Population and Migration
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Crude Birth Rate (CBR)
The number of live births each year per thousand of the population in an area.
Crude Death Rate (CDR)
The number of deaths each year per thousand of the population in an area.
Natural change
It is achieved when there is an imbalance between the CBR and the CDR.
Natural Increase
It’s achieved when there is a higher birth rate than death rate.
Natural Decrease
It’s achieved when there is a higher death rate than the birth rate.
1 ⇢ Birth rate + Death rate = High.
Total population does not grow but it is balanced due to high birth rates (36/37 per 1,000) and high death rates (36/37 per 1,000). Countries at this stage will usually be undeveloped. However, there are no longer any countries at this stage of the model.
2 ⇢ Death rate falls = Population increases.
Birth rates will remain high due to: Previous high rates of infant mortality, children being used to on family farms, tradition and culture, no availability of contraception.
3 ⇢ Birth rate falls = Natural Increase drops.
The death rate continues to fall but much more slowly. Total population is rising rapidly. The gap between birth and death rates will narrow. Birth rates fall due to: Much lower infant mortality rates will mean that more children will survive and there is less need to have as many babies, increased opportunity for employment in factories means that fewer people are required to work on the land, laws that say children must attend school.
4 ⇢ Birth rate drops to = Death rate, population stops growing.
Total population is high and growing slowly. It is balanced by a low birth rate (15 per 1,000) and a low death rate (12 per 1,000). Contraception is widely available and there is a social desire to have smaller families.
5 ⇢ Birth rate falls below Death rate.
Total population is still high but starting to decline due to the birth rate falling (to 7 per 1,000) below the death rate (9 per 1,000). The population will start to fall as it is no longer replacing itself and may go into decline. The population is ageing and will gradually be dominated by older people.
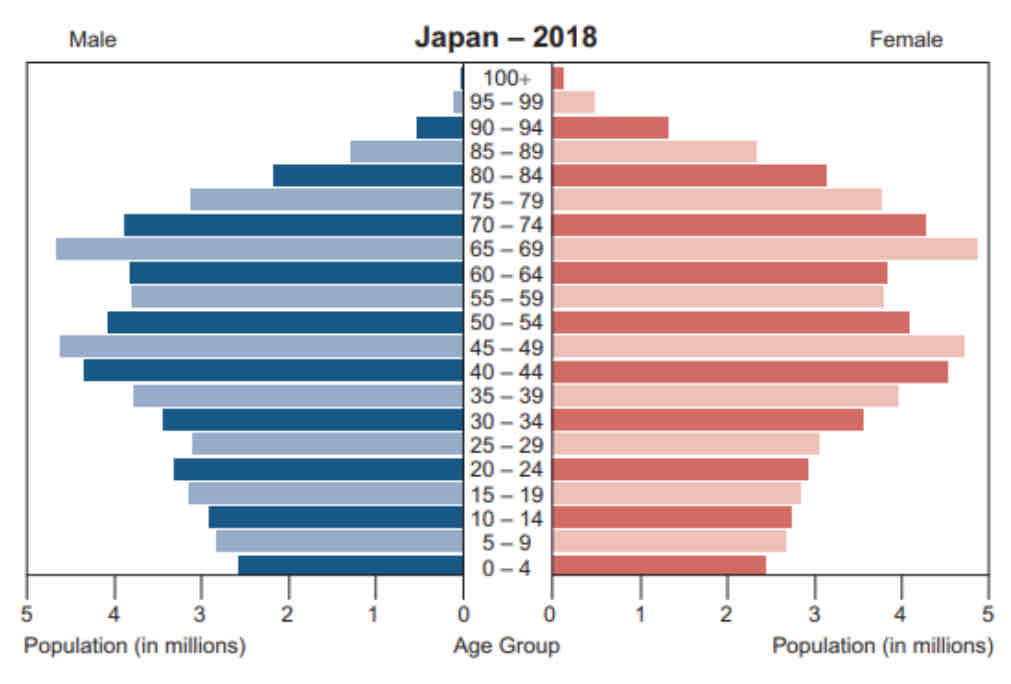
Comparing Population Pyramids
The wide top of the population pyramid for Japan shows an ageing population. The biggest number of people in the population pyramid are aged 65 to 69 – 4 ½ million males and 4 ¾ million females. However, in Chad there are very few people as shown by the narrow pyramid top, only 0.2 million males and 0.2 million females aged between 65–69.
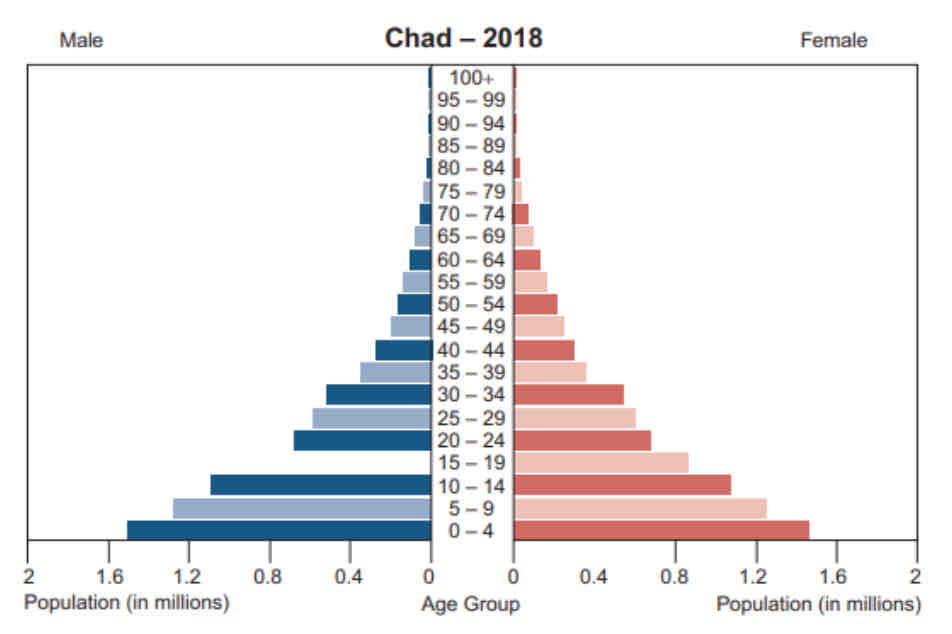
Comparing Population Pyramids
The population pyramid for Chad shows a youthful population with a wide pyramid base. The largest cohort for Chad is those aged between 0–4 with 1.4 million males and 1.5 million females. However, Japan’s pyramid is much narrower at the base with 2.5 million males and 2.4 million females.
SOCIAL IMPLICATIONS OF A AGED DEPENDENT POPULATION
Family Life
Hard decisions have to be taken about the best care for an elderly person. 65 year old children will end up caring for their 90 year old parents.
SOCIAL IMPLICATIONS OF A AGED DEPENDENT POPULATION
Medical Advantages
People live longer. However, many older people now struggle with late onset and degenerative illnesses such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
SOCIAL IMPLICATIONS OF A AGED DEPENDENT POPULATION
Loneliness
Often women live longer than their male partners.
ECONOMIC IMPLICATIONS OF A AGED DEPENDENT POPULATION
Benefits
Each pensioner will receive a pension in an MEDC for 20 or more years. Additional benefits such as free bus passes, TV licences and winter fuel payments will be a large cost to the taxpayer.
ECONOMIC IMPLICATIONS OF A AGED DEPENDENT POPULATION
Healthcare
Cost of residential care and healthcare can be expensive. Prescriptions, dental care, home help and hospital care can all cost a lot of money.
ECONOMIC IMPLICATIONS OF A AGED DEPENDENT POPULATION
Residential Care
More money needs to be set aside to help look after the older people. Accommodation might need to be modified or special pensioner bungalows built that have been adapted for pensioner-use.
SOCIAL IMPLICATIONS OF A YOUTHFUL POPULATION
Opportunities for young people
Lack of education and employment opportunities may lead young people to crime in order to survive and make a living.
SOCIAL IMPLICATIONS OF A YOUTHFUL POPULATION
Medical Care
Very little free healthcare for children in LEDCs. In many cultures it is easier to allow a sick child to die and be replaced by having another child than by spending money on medicine.
SOCIAL IMPLICATIONS OF A YOUTHFUL POPULATION
Overcrowding
Children often live in very squalid, cramped conditions which will allow illness to spread quickly. Many children will have lost their parents and will be forced to live in orphanages.
ECONOMIC IMPLICATIONS OF A YOUTHFUL POPULATION
Employment / Education
The large number of people aged 0 – 15 will put a huge pressure on the education system. Many LEDCs will not have enough money for universal education. There are often few employment opportunities.
ECONOMIC IMPLICATIONS OF A YOUTHFUL POPULATION
Healthcare
In LEDCs people cannot afford the most basic of healthcare and will rely on charities. Medicine will be basic and expensive – people will continue to die from treatable illnesses.
Push Factors of Migration
Lack of services
Low employment
Lack of safety
High crime
Crop failure
Drought
Flooding
Poverty
War
Pull Factors of Migration
Better services
Higher employment
Safe society
Less crime
Fertile land
Lower risk of natural hazards
Good climate
More wealth
Political stability
Human Barriers to Migration
Documentation is required to allow migration. Within the European Union migrants only need a passport. However, to migrate into other countries long application processes for visas or work permits are necessary.
Each country will have a specific set of rules about how many visas they give out each year or the type of skills and qualifications that someone might need to have.
Physical Barriers to Migration
Economic migrants will often arrive by aeroplane, but refugee asylum seekers and illegal immigrants might all try to find the easiest way to cross a border.
From 2015 to the present, a huge number of illegal migrants have journeyed across the Mediterranean Sea to get to Gree‹ Turkey, Italy or Spain.
Many of these people might already have made their way acr deserts or mountain ranges to escape persecution, conflict
Economic Migration
Someone who chooses to move to improve the standard of living by gaining a better paid job. It is economic pressures, concerns or opportunities that provide the main reason for a migration move. People want to improve their wages and will be prepared to move to facilitate this. When Poland and seven other Eastern European countries joined the EU in 2004, the UK received many economic migrants.
Refugees
A person who is fleeing from things such as civil war or a natural disaster but not necessarily facing persecution. Refugees are living in cramped and unsanitary conditions, and many have lost family members in the conflict or from disease. Water is scarce and most people rely on aid agencies for food, shelter and medicine. However, the aid efforts are being hampered by the Sudanese government and refugees are dying of disease, starvation and malnutrition. Chad is one of the poorest countries in the world, and the refugees from Sudan are putting a strain on already scarce resources.