Lecture 24: Practical Application of Sample Collection Techniques/Diagnostic Tools
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
True or false: all neoplasms are the same.
false: they look different, act different, and grow different
While it may be quicker, lower cost, and minimally invasive, what is the downfall of cytology?
you are unable to see what the neoplastic cells are doing in relation to the stroma/environment
What are some considerations when determining what types of samples to take?
money
how capable clinician is in sampling
what is needed for a diagnosis
Why does location of sampling matter?
certain samples may not give you the info you need
What is the general rule of thumb for biopsies, especially neoplasia?
take a sample at the interface so the pathologist can see the tumor cells, the normal cells, and how they interact with each other
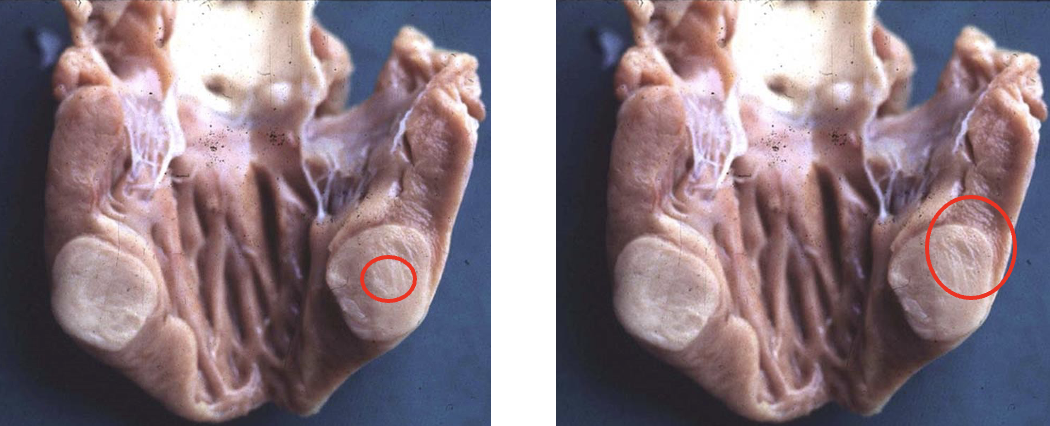
Which picture shows the correct area for a biopsy?
right
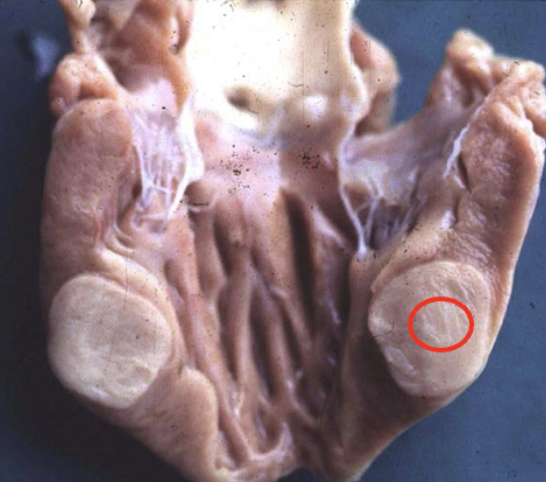
Why should a biopsy not be taken from this area?
it is at the center of the mass which is usually the most dead, necrotic area and it is not at the interface
What is the goal of an incisional vs excisional biopsy?
I: give me a diagnosis
E: did I get it all
When performing an incisional biopsy, how many samples should be taken?
samples from more than one site for the best diagnosis
What is the normal ratio of formalin to a tissue?
9:1
What should be submitted for excisional biopsies?
the whole tumor
What is the difference between tumor grading and tumor staging?
grade: how similar/dissimilar neoplastic cells are to normal counterparts
stage: indication of the extent of tumor growth and spread in animal
What is the underlying assumption of a tumor grade?
grade provides indication about biologic behavior (not universally true)
What is used to determine tumor stage?
TNM system: based on size of primary tumor (T), degree of lymph node involvement (N), and extent of metastasis (M)