Unit 4, some of 2 and 5 for APES: soil formation, succession, agriculture)
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
rock cycle
no matter which rock you’re at, you can generate the other two
fossil fuels at/core from sedimentary
sedimentary, metamorphic, igneous
Sedimentary rock
form from the accumulation and compaction of sediments or organic materials
Metamorphic rock
form when existing rocks are transformed by heat, pressure, or chemical processes
Igneous rock
form from the cooling and solidification of molten rock
soil formation
primary succession
where we develop ecosystems over time, soil isn’t present so starting with bare rock and it gets weathered
Physical weathering
wind, waves, rain, streams, friction from other rocks, freezing and thawing (temp.)
Chemical weathering
acid rain (pH changes)
soil horizons
C forms first
then O
then A
then B which is mix of C and A
Then E is last and is not always there unless it rains a lot
O horizon
primarily composed of decomposing and partially decomposed organic matter
A horizon
commonly known as topsoil, is the surface layer of mineral soil, located just below the organic O horizon
E horizon
eluviation horizon, is a light-colored, leached soil layer found beneath the O and A horizons in some profiles, particularly in forested areas
It consists primarily of sand and silt particles, with most clay, iron oxides, and organic matter removed (eluviated) and washed into the B horizon below
B horizon
subsoil or illuvial horizon
is a subsurface layer of soil that is primarily a zone of accumulation, where materials leached from the upper horizons are deposited
less nurtients
located below A horizon or the topsoil
C horizon
the parent material or regolith, is the deepest layer of soil
is located above the unweathered bedrock (R horizon) and below the subsoil (B horizon)
is primarily made of slightly altered and weathered rock and minerals
permeability
soil property
physical test
measure of the soil’s ability to move water through it
rate: amount of water per unit of time
percolate
soil texture triangle and jar
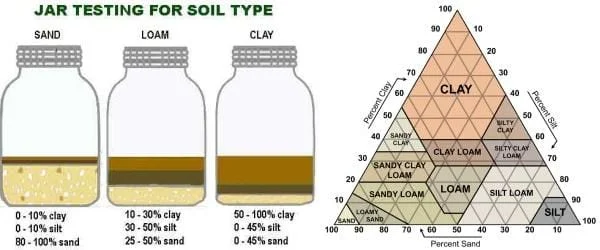
soil composition/texture
the mixture of its four primary components: mineral matter (sand, silt, and clay), organic matter, water, and airgravel:biggest
sand
silt: small
clay: very small, stick together
25% air
25% water
45% mineral
5% OM
largest to smallest
pH
chemical test
pH of most soils ranges from 4-8
it affects the solubility of certain plaint nutrients
the optimum pH is 6-7 (plant nutrients are most available)
soil amendments (ex.~ lime) can be used to achieve this pH
too acidic soil
low pH
an abundance of heavy metals are leached from the soil
heavy metals are dissolved by water and carried down through the soil, often to contaminate groundwater
cation exchange capacity happens too quickly
cations are exchanged for H+ ions obtained from carbonic acid or from the plant itself
net nutrient loss
too basic soil
nutrients cannot dissolve in water
don’t release many nutrients at all
cation exchange capacity (as it relates to nutrient holding)
chemical test
increased exchange= losing nutrients
ability of soils to absorb and exchange cations (ion with + charge)
contribute the most to the chemical properties of soil
agricultural soils require some level of clay to hold nutrients
more than 20% holds too much water
primary succession
the ecological process where a life-less environment, like bare rock exposed by a volcanic eruption or retreating glacier, is gradually colonized by organisms, leading to the development of soil and a complex ecosystem
ex.~ volcanic eruption: new land formed by cooling lava flows can be colonized
secondary succession
the ecological process of regrowth and reorganization in an area that has been disturbed, but where soil and some life remain, don’t start from bare rock
ex.~ wildfires: destroys the trees but the soil remains fertile for new growth
commercial farming practices
tilling
monoculture
desertification
tilling
is the mechanical agitation of soil
is typically done with tools like hoes, plows, rototillers, or large machinery like tractors
advantages: Weed Control, Incorporates Organic Matter
disadvantages: soil erosion, loss of soil structure, increased carbon release
solution: no-till farming
shortcomings: requires herbicides like glyphosphate which can harm the environment
monocultures
is the agricultural practice of growing a single crop species over a large area of land, year after year
It’s common in industrial agriculture — for example, vast fields of just corn, wheat, or soybeans
advantages: high efficiency, predicted yields, easier management
disadvantages: soil degradation, high chemical input, biodiveristy loss
solutions: intercropping, IPM
shortcomings: complex to manage, requires more labor and monitoring
Desertification
is the process where fertile land becomes degraded and turns into desert-like conditions, losing its ability to support life
caused by overgrazing, deforestation, etc.
advantages: n/a?
disadvantages: loss of arable land, food insecurity, biodiversity loss
solutions: education and policy, reforestation,
shortcomings: slow process, may lack funding
fertilizers
Substances added to soil/plants to provide nutrients and boost growth.
Synthetic: Made in factories (e.g., urea, NPK, from ammonia, phosphate, potash).
Organic: Natural sources (e.g., manure, compost, bone meal).
Advantages: Fast plant growth, Higher yields, Replenishes poor soil
Disadvantages: Soil degradation (chemicals), Water pollution (runoff)
Solutions:Use compost, crop rotation, Soil testing
Shortcomings of solutions: expensive, slow
Irrigation
Artificial application of water to soil for growing crops
Surface: Water flows over land (furrows, basins
Sprinkler: Water sprayed like rain
Drip: Water drips near roots (efficient)
Subsurface: Underground pipes deliver water
Advantages:Increases crop yields, Allows farming in dry areas
Disadvantages: Waterlogging & salinization
Solutions:Drip & sprinkler systems (efficient), Use rainwater harvesting
Shortcomings of solutions: high cost, maintenance, rainwater storage is limited in dry years
furrow irrigation
ditches w/ water
inexpensive
1/3 of water lost to evaporation and runoff
risk of soil erosion too
getting water close to crops
flood irrigation
floods the agricultural field w/ water
water-logging
20% of water lost to evaporation and runoff
methane
spray irrigation
more efficient then furrows and flood (<25% water loss)
more expensive and requires energy
salinization
drip irrigation
expensive
5% is lost to evaporation
targeted to release water at the plant
pesticides
chemicals used to control pests, weeds, fungi, and rodents
synthetic (lab-made chemicals like DDT, glyphosate), natural (plant-based or microbial like neem or Bt)
Advantages: protects crops, increases yield, fast action, reduces labor, easy to use
Disadvantages: kills beneficial insects, pest resistance, water and soil pollution, human health risks, bioaccumulation
Solutions: integrated pest management, bio-pesticides, crop rotation, resistant crop varieties, farmer education
Shortcomings: IPM is complex, bio-pesticides act slowly, not always effective, lack of training, pests may still adapt
sustainable practices
crop rotation, intercropping, no till, countour
GMOs
IPM
crop rotation
the practice of growing different crops in the same area in a planned sequence over seasons or years
alternating crop types (e.g. cereals, legumes, root crops) to balance soil nutrients and break pest/disease cycles
Advantages: improves soil fertility, reduces pests and diseases, lowers need for chemical inputs, controls weeds, increases biodiversity
Disadvantages: requires planning, crop choice limitations, not always profitable short-term, may need different equipment, knowledge-intensive
Solutions: farmer training, government support, market access for diverse crops, research on rotation-compatible varieties
Shortcomings of solutions: training may be unavailable, market demand may favor monocultures, limited access to equipment, resistance to change
intercropping
growing two or more crops together on the same land at the same time
combining crops with different growth habits or needs (e.g. maize + beans, tomato + basil) in rows, strips, or mixed patterns
Advantages: better use of space, improved soil health, pest and disease control, reduced erosion, higher total yield
Disadvantages: complex management, competition between crops, difficult harvesting, may reduce individual crop yield, needs more labor
Solutions: farmer training, research on compatible crops, use of simple tools or machinery, government support
Shortcomings: lack of knowledge, not suited for all crops, limited equipment access, more time and effort required
no-till farming
farming method where soil is not disturbed by plowing before planting
seeds are directly planted into residue-covered soil using special equipment like no-till drills
Advantages: reduces soil erosion, improves soil structure, retains moisture, saves fuel and labor, increases organic matter
Disadvantages: initial cost of equipment, weed control challenges, possible increased herbicide use, slower soil warming in spring
Solutions: integrated weed management, crop rotation, cover crops, government incentives for equipment purchase
Shortcomings: requires farmer training, herbicide reliance can cause resistance, cover crops need extra management, upfront costs remain high
countour farming
farming along the natural contours of the land to reduce soil erosion
planting crops in rows that follow the slope’s curves instead of up and down the hill
Advantages: reduces water runoff and soil erosion, improves water infiltration, conserves soil moisture, increases crop yields
Disadvantages: requires planning and skill, may reduce planting area, machinery use can be difficult on slopes, initial setup time and cost
Solutions: farmer training, use of contour plows, government support and incentives, combining with other soil conservation methods
Shortcomings: training may be limited, equipment may not be affordable, not suitable for very steep or irregular terrain, adoption can be slow
GMOs
genetically modified organisms with altered DNA for desired traits
scientists insert genes from other species into plants or animals to enhance traits like pest resistance or drought tolerance
Advantages: increased crop yields, pest and disease resistance, reduced pesticide use, improved nutritional content, longer shelf life
Disadvantages: potential environmental risks, gene transfer to wild species, ethical concerns, dependence on seed companies, possible health risks
Solutions: strict regulation and testing, development of biosafety protocols, public education, promoting transparent labeling
Shortcomings: regulatory gaps in some countries, public mistrust, high costs for small farmers, slow policy adaptation, ongoing scientific debate
IPM
a pest control strategy that uses a combination of biological, cultural, physical, and chemical methods to manage pests sustainably
monitoring pest levels, using natural predators, crop rotation, selective pesticide use only when needed, and habitat management
Advantages: reduces chemical pesticide use, lowers environmental impact, delays pest resistance, cost-effective over time, protects beneficial organisms
Disadvantages: requires knowledge and training, more labor-intensive, slower results compared to chemical spraying, complex decision-making
Solutions: farmer education programs, government support, development of easy-to-use monitoring tools, research on biological controls
Shortcomings: limited access to training, initial costs and labor demands, resistance to change from traditional methods, uneven government support
CAFOs (concentrated animal feeding opterations)
large-scale industrial livestock farms where many animals are confined in a small area
animals like cows, pigs, or chickens are kept in high densities to maximize production efficiency
Advantages: high production efficiency, lower costs, year-round meat/dairy supply, better disease control under some conditions
Disadvantages: environmental pollution (manure runoff, air quality), animal welfare concerns, antibiotic resistance, disease outbreaks risk
Solutions: improved waste management, stricter regulations, alternative farming methods (free-range), better animal welfare standards
Shortcomings: enforcement challenges, higher costs for farmers, resistance from industry, limited scalability of alternatives
commercial fisheries
large-scale fishing operations that catch fish and seafood for sale and consumption
using fishing vessels with nets, trawls, longlines, or traps to harvest large quantities from oceans, rivers, or lakes
Advantages: provides food and jobs, supports economies, supplies global seafood demand,
Disadvantages: overfishing, habitat destruction, bycatch (unintended species caught),
Solutions: fishing quotas, marine protected areas, sustainable fishing certifications, improved gear to reduce bycatch, aquaculture development
Shortcomings: enforcement difficulties, illegal fishing, economic pressure on fishermen, limited awareness, aquaculture environmental impacts
aquaculture
farming of fish, shellfish, and aquatic plants in controlled environments
raising aquatic species in ponds, tanks, cages, or raceways, often with feeding and water quality management
Advantages: supplements wild fish supply, creates jobs, supports food security, can be more efficient than wild fishing
Disadvantages: water pollution, disease spread, habitat destruction, genetic issues from escaped farmed species, reliance on wild fish for feed
Solutions: improved farm management, use of sustainable feed, disease control measures, habitat protection, regulations and monitoring
Shortcomings: high costs, enforcement challenges, variable farmer knowledge, environmental trade-offs remain