Epidermis & Dermis (Layers, Structure, and Function)
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
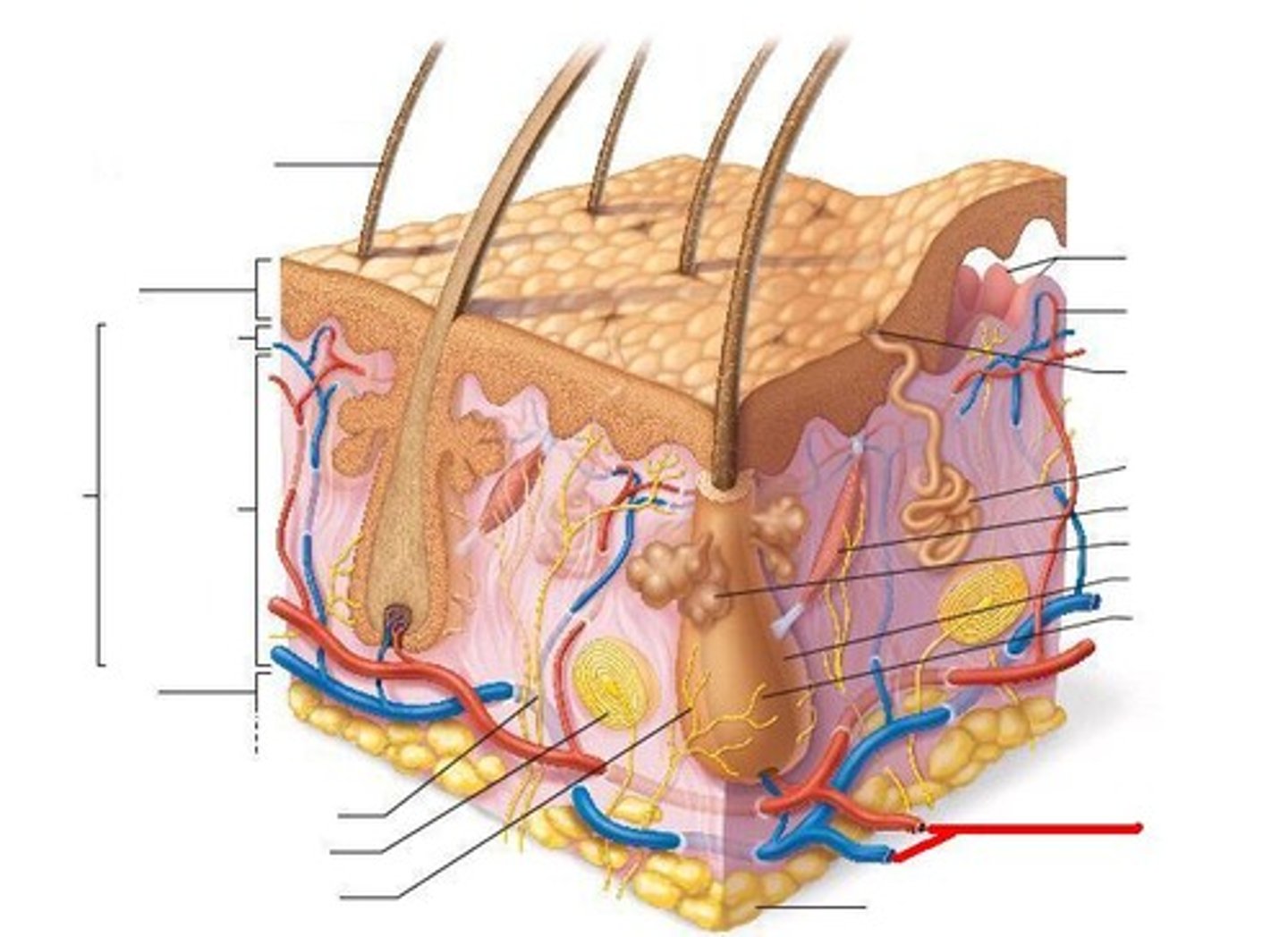
Epidermis
superficial region
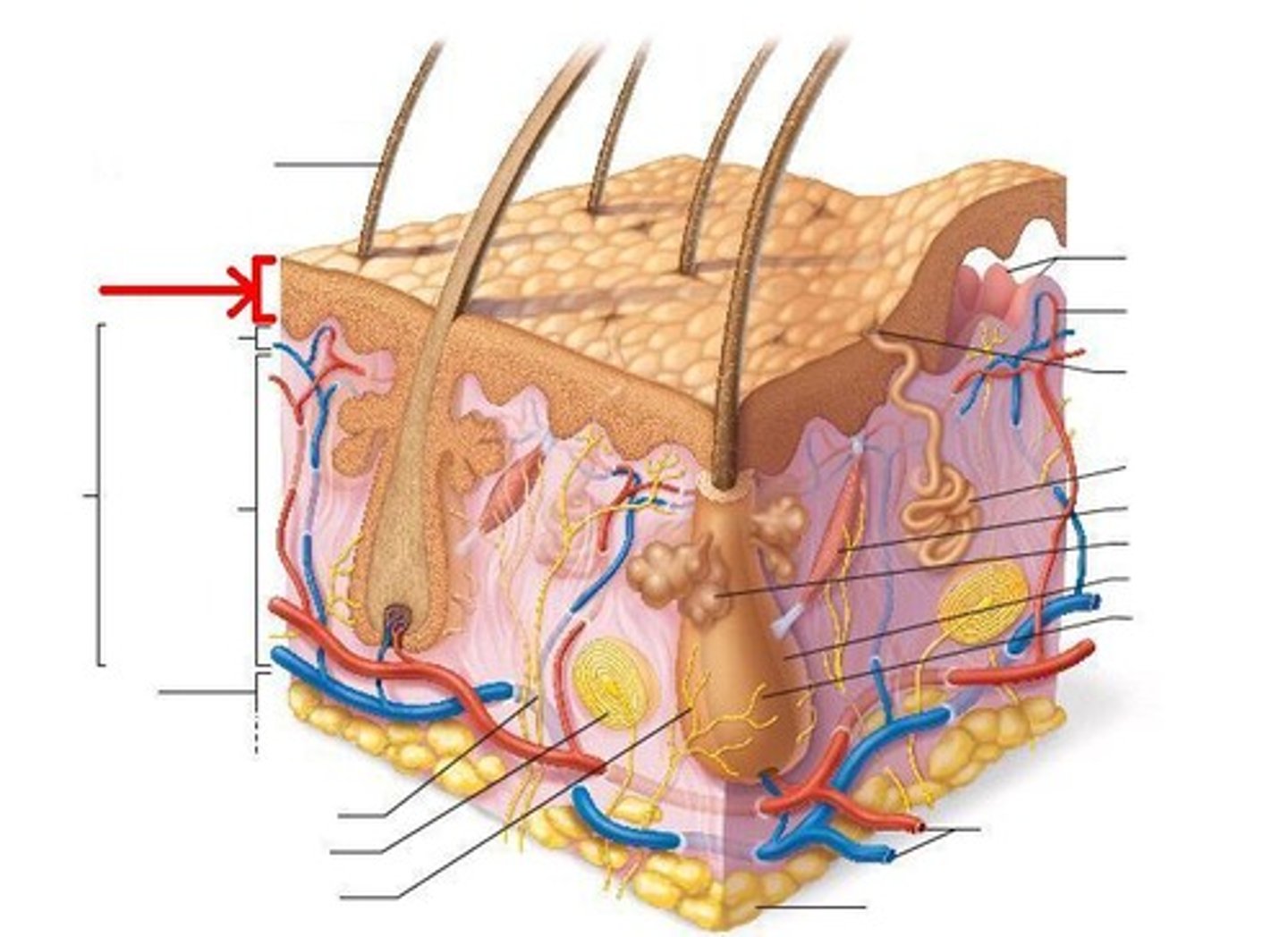
Epidermis consists of _______ tissue
Avascular epithelial tissue
Dermis
underlies epidermis
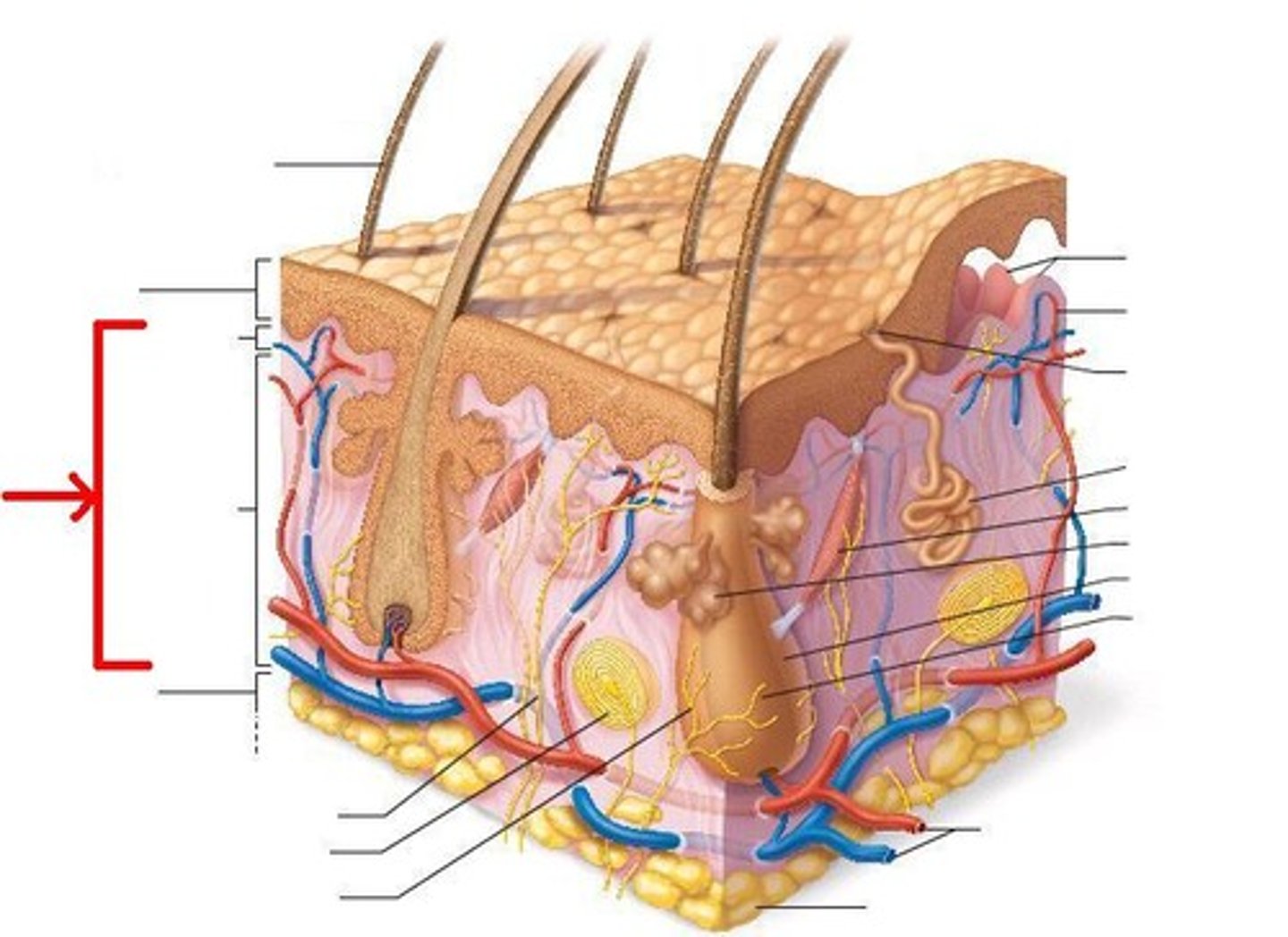
Dermis consists of ______ tissue
Fibrous connective tissue
Hypodermis
subcutaneous layer
Hypodermis consists of _______ Tissue
Adipose tissue
(absorbs shock and insulates)
Specific tissue type in epidermis
keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
Keratinocytes produces
keratin
What is keratin
tough fibrous protein
How are Keratinocytes connected?
desmosomes
Melanocytes
spider-shaped
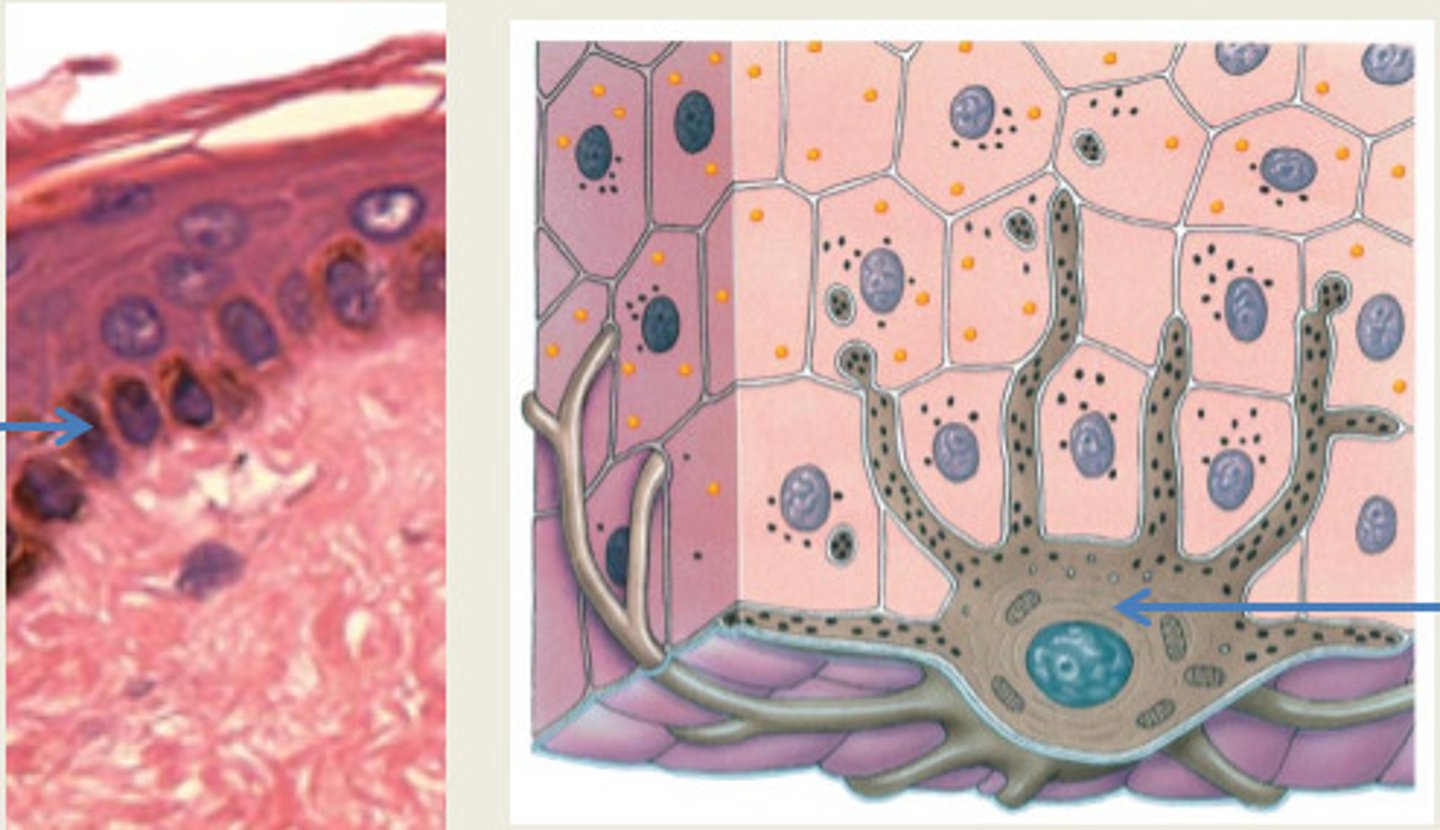
Melanocytes produces
melanin
Melanocytes location
stratum basale
Melanosomes
Pigment carrying granules
Dendritic Cells
star-shaped
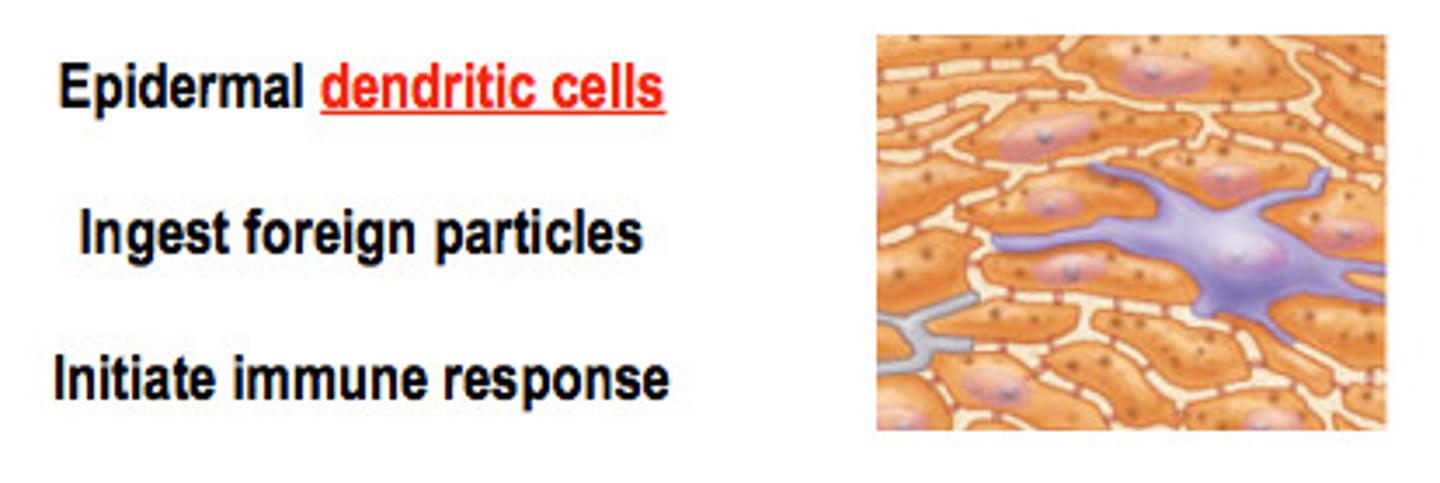
Dendritic Cells function
macrophages that patrol deep epidermis (activates immune system)
Dendritic Cells location
stratum spinosum and stratum granulosum
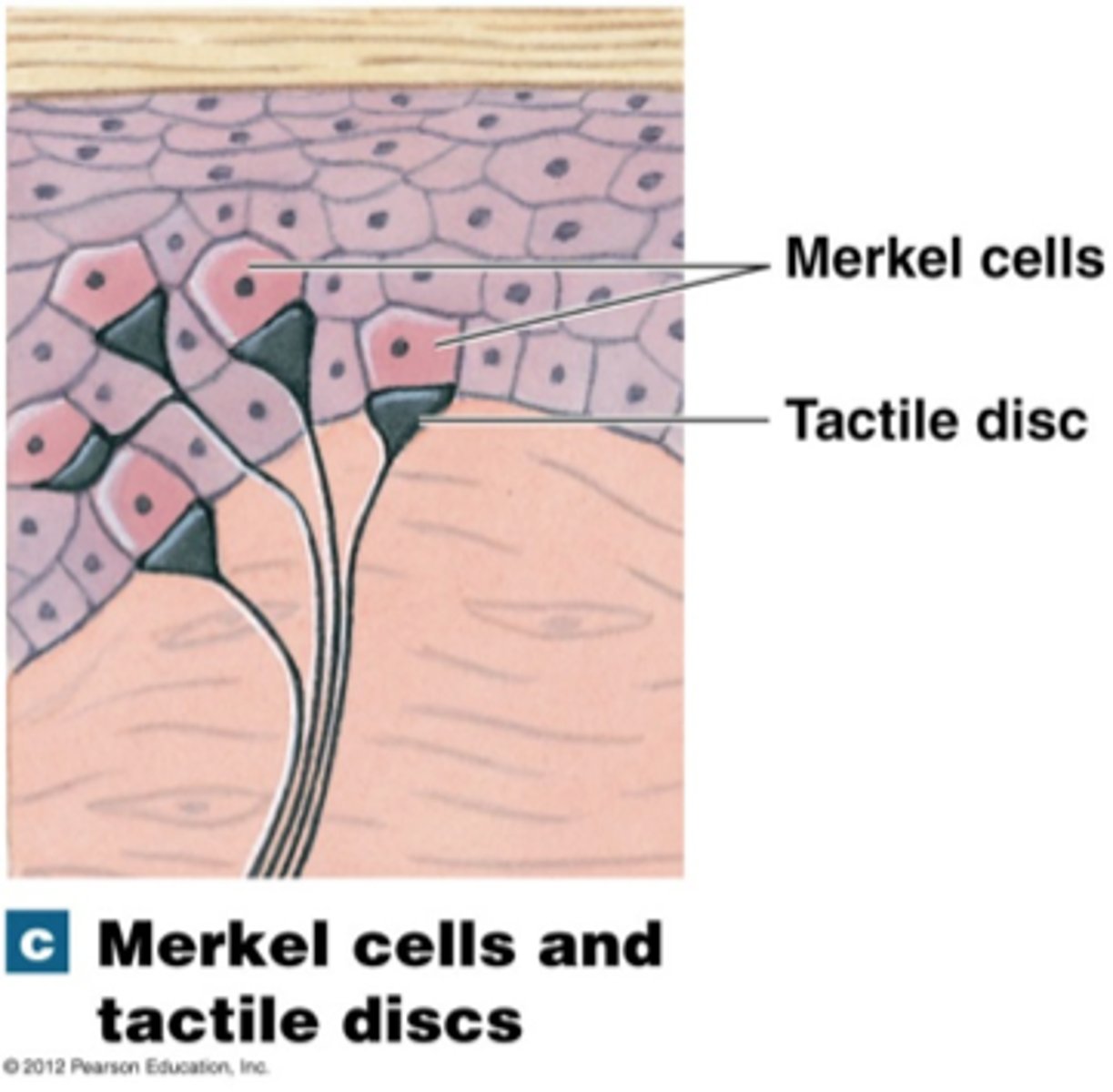
Tactile Cells function
sensory detection
tactile cells location
stratum basale
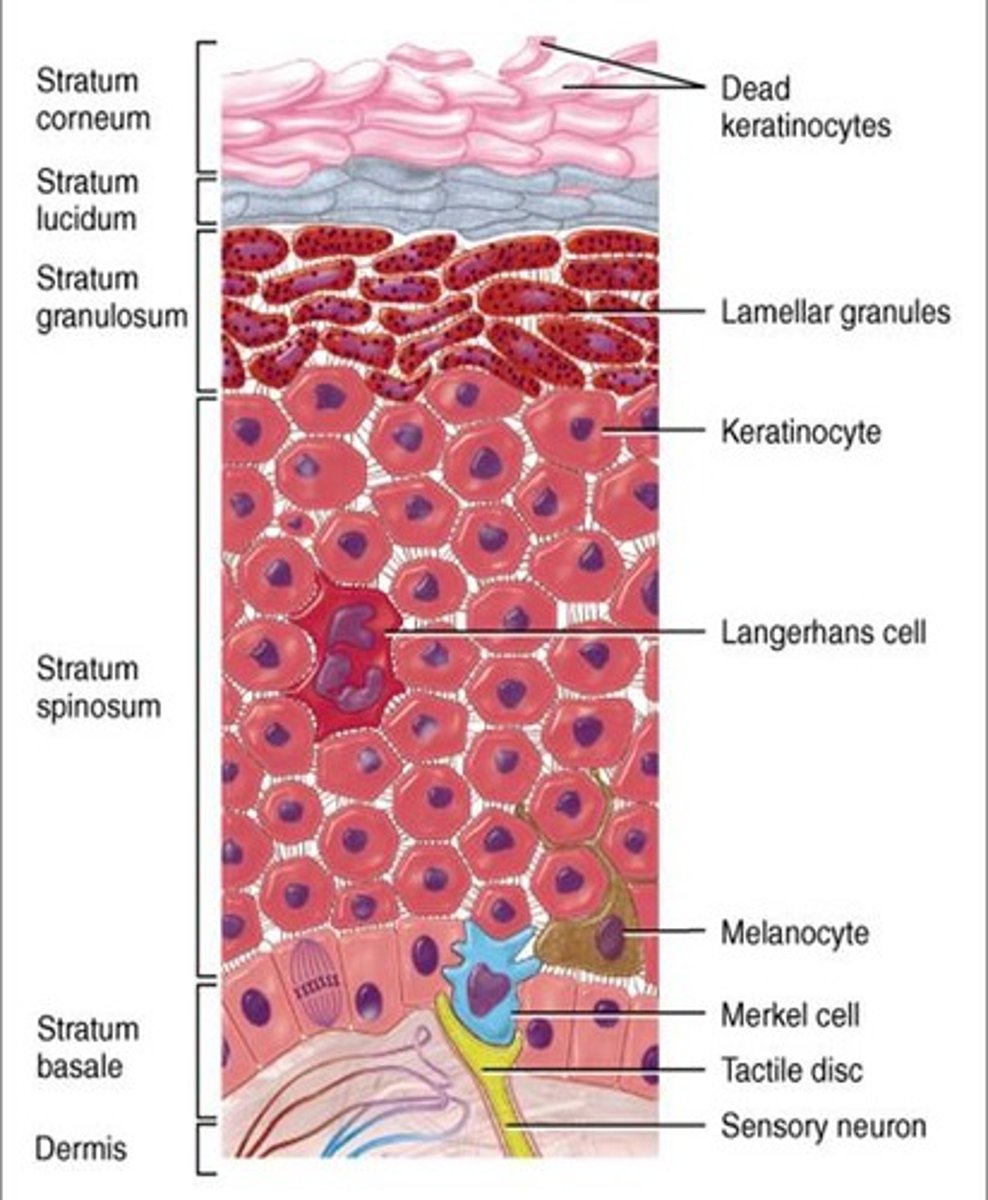
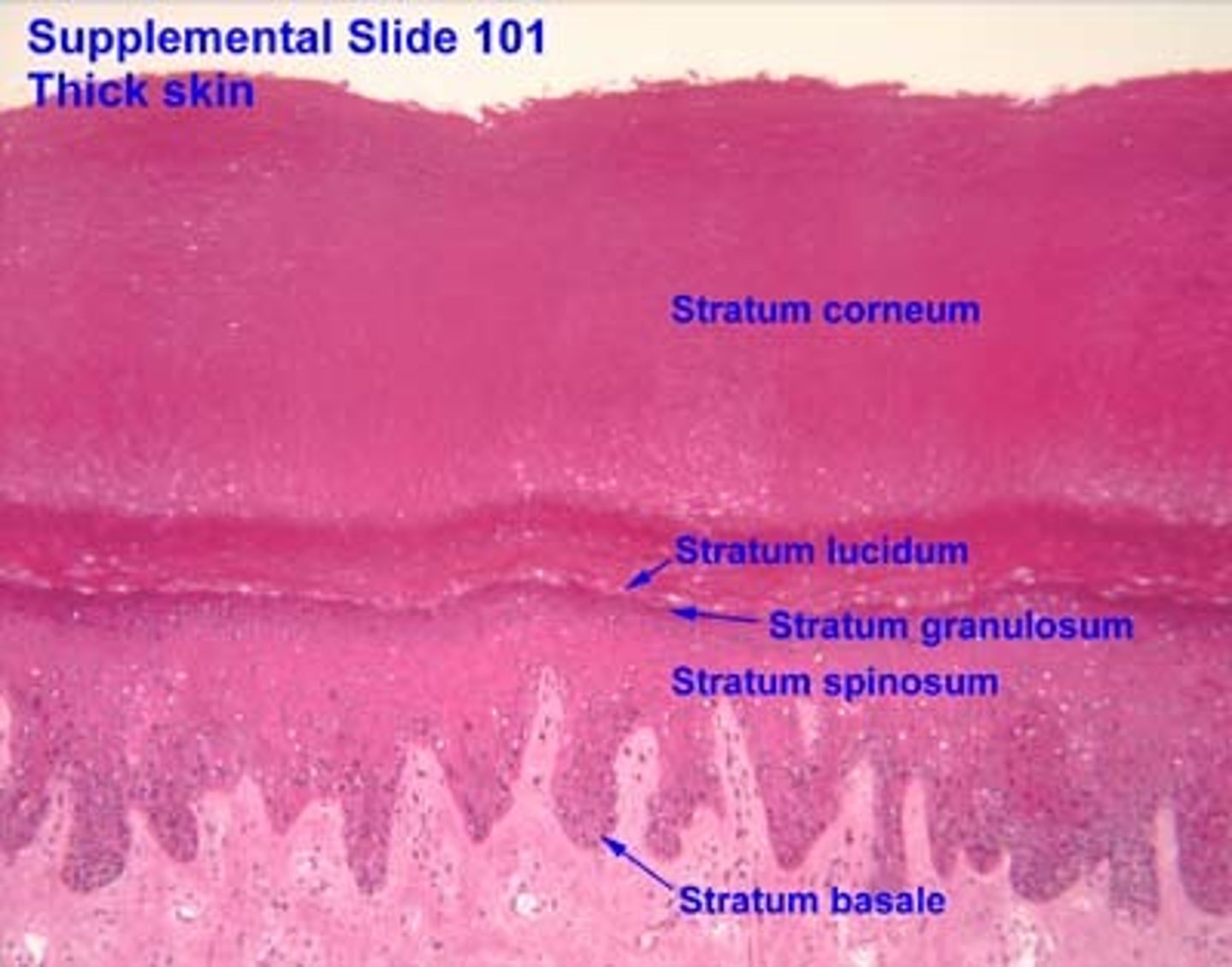
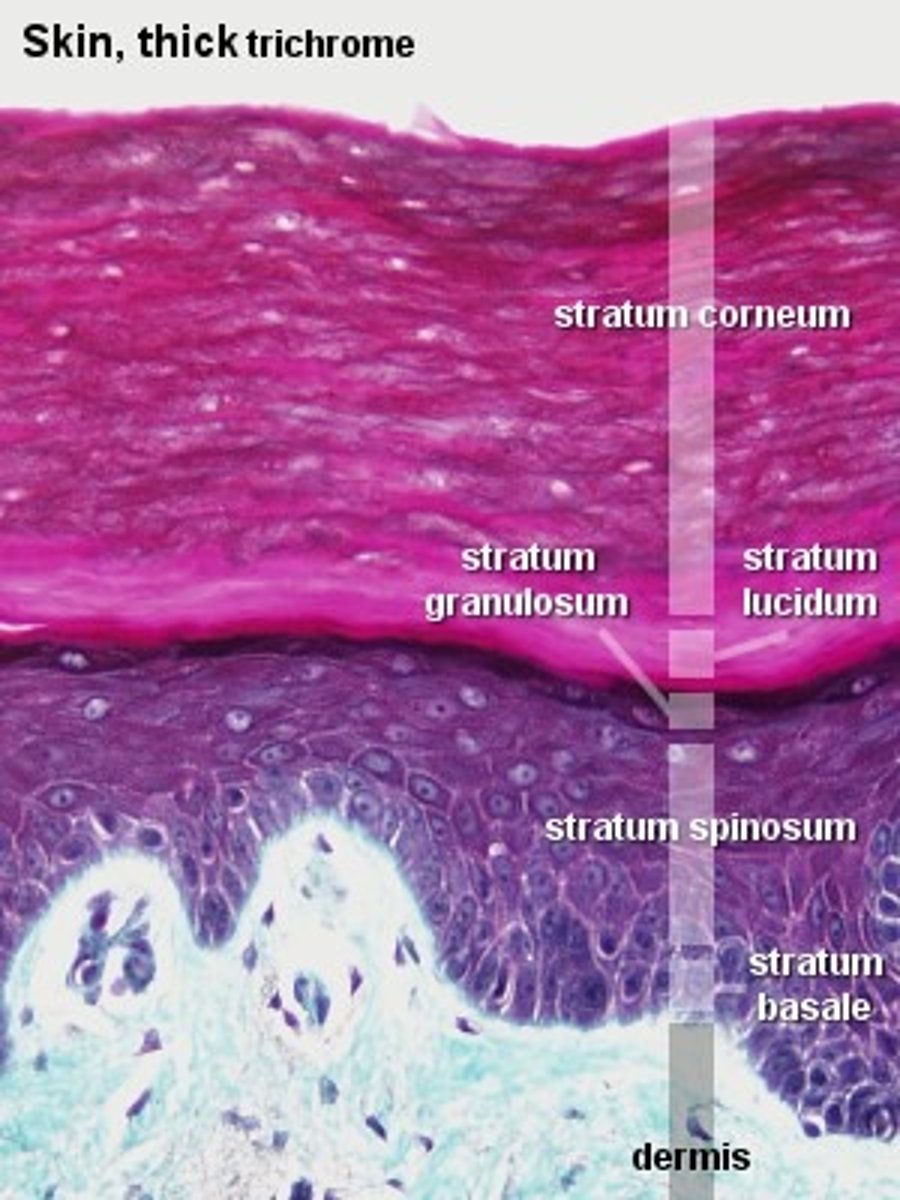
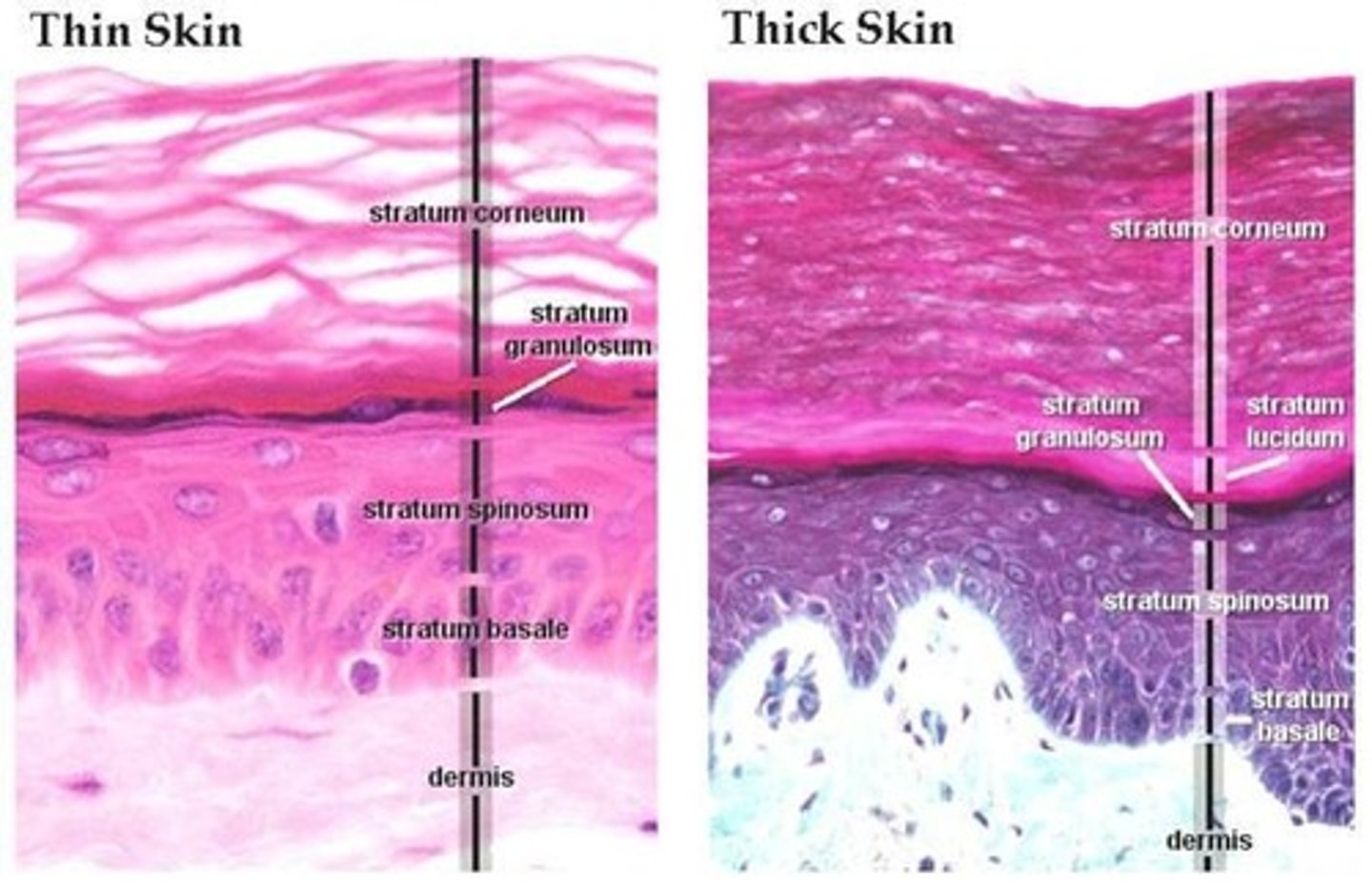
Layers of the epidermis
stratum basale, stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum, stratum lucidum, stratum corneum
Epidermis Mnemonic
Can Lucy Give Some Blood
Stratum Basale
Deepest layer & single row of stem cells
Stratum Basale contains
Melanocytes and tactile cells
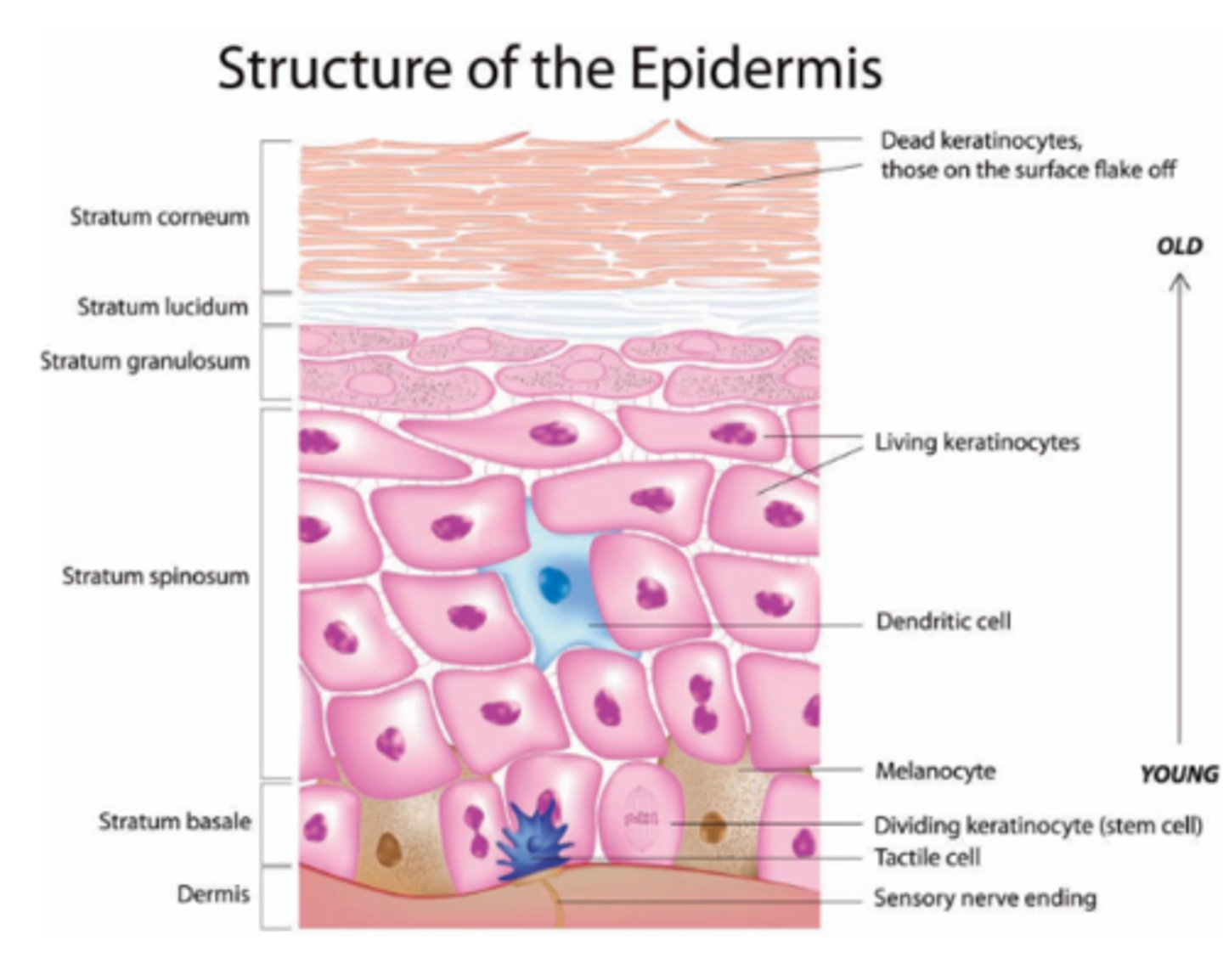
Stratum Spinosum
Several layers of prekeratin filaments
Strata Spinosum contains
dendritic cells and melanosomes
Stratum Grandulosum
Flatten cells w/ deteriorating organelles
keratohyaline granules
help to form keratin in the upper layers
Lamellar granules
creates hydrophobic layer
Stratum Lucidum
2 to 3 rows of clear, flat, dead keratinocytes

Strata Lucidum is only found in
thick skin
Thick Skin
Palms and Soles
Five layers of keratinocytes
Stratum Corneum
Outermost layer with 20-30 flat, anucleate, keratinized dead cells
Strata Corneum functions to
Protect deeper cells
Prevent water loss
Protect from abrasion and penetration
Biological, Chemical, Physical barrier
Keratinization
process in which the outermost cells of the epidermis are replaced by dead cells containing keratin
The Dermis is a
strong, flexible CT
Fibroblasts
cells that secrete the proteins of the fibers.
Macrophages
phagocytize foreign substances and help activate T cells
Mast Cells
Cells that release chemicals to promote inflammation.
Leukocytes
white blood cells
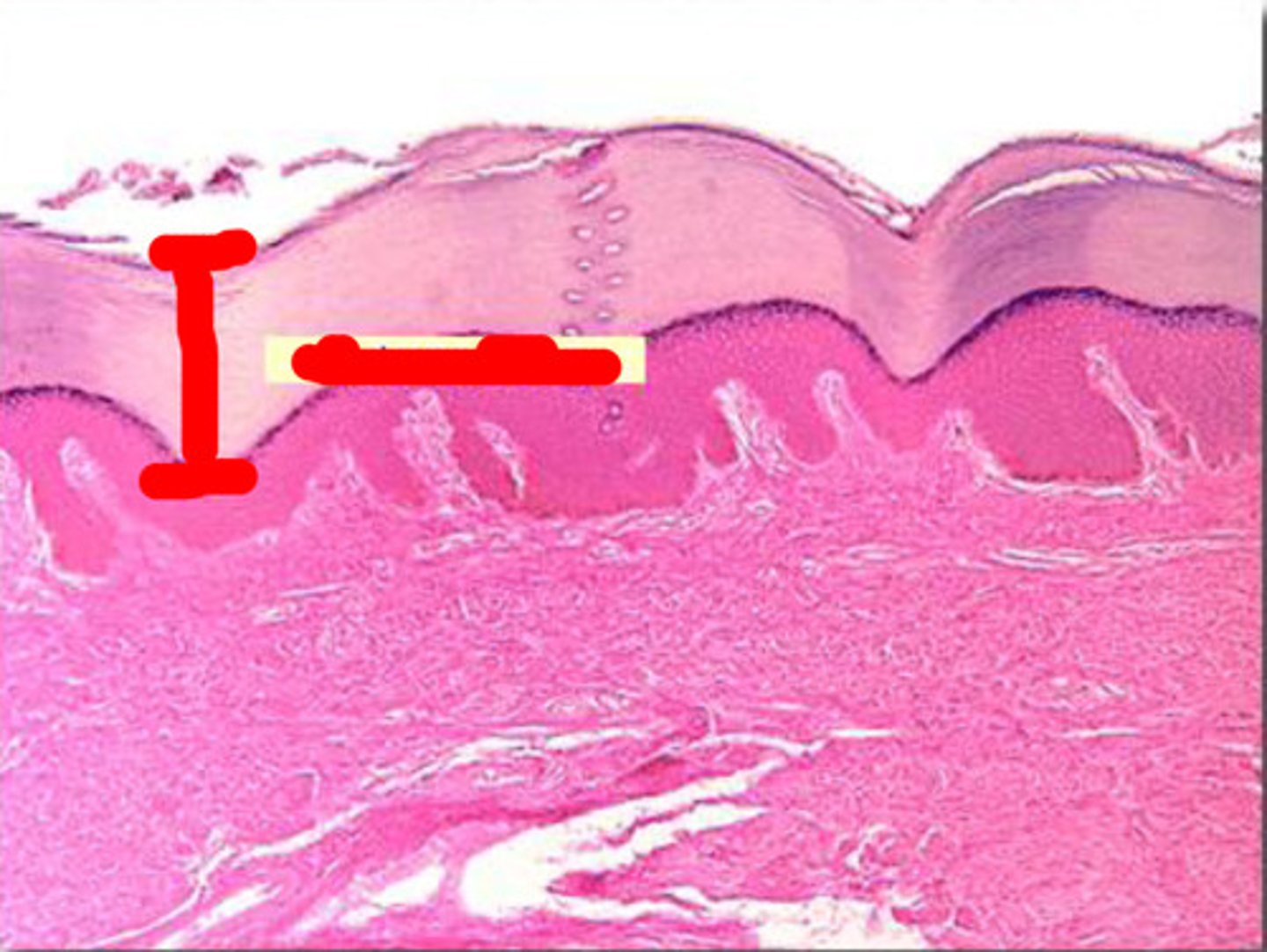
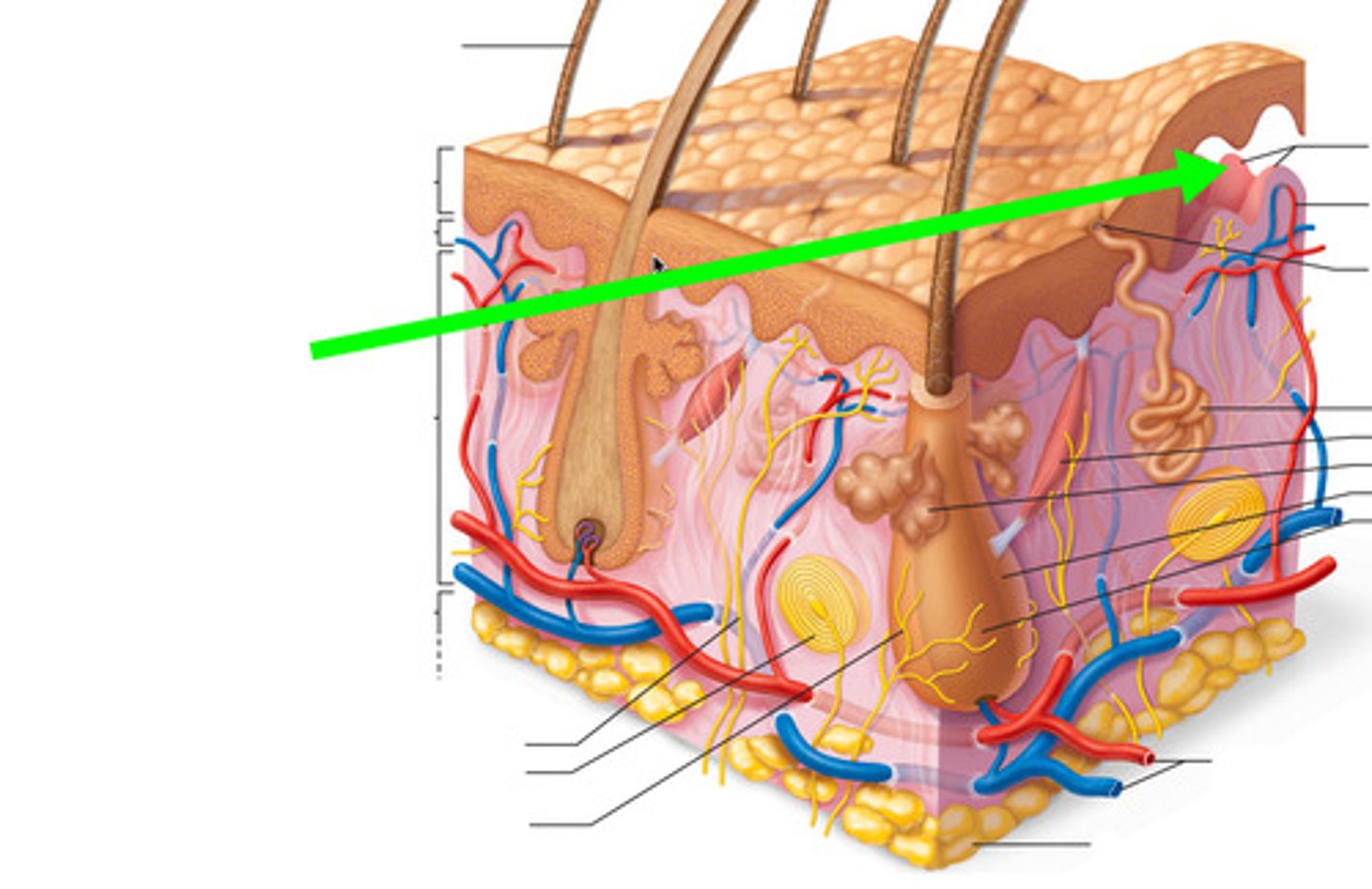
Papillary Layer
Outermost layer of the dermis, directly underneath the epidermis
Papillary Layer is made of
Areolar CT
Dermal Papillae
fingerlike projections
Dermal Papillae contains
Capillary loops
Meissner's corpuscles
Free nerve endings
Friction Ridges
epidermal ridges that lie on top of dermal ridges
Friction Ridges functions
enchance gripping, sense of touch, sweat pores create fingerprint pattern
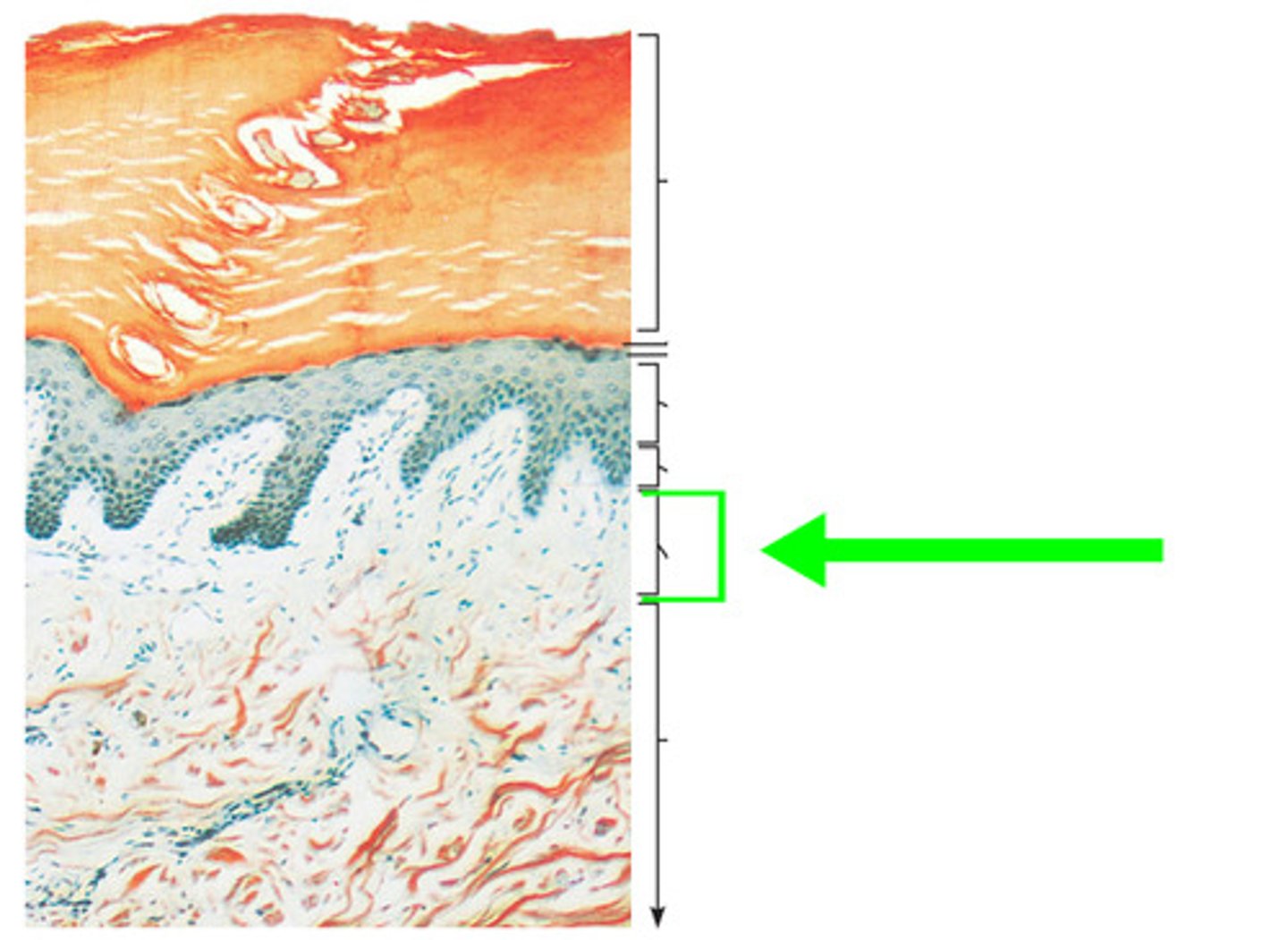
Reticular Layer
deepest skin layer
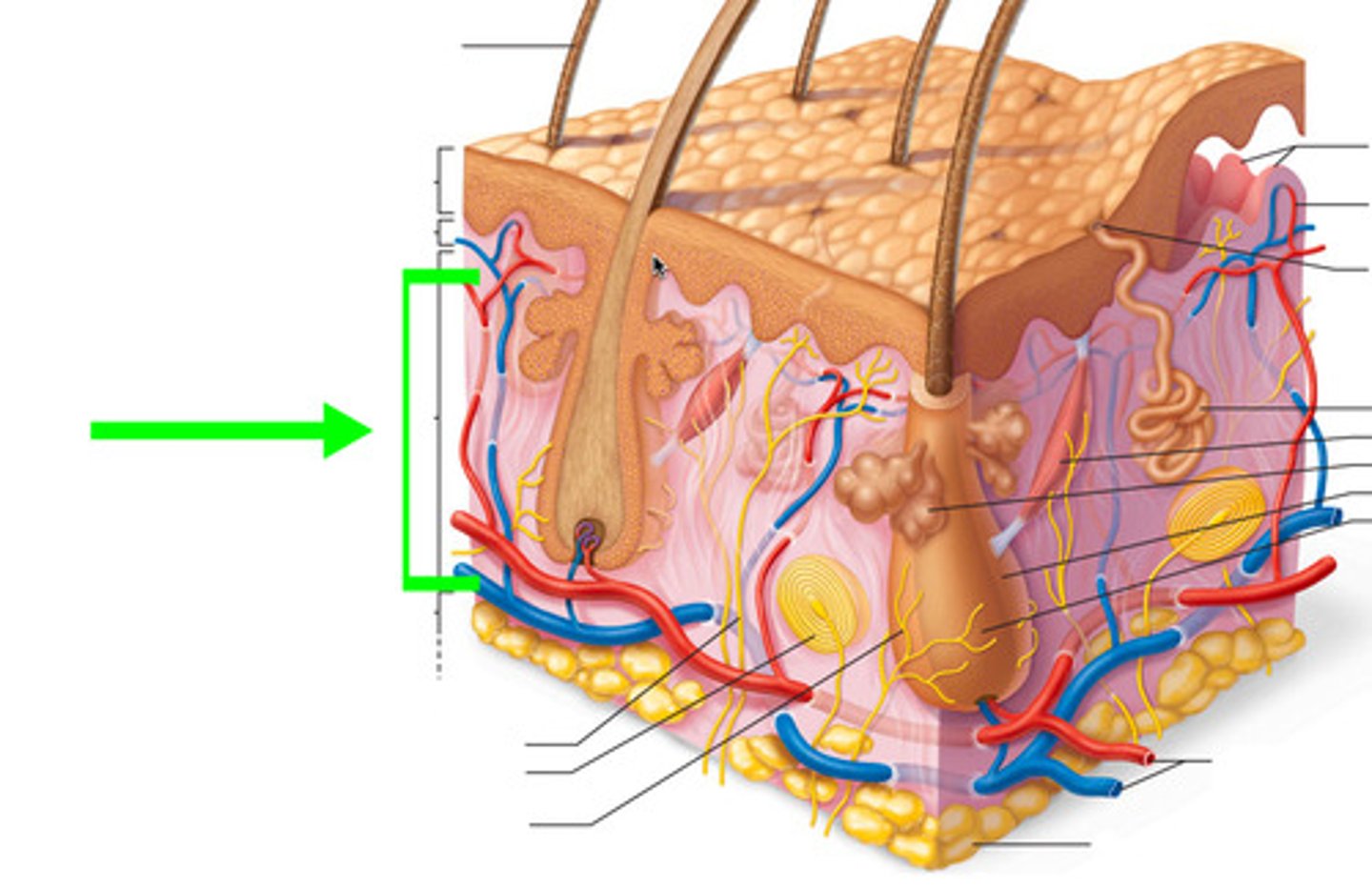
Reticular layer consists of
Dense irregular CT

Cutaneous Plexus
network of blood vessels between reticular layer and hypodermis
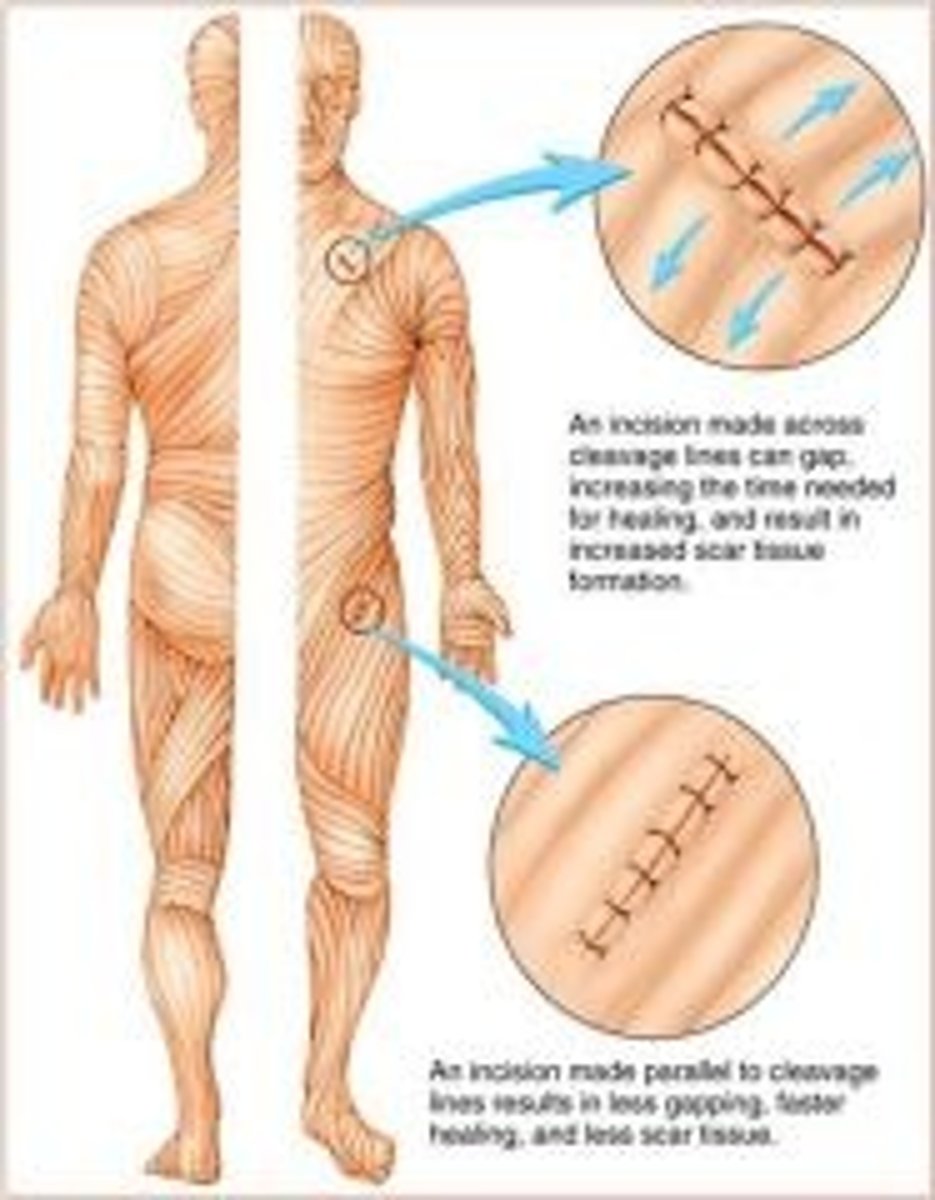
Cleavage (tension) lines
elastic and collagen fibers oriented in some directions more than in others
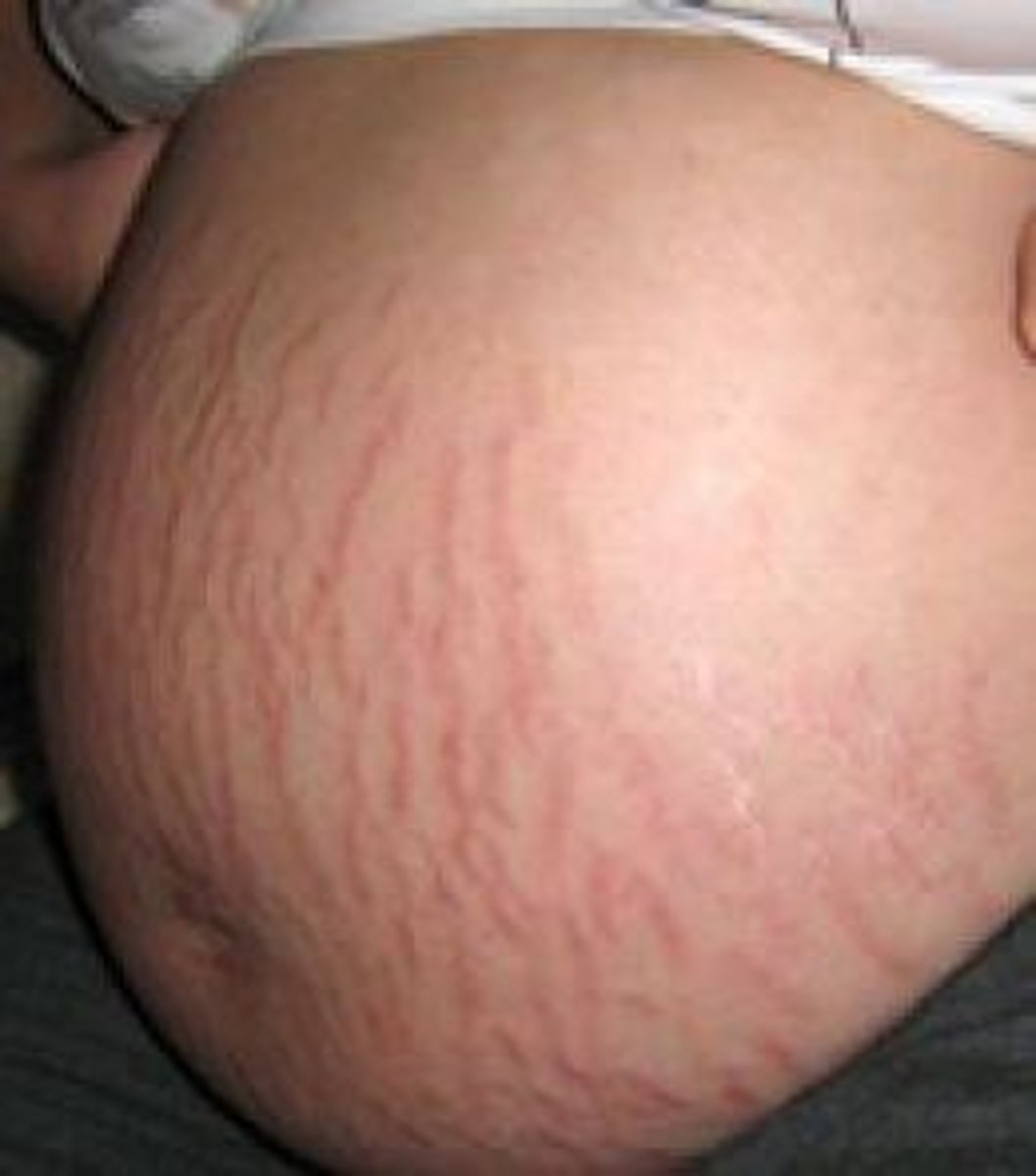
Striae
Stretch Marks
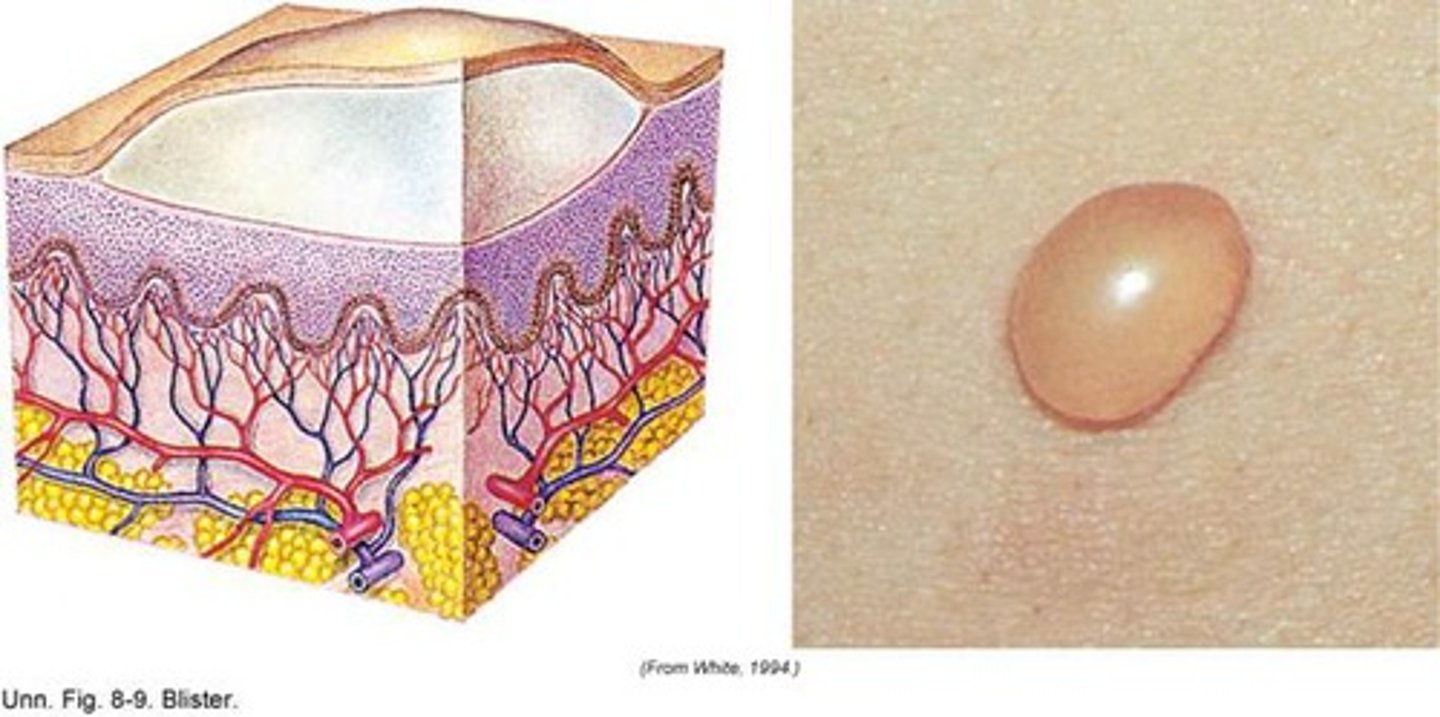
Blisters
acute, short-term trauma
fluid-filled pockets