Freshwater Ecology - Unit 1
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
Ecology
the study of the interaction between an organism and its environment
Goldilocks Zone
orbital distance where liquid water sits on a planet’s surface
Water withdrawal
water diverted or removed from a surface or groundwater source
Water consumption
use of water that does not return to its source
Millenium Ecosystem Assessment
studies human impact and “ecosystem services”
Ecosystem services
values humans gain from healthy ecosystem
Describe influences of water on human lives
Need it to regulate temperature, hygiene, food source, electricity, economics, body functions
What defines the potential habitability of planets?
Needs to be at a temperature where liquid water is on the planet’s surface
Explain the connection between human distribution and water runoff
Human populations are often more dense around areas that get the most water runoff
Which activity accounts for most of our global water withdrawal? What percentage is attributed to this activity?
Agriculture at 70%
While the U.S. population is rising, what is happening with the total amount of water we use?
It is starting to decrease
Name the top 3 uses of water withdrawal in the U.S.
Thermoelectric, irrigation, public supply
How does domestic vs. agricultural use change with level of development of a country?
The more developed a country, the more water use is for domestic and industrial purposes, rather than agriculture
Explain how the phrase “dilution is the solution to pollution” may have made more sense historically, but does not work presently
Concentration of waste products has increased
New types of waste production which organisms have no evolutionary experience
Biomagnification
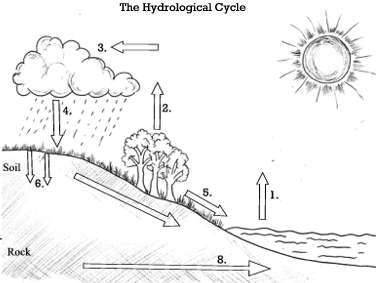
Label the water cycle
Evaporation
Transpiration
Condensation
Precipitation
Runoff
Infiltration
Name some ways humans and climate change can alter the water cycle
Not creating spaces for water to infiltrate into the soil, higher temperatures changing how much water evaporates and where the water goes
Explain how the GRACE satellite monitors water on Earth
When pulled to a water source with a high mass, one satellite slows and gets closer to the second, and then later on the second satellite gets further from the first
What have we learned from the GRACE satellite measurements?
Groundwater is increasing in some places and decreasing in others
Name each category of ecosystem service values under the millennium ecosystem assessment and give examples of each
Provisioning services: products - water
Regulating services: an ecosystem cleaning water for us
Cultural services: aesthetic beauty
Supporting services: A river providing clean water for a wetland environment further downstream
How can communities increase ecotourism?
Improve access to ecosystems, partnering the community to learn and value conservation, volunteer programs to clean up ecosystems to make them more attractive
What are some challenges for ecotourism in Kansas?
Lack of public land, lack of funding for the parks department, lack of government action
Explain how it can be dangerous to conserve based solely on economic value.
Could cause ecosystems to be compared to each other, could lead to human developments that are valued higher to replace ecosystems, easy to undervalue ecosystems
Channelized Stream
A stream that has been made straight by humans
Meandering stream
A stream that is not straight, often meanders more as time passes
Floodplain
Flat area above the bankfull where water will flood over
Bankfull
The total height a river can have before it floods
Point bar
An area of deposition that occurs on the inner side of expanding streams
River mouth
the end of a river. Usually v shaped
Name consequences of stream channelization
Increases the speed of the water, making more erosion happen downstream
How does rainfall influence cutbanks and deposition?
More rainfall, increase in erosion and makes cutbanks higher. Can also increase deposition.
Orange roots
Means they have been exposed for less than a year
Brown roots
have been exposed for more than a year
Why is it not considered ideal to use a straight retaining wall for erosion control?
Speeds up the water and will also throw the water at the other side at a fast speed.
How are rocks used for erosion control stabilized?
Placed on top of soil with nets and vegetation
Name and explain 4 steps homeowners can take to protect streams
Don’t mow to the edges of the stream bank, use less fertilizers, don’t dump lawn clippings, and use native plants in your landscaping
Sublimation
water goes directly from solid to a gas. Occurs in low pressure places like mountains
Deposition
water goes directly from a gas to a solid. Occurs in low pressure places like mountains
Fog drip
Droplets of water from fog adhere to the ground. Happens in low lying areas
Seepage
Occurs when ground water reaches the surface
River source
the source of a river
riffle
shallow area with fast, turbulent water running over rocks
Pool
deeper, slow zone in a river
Run
Area with little turbulence
Thalweg
where the most rapid water flows
Wetland
area with water that supports vegetation adapted to being saturated with water
Hydrophytes
a plant that grows in water
Riparian
the space along water where the plants growing are still affected by that water
What is the difference, between a river, stream, and creek?
No set difference. Generally river>stream>creek
Name some common differences in river organisms vs. stream organisms
River organisms will be larger and heavier than stream organisms
Name some watersheds which include JCCC
Mississipi watershed, Indian Creek Watershed, Lower Republican Watershed
What is the largest watershed in the U.S.?
Mississipi River Watershed
How do discharge hydrographs change with weather?
Spike during high rain events
Which organization posts real time hydrographs online?
USGS (United States Geological Survey)
Give an example of discharge influencing wildlife survival
If there is a lot of fast, frequent discharge, organisms that reproduce in the water may struggle to establish
Zone of erosion
On the outer curve of a river. Fast moving water cuts into the bank
Zone of deposition
On the inner curve of a river. Slow moving water deposits particles
Where is the thalweg in a meandering stream?
The outer side of each curve
Fen
ground water wetland that forms peat
Bog
rainwater wetland with peat and sphagnum moss
Swamp
forested wetland that sometimes floods
Marsh
A softstem, flooded wetland
Which is more acidic: bog or fen?
bog, because it is supplied by rainwater
Where are peatlands typically located?
North
Where are swamps normally located?
Costal
Where are marshes mostly located?
Inland
Explain the importance of transpiration in wetlands
Wetlands transpire a lot of water during the day, meaning surface water greatly decreases throughout the day and then collects again at night
Lentic
standing water
Lotic
running water
Lake
a lentic, open body of water in a depression not in contact with the ocean
Oxbow lake
A lake formed by a bend in a river being cuttoff by the river finding the path of least resistance. U shaped
Seiche
oscillation in the water level of a lake
Dimictic
Mixes twice, once in the spring and once in the fall
Monomictic
Mixes once in the fall
Polymictic
mixes frequently with wind and storms. Mostly in tropical areas
Artesian well
a well that brings groundwater to the surface without pumping because it is under pressure
Permeability
The amount of space between particles that water can flow through
Water table
the boundary between water-saturated ground and unsaturated ground.
FETCH
Looking at the direction of the wind and how long the stretch of lake it will affect. Helps determine if a lake is going to mix
Capillary Fringe
Water sticking to places where there is a lot of surface area
Fossil Water
Aquifers confined by multiple confining beds that can take centuries to millennia to refill. Non-renewable resource
Glacial lake
rounded form, carved by glaciers coming down
Graben lakes
formed by tectonic plates, long, skinny and very deep
Human made lakes
Jagged, fingerlike shape from damming, always a flat piece where the dam started
Littoral zone
Where light is getting to the shore
Penetrates all the way to the ground
High diversity
Pelagic zone
Open water, not near the shore
Photic zone
Very diverse
Profundal zone
Also known as Aphotic (without light)
Not very diverse, only supports tolerant organisms
Decaying material
Calculate retention time in lakes when given the volume and water loss
R = V/L
How does retention time influence the effects of pollutants?
Longer the retention time, the harder it is to recover from pollutants
In a dimictic lake, how do the temperatures separate in summer?
Cold water on the bottom, warm water on top
In a dimictic lake, how do the temperatures separate in winter?
Cold water on the top with ice, warm water on the bottom
When is a monomictic lake stratified? When is it mixed?
Stratified in the summer, mixed in all other seasons
What causes the difference in dimictic and monomictic lakes?
Whether or not it gets cold enough for an ice layer to form
At what temperature is water most dense? How is density different from most materials in solid form?
4* C. Different from most materials because ice in its solid form is less dense than its liquid form
What is rocking in an internal seiche?
The thermocline
Which lasts longer, an internal or external seiche?
internal seiche
hypolimnion
bottom layer, O2 poor
Epilimnion
Upper layer, O2 rich
Thermocline
Where the temperature shifts, O2 decreased
What causes Langmuir circulation cells?
wind pushes against water, causing each side to rotate in a different direction and form a gutter of bubbles and debris