AMI - Lecture 3 - Dendritic cells in tailored adaptive immunity
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
3 main phases initiated when first infected with a pathogen
innate (0-4 hours) → complement activation
anaphylatoxins (C3a → increased vascular permeability, leukocyte, neutrophils, recruitment)
opsonization (C3b → enhanced phagocytosis)
Membrane attack complex formed
early induced innate response (4-96 hours) → phagocytosis happens
adaptive (>96 hours) → DCs activate adaptive immune system. macrophages pahgocytose + interact with T cells.
Phagocytosis
MQ + DC use pathogen recognition receptors to recpognize
PAMP (pathogen)
DAMP (danger)
SAMP (self)
difference between naive and effector T and B cells
Naive T → immature waiting to be activated,
effector T → activated + differentiated, T helper subsets, have undergone clonal expansion, short lived or turn into memory T cells
Naive B → resting, circulating through body looking for ag. typically IgM
effector B → activated, have encountered specific ag, have proliferated + differentiation, memory B cells or plasma cells, there have been isotype switching
3 signals required for T cell activation
ag presentation → MHC1 - CD8, MHC2 - CD4
co stimulation → CD28-CD86 → proliferation
cytokines secretion by APCs → T helper cell differentiation
C type lectin receptors
expressed at cell surface of immune cells → important for phagocytosing
ag uptake, presentation, signalling
carbohydrate recognition domain (CRD) → bind carbohydrate structures
CLR have intracellular signalling motifs → will lead to
maturation of dendritic cells,
cytokine production,
type 1 interferon activation,
Toll like receptor
recognize pathogens via PAMP
found on cell surface and intracellular on endosomes
activation results in cytokine secretion by DCs
IRF 3/7 are activated leading to type 1 interferon production
NOD like receptor
inside cytoplasm
detects intracellular bacteria + cell wall damage
detects bacterial DAMPs + PAMPs
activates NfKb pathway → important of IL1 production
RIG like receptor
inside cytosol
detect viral RNA
activate type 1 interferon
signalling happens via RIG1 (ssRNA) + MDA5 (dsRNA) → then activation IRF3 → type 1 interferon production
inflammatory cytokines
signaling molecules that are produced by immune cells (MQ, DCs) in response to infection
these cytokines coordinate immune responses through NF-kB
NF-kB (transcription factor) activated by; inflammatory cytokines, PAMPs, ROS → promote expression of genes encoding for pro-inflammatory cytokines
IL4, IL6, IL12, TNFalpha, TNFbeta
Type 1 interferons
viral infection
IRF3/7 are the transcription factors activated in response to viral RNA/DNA → once activated IRF3/7 translocated to nucleus → induce transcription type 1 interferons (IFNalpha, IFNbeta) → block viral replication, degrade viral RNA
IL1 family
these cytokines are released in response to intracellular infections
inflammasome activates cytokines (IL1)
IL1alpha, ILbeta, IL18
TLR signalling via My88 and TRIF
My88 → signalling molecule
pathogen binds TLR → My88 recruits kinases → activation of NF-Kb → production pro inflammatory cytokines
TRIF → signalling molecule
pathogen binds TLR → TRIF recruits kinases → activation of IRF3/7 and NF-Kb → production of type 1 IFN + pro inflammatory cytokines
REMEMBER; NF-Kb pro inflammatory, IRF interferon 1
TLR can induce both, depending on which ones are activated
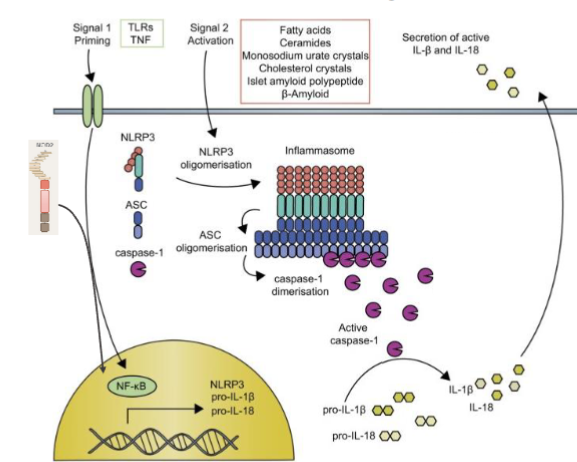
2 step IL1 cytokine production
DC needs two steps before it can start producing IL1 cytokines
priming transcriptional activation;
NOD like receptors are important → recognize PAMP → NF-Kb activated → NF-Kb translocates to nucleus → induces expression of pro IL-1beta
activation post translational;
PAMP + DAMP activated → inflammasome formation → caspase 1 activated → caspase 1 cleaves pro IL-1beta into active form
IL1 is crucial in inflammatory response → enhances proliferation and differentiation of T cells. Promotes CD4 and specifically TH17
Cross presentation route
cross over is between exogenous (MHC2 + CD4) and endogenous (MHC1 + CD8)
effect; exogenous ag expressed on MHC1
crucial for initiating cytotoxic T cell responses against viruses, tumors, or pathogens that do not infect (APCs) directly
TLR4 enhances cross presentation
depending on which PRR are activated will have an effect on all the signals of DC
can enhance specific T helper cell responses
inhibit signalling cascades to change ag handling and cytokines responses
intracellular signalling cascades can cross talk → can induce synergy and cross inhibition
2 things a vaccine always needs
antigen → immune system will recognize this as foreign substance
adjuvant → immune stimulating substance, enhances body’s immune respons to ag. will activate DC and PRR
what do tumour vaccines induce
cytotoxic T cell responses
cross presentation of ag is needed for this
mature DCs needed → provide all 3 signals
CD4 + Th1 cells are needed to help the memory response of CD8 cells
CTL receptors needed to enhance cross presentation
why is intradermal vaccination often used
skin is rich in DCs
skin highly vascularized by blood and lymphatics. will facilitate transport of immune cells + ag to lymph nodes where adaptive immunity is activated
easy accesible
Why are cytotoxic T lymphocytes often used in anti tumor vaccination
want a long lasting cytotoxic T cell response
optimal CTL response requires;
ag cross presentation
mature DC to provide signal 1-2-3
CD4 T helper help