POD Unit 5: Bacteriology
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
Bacteria - characteristics
- UNICELL, MICROSCOPIC PROKARYOTES (0.5-5ug)
- Most are HARMLESS/HELPFUL
- Contain BOTH DNA and RNA,
- Cell wall RIGID, Peptidoglycan or cellulose?
- Replicate via BINARY FISSION
What is Microbiota? How is it affected?
- Collective of bacteria that inhabits body of animal
- Beneficial bacteria can keep host HEALTHY: Absorb nutrients, break down food, preventing growth of harmful bacteria
- Changes w body location, age, host, etc...
- Associated w physio and pathologies of animals
Explain the parts of the Bacterial Structure:
- Cell Envelope
- Flagella and Pili
- Spores
1. CELL ENVELOPE:
- Use for Dx
- Usually VIRULENT
- Some are PAMPs => target for antibiotics and disinfectants
2. FLAGELLA and PILI/FIMBRIAE
- Filament, protein
- Flagella => Motility
- Pili/Fimbriae: 2 types:
+ COMMON: Adhere to cell surface
+ SEX: Genetic exchanges
3. SPORES: Most dominant form
- Minimal metabolism and respiration
- Reduce enzyme production
How to do Bacterial Identifications? Based on what?
- Morphology
- Staining
- Culture
- Biochem rxn
- Molecular methods
- Immunological methods
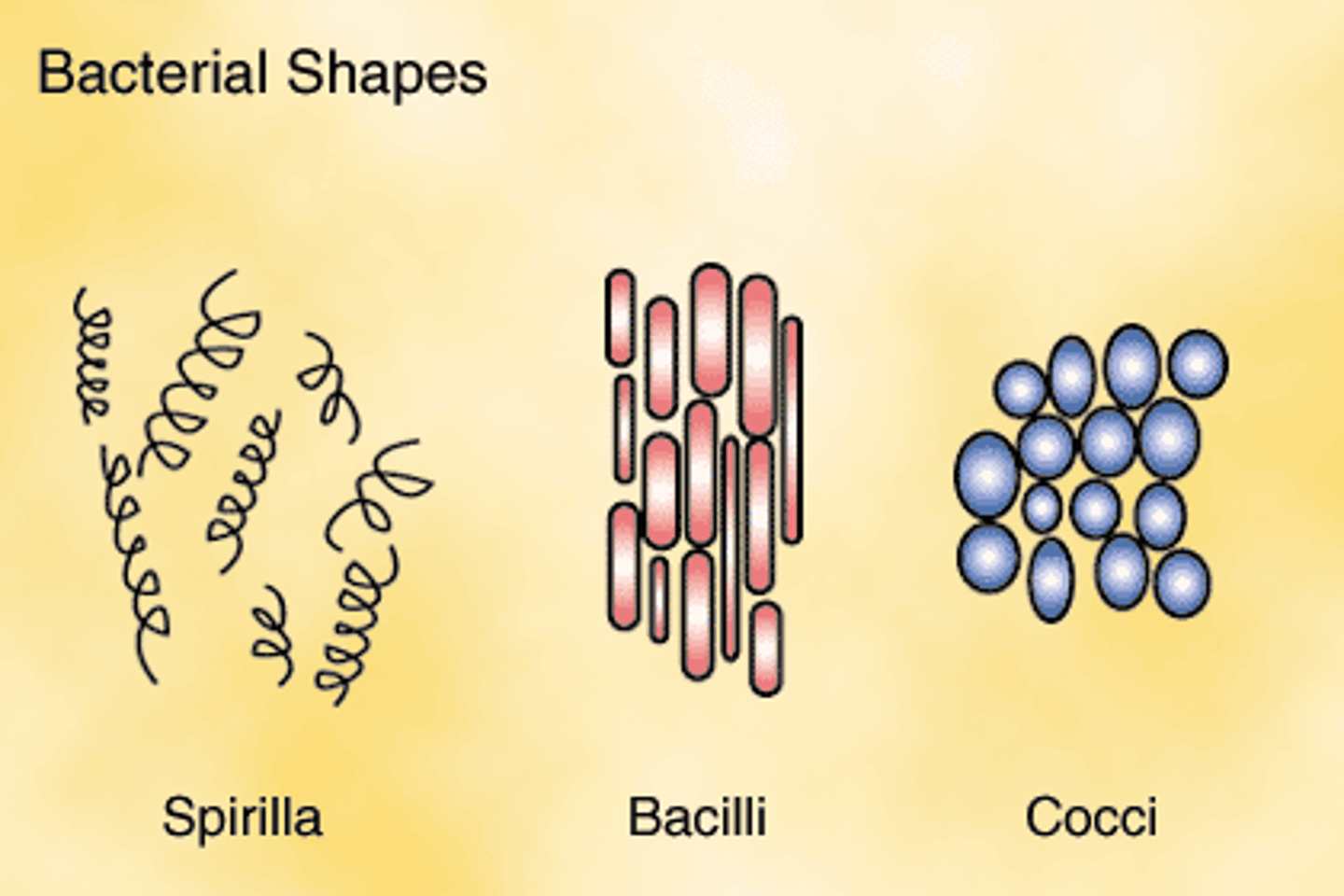
3 Morphology of Bacteria?
1. Cocci (sphere)
2. Bacilli (rod)
3. Spirochetes (spiral/helix)
Difference between Gram (+) and Gram (-) bacteria
Differ in CELL WALLS/MEMBRANES:
(+):
- Has TEICHOIC acids => ANTIGENICITY
- Stain PURPLE (Positive for P)
(-):
- 2 layers
- High lipid
- Little peptidoglycan
- Stain RED
=> They have DIFFERENT ANTIBIOTIC RESPONSES!
Cultural methods: Media Forms and Media Types?
FORMS:
- Solid
- Semi solid
- Fluid
TYPES:
- Basic/all purpose
- Enriched
- Enrichment
- Selective (differential or transport)
How long do bacteria take to grow under optimal condition?
Divide every 20 minutes
=> Can use this to draw a bacterial growth curve
What Biochemical Rxn can be used to identify bacteria? (2)
1. CATALASE test:
- Differentiate those that produce catalase to break down H2O2 to O and H2O
- To differentiate STAPH. from STREP (staph is (+))
2. COAGULASE test:
- Identify those that produce coagulase, which converts fibrinogen => fibrin
- To differentiate between STAPH. SPECIES (S. aureus is (+))
=> These tests are EASY and CHEAP
What Molecular Methods can be used to identify bacteria? Pro of using this, and some examples?
- Study GENOME
- MOST ADVANCED and ACCURATE
- Classify bacteria into species, strains, serotypes, pathovar levels
- Examples:
+ PCR
+ DNA/RNA probe tests
+ Microarray
+ Electrophoresis
+ Proteomics
What Immunological Methods can be used to identify bacteria? When can we use this?Examples?
- Only useful for PATHOGENIC bacteria => Identify Ig or antigens
- Examples:
+ ELISA
+ RadioIA
+ FluoroIA
+ Chromatography
What are fungi?
- EUKARYOTES
- Majority = SAPROPHYTES = Live on dead organisms
- Reproduce via SPORES (not like bacteria)
- CHITIN cell wall
- Uni or Multicell
Ex. Yeast, mold, mushrooms
Codes for ID bacteria
- 1 =
- 2 =
- 3 =
- 4 =
- OBL =
- PR =
- OPP =
- Z =
- R =
- 1 = Extremely familiar
- 2 = Very familiar
- 3 = Aware of name and info
- 4 = Heard of name and know where to find info
- OBL = Obligate
- PR = Primary pathogen
- OPP = Opportunist
(not clearly different from PR)
- Z = Zoonotic
- R = Reportable
Difference between Obligate, Opportunist, Facultative, and Primary Pathogen? Important note about them?
- Obligate = ONLY FOUND in DZ host
(Obligate intracellular: can only multiple within host cells)
- Facultative intracellular - Can multiply inside AND outside cells
- Opportunist = Only cause Dz when host's IMMUNO-compromised (found always, but ony cause dz in certain circumstances)
- Primary = Cause Dz REGARDLESS of host's immune system
**Primary pathogen and Opportunist aren't clearly different => Classifying them are arguable!**
Types of Fungi - differentiate? (3)
1. YEAST:
- UNIcell
- BUDDING to divide
- May have pseudohyphae
2. MOLD:
- MULTIcell
- Extending spores ASEX/SEXUALLY into tubes (HYPHA) or cotton-wool mass (MYCELIUM)
3. DIMORPHIC FUNGI:
- Both yeast and mold forms
5 steps to Sequence of Pathogenesis
1. Enter/attach
2. Evasion of Host's Defences
3. Multiplication + Colonization
4. Damage to Host
5. Transmission to other hosts (infectious stage)
Characteristics of Bacterial Colonization?
- What determine host and organ specificity?
- Difference btw Obligate, Primary, and Opportunistic pathogen in this step?
- ADHESINS => Determine host and organ specificity
- Obligate and Primary bacterial pathogens are host and organ specific
- Opportunists are often non-host specific. However, pathogen, envi, and host factors still determine colonization.
What molecules from Bacterial cause Host Damage (4)?
- Toxins = Endotoxin and Exotoxins
- Lytic enzymes
- Inflammation from PAMPs, TLRs
- Immune-mediated
Gram-Positive Aerobic Cocci - What Bacteria are they? Their habitats? (3)
3 major genera:
1. Staphylococcus
- In MUCOSAL surfaces
- POSITIVE Catalase test - Catalase = enzyme breaks down H2O2 => Resist oxidative damage from phagocytes
2. Streptococcus
- In THROAT and UROGENITAL
- Negative catalase test
3. Enterococcus
- In INTESTINE
- Negative catalase test
Staphylococcus - Characteristics?
CHARACTERISTICS:
- CATALASE (+)
- GRAPE-like clusters
- Most are non-pathogenic, COMMENSALS of skin and exposed mucosae
=> Some become OPPORTUNISTIC PATHOGEN
- SURVIVE well in envi
- Some host specificity
- Cause PURULENT INFECTIONS and necrosis
- PATHOGENICITY: More pathogenic = COAGULASE (+) as well
Virulence factors of Staphylococcus?? FIX
- Fibronectin-binding proteins => Adhesin colonization of wound activity
- DNAs, Lipase, etc. => Host tissue penetration
- Hemolysin => Damage cell membranes
- Leucocidins => Cytolysis of leukocytes
- Enterotoxin => D+
- Toxic-shock-syndrome toxin => Superantigen that cause shock
- Coagulase => Make Fibrin shields to hide from phagocytes
- Protein A => Bind Fc in immunoglobins
- Biofilm => Shield from host defences
Chemical nature of Endotoxin?
= LPS or lipopolysaccharides
Different species and disease of Staphylococcus?
1. S. AUREUS:
- in HUMAN and some animal
- Infection: SKIN and WOUND, Local NECROSIS, PUS, abcess
- Also cause: UTIs, Bacteremia, MASTITIS, Arthrisis, BUMBLEFOOT
- Toxic SHOCK syndrome when food-borne (by enterotoxins)
- Contagious => 1 common Hospital acquired infections in the ESKAPE group
- MRSA = Methicillin-resistant S. aureus = RESISTANT TO ALL B-LACTAMS so resistant to many antibiotics!
2. S. PSEUDINTERMEDIUS, SIG (intermedius group):
- In DOGS and CATS
- Most common OPPORTUNISTIC PATHOGEN in dogs
- Similar virulence factors, pathogenesis, epidemiology like S. aureus
- Cause: PYODERMA, OTITIS, UTIs, wound, Bacteremia, vaginitis, metritis, conjunctivitis, abcess
- MRSP: Methicillin-resistant S.pseudin: MULTIRESISTANT to many antibiotics
3. S. HYICUS:
- In PIGS, affect young pigs (under 6wk)
- Morbidity: 10-90%; Mortality: 5-90%
- Cause EXUDATIVE EPIDERMITIS and non-pruritic pustules (Greasy Pig Dz)
How do you differentiate or Dx between Staph species?
- Use SMEAR and GRAM stain of clinical materials
- Culture and ID within 1 day
- Use MALDI-TOF MS to differentiate (a molecular test)
- Other methods: mecA for MRSA and RSP
- Antimicrobial susceptibiity test (1 day)
How to treat and prevent Staph infection?
- TX: Antimicrobials AND eliminating primary cause (as it's opportunistic)
- Aseptic SX, wound hygiene
- MASTITIS: Prevent by detecting subclinical infections, hygiene, dry cow therapy
- Susceptibility testing because there's frequent antimicrobial resistance!
Characteristics of Streptococcus?
- Chains of cocci
- Commensals of MUCOUS MEMBRANES (NOT skin)
- DO NOT SURVIVE well in envi
- Fastidious
- Strong Host SPECIFICITY
- Cause PYOGENIC INFECTIONS
Virulence factors of strep - FIX
Different species of Streptococcus? - FIX
1. S. EQUI subsp EQUI
- In HORSES, PRIMARY pathogen
- Cause STRANGLES
- Highly contagious and morbid (Mortality: 10%)
- Abcess in LNs OF HEAD/NECK
- Transmission via DISCHARGE + GUTTURAL POUCH carrier
- TX: Isolation, quarantine, clean, penicillin
- Vax available but not 100% effective
2. S. EQUI subsp ZOOEPIDEMICUS
- In HORSES, OPPORTUNIST pathogen (meaning will only cause DZ when there's immuno-suppress)
- Cause PURULENT INFECTION, 2nd PNEUMONIA, septicemia, abcess, wounds, UTI, mastitis,
FIX THIS
3. S. AGALACTIAE
- In CATTLE, PRIMARY PATHOGEN of udder
- Cause CONTAGIOUS MASTITIS
- May cause SUBCLINICAL mastitis w chronic fibrosis and atrophy
- Cause Neonatal septicemia in humans and not cows
- TX: FIX
4. S. SUIS
- In PIGS and HUMANS, PRIMARY Pathogen
- In TONSILS of carriers
- Cause SEPTICEMIA in WEANER pigs
FIX THIS ONE
5. S. CANIS:
- In CATS/DOGS, OPPORTUNISTIC
- Cause PURULENT INFECTIONS
- Minor pathogen, Cause: UTI, wound infection, ... FIX
How to DX Streptococcus?
- Smear and Gram stain
- Culture and ID
- Antimicrobial susceptibility testing usually NOT NEEDED!
- Need to use:
+ Transport media
+ Lancefield serogrouping
+ Hemolysis ?
How to prevent and treat Streptococcus? - FIX
Characteristics of Enterococcus?- FIX (add last slide in)
- FACULTATIVE ANAEROBES
- Low-grade OPPORTUNIST
- INHABIT GI tract, tolerate bile
- Cause diverse GI infections
- 2nd Infections are: Mastitis, UTIs, Wound infections
- Cause NOSOCOMIAL/hospital acquired dz (ESKAPE)
Different species of Enterococcus (3) - FIX
1. E. FAECALIS:
Answer the questions at the end of slide? AND end of notes?
Lec: GRAM POSITIVE AEROBIC RODS: Characteristics and Genera? How to Dx? - FIX!!!
2 groups: (second group is Mycolata)
This group has 4 genera
- Diverse morph and genetics
- THICK CELL WALL, susceptible to PENICILLIN G
- Some are agents for zoonoses, septicemia, bacteremia
- Rod-shaped
1. BACILLUS
- In Human, animals, soil
2. LISTERIA:
- In Throat and Urogenital tract
3. TRUEPERELLA:
- In Intestine
- Same order as 4: Actinomycetales
4. ACTINOMYCES:
- In Mouth flora
- Same order as 3: Actinomycetales
DX:
- GIEMSA stain => Pink capsule
Bacillus bacteria: Characteristics, Virulence, Pathology, and Prevention/Tx?
- Large gram (+) ROD
- OBLIGATE Pathogens
- FORM SPORES
- AEROBIC, fast growing
- Mostly saprophytes (anthrax)
- Skin contaminant
- REPORTABLE, ZOONOTIC DISEASE!
VIRULENCE:
- Highly resistance endospore/capsule => ANTIPHAGOCYTIC
- Toxins to phagocytes:
+ PA: PROTECTIVE ANTIGEN = make pores for transportation of the other toxins
+ EF: EDEMA FACTOR = Perinuclear endosomal membrane factor
+ LF = LETHAL FACTOR = Affects cellular activities and apoptosis
- Release pro-inflammatory cytokines from macrophages
- These toxins help proliferates bacteria in body => Cause SEPTICEMIA
PATHOLOGY: Cause:
- Septicemia => Sudden death (Ruminants)
- No blood clotting => Hemorrhage
- Large, dark spleen (Ruminants)
- Enlarged LN (Ruminants)
- Marked localized edema (Dogs, swine)
- BIRDS UNAFFECTED
TX:
- DX quickly => Dispose carcasses safely (burning)
- DRUGS: Penicillin G, aminopenicillin, macrolides
- VACCINATE endemic regions
=> IM/SubQ = excellent
3 species of Bacillus?
3 Species:
1. B. ANTHRACIS: - MOST IMPORTANT
- In human, herbivores, soil
- Zoonotic
- REPORTABLE in Canada
- SPORULATION IN AIR (so don't open carcass!)
- Spores can PERSIST DECADES in the ground!
- Infection: ANTHRAX (animals and humans), fatal contagious in ruminants
2. B. CEREUS:
- In Humans (food, soil, water), cattle
- Infection: Mastitis, abortion, food poison
3. PAENIBACILLUS LARVAE:
- in BEES
=> American Foulbrood Dz
Characteristics of Anthrax in Canada? In Humans? How to dispose of anthrax carcasses?
- RARE and REPORTABLE in Canada
- ENDEMIC in Wood Buffalo National park
- From SPORES in SOIL from DEAD ANIMALS from anthrax
=> Why you should NEVER OPEN CARCASS OF ANTHRAX!
=> Dispose viz BURNING + FORMALDEHYDE >10%
HUMANS:
- Cutaneous = Woolsorter's dz (malignant carbuncle)
- Aerogenous (air) = Pulmonary anthrax (used in bioterrorism)
- Oral = Intestinal and Oropharyngeal anthrax
Listeria: Characteristics, pathogenesis, consequence of Dz in animals/humans, DX, TX and Prevent
= Listeria monocytogenes
- OPPORTUNISTIC
- ZOONOTIC Dz: Contaminate human food => outbreak (usually FOOD-BORNE)
- Gram (+) Coccobacillus - ROD
- AEROBIC
- HEMOLYSIS
- SAPROPHYTIC
- Can tolerate pH low (5.5) => Grow in bad silage = SILAGE DZ
- Still grows slowly at low temp (4C) => Psychrophilic
- ASYMPTOMATIC ENTERIC Carriers
PATHOGENESIS:
- Penetrate epithelial cells
- Escape phagolysosome
- Moves from cell to cells directly
- Remain cellular => Escape immune response
DISEASE
- Cause: NECROSIS, micro-ABSCESS, SEPTICEMIA
- Mainly in ruminants: NEURO ENCEPHALITIS (trigeminal nerve + brainstem abscess), ABORTION (septicemia -> transplacental)
- Abortion in chinchillas
- Mastitis, keratoconjunctivitis
- Humans: Meningitis, abortion, septicemia (usually weak = predisposed), MORTALITY 30%
DX:
- Clinical signs
- Culture/pathology (histology of encephalitis)
TX: Treat in early stage: Penicillin, ampicillin, tetracyclins
PREVENT: Check silage quality + VAX
SAPROPHYTIC meaning
Feed off dead organic matter
Trueperella: Characteristics, Consequence of Dz, Virulence, DX, Prevention
= Trueperella pyogenes
- Gram (+) ROD
- AEROBIC but FACULTATIVE ANAEROBIC, Slow growing (48h)
- Live in SKIN and EXPOSED MUCOSA and INTESTINE of ruminants + pigs
- OPPORTUNISTIC
- HEMOLYSIS
- Survive in envi then multiples in host
DISEASE:
- PURULENT INFECTION (chronic)
- Disseminate => BACTEREMIA
- Mixed w other anaerobic bacteria => Toxin synergy
- Infections: METRITIS, Bacteremia caused ENDOCARDITIS, Abscesses, Abortion, Arthritis
- Cause: Footrot, wounds, navel infections, pneumonia
VIRULENCE: Poorly understood
DX:
- Smear
- Culture
PREVENTION:
- Avoid primary cause/lesion (as it's OPP)
- NO VACCINE!
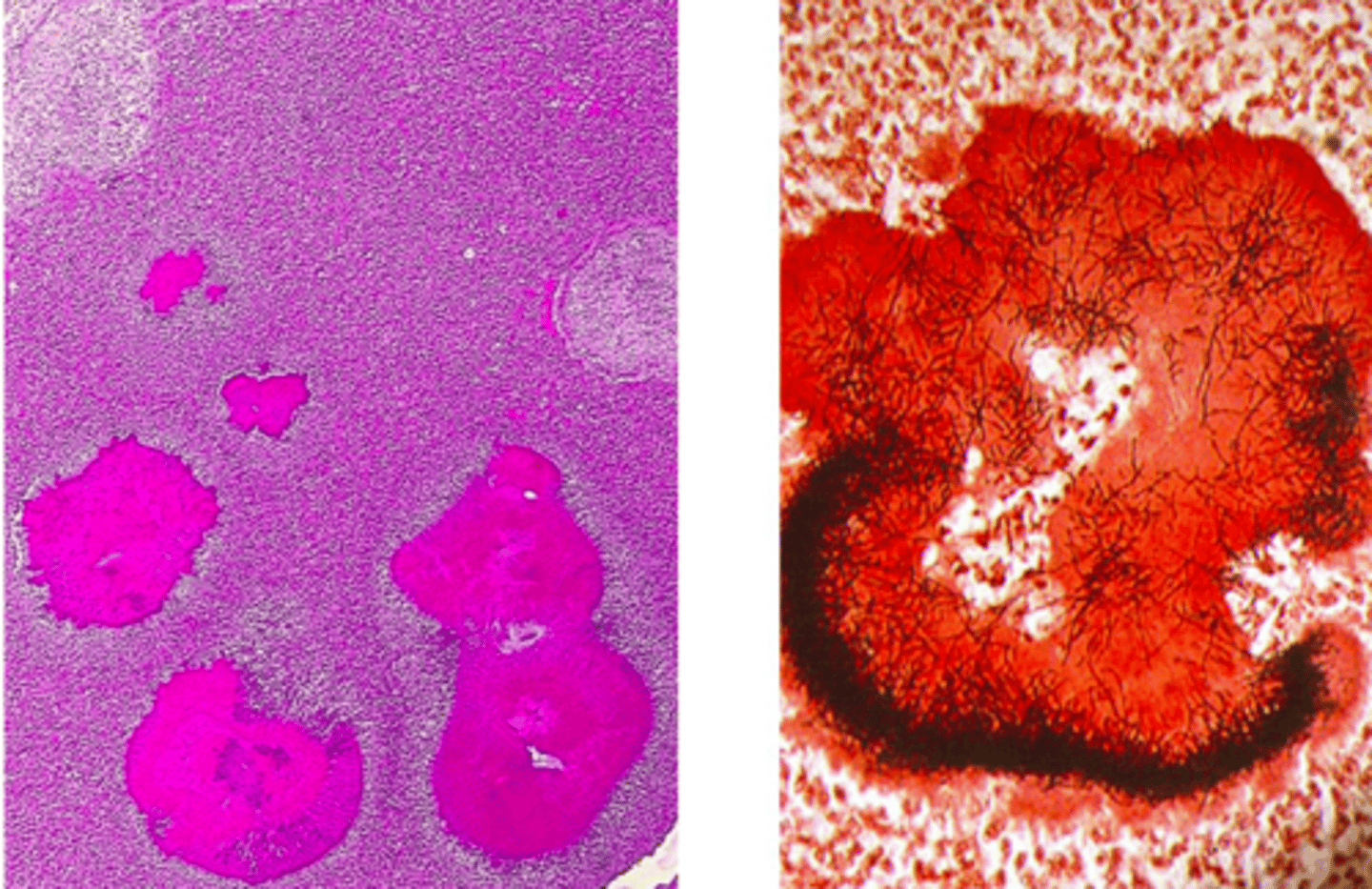
Actinomyces: Characteristics, Consequence of Dz, DX, TX
- BRANCHING FILAMENT
- Live in MOUTH FLORA
- Cause CHRONIC INFECTION w mouth, bites
- In colonies surrounded by SULFUR GRANULES (calcifed macrophages)
DISEASE:
- In Cow: LUMPY JAW DZ: Mandible Suppurative osteomyelitis (trauma/teething associated)
DX: Gram-stain, sulfur granules
TX:
- Since chronic and walled-off micro-colonies => Hard to treat
- SX + Antimicrobials long-term
Go through questions!!!
GRAM-POSITIVE AEROBIC RODS - Mycolata group - Characteristics and genera
MYCOLATA GROUP:
- Has lipid-rich outer envelope w mycolic acid
- FACULTATIVE INTRACELLULAR, can survive out or inside macrophages
- Cause GRANULOMATOUS inflammation => Chronic infection
- Cellular Type 1 Immunity => Can do gamma interferon test/serology to check
4 Genera:
1. Corynebacterium:
- In Human, Animals, Ruminants
2. Mycobacterium:
- In Human, birds, ruminants, horse, pigs
3. Rhodococcus:
- in Herbivore manure-contaminated soil
Corynebacterium - Characteristics, Dx, Infection, and Prevention/Tx
- Gram (+) rod, small, PLEIOMORPHIC (coccoid or club or rod shape)
- AEROBIC, takes 1-2d to grow
- COMMENSALs in mm. and skin
- OPP pathogen, ZOONOTIC, HOST SPECIFIC
- Cause: PYOGENIC INFECTIONS, Pseudotuberculosis => CASEOUS LYMPHADENITIS
- ONION RING STRUCTURE = typical of this dz
- Infection from: Wound contamination, sheering, ticks
- Infect other animals in the herd
DX:
- PE
- Pathology, culture
- SEROLOGY and BLOOD GAMMA INTERFERON TEST
TX/Prevent:
- Antibiotics: Problem w PENETRATION in vivo (as it's facultative intracellular) + Resistance => Not efficient
- Eradication through CULLING based on blood tests
- Hygiene and isolate infected
- VACCINE (partial protection) => Side effect: Abscess
Check all slides and see the "infection" part - meaning how the animal can be infected w the bacteria! (and not mean "what infections this bacteria cause)
Mycobacterium - Characteristics, Cause what, Species
- WEAKLY Gram (+) rod, aerobic
- Has LIPIDS in cell wall => ACID-FAST STAIN
- SURVIVE WELL in envi
- FACULTATIVE INTRACELLULAR
- Many species! (saprophytic, opp, obligate)
- SLOW growing (24h to divide, WEEKS to isolate)
- Cause: Chronic GRANULOMATOUS infections
Many species:
1. M. tuberculosis => Human, primates
2. M. bovis => Cattle, human, ruminants, horse, pigs
3. M. avium => Birds, ruminants (paratuberculosis)
Mycobacterium bovis - Characteristics, hosts, pathogenesis, outcome dependent on what?, Fate in Canada, DX, TX, Prevention
- OBLIGATE, REPORTABLE, ZOONOTIC Dz
- Human => Turn to M. tuberculosis
- Wildlife and Domestic animals => M. bovis
- WILDLIFE = RESEVOIR for domestic
- Cause: GRANULOMA
PATHOGENESIS:
- Airway/ingestion infection
=> Innate host control:
- Local multiplication
- Macrophages uptake => bacteria survive in macrophages => activate TH1 response w gamma interferron => Form tubercle and chronic granulomatous activation
- LN migration => Lymphadenitis
=> Containment
==> Cause Acute Dz
==> OR Spontaneous healing
=> Latency
=> Reactivation
=> Dz/Transmission
- Outcome is dependent on CELLULAR IMMUNITY
CANADA:
- Persist in WOOD BUFFALO NATIONAL PARK
- Some outbreaks detected from meat inspection surveillance
DX:
- Detected at slaughter
- Tuberculin skin test => Slaughter
- PE and Pathology
- ACID FAST-STAIN
- PCR, Slow culture
- DNA methods
TX:
- Culling
- Human: Amtimicrobials
- Other mycobacteria: use fluoroquinolones, macrolides, minocycline etc.
PREVENT:
- Slaughter surveillance, meat inspect
- Test-slaughter (DTH, gamma interferon assay)
- Quarantine, retesting
- MOVEMENT controls
- Hygiene and Milk pasteurize
- Vaccine
Mycobacterium avium complex - Characteristics, hosts, Prevention
= AVIAN TUBERCULOSIS = CHRONIC infection
- PRIMARY, ZOONOTIC
- Infected via AIR, intesting, dissemination
- Prevention similar to M. Tuberculosis
Mycobacterium marinum - Characteristics, hosts, Cause what?
- OPP, ZOONOTIC, saprophytic
- Infected via SOIL/WATER
- FAST GROWING
- Cause: Fish tank granuloma, pyogranulomatous skin lesions
Mycobacterium avium sbs paratuberculosis (MAP) - Characteristics, hosts, where it reside, cause what, factors affecting infection?
Epidemiology? DX? TX and Prevent?Clostridium
= JOHNE's Dz
- AEROBIC ROD
- Grow 3-6wk on LIPID RICH media w mycobactin
- ACID-FAST
- Infection via MILK, pasture, utero
- Reside in INTESTINAL MACROPHAGES and LOCAL LNs
- Last LONG - several months, can delay for years
- Cause: GRANULOMATOUS ENTERITIS, CACHEXIA
- Factors affecting: HIGH MILK YIELD, dose, breed, age at infection, calving
EPIDEMIOLOGY:
- Asymptomatic shedders (milk, feces)
- Has genetic predisposition
Check vinson's slides, improve notes too
(Lab 5.3) Extracellular vs Facultative intracellular Bacteria: Differences in:
- Cell type habitate
- Disease process
- Illness length
- Immunity
- Vaccination
- Antibiotics
EXTRACELLULAR:
- Cell types: Neutrophils
- Disease: Purulent
- Length: Short/Acute
- Immunity: Humoral, Th2
- Vax: Bacterin, toxoids
- Antibiotics: Effective, based on susceptibility
FACULTATIVE INTRACELLULAR
- Cell: Macrophages
- Dz: Granulomatous
- Length: Long/Chronic
- Immunity: Cellular, Th1
- Vax: Live attenuated (not complete)
- Antibiotics: Depends on penetration into host cells!
What diseases are REPORTABLE? - FIX
- Write out the list!!!
Clostridium - Characteristics and Pathogens - FIX
CHARACTERISTICS:
- Fix
- Aerotolerant
- Can survive low O2 envi
3 SUBGROUPS:
1. C. difficile, C. perfringens (A-E) => Intestine-formed toxins => Blood => TOXEMIA
- Toxin: ENTEROTOXIN
2. C. septicum, perfringens (A), chauvoei, sordellii => Invasive, Gas-gangrene-producing
- Toxin: HISTOTOXIN
3. C. tetani, botulinum => Non-invasive, colonize host limitedly
- Toxin: NEUROTOXIN
Clostridium Perfringens - Characteristics, Dx, Tx, Control
- PRIMARY PATHOGEN, OPPORTUNIST
- Widespread in intestine, via FECAL contamination
- FASTEST GROWING bacteria
- Some are lethal, mostly PORE-FORMING
- 7 types
- Type A also cause HISTOTOXIC GAS GANGRENE Mastitis (from wound infections)
DX:
- Swab/fluids send to lab
- Gram stain + Culture under anaerobic conditions => Confirm for anaerobes
- MALDI-TOF to confirm organism
TREAT:
- DEBRIDING (if wound) + rinse and drain
- ANTIBIOTICS
PREVENT:
- Antimicrobials to broilers (prophylaxis)
- VAX (toxoid, for pulpu kidney dz)
- Hygiene
7 types of C. perfringens - Their Dz and Toxins? - FIX
1. Type A:
- Mostly commensals - Normally found in gut
- Usually produce Alpha toxin = Normal
- If produce other toxin => DISEASE:
+ Hemorrhagic necrotizing enteritis in dogs and foals (NetF Toxin)
+ Abomasitis in calves
- Also cause: HISTOTOXIC GAS GANGRENE Mastitis (from wound infections)
....
Clostridium Difficile - Characteristics, Pathogenicity, Tx, Control - FIX
- Common in HORSES, pigs, rabbits, guinea pigs, humans
- ZOONOTIC, PRIMARY pathogen
- Difficult to culture!
??? Notes about antibiotics?
PATHOGENICITY:
- SPORES => transmit => Stomach, bile acids
- HX OF ANTIBIOTICS => compromise normal gut flora => C.difficile grow rapidly!
- 2 toxins: A = ENTERO/CYTOtoxin; B = CYTOtoxin
- Virulent type has 027 additional toxin gene = More toxin production!
DISEASE:
- Major HOSPITAL ACQUIRED infections in humans
- From meat
- Cause milder dz => COLITIS => TOXEMIA
- Horses: also have TYPHLOCOLITIS (cecum + colon)
DX: ??
TX: (from lab so fix!)
- Eliminate causing factor (the antibiotics used to begin with)
- Probiotics supplement
- Antibiotics may help but some may aggrevate C. difficile (?)
Blackleg Dz - Agent, Pathogenesis, Dx, Tx? - fix
- C. Chauvoei (also C. septicum and C. novyi)
PATHOGENESIS:
- INGEST spores from soil/other animals
=> Reach liver and intestinal blood (?)
=> Go dormant in muscles
- Trauma that cause ANOXIA (reduce O2 pressure in muscle) => ACTIVATE latent growth of spores
- Spores' toxin => ACUTE, INFECTIOUS, NECROTIZING MYOSITIS + SYSTEMIC TOXEMIA in calves in summer => Death
- They produce gas => CREPITATION under skin
- TX?
DX: (from lab 5.4) - fix
- Send the animal OR piece of affected muscles
- Smear + Stain w SPECIFIC ANTIBODIES for C.c
- Immunofluorescene
- PCR
- Culture
PREVENT:
- VAX (bacterial and toxoid) = most efficient (?)
Malignant oedema/Gas gangrene - Agent, Pathogenesis, Dx, Tx? - fix
-
What's pulpy kidney disease? - FIX
Tetanus - Agent, Pathogenesis, Signs, Dx, Tx? - fix
- C. tetani
- ZOONOTIC: HORSE > Humans > Others (ALL species can have this)
- Infect at DEEP WOUNDS (ex. castration wounds in horses)
- From soil and animal intestine, esp. HORSE MANURE
- Survive as SPORES (Tennis-racket shape spores)
PATHOGENESIS
- Produce TETANOSPASMIN toxin at infection site (= cytolysin)
- Migrate via ascending peripheral nerves to CNS => Inhibitory neuron => INHIBIT the release of inhibitory NT (GABA and glycin)
=> Make motor neurons fire endlessly => SPASMS
SIGNS:
- STIFF PARALYSIS
- Stiff tail, neck, ears
- Muscular spasms
- Protruding third eyelid
DX: fix
- Clinical signs
- Toxin test: mice (rarely done)
TX:
- Calm, darkness, silence
- MUSCLE RELAXANTS, artificial respiration
- ANTISERUM => Stop toxin migration to nerves
- Antibiotics
- Artificial O2 if needed
PREVENT
- VAX (Toxoid) = EFFECTIVE in human and horses (not others)
- Wound hygiene
- Avoid trauma
Botulism - Agent, Pathogenesis, Dx, Tx?
- PRIMARY Pathogen
- Everywhere in the environment
- MOST POTENT TOXIN = BOTULINUM - from anaerobic spoilage of decaying animals/plant
+ 1ug = Kill a person!
+ Similar to Tetanospasmin
PATHOGENESIS:
- INGESTION of agent => Cross intestinal mucosa => Go to PERIPHERAL nerves
- Target Cholinergic cells @NMJ
- INHIBIT Ach release
- Cause peripheral effects
DISEASE:
- Mostly INTOXICATION (ingestion) => FLACCID PARALYSIS
- Also cause TOXICO-INFECTIOUS: Produced in intestine by vegetative bacteria, ex, in chickens
- Also cause WOUND BOTULISM: Rare, pathogenesis like tetanus. Ex. Navel infections, drug addicts
DX:
- Toxin test: Mouse, ELISA
- Mouse test = MOST SENSITIVE: Botulinum toxin => Wasp-waist (diaphragmatic paralysis) in mice
- PCR - can have false positive
A positive usage for Botulinum toxin?
= BOTOX
Explain pathogenesis of Botulism Type E in Great Lakes
- Putrefaction + Less O2 => Grow C.botulinum
- Fish eats toxin from feed
=> Concentrated along food chain
- Birds pick up slow + dead fish => DEATH
REVIEW QUESTION
Lab 5.4: Importance of Plasmids for C. Perfingens?
= Circular DNA, carrying extra genes (ex. for virulence and antiobiotic resistance)
- Plasmids are NOT required for normal bacterial function
- Genes from plasmids are NOT always actively expressed
- Plasmids can be copied and transferred btw bacteria (same or different species!)
Difference between Tetanus and Botulism
- Agent different
- Toxin different
- Entry different (Tetanus via wound, Botulism PO)
- Route and Target different (Tetanus via peripheral nerves => CNS, Botulism via intestine => peripheral NMJs)
- Mechanism different (Tetanus inhibits release of inhibitory NT, Botulism inhibits release of Ach)
- Signs different (Tetanus STILL paralysis, Botulism FLACCID paralysis)
CATCH UP LEC 5.5 5.6
5.7: Pasteurellaceae - Characteristics, host, virulence factor, reside @?
- Gram (-) bacteria
- (+) for Cytochrome C Oxidase test (does produce this)
- Facultative ANAEROBIC
- Nutritionally fastidious, takes 2 days to grow
- 3 Genera: Pasteurella, Mannheimia, Actinobacillus
- Reside at MUCOSAL surfaces (URT, Mouth), survive poorly in environment
- EXTRA-CELL pathogen
- Host specific, broad range, from commensals to primary - NOT HUMAN
- 16 O antigen types
- Cause SEPTICEMIA +/- PNEUMONIA
- Virulence factors: Capsule, adhesins, iron-acquisition system, TOXIN: RTX, PMT, ENDOTOXIN
Pasteurella multocida - Characterisitcs? Which type cause what disease? Dx? Treat and Prevent?
- OPPORTUNIST-PRIMARY PATHOGEN, ZOONOTIC (via bites)
- Normally inhabit Upper Resp Tract (URT) and Mouth of animals (NOT HUMAN)
- Haemorrhagic Septicemia = Asian/African cattle (Type B, E)
- Fowl cholera = Birds septicemia (Type A)
- Swine Suppurative bronchopneumonia = Swine, BRDC Cattle (Type A) (usually occurs with Mycoplasma)
- Rabbit "snuffles" complex = Rabbit's Otitis, rhinitis, septicemia, pneumonia, abscess (Type A)
- Cat/dog bite abscess = Anaerobes
- Swine Atrophic rhinitis = Swine URT infection (twisted snout, turbinate atrophy), PMT Toxin (Type D)
DX: Culture + Oxidase MALDI-TOF
TREAT/PREVENT:
- Antimicrobial prophylaxis, beta-lactams, sulphonamide trimethoprim (some resistance)
- VAX TURKEYS w bacterins
- VAX for Swine rhinitis w PMT toxoids
- Manage Dz!
Mannheimia haemolytica - Characteristic, infection, pathogenesis/virulence, predisposing factors, DX, TX and Prevent
- Within Pasteurellaceae group
- Normally seen in upper resp of cattle
- OPPORTUNIST => PRIMARY PATHOGEN
- Several serotypes with variable virulence (A1 = MOST VIRULENT)
INFECTION:
- Cause RUMINANT PNEUMONIA
- Often mix w other bacteria: Mycoplasma, P. multocida, Histophilus somni
- Main pathogen in BRDC in CATTLE
- Cause SEPTICEMIA + PNEUMONIA SHEEP
PATHOGENESIS/VIRULENCE:
- Fimbrial and afrimbial ADHESINS
- Bacterial CAPSULE resistant to phagocytosis => Evade host's immune
- LEUKOTOXIN RTX => Kill alveolar macrophages and neutrophils PMNs
- IRON acquisition system
PREDISPOSING FACTORS:
- Viral agents: IBR, BVD, Corona
- Environmental + Host factors: Weaning, immunity, transporation, carriers, air/water quality
DX: Culture (slow) + MALDI-TOF
TX and PREVENTION:
- Control predisposing factors
- Precondition: Adapt to bunk feed, dehorn, socialize, deworm, vaccines for other bacteria, avoid stress when transport
- Prophylactic antibiotics (resistance tho!)
- Early recognition + treat, hygiene
2 diseases and agents of Actinobacillus? (toxin, disease, DX, Tx, prevent)
1. A. PEUROPNEUMONIAE:
- Live in Swine URT
- Cause Fibrino-haemorrhagic pleuropneumonia (peracute-chronic) in SWINE (usually mixed flora with other bacteria)
- OPP => PRIMARY
- Complex/fastidious nutrition, need NAD
- Trigger by stress
- Ranges from healthy carriers to chronic and peracut Dz
- VIRULENCE:
+ Iron-scavenging system
+ 16-18 serotypes/capsules, vary in virulence
+ TOXIN: 4 types RTX = Apx
+ ALL serotypes express Apx4
+ Virulent serotypes express Apx1 and 2 => Cytotoxic (macrophages) + Endotoxic (inflammation)
- DX: MALDI-TOF
- TX/PREVENT: Antibiotics, Vax toxoids and bacterins, Manage (don't mix pigs w different serotypes)
2. A. SUIS:
- OPPORTUNIST
- SEPTICEMIA and PNEUMONIA swine, broader host range
- Mortality in high health status herds
- Pathogenesis: Toxin Apx1 and 2, LPS and capsule important
- Same TX/PREVENT as above
Haemophilus - Characteristics?
2 diseases and agents of Haemophilus? (toxin, disease, Tx, prevent)
- Gram (-), coccobacilli, 'blood-loving"
- Non hemolytic, Fastidious, needs NAD or Haemin
- Commensals of MUCOSA (URT)
1. GLAESSERELLA H. PARASUIS:
- CATALASE (+)
- Cause Glasser's dz: POLYEROSITIS, polyarthritis, menignitis, pneumonia
- Higher health = more prone to this
- Fastidious, grow slowly
- Manage + Vaccine (AUTOGENOUS BACTERINS)
- TX w antibiotics
2. HISTOPHILUS SOMNI:
- Live in GENITAL TRACT cattle
- Cause CATTLE: SEPTICEMIA + PNEUMONIA + Myocradial abscesses + Endometritis + BRDC
- Cause SHEEP: SEPTICEMIA, Mastitis, POLYARTHRITIS
- CONTROL: VAX
- TX: Anbitiotics
Bordetella bronchiseptica - Characteristics, Infection Types, Pathogenesis, Dx and Tx/prevent
- Cause dz in immuno-compromised patients
- PRIMARY + ZOONOTIC
INFECTION TYPES:
- Dog & Cat's Kennel cough, infectious tracheobronchitis
- Pig: Atrophic ehinitis predisposition, pneumonia
- Rabbis, guinea, horses: URT infections, tracheobronchitis
PATHOGENESIS:
- CILIOSTASIS: Fimbria + Haemaglutinin attaches to ciliated epithelium @ tracheobronchial; then Toxin destroys them
- Adenylate cyclase-hemolysin enters cell => Inhibits phagocytosis + cause Neutrophil (PMNs) apoptosis
=> Persistent chronic TRACHEAL INFLAMMATION + COUGHING
- In pigs: Dermonecrotic toxin + Osteotoxin => Osteosynthesis inhibition => Atrophic rhinitis in pigs
DX: Tracheal aspirate, culture, MALDI-TOF
TX/PREVENT:
- Vaccine
- Long antimicrobials treatment
- Hygiene
- Isolate case
Taylorella equigenitalis - Characteristics and Dx
- PRIMARY + REPORTABLE
- Never found in Canada, but currently absent in US as well
- Cause CONTAGIOUS EQUINE METRITIS (CEM) => Temporary infertility in mares
- DX: Culture and PCR genital tract for carrier state. Need specific medium. Carriers are usually HEALTHY!
5.8: Brucella bacteria - Characteristics? Types of sub species (5) and Zoonotic potential
- Small GRAM NEGATIVE coccobacilli
- Acid-fast stain
- AEROBES but facultative anaerobes, CAPNOPHILIC
- Host-specific
- Facultative INTRACELULAR
- Target: REPRODUCTIVE organs
- ZOONOTIC
- Cause UNDULANT FEVER HUMANS
TYPES
- B. Abortus: Cattle, bison => In Wood Buffalo National Park (REPORTABLE)
- B. suis: Caribou (free-ranging) (REPORTABLE)
- B. canis: Dogs and humans (rare)
- B. ovis: Sheep (rare)
- B. melitensis: Sheep, goat (not in Canada) (REPORTABLE)
ALL except B. ovis are ZOONOTIC
- Resevoirs: Infected animals and products
- Transmission: Ingestion, skin breaks, airborne (labs)
- Incubation: 2-4wks
Brucella abortus - Characteristics, pathogenesis, infection, explain Surveillance program?
- OBLIGATE, ZOONOTIC, REPORTABLE
- In cattle
- Eradicated in Canada, except Wood National Buffalo Park
- Non-motile, non-capsulated, non-spore => SURVIVE IN ENVIRONMENT FOR MONTHS (but doesn't grow)
- Transmission: Ingestion, wounds, nasal and oral MUCOSAE
PATHOGENESIS:
- Invade epithelial cells via MUCOSAL invasion and Intestine M-cells
- Survive in phagocytes and non-phagocytic cells => Block phagosome-lysosome infusions
- Persistent infection of reticulo-endothelial system
- Can reach placenta via macrophages => Use erythritol => Mass multiplication in placenta => PLACENTITIS
INFECTION:
- CONTAGIOUS ABORTION in cattle (abort once then becomes carrier, shed at parturition)
- Epididymitis + ORCHITIS in bulls => Sterile
- CALVES: <6mth = clear, >6mth = persist for life
SURVEILLANCE:
- CFIA Bovine surveillance system BSS for brucellosis
- Random sampling at slaughter (esp. around Wood Buffalo), at import/export and AI
- DX Tests: RAPID BUFFERED PLATE TEST (cheap, but not specific)
=> If test (+) => Need to do 2nd test: SERUM AGGLUTINATION + COMPLEMENT FIXATION TEST ($, less sensitive, more specific) to confirm
- If still (+) => Quarantine, further tests, destroy animals => Compensate producers
Brucella suis - Characteristics, infection, Dx?
- OBLIGATE, ZOONOTIC, REPORTABLE
- 4 strains:
+ Biovar 1-3 = Swine
+ Biovar 4 = Reindeer & Caribou***
- Prevalent in South America, EU, Asia
=> CFIA does SEROLOGICAL SCREENING at slaughters
INFECTION:
- Chronic INFLAMMATION of REPRO tract
- Stillbirth, Neonatal mortality
- Temporar sterile
DX: Serology: ROSE-BENGAL PLATE AGGLUTINATION, ELISA => Culture + PCR
Brucella canis - Characteristics, infection, Dx and Tx?
- OBLIGATE, ZOONOTIC (rare in humans)
- In free-ranging dogs
INFECTION:
- Chronic, persistent reticuloendothelial infection
- Bacteremia
- VERTEBRAL OSTEOMYELITIS
- Abortion in late pregnancy
- Epididymitis, orchitis (pyogranulomatous inflammation in testes)
DX:
- Serology, rapid slide agglutination (RSA) (low specificity)
=> Confirm w ELISA + Agar gel immunodiffusion assay (more specific)
TX: Tetracycline LONG TERM + Aminoglycosides
Brucella ovis - Characteristics, infection, Dx?
- OBLIGATE
- Present in most all sheep countries
INFECTION:
- EPIDIDYMITIS (unilateral)
- ABORTION
- LAMB MORTALITY
- Genital lesions in rams
- Placentitis in ewes
DX:
- Bacteriological Isolation from semen, vaginal discharge, milk
- SEROLOGICAL TESTS: CFT, AGID, ELISA with SOLUBLE SURFACE ANTIGENS
Pseudomonas aeruginosa - Characteristics, virulence, diseases, Dx, Tx?
- Gram-NEGATIVE, Strictly AEROBE
- Superficial, rarely systemic
- Large genome, metabolically versatile
- Ubiquitous (everywhere) in water and soil
- OPPORTUNIST, ZOONOTIC w broad host => esp. IMMUNOCOMPROMISED HOSTS and burn patients
- Usually killed by neutrophils so Dz usually occurs in neutropenic patients
VIRULENCE:
- Alginate (slime)
- Elastases
- Hyalyronidases
- Collagenases
- Haemolysins
- Exotoxins
DISEASES:
- Dog: OTITIS externa, corneal ulcers, wounds
- Horses: CORNEAL ULCERS, infectious metritis
- Cattle: Nosocomial mastitis
- Mink: HEMORRHAGIC PNEUMONIA
- Sheep: FLEECE ROT
- Humans: Corneal ulcers, burn infectious, cystic fibrosis
DX: Fruity smell
TX:
- NO VACCINE (except in mink!)
- RESISTANT TO ANTIBIOTICS and disinfectants
- Need to do antimicrobial susceptibility testing
- Part of the ESKAPE group
Moraxella bovis - Characteristics, infection, virulence, Tx and prevent?
- Seen in pairs
- PRIMARY pathogen
- Animals carry bacteria in CONJUNCTIVA
- Spread by FLIES + Direct contact from carrier cows
- Organism host-adapted
INFECTION:
- BOVINE KERATOCONJUNCTIVITIS (pink-eye) => ulcers => blindness
- Animals don't eat well => Welfare and Production issues
- INCREASED SUNLIGHT SENSITIVITY + Darkening below eye
VIRULENCE:
- RTX HAEMOLYSIN
- Fibrinolysin
- Hyaluronidase
- Adhesive pilus => Antigenic variation
- Cause POOR IMMUNITY following infection
TX and CONTROL:
- Early Dx
- FLY CONTROL w insectivide impregnated ear tags
- Predisposing factors prevent: Cut tall grass, prevent viral infections, avoid dust and pneumonia
- Antibiotics topical, Aminoglycosides, beta-lactams, macrolides, tetracyclines
- NO VACCINE!
Bartonella - Characteristics, infection, vector, virulence, diseases, Dx, Tx
- Gram NEGATIVE, AEROBIC coccobacilli, INTRACELLULAR (in RBCs, affect Bascular Endothelium)
- Numerous species, some highly host adapted
- Vector: FLEAS and TICKS
- Cause persistent, SUBCLINICAL BACTEREMIA
VIRULENCE:
- TYPE 4 secretion system
- Trimeric autotransporter
- Hemin binding protein
DISEASES:
1. B. Henselae: Cats, dogs, HUMANS => Bacteremia and CAT SCRATCH FEVER
- ZOONOTIC, OPPORTUNIST
- In feral cats => asymptomatic bacteremia (esp. young kittens)
- In humans: Erythematous lesion => Fever, bacilliary angiomatosis
- Present in RBC + ENDOTHELIAL CELLS
- DX: PCR blood
- TX: Antibiotics that can penetrate host cells (tetracycline, flutoquinolones) - poor response tho (so only use for immunocompromised humans; Will recur in cats)
- PREVENT: Hygiene, flea control
2. B. Clarridgeiae: Cats, dogs only => Bacteremia and Cat scratch fever
DX:
- DIFFICULT TO CULTURE (weeks on agar)
- Seen in tissues w Silver stains
- PCR from whole blood
Acinetobacter baumannii - Characteristics
- OPPORTUNIST (low-grade)
- Part of ESKAPE
- Commensal in environment
- Resistant to most antimicrobials; acquire resistant genes via reproduction
- IMPORTANT NOSOCOMIAL PATHOGEN (from Iraq and Afghanistan soldiers, vet hospitals)
Capnocytophaga canimorsus - Characteristics, predisposing factors, Dx, and Tx
- OPPORTUNIST, ZOONOTIC
- Slow growing, fastidious GRAM NEGATIVE ROD
- In ORAL FLORA of cats and dogs
- Cause SEPTICEMIA + MENINGITIS following bite/lick in humans (not a problem in healthy patients)
PREDISPOSING FACTORS:
- Alcoholism
- Splenectomy
- Cytotoxic cancer
DX:
- PCR Dx difficult
TX:
- Long-term antibiotics w Penicillin G
What is ESKAPE?
Multidrug resistant hospital-associated pathogens
E: Enterococcus faecium
S: Staphylococcus aureus
K: Klebsiella pneumoniae
A: Acinetobacter baumannii
P: Pseudomonas aeruginosa
E: Enterobacter species