Final Study Guide
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
118 Terms
near zone length (NZL)
the distance from the transducer face to the location where the beam is the smallest in diameter
increase
an increase in diameter of element/aperture causes a ___________ in NZL
increase
an increase in frequency causes a ____________ in NZL
decrease
an increase in diameter causes a ______________ of beam divergence in far field
decrease
an increase in frequency causes a ____________ of beam divergence in the far field
phantom
stimulates tissue properties of soft tissue, cystic, and solid structures
attenuation is similar to soft tissue
resolution
small nylon fibers in phantoms are used to evaluate __________
hydrophone
a microphone that detects sound waves under water
electrical interference
strong electrical interference from other nearby electrical devices can create interference patterns
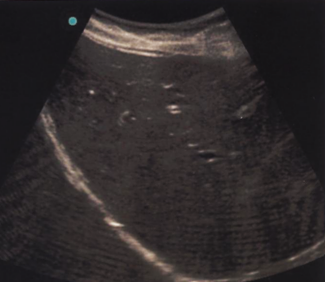
faulty elements
piezoelectric crystals may become damaged or breaks in wiring can occur; displayed as anechoic vertical lines
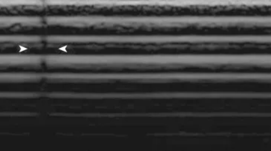
focal banding
horizontal brightness at the level of the focus
occurs because of the increased intensity in the focal zone
adjust the TGCs
to fix focal banding:
side lobes
caused by echoes from strong reflector outside central beam; single element
grating lobes
echoes from weaker beams outside the main beam from an array transducer; appears as duplicated structures laterally
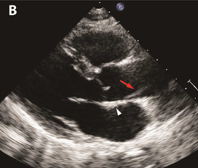
harmonics
side lobes/grating lobes are reduced with:
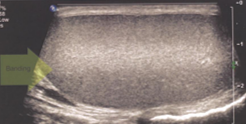
slice thickness (partial volume filling)
beam is too thick in elevational plane; gives the appearance of debris in an echo-free structure
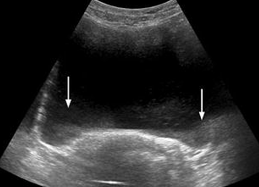
speckle
the granular appearance of images that is caused by interference of echoes from the distribution of scatterers in tissue
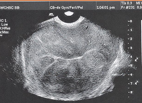
spatial compounding & persistence
speckle can be reduced by using:
mirror image
occurs when beam encounters a large specular reflector that acts as a mirror
appears as duplication of objects opposite of a highly reflective structure
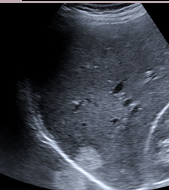
reverberation
occurs between two strong reflectors→sound waves bounce back and forth between structures
appears as equally spaced reflectors on the image
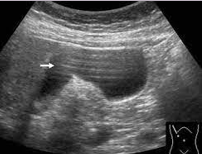
harmonics
reverberation can be reduced with:
comet tail
type of reverberation artifact
small focal reflectors cause a narrow reverberation artifact
useful in diagnosis of adenomyomatosis/cholesterolosis of the GB and colloid thyroid nodules
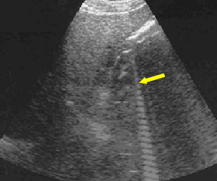
ring-down
type of reverberation artifact
associated with gas→helps diagnose gas conditions
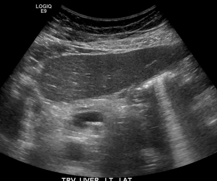
refraction
aka duplication or ghost artifact
change in beam directions when beam encounters boundary between two materials with different propagation speed
causes object to be projected laterally
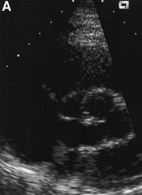
sliding transducer laterally
refraction can be reduced by:
edge shadowing
type of refraction artifact
caused by a combination of reflection and refraction at the margin of a well-defined object
appears as a shadow originating from the edge of a structure
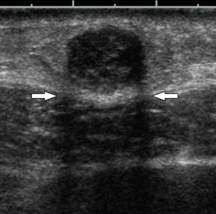
spatial compounding
edge shadowing can be reduced with:
multipath
beam reflects off the structure at an angle
displays object deeper than it really is because beam does not travel in a straight line
propagation speed error
a structure of lower or higher propagation speed than 1540m/s; cannot be eliminated
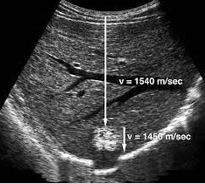
range ambiguity
occurs when echoes from the preceding pulse arrive at a time when another pulse has been emitted
decrease output power/gain, switch to one focal zone, decrease PRF
to reduce range ambiguity:
shadowing
caused by a highly attenuating structure
dirty shadow
occurs behind a strongly attenuating structure but the structure produces some echoes
appears as hypoechoic shadow behind structure
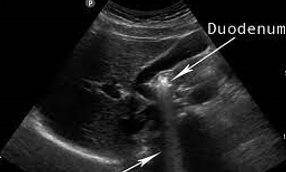
enhancement
caused by a structure of low attenuation adjacent to a structure of normal attenuation
gain & TGCs and spatial compounding
enhancement can be reduced by:
aliasing
most common Doppler artifact
display of Doppler information in the wrong color or on the wrong side of the baseline
Doppler shift exceeds one-half of PRF (Nyquist limit)
the cause of aliasing is:
shift baseline
increase PRF
increased Doppler angle
use a lower operating frequency
switch to CW
Ways to fix aliasing
mirror image
duplication of Doppler shifted echoes on the opposite side of a strong reflector or the baseline
causes: highly reflective surface, high Doppler gain, Doppler angles near 90 degrees
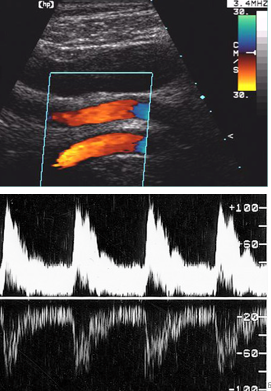
change transducer position, decrease Doppler gain
How to fix mirror image in Doppler
change transducer position
to fix shadowing:
clutter/wall thump
type of noise artifact
caused by tissue, heart wall, valve, or vessel wall motion
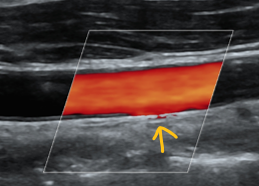
wall filter
to fix clutter, increase:
flash (ghosting)
sudden burst of Doppler signal caused by tissue motion, transducer motion, talking/coughing, bowel
increase PRF, decrease gain, hold still/wait
how to fix flash
twinkle
reverberation artifact
similar to comet tail but with color
useful in identifying kidney stones
axial resolution
minimum reflector separation necessary to resolve reflectors parallel to sound beam
does not change with depth
SPL
axial resolution is determined by:
SPL
axial resolution is improved by reducing:
lateral resolution
minimum reflector separation necessary to resolve reflectors perpendicular to the beam
varies with depth
beam width
lateral resolution is determined by:
focusing
lateral resolution is improved with:
temporal resolution
the ability to follow moving structures in temporal detail
directly
temporal resolution is _____________ related to FR
line density, lines per frame, depth & PRF, sector width, and number of foci
temporal resolution is dependent on:
contrast resolution
the ability of the gray scale display to distinguish subtle differences in echogenicity of adjacent tissues
contrast resolution
____________ is determined by # of pixels in an image and # of shades of gray that can be displayed in each pixel
system’s memory and dynamic range settings
contrast resolution is controlled by:
resolution
increased bandwidth improves _______________
quality factor
increased bandwidth reduces:
damping (backing) material
epoxy resin attached to back of element that absorbs vibrations and reduces # cycles/pulse
matching layer
has impedance value between crystal and tissue to improve sound transmission into body; minimizes reflection
coupling gel
eliminates air layer between transducer and skin
transducer arrays
transducer assemblies with several elements
each element is independently controlled
required for real-time scanning
use electronic means of sweeping, steering, and focusing beam→accomplished by sequencing and phasing
sequencing
voltage pulses are applied to small groups of elements in succession, time delay set between pulses
phasing
voltage pulses are applied to elements in rapid succession
allows for sweeping, steering, and focusing beam
beam steering
sweeping the beam to produce automatic scanning
accomplished with phasing
electronic (transmit) focusing
longer time delays (greater curvature) create a more superficial focus
shorter time delays (less curvature) moves focus deeper
aperture focusing (variable aperture)
smaller groups (less elements) used for short focal lengths
larger groups (more elements) used for foci located at increasing depths
aperture, focal length, and wavelength
____________ determine beam width at focus
aperture
to maintain the same beam width for increasing focal lengths, ______________ must also be increased
dynamic aperture
aperture changes as focal point is moved
dynamic (receive) focusing
focusing occurs during echo reception
improves lateral resolution
dead zone
the distance between the front surface of the transducer and the first identifiable echo
thermal index (TI)
the ratio of total acoustic power required to cause a rise in temperature of 1 degree C anywhere in the beam
attenuation (heat) & SPTA intensity
thermal index relates:
output power and exposure time
thermal index is directly related to:
frequency
TIS increases with an increase in:
focal diameter
TIB increases with:
2
the thermal index in adults should be less than:
0.7
the TI for fetuses should be less than:
mechanical index (MI)
a measure of pressure amplitude that occurs in tissue
indicator of cavitation
peak rarefactional pressure
mechanical index is directly related to:
1.9
the FDA limit says mechanical index should be less than or equal to:
0.3-0.7
the mechanical index for fetuses should be less than or equal to:
A-mode (amplitude mode)
was displayed on a graph with x-axis being depth and y-axis showing strength
B-mode (brightness mode)
2D images called B-scan
displayed dots with brightness showing strength and location
spatial compounding
aka compound imaging
multiple frames are formed at varying angles which are averaged together to create one image
uses phasing
improves image quality by reducing speckle, reducing clutter & reverberation artifacts, reducing shadowing, and improving presentation of specular reflections
frame rate
spatial compounding does not affect:
persistence (frame averaging)
goal is to reduce signal to noise ratio
angle not changed between frames
useful in color Doppler but movement of anatomy must be minimal
frequency compounding (frequency averaging/frequency fusion)
averages 2 or more frames created at different frequencies to form an image
improves texture because it combines multiple frequencies
broad bandwidth transmitted, narrow bandwidths received
edge enhancement
sharpens boundaries to make them more detectable and allow for more precise measurements
preprocessing technique
harmonics
transmit at a lower frequency and receive at higher frequency
improve image quality and lateral resolution
reduce grating lobe, reverberation, and clutter artifacts
depth
__________ is inversely related to PRF and FR
dynamic range
the ratio of maximum to minimum amplitude a system can handle
compression
technique that decreases the dynamic range
some is controlled by operator but some is not
weak echoes can be lost
Doppler effect
change in frequency (and wavelength) caused by motion of a sound source, receiver, or reflector
Doppler shift
the difference between the frequency of the received sound and the frequency of the emitted sound
can determine direction (positive or negative) and velocity
units are in kHz
fD=fR-fT
Doppler equation
we measure shift to calculate velocity
fD= (2/c) x v x fT x cos0
wall filter
allows us to filter out unwanted motion from the vessel walls