Biology Population and Conservation Y10
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Biosphere
the thin outer layer of the earth inhabited by organisms
Biome
a collection of ecosystems sharing climatic conditions
Community
a group of populations living and interacting with each other in an area.
Consumer
an organism that ingests other organic matter that is living or recently killed.
Ecosystem
a community and its abiotic environment.
Ecology
the study of relationships between living organisms and their environment.
Habitat
the environment in which a species normally lives or the location of a living organism.
Niche
an organism's spatial habitat, its feeding activities and its interactions with other species.
Population
a group of organisms of the same species who live in the same area at the same time.
Species
a group of organisms that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring.
J Curve
Exponential growth curve, rate of recruitment is increasing, little to no environmental reistance
Environmental Resistance
Factors that can limit or slow down the growth of a population, Resources limited, Predation or parasitism / disease.
S Curve or Sigmoid
Rate of recruitment changes from increasing to zero, Moves from no environmental resistance to balance with it
Rate of recruitment
The rate in which a population increases by adding of individuals to the population
Phases of S Curve
1. Exponential 2. Transitional 3. Plateau
Exponential Phase
Population size is growing rapidly, little to no environmental resistance, abundant resources for all, births and immigrants rates are more than death and emigrant rates. B+I >> D+E.
Transitional Phase
Population growth is slowed down as resource become more scarce, birth and immigrants rates decrease and death and emigrant rates increase. B+I decreases or D+E increases But B+I > D+E.
Plateau Phase
Population growth comes to a stop, the population has exceeded the environments carrying capacity which causes deaths and emigrants to rise to equal with the births and immigrants. B+I = D+E.
Population Change
(births + immigration) - (deaths + emigration)
Carrying Capacity
The maximum number of individuals an environment can support considering the resources available.
Individual
a single or separate organism
Organism
A living thing
CMRR Method
A method used to estimate the population of mobile species in a closed area. A species is captured mark released, the area is re-sampled, the numbers are put through the Lincoln index to estimate the population.
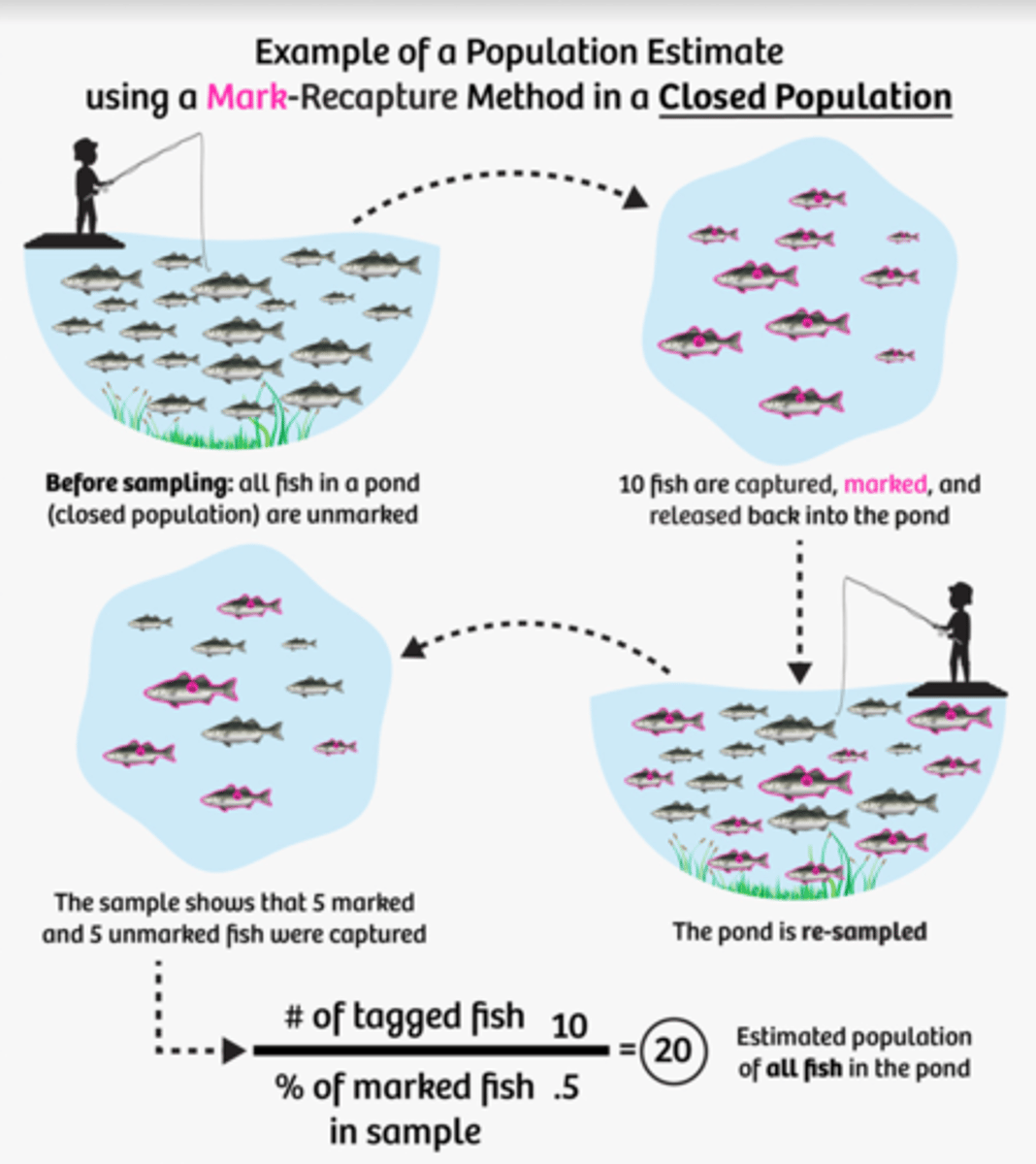
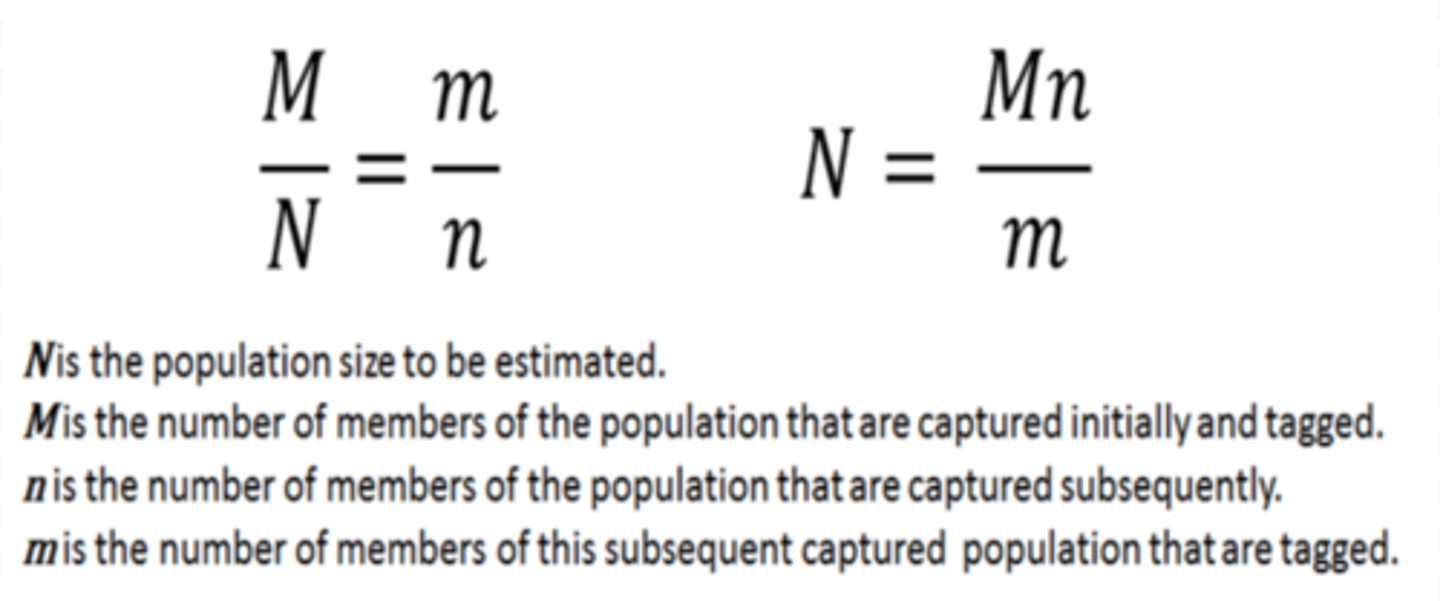
Lincoln Index
A formula used to estimate the population of a closed environment while using CMRR method.
Quadrat Method
A method used to estimate the population of non-mobile species in an area. A grid is put on the area and quadrants are numbered. The species in randomly picked quadrants are counted(the more quadrant counted the more the accurate estimation). The average is found and multiplied by the total amount of quadrants in the grid area.