomes at the metaphase plate involves both - and - of chromosomes
plus end - push tips of chromosomes along - microtubules
- of - microtubules at the plus end pulls chromosome at the -
pulling, pushing
kinesins, interpolar
depolymerization, kinetochore, kinetochore
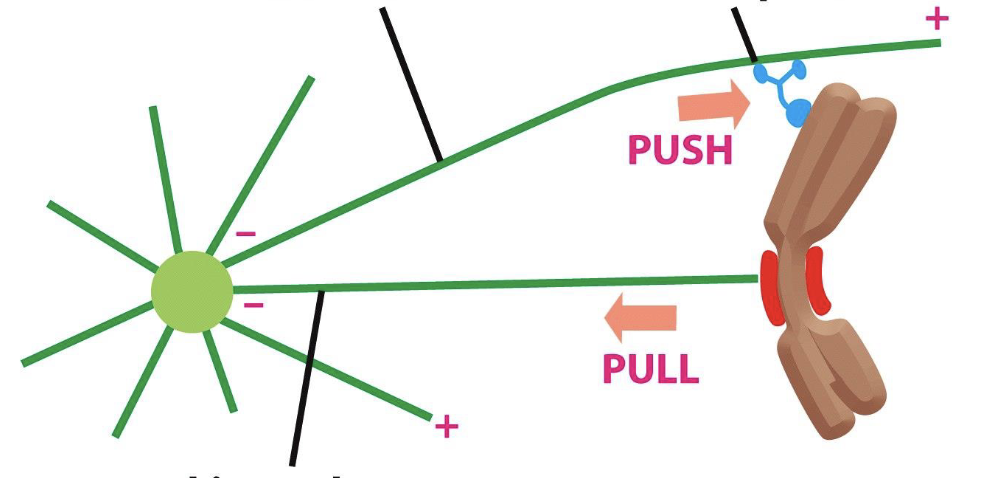
top left line?
top right line?
bottom line?
top left line points to interpolar or astral microtubule
top right line points to plus-end-directed kinesin
bottom line points to kinetochore microtubule
there is a - of - microtubules during anaphase A
shortening, kinetochore
separation of sister chromatids and movement to poles are mediated by - (shortening/lengthening) of - microtubules by - (de/polymerization) at - (minus/plus) ends
shortening, kinetochore, depolymerization, plus
how can microtubule plus ends de-polymerize while attached to the kinetochore?
microtubule collar connects microtubule to the kinetochore, sliding down the microtubule as it shortens
there is a - of - microtubules at anaphase B
lengthening, interpolar
just after sister chromatids detach from each other and begin to separate, the poles themselves begin to move - (together/apart)
apart
separation of poles is mediated by - microtubules
polymerization at - ends of interpolar microtubules in - region
at the overlap region, - will cause the microtubules to slide against each other, pushing the poles -
interpolar
plus, overlap
kinesins, apart
kinesin motor proteins connect interpolar microtubules at overlapping regions, walking towards - (shortening/lengthening) - ends creating the sliding force that helps push the poles -
lengthening, plus, apart
dynein motor proteins anchor - microtubules to the - and when walking toward the - end, it generates - force on the centrosome, pulling the poles -
astral, cell cortex, minus, pulling, apart
actin specific drugs
phalloidin
cytochalasin
swinholide
latrunculin
microtubule-specific drugs
taxol
colchicine
vinblastine
nocodazole