S3.1.3 Electron shielding/effective nuclear charge
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Electron shielding
When inner shielding electrons reduce the electrostatic force (attraction) between the outer valence electrons and the nucleus.
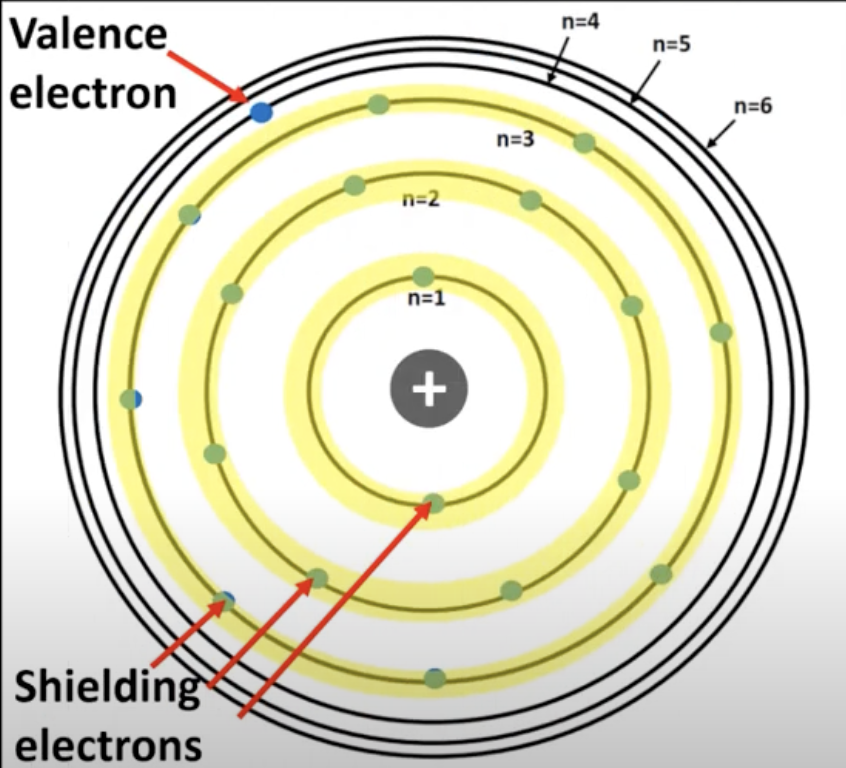
Shielding electrons
Electrons in energy levels n=1 to n=3
The difference between the amount of charge required to remove valence electrons versus inner electrons is…
that inner electrons require significantly more energy, whereas valence electrons require less energy.
Electron shielding across a period..
remains constant as shielding electrons don’t change
Electron shielding down a group..
increases as shielding electrons increase
Effective nuclear charge
Net positive charge experienced by valence electrons
Atomic radius across a period…
decreases, because:
Nuclear charge increases
Shielding effect constant
Attraction between nucleus and outer electrons increases
Atomic radius down a group…
increases, because:
number of occupied energy levels increases
Which period has a large increase in ionic radius?
Period 3 from silicon ions to phospide, because:
There is an additional occupied energy level
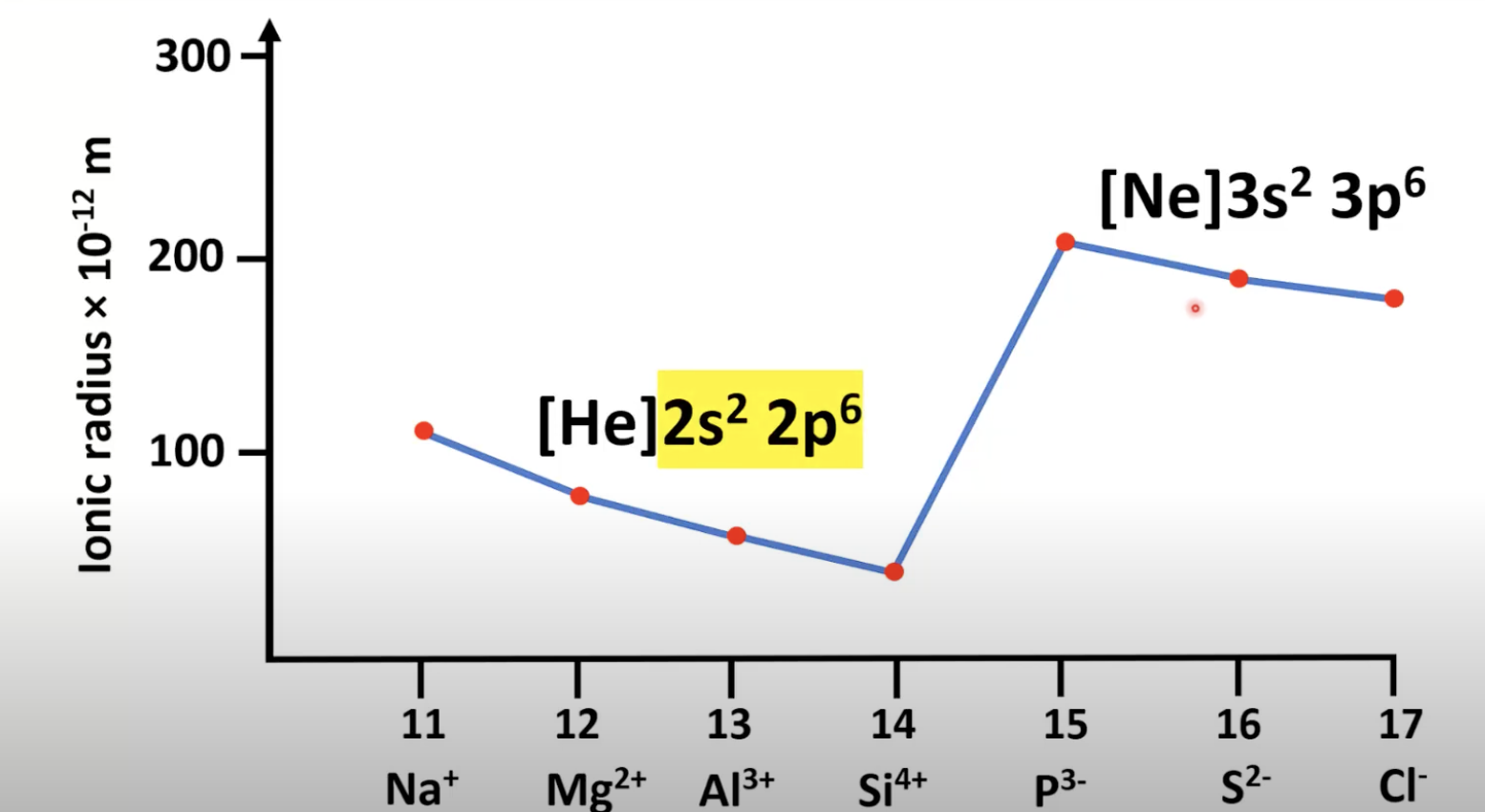
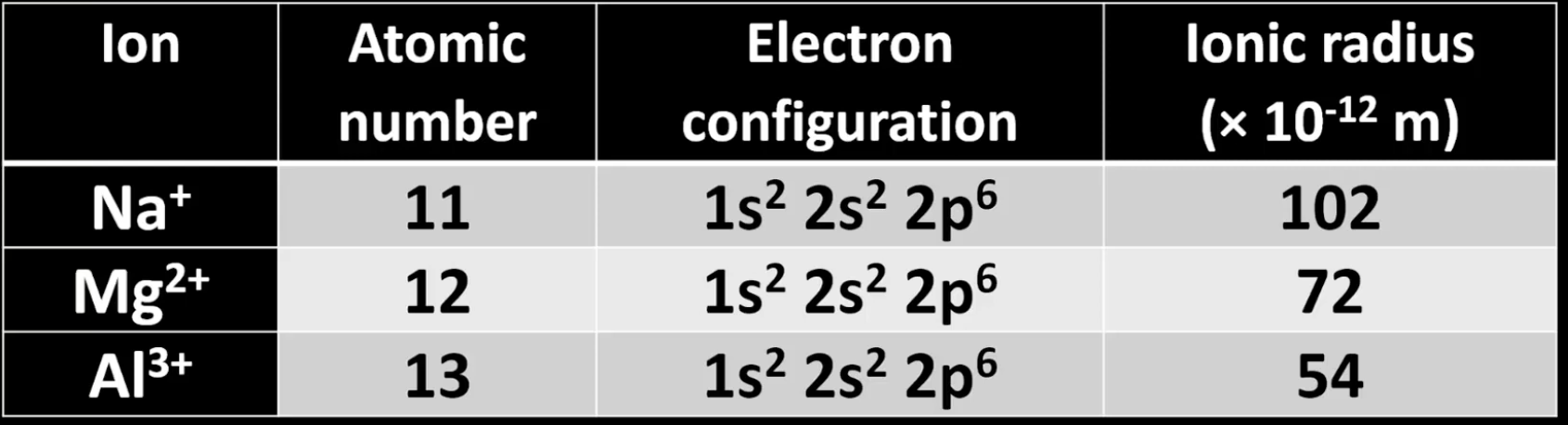
For first 3 ions in period 3…
Ionic radius decreases, because:
Electron configuration stays the same, but atomic number increases.
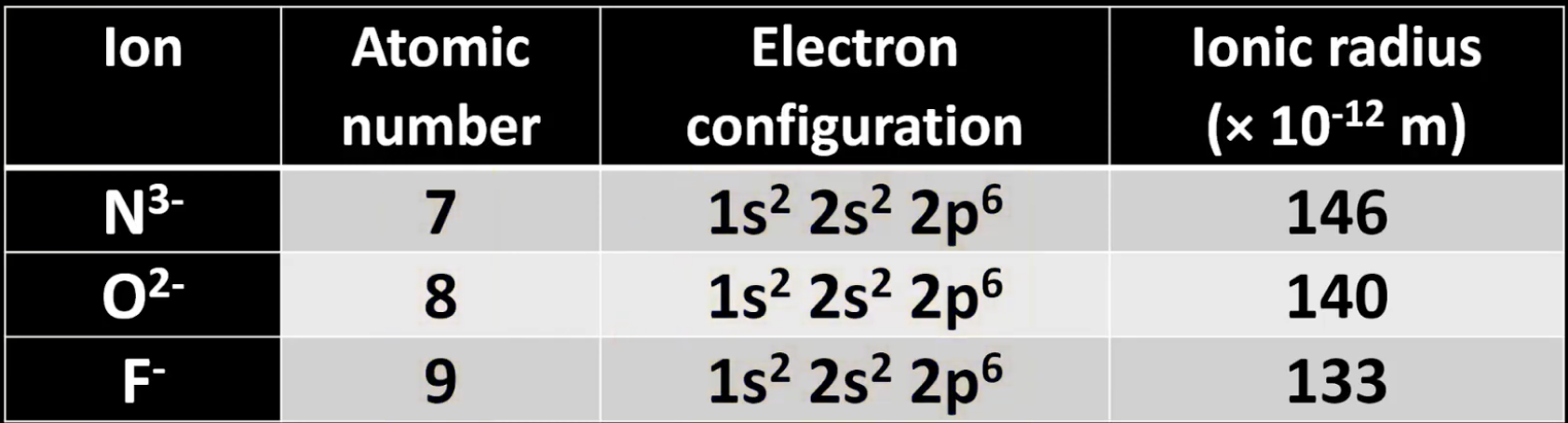
For ions of elements nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine in period 2…
Ionic radius decreases, because:
Electron configuration stays the same, but atomic number increases.
Positive ions have ______ radii than atoms
Smaller, because:
Positive ions must lose electrons to obtain a full outer shell due to larger charge difference
Thus, there is a stronger electrostatic force of attraction
Negative ions have ______ radii than atoms
Bigger, because:
Negative ions must gain electrons to obtain a full outer shell
Thus, there is a weaker electrostatic force of attraction
First ionization energy
Energy required to remove one mole of electrons from one mole of gaseous atoms to produce one mole of gaseous ions

Ionization energy’s sign is…
positive, as energy is required to overcome the electrostatic force between the valence electrons and the nucleus
Ionization energy across a period..
increases, because:
Nuclear charge increases, atomic radius decreases across period
Thus, greater electrostatic force of attraction
Ionization energy down a group..
decreases, because:
Number of occupied levels increases down group, increased electron shielding
Thus, weaker electrostatic force of attraction
First electron affinity
Energy released when one mole of electrons is added to one mole of gaseous atoms to form one mole of gaseous 1- ions
Second electron affinity
Energy released when one mole of electrons is added to one mole of gaseous 1- ions
Electron affinity _________ when atomic radius is greater and electron shielding is greater
decreases
Second electron affinity values are positive when..
the ion is already negative (due to extra repulsion when adding negative electrons)
The difference in the electron affinities of non-metals and metals is..
Non-metals have more exothermic electron affinities (greater positive value)
Electronegativity
Measure of the attraction of an atom for a bonding pair of electrons
Electronegativity across a period..
increases, because of:
increasing nuclear charge, as this increases attraction force.
Electronegativity down a group..
decreases, because of:
increasing atomic radius
Metallic character
How easily an atom can lose electrons (opposite of electronegativity)
Metallic elements’ ionization energies..
are low, and they tend to lose electrons to form positive ions
Non-metallic elements’ ionization energies..
are high, and they tend to gain electrons to form negative ions
Metallic character down a group..
increases, because of
increased atomic radius (due to more energy levels being occupied) resulting in weaker electrostatic force of attraction.
Metallic character across a period..
decreases, because of:
increased nuclear charge, and smaller atomic radius, resulting in stronger electrostatic force of attraction.