Chapter 1: Introduction
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Producer Goods
goods manufactured for other companies to use to manufacture either producer or consumer goods
Consumer Goods
goods purchased directly by the consumer or the general public
Product life-cycle curve
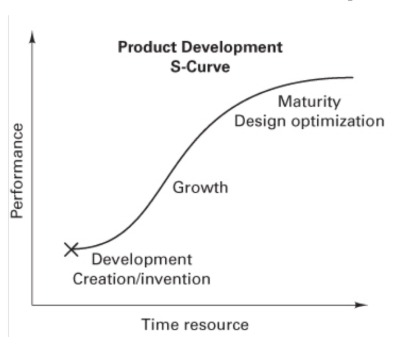
Sustaining Technology
Innovations in materials, processes, and design that bring more value to the consumer of existing products and services
Manufacturing System
A collection of operations and processes to produce a desired product(s) or component(s)
___________ __________ are arranged in the factory to form a manufacturing system
Manufacturing Processes
Production System
the total company and includes manufacturing systems
Goods
Material Things
Services
Nonmaterial things (i.e. transportation, banking, health care, education, etc.)
Manufacturing Processes
converts unfinished materials to finished products, often using machines or machine tools
Process
a sequence of steps, processes, or operations for production of goods and services
Machine Tool
an assembly of related mechanisms on a frame or bed that together produces a desired result
Job
the total of the work or duties a worker performs
Station
a location or area where a production worker performs tasks or a job
Operation
a distinct action performed to produce a desired result or effect
Treatments
operations that change or modify the product-in-process without tool contact
Tools
used to hold, shape or form the unfinished product
Lowest mechanism in the production term rank
Fabricating
the manufacture of a product from pieces such as parts, components, or assemblies
Processing
the manufacture of a product by continuous series of operations
Primary objective of manufacturing
to produce a component having a desired geometry, size, and finish
5 manufacturing system designs
Job shop
Flow shop
Linked-Cell shop
Project shop
Continuous process
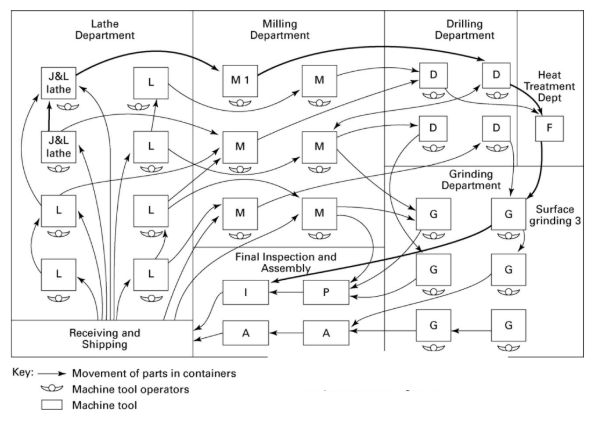
Job Shop Characteristics
Low Volume of production
General-purpose machines
Large variety
Flexible
Functional Layout
Functional Layout
Machines are collected by function (all lathes together, all
mills together, all grinding machine together)
Parts are routed around the shop in small lots to the various
machines
Material is moved from machine to machine in carts or
container
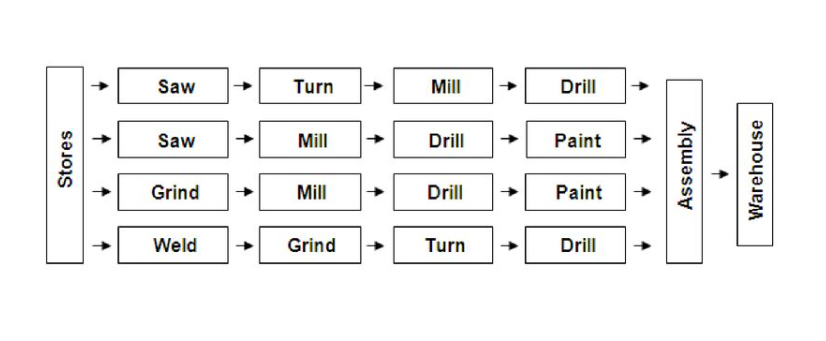
Flow shop
has a product-oriented layout composed of mainly flow lines
Flow Shop Characteristics
Larger Volume of the same part
Special-purpose machines + equipment
Less variety
Less Flexible
More mechanization
Flow line layout / Assembly Line
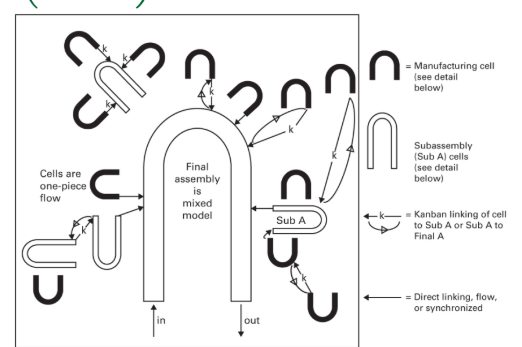
Linked-cell Manufacturing System (L-CMS)
Manufacturing and subassembly cells connected to final assembly by kanban links
U-Shaped Cells
One-piece-flow basis
Kanban
unique form of inventory and information control
Project Shop
Fixed position layout
immobility of the item being manufacturing
Workers, machines, and materials are brought to the site and removed after job is completed
Continuous Processes
Manufacturing of liquids, oils, gases and powder
Most efficient, but least flexible
Involve complex chemical reactions
Heat Treatment
heating and cooling of a metal for specific purpose of altering its metallurgical and mechanical properties
Packaging
to protect the product from the
environment
to protect the product during shipping
to hold fixed numbers of products for sale.
Product Life Cycle
Startup
Rapid Growth
Maturation
Commodity
Decline
Startup Stage Chracteristics
new product/company
low volume
small company
Rapid Growth Stage
products become standardized and volume increases rapidly. The company’s ability to meet demand stresses its capacity
Maturation Stage
Standard design emerges. Process development is very important
Commodity Stage
Long-life, standard-of-the-industry type of product
Decline Stage
Product is slowly replaced by improved products
Life Cycle Cost of a product
cost of materials
cost to manufacture
cost to use
cost to repair
cost to dispose