Labor Law Midterms
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Sources of Labor Law
1987 Constitution
Article XIII Section 3
Presidential Decree No. 442
Labor Code
Rights of Workers under Constitution
Self-organization
Collective bargaining and negotiations
Peaceful concerted activities
Including right to strike in accordance with law
Security of tenure
Humane conditions of work
Living wage
Participation in policy and decision making processes affecting their rights and benefits
Principle of shared responsibility between workers and employers
Right of labor to its just share in fruits of production
Right of enterprises to reasonable returns to investments
Factors Determining Employer-Employee Relationship
Four-Fold Test
Selection and engagement of worker
Payment of wages or salaries
Power of dismissal
Power of control not just end result but manner and means utilized
Economic Reality test
Based on totality of circumstances → if economic dependency
Kinds of Employees
Found in labor code
Regular → employee engaging in desirable activities
Casual → employment not covered in 1st paragraph of article 295
Project → employment fixed for a specific project
Seasonal → work performed is seasonal in nature and employed for duration of the season
Other kinds
Probationary
Fixed Term Employment
Learners and Apprentices
Women Workers
Minor Employment
Kasambahay
Persons with Disability
Employees Becoming Regular Employees
Casual:
Rendered at least 1 year of service, continuous or broken
Probationary employees
Working after the probationary period ended
Project Employee
Continuous rehiring of project employees even after the end of the project
Tasks performed by employee are vital, necessary and indispensable to business or trade of the employer
Seasonal
Hired repeatedly for the same task or work
Learners:
Employer obliged to hire learner after lapse of learnership period
Probationary Employment
Period to determine whether employee meets standards to become a regular employee
Period shall not exceed 6 months
If past 6: becomes regular employee
Employer makes known to employee the standards being considered
Employment of probationary employee may be terminated only for a just cause, or if they fail to qualify as a regular employee based on the standards
IF NO STANDARDS MADE KNOWN: employee deemed regular
Fixed Term Employment
Contract of employment with fixed term should comply w/:
Fixed period known and agreed upon by parties
Appears that employer and employee dealt with each other on more o r less equal terms with no moral dominance
Learners and Apprentices
Learners employed when:
No experienced workers available
Employment of learners necessary to prevent curtailment of employment opportunities
Employment doesn’t create unfair competition (labor costs or lower working standards)
Apprentices
Employer has to be in highly technical industry
Apprenticeship is in an apprenticable occupation
Approved by Secretary of Labor and employment
Must be signed
WAGES: 75% of legal wage
Duration of apprenticeship: Not exceed 6 months, but not less than 3 months
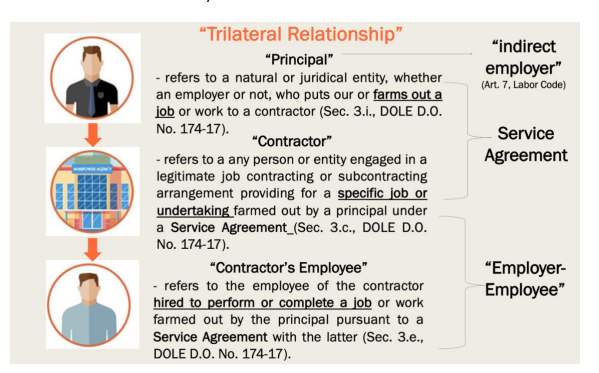
Subcontracting
Trilateral Relationship
Principal
Subcontractor
Subcontracted
Kinds of Subcontracting
Labor only contracting
Person supplying workers to an employer doesn’t have substantial capital or investments in tools, equipment, etc. Basically they are just agents.
Job Contracting
Distinct Business
Substantial Capital
Free from principal’s control
Workers’ rights are ensured
Facilities for Women (Article 130 of labor code)
Proper seats for women to use when free from work or during work hours
Separate toilet rooms
Dressing room
Nursery in the workplace
Appropriate minimum age and other standards for retirement or termination
But not required ^^
Leaves for Women
Maternity Leave (R.A. 11210)
105 days
If solo parent: + 15 days
Leave under R.A. 9262
10 days
Leave due to Gynecological Surgery (R.A. 9710)
2 months
Solo Parent’s Leave (R.A. 8972)
7 working days per year
Prohibitions against Discrimination of Women (Article 133 of labor code)
Payment of lesser compensation to a female employee as against a male employee for work of equal value
Favoring a male employee over a female employee with respect to promotion, training opportunities, etc. solely on account of their sexes
Favoring a male employee over a female employee with respect to dismissal of personnel
Stipulations against Marriage (Article 134)
Unlawful for employer to:
Make a condition of employment be that woman employee shall not get married
That woman employee shall be deemed resigned upon marriage
Dismiss, discharge, discriminate or otherwise prejudice a woman employee by reason of her marriage
Prohibited acts against Women (Article 135)
Deny any women employee the benefits provided for in the labor code or to discharge woman employee to prevent her from enjoying any of the benefits
Discharge a woman on account of her pregnancy, or while on leave or confinement due to pregnancy
Discharge or refuse admission of such woman upon returning to her work for fear that she may again be pregnant
Disabled persons / Handicapped
Those suffering from restriction of different abilities, mental physical or sensory
Equal Opportunity R.A. 7277
Qualified disabled employee shall be subject to same terms and conditions of employment and same compensation, benefits, etc. as a qualified able-bodied person
Sheltered Employment
Provision of productive work for disabled persons through workshop providing special facilities, income producing projects or homework schemes enabling them to acquire a working capacity required in open industry
Incentive for Employers in hiring Disabled Persons
25% deduction from gross income of employed disabled persons
Private entities that modify or improve physical facilities for accommodation are entitled to deduction from net taxable income equivalent to 50% of direct costs of improvements or modifications
Child and Working Child
Child: Anyone below 18 years old
Working child: Any child engaged in work or economic activity
Working Child below 15 Years Old
Child works directly under sole responsibility of his parent/guardian and doesn’t interfere with schooling
Child’s employment in public entertainment or information through cinema, etc. is essential
Working Hours of a Child
Below 15
Max 4 hours a day
20 hours a week
Curfew: 8PM to 6AM
15-17
Max 8 hours a day
40 hours a week
Worst Forms of Child Labor
All forms of slavery
Use, procuring, offering or exposing of a child for prostitution
Use, procuring or offering of a child for illegal or illicit activities (production and trafficking of dangerous drugs)
Work which is hazardous or likely to be harmful to the health, safety or morals of children
Employment of children in certain advertisements
Children can’t be models in advertisements promoting alcoholic beverages, intoxicating drinks, tobacco, gambling, violence or pornography
Coverage of Kasambahay Law
General househelp
Nursemaid / yaya
Cook
gardener or laundry person
Any person who regularly performs domestic work in one household on an occupational basis
DOESNT INCLUDE: children under foster family arrangement
Rights of Kasambahay
Just and human treatment
Lodging, food, medical attendance
Privacy
Access to outside communication
Education and Training
Terms and Conditions of Employment of Kasambahay
Minimum age of 15
8 hours a day
1 rest day a week
Can’t be assigned to work in commercial, industrial or agricultural enterprise at wage lower than what would be provided for those workers
NCR 5,000 minimum wage
Pay wage at least once a month in cash
Entitled to 13th month pay
Worker who rendered at least 1 year of service = gets annual leave of 5 days with pay
Worker who rendered at least 1 month of service = covered by SSS, PhilHealth, Pag-IBIG
Premium payments or contributions shouldered by employee
Unless domestic worker receiving wage of PHP 5000 and above = pay proportionate share
Wages definition (Article 97 f of Labor Code)
Remuneration or earnings expressed in terms of money
Payable by an employer to an employee under a written or unwritten contract of employment for work done or to be done
Generally, employer and employee agree on amount of wage an dhow it is determined
Fixed for a period or by task or result
Minimum Wage
Minimum amount employer is required to pay wage earners, that cannot be reduced.
2 bodies that determine minimum wage for regions: National wages and productivity Commission (policy making body),
Regional Tripartite Wages and Productivity Boards (minimum wages in specific regions)
What should Wages be paid in
Legal Tender
Payment by check, postal money order or ATM is allowed if
Bank or other facility for encashment within a radius of 1 km from workplace
Employer doesn’t receive any benefits from the arrangement
Employees given reasonable time during banking hours to withdraw wages from bank (time considered compensable hours worked if done during working hours)
Check payment with written consent of employees
When should wages be paid
Paid at least once every 2 weeks, or not more than 16 day interval
Where should wages be paid
Made at or near the place of undertaking
To Whom should wages be paid
Paid directly to workers to whom they are due except:
Where fore majeure prevents payments → workers paid through another person
If worker is dead = employer may pay to the heirs
Rules on Wages
No Interference → employer can’t interfere with freedom of employee to dispose of their wages
No deductions except
Reimbursment of insurance paid by employer
Union dues where right to check off has been recognized by employer
When employer is authorized by law such as for taxes and payment of SSS, PhilHealth, PAG-Ibig
No deposits for tools
Forcing, intimidating or otherwise causing worker to give up part of their wage without consent
Coverage of Wage Related Benefits
All except:
Government employees
Managerial employees
Feild personnel
Members of family of employer
Domestic Helpers
Persons in the personal service of another
Workers who are paid by results as determined by Secretary of Labor
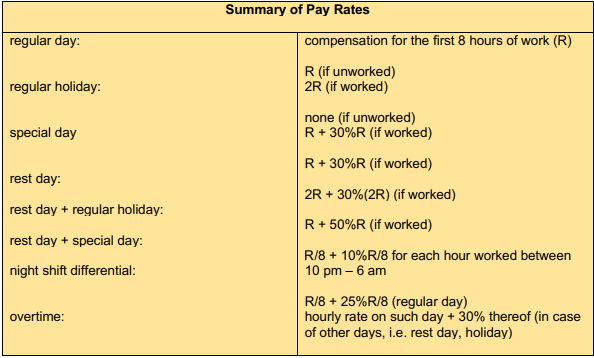
Hours of work and Overtime pay
Normal hours: 8
Meal periods of 1 hour or less: not counted in hours worked
Rest periods and coffee breaks of 5-20 minutes: considered hours worked
Overtime pay: Regular wage + 25%
Overtime on holiday or rest day: Additional compensation equivalent to rate of first 8 hours on a holiday or rest day plus 30%
Night Shift Differential in Wages
Minimum additional of 10% of regular wage for each hour of work during 10PM to 6AM
Weekly Rest Periods
Employees entitled to a rest period of minimum 24 hours after every 6 normal work days
-If worked on rest day: additional compensation of 30% of regular wage
-If worked on rest day that is also holiday: premium is 50% of regular wage
Holidays
2 kinds:
-Regular: 200% of wage if worked, 100% if not
-Special: 130% of wage if worked, 0% if not
Regular Holidays
New Year’s Day- Jan 1
Maundy Thursday, Good Friday, Edul Fitr, Eidul Adha - all movable dates
Araw ng Kagtingan - Monday nearest April 9
Labor Day- Monday nearest May 1
Independence Day- Monday nearest June 12
National heroes Day- Last Monday of August
Bonifacio Day - Monday nearest November 30
Christmas - December 25
Rizal Day - Monday nearest December 30
Special Days/ Special Holidays
Ninoy Aquino Day- Monday nearest August 21
All Saints Day- November 1
Feast of the Immaculate Conception - December 8
Last Day of the Year- December 31
Service Incentive Leave
Every employee who rendered at least 1 year of service: yearly service incentive leave of 5 days with pay
NOT AVAILBLE TO ESTABLISHMENT SWITH LESS THAN 10 EMPLOYEES
Leave days unused by end of year : converted to cash, can’t be added to next year
Service Charges
Service charges collected by hotels, restaurants, etc. will be distributed equally among workers
13th Month Pay
All rank and file employees who worked at least one month during calendar year: Entitled to not less than 1/12 of total basic salary earned within a calendar year
SHOULDN’T BE PAID LATER THAN DEC 24
Summary of Pay Rates