alevel biology transport
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Diffusion (definition + 2 types)
Passive movement of particles from a high concentration to low concentration, down a concentration gradient until an equilibrium is reached.
1. Simple (partially permeable): Particles pass across the membrane, permeable to non-polar, lipid-soluble molecules (exception: water) Hydrophobic tails repel ions
2. Facilitated (selectively permeable): Membrane is a barrier to polar molecules, passive movement of polar molecules via a hydrophilic channel proteins
No. of intrinsic proteins can effect rate of diffusion
Plasma membrane (use of membrane, properties, fluid mosaic model)
phospholipid bilayer - controls movement of substances in/out of the cell. Acts as an impermeable barrier to polar substances, water-soluble; permeable to lipid-soluble, non-polar across membrane. Phospholipid bilayer allows membrane to be flexible, and self-sealing
Fluid mosaic model - mosaic as many molecules embedded within membrane structure. Fluid as phospholipid molecules can move.
Proteins within/ on plasma membrane
Glycoprotein + Glycolipid
Cholestrol
Extrinsinc protein - mechanical support
Intrinsic proteins - channel proteins - hydrophillic channel allowing water-soluble/ polar molecules across membrane. Carrier proteins - active transport
Glycoprotein + Glycolipid - acts as recognition molecule/ receptor for hormones due to branching of carbohydrate, can be used for cell adhesion
Cholestrol - flexibility, stability. Hydrophbic so attracts fatty acids, preventing rigidity, prevents loss of water ions due to repulsion.
Factors effecting diffusion rate
SA:V ^, larger area for substance to diffuse across
Diffusion distance ↓, shorter distance to diffuse across.
Temperature ^, more kinetic energy, so more particles move across quicker + phospholipid molecules vibrate faster, so more permeable. too high tertiary structure denatures, meaning permanent disruption
number of intrinsinc proteins along phospholipid bilayer
Active Transport
Active movement of molecules from a low-high concentration, against a concentration gradient, via a carrier protein, using ATP (from respiration)
Molecule binds to specific receptor of carrier protein
ATP → ADP + Inorganic Phosphate, phosphate binds to protein, changing shape of protein,
Molecule released into cell, ADP + Pi → ATP
Exocytosis - vesicles fuse with cell membrane, molecule is released to outside. ATP required for fusion
Endocytosis - membrane invaginates to make vesicle around material, vesicle pinches off membrane, ATP required.
Osmosis (solutions conditions, water potential, definition)
Isotonic (same),
Hypertonic (Cell has higher water pot) = crenated/plasmolysed,
Hypotonic (Cell has low water pot) = lysed/turgid
Water potential - pressure exerted by a water molecule colliding with a membrane/ container (0 = highest concentration)
Cotransport
Sodium ions actively transported out of cavity in blood, lower concentration in the cavity, so sodium from the ileum diffuses into cavity, glucose transport into cavity via attachment to sodium, then facilitated diffusion into the blood.
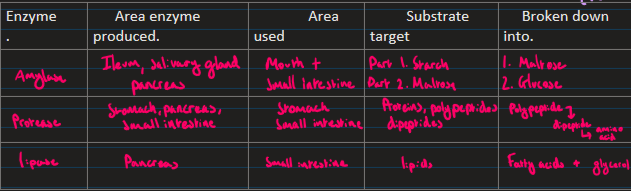
Digestion pt1
Mouth: Mechanical digestion. Release of amylase to break starch into disaccharides.
Stomach: Mechanical + Chemical digestion, HCl + protease(endo/exopeptidase) proteins→ dipeptides
Digestion pt2
Duodenum: Bile released (emulsification + neutralisation), amylase + protease + lipase. Pancreatic juices released with enzymes
Ileum: Membrane bound dipeptidases, disaccharides, absorption of molecules'
Large intestine: Reabsorption of water/ molecules
Digestion of Glucose
Amylase hydrolyses starch into maltose, carbohydrase/ polysaccharidases hydrolyse polysaccharides into disaccharides
Membrane bound disaccharidases hydrolyse disaccharides
Maltase: Maltose → glucose
Sucrase: Sucrose → glucose + fructose
Lactase: Lactose→ glucose + galactose
Diffuse into the cell by cotransport membrane
Digestion of Proteins
Endo/exopeptidases hydrolyses peptide bonds, polypeptide → dipeptide
Membrane-bound dipeptidases hydrolyses dipeptides → amino acids
Enters via cotransport/ Diffusion
Digestion of Lipids
Bile emulsifies lipid into soluble small lipid
Lipase hydrolyses lipid in monoglycerid + 2 fatty acids
Bile salts bind and increases SA:V
Monoglycerides + Bile Salt + Fatty acid forms a micelle
Micelle transports monoglyceride, fatty acids to membrane of epithelial cell, maintaing higher concentration at cell membrane,
Monoglyceride, fatty acids diffuse into cell down concentration gradient
Monoglycerid + fatty acid recombine by SER
Triglyceride is combined with proteins and cholestrol (SER)
Packaged into chylomicrons, leaving cell by exocytosis into lacteal
Enzymes in digestion
Water transport (2 pathways, water up the xylem)/ Ion transport
Xylem:
Mineral ions actively transported into, and across root hairs, dissolved in water and pulled up xylem
Water enters via osmosis and move through:
Apoplastic pathway:
Moves through gaps in the cell wall, Then diffuses and moves through cell at caspian wall
Symplast pathway:
Moves through cell cytoplasm and across plasmodemata (slower)
Transpiration causes difference in water potential, causing water from xylem to move into cell by osmosis, due to cohesion causing tension, water column is pulled up
Gas exchange fish + adaptations of gills
Fish:
Floor of mouth lowers (pressure ⬇, vol ⬆) causing pressure difference, water moves into the mouth, passes over the gills, water contains dissolved oxygen.
Concentration gradient of oxygen between blood and water. Oxygen diffuses from water into blood
counter current, water flows in the opposite direction that blood flows, ensuring gas exchange happens across entire gill, as it ensures a concentration gradient of oxygen being maintained.
adaptations;
Counter current- maximise absorption
Large SA - Many gill filaments + lamellae → more diffusion across greater area
Thin lamellae → shorter diffusion distance
Plant gas exchange, (Adaptations of normal+desert plants)
Plants
Guard cells control the opening/closing of stomata, evaporated water can diffuse out.
Many stomata to increase rate of diffusion
Large SA:V ratio
Many air spaces in spongy mesophyll, reducing diffusion distance to palisade mesophyll
Desert plants have less stomata (none on upper epidermis), more closed stomata, (all to reduce water evaporation)
no leaves or rolled + hairy leaves (reduced sa:v for water to evaporate, or traps moisture, creating a diffusion gradient where water does not leave the leaf)
Human gas exchange (Inspiration + expiration)
Diaphragm contracts, diaphragm moves down, external intercostal muscle contracts (internal relaxes), ribs move up and out, pressure ⬇ volume ⬆, pressure difference causes air to enter lungs (lungs expand)
Air moves through trachea, through bronchi, and bronchioles into alveoli
Concentration gradient between red blood cells and alveoli, so oxygen diffuses across epithelium of alveoli, and endothelium of capillary, then into red blood cell.
Expiration:
Concentration gradient (of CO2) between red blood cells and alveoli, so CO2 diffuses across endothelium of capillary, and epithelium of alveoli
Diaphragm relaxes, external intercostal muscle relaxes (internal contracts), ribs move down and in, volume ⬇ pressure ⬆, pressure difference causes air to be forced out of lungs, lungs are elastic so recoil to further force air out
Lung adaptations
One cell thick, shorter diffusion area, and flattens + slows down red blood cells, allowing for more time for diffusion
Many capillaries to maintain diffusion rate
Moist - easier diffusion
Alveoli - increased sa:v
Goblet cells - produce and secrete mucuous to protect the lungs and prevent bacteria moving into blood stream
Haemoglobin (structure, bohr effect, affinity of oxygen in certain conditions/ animals
4 alpha helices associated with haem groups
affinity of oxygen increases as pressure of oxygen increases (conc ⬆)
so oxygen more readily associates to haem/ CO2 more readily dissociates
bohr effect: CO2 increase in pressure causes more ready dissociation of oxygen from haemoglobin
Association of first oxygen is the hardest, once bound causes haemoglobin to change shape, which makes oxygen able to associate more easily
Different animals/ organisms have differen affinities, fetal haemoglobin has higher affinity as oxygen pressure has already decreased when reaching the baby.
Cardiac cycle
Sequence of events which occur within a heart beat
Atrial systole: Atrial muscle contracts, pressure ⬆, volume ⬇, higher pressure in atria than ventricle, so atrioventricular valve opens. Ventricular diastole occurs at same time (muscle relax, pressure ⬇)
Ventricular systole: Ventricle muscle contracts, pressure ⬆ volume ⬇, higher pressure in ventricle than aorta and atria, causing av valve to close, and aortic valve (semilunar valve) to open.
High pressure in aorta causes aortic valve to close
Blood vessels + blood content
Vein: towards heart, thinner muscle and elastic tissue, less pressure, contains valves to prevent backflow
Artery: Away from heart, thick muscle tissue to contract, thick elastic layer allow recoil (maintaining blood pressure), narrow lumen to maintain blood pressure
Arteriole: Muscle Contracts to narrow/ widen lumen to control movement of blood into the capillary.
Capillary: allow substances to reach tissue, thin wall allows quicker diffusion, porous to allow blood plasma out, branched between cells + one cell thick - shorter diff dist
increased blood content causes blood to thicken, which will cause clots to more likely form.
Tissue fluid
Hydrostatic pressure of blood created by heart contractions,
arterial end of capillary:
higher hydrostatic pressure than tissue, plasma moves out,
lower water potential (larger solutes cannot pass through pores) water moves in by osmosis, Greater hydrostatic pressure than osmotic pressure so tissue fluid moves out of capillary
Venous end:
Hydrostatic pressure decreases, lower pressure, plasma moves in, osmotic pressure remains same (lower water potential water moves in by osmosis) Greater osmotic pressure than hydrostatic pressure, so net movement into capillary
Excess tissue fluid moves into lymphatic capillary
Insect respiration
Insects:
Respiring tissue use up oxygen, creating a concentration gradient
Valve periodically opens allowing air to move into the trachea down a conc gradient
Moves through trachea, and tracheoles into the respiring tissue
During movement, water from ends of tracheoles moves into respiring tissue, creating air space, and allowing oxygen to diffuse more efficiently from air into the tissue
Plant transport sugars (Loading, Mass transport theory)
Phloem - translocation (movement of assimilates from source to sink)
Loading:
Hydrogen ions are actively pumped out of cytoplasm into cell walls by proton pump using ATP, creating a conc gradient of H+
Hydrogen ions diffuse down a concentration gradient into sieve tubes and cotransports sucrose across a cotransport protein against sucrose conc gradient
Unloading:
Same
Mass flow:
Sucrose is actively transported into the sieve tube by companion cells,
sucrose in phloem creates a water potential difference, so water from xylem moves into the phloem by osmosis
Pressure increases, forming pressure difference between source and sink, causing sucrose to move to sink
At sink the sucrose is converted to glucose for respiration to release energy
Ringing (cutting part of stem), Tracing (radioactive carbon-13) experiments