Bio Exam Review
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
3UW terms + description + more
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Characteristics of Life
Nutrition, reproduction, respond to stimuli, growth and development, metabolism, excretion, evolution, made of cells, and homeostasis.
Homeostasis
Maintaining a stable internal environment
Metabolism
All biochemical reactions that occur in an organism
Chemical properties of water
Polar molecule, cohesion (molecules stick together), adhesion, high boiling point due to H-bonds, can become habitats because of H-bonds, universal solvent
Hydrophilic + examples
Any substance that water dissolves.
Examples: glucose in blood, oxygen in blood
Who proposed cell theory?
Schwann and Schleiden in 1838
6 Laws of Cell Theory
All living things are made of cells
Cells are the fundamental units of structure and function in living organisms
All cells come from pre-existing cells
Cells contain a blueprint for growth, development, and behaviour (DNA)
Energy flow occurs within cells
Site of chemical reactions
What are the exceptions to cell theory?
Where did the first cell come from?
Algae growing up to 100 mm in size but still only being one cell big
Aseptate fungi hyphae are long thin string like structures with multiple nuclei
Striated muscles in humans have multiple nuclei
Red blood cells do not have a nucleus
Xylem and Phloem don't have nuclei
What 5 features do all cells share?
Cell membrane
DNA
Enzymes to catalyze chemical reactions
Store energy in form of ATP
Carry out functions of Life
Why are cells good building blocks?
Limited by surface to volume ratio
Rate of exchange is affected if cell gets too big
Cell may overheat if cell is too small as metabolism is too fast
Properties of unicellular organisms?
Face environment on all sides
Damage to cell could mean death
Good ability to regenerate
Lower levels of efficiency
Emergent properties of multicellular organisms?
High operational efficiency
Different cells perform different functions
Only outer cells are specialized to face outside environment
In case of injury and death of cells, it can be replaced
Differentiation
Certain groups of cells perform specific functions while other groups perform other functions. It involves the expression of some genes and not others.
Advantage of differentiation
Allows for more cell efficiency
STEM cell definition
undifferentiated cells which are found in multicellular organisms and have the ability to divide and differentiate along different pathways
Types of STEM cells and definitions?
Totipotent - eight cells can become any cell or organism
Pluripotent - can become any type of body cell from the blastocysts
Multipotent - umbilical cord stem cells, can become any closely related cell (used in spinal injuries and bone fractures)
Unipotent - cells that can become cells like themselves found from adult tissues (liver cells become liver cells, used in transplants)
Uses of STEM cells
Leukemia - bone marrow transplants, allowing tissues to produce healthy blood
Type 1 Diabetes - embryonic stem cells that tun into islet cells, producing insulin
Stargardt's Disease
Ethical Arguments
When STEM cells are harvested, the embryo dies
Cells harvested from umbilical cord have limited capacity to differentiate
Adult STEM cells are difficult to obtain and limited potential
List 5 characteristics of Light Microscopes
natural colour
large field of view
cheap and easy preparation
view live, moving, and dead
view whole
mag up to 2000x
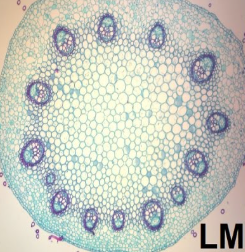
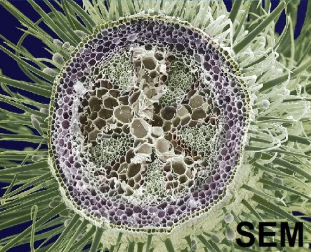
List 5 characteristics of Scanning Electron Microscopes
View in black and white
limited FOV
must be places in a vavuum
view surface only of organism
mag up to 500,000x
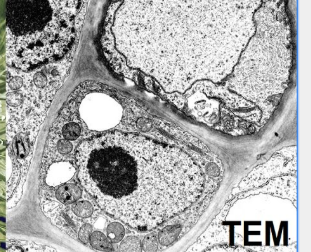
List 5 characteristics of Transmission Electron Microscopes
view in black and white
limited FOV
difficult and expensive preparation
view dead or frozen objects
magup to 1 million
view a thin section of sample
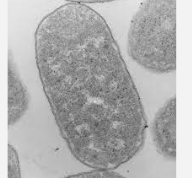
Which is type of microscope is this? (E.coli under microscope)
Transmission Electron Microscope

Which is type of microscope is this? (E.coli under microscope)
Scanning Electron Microscope
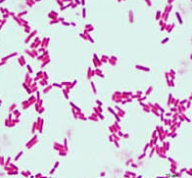
Which is type of microscope is this? (E.coli under microscope)
Light Microscope
Characteristics of prokaryotes + example(s)
unicellular
small
simple structure
found everywhere on earth
ex: bacteria and archaea
DNA in prokaryotes
lack nucelus
found in a circle (nucleoid region)
some DNA found in forms of plasmids
What are plasmids?
They are small pieces of DNA that replicate independently of the DNA nucleoid. They often contain the genes for antibiotic resistance.
Cell Wall characteristics in prokaryotes
some made of peptidoglycan (sugar and protein)
Many have glycocalyx - sticky layer made of sugar and amino acids which form protective layer around the bacteria
Parts of prokaryote
DNA
Cell well
Plasma membrane - phospholipid bilayer that controls movement in and out the cell
Cytoplasm
Ribosomes - free floating in cytoplasm, site of protein production
Fimbriae - short protein tubules for attachment
Plli - longer protein tubules used for attachment and transfer of DNA
Some have flagella - allow bacteria to move
How do prokaryotes reproduce?
binary fission - the DNA replicates and the cell divides forming two cells with identical DNA (mitosis)
transduction - virus
conjugation - transferred
transformation - cytoplasm
Characteristics of eukaryotes
larger than prokaryotes
contain nucleus and nucleolus
plasma membrane and phospholipid bilayer
multiple strands of DNA
cytoplasm
cytoskeleton
contains many membrane bound organelles - mitochondria, smooth and rough er, lysosomes, vacuoles, chloroplasts
What is compartmentalization?
The organization of eukaryotic cells into various organelles that perform specific functions
What are the advantages of compartmentalization?
allows for unique processes to occur without interference
chemicals can be more concentrated, like enzymes
cells are much more efficient
larger area for process to occur
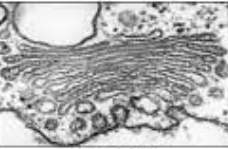
What organelle is this?
Golgi apparatus

What organelle is this?
Chloroplast

What organelle is this?
Endoplasmic reticulum
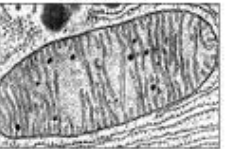
What organelle is this?
Mitochondria
What are phospholipid molecules made of?
Hydrophilic phosphate head with glycerol (water loving)
Hydrophobic lipid tails (water hating), tails are attracted to one another
Amphipathic - parts of same molecule are attracted to water and other parts are not
Characteristics of plasma membranes
semi fluid
moves laterally (floating)
can flip-flop
semi-permeable
viscosity of vegetable oil at room temp
contains proteins and cholesterol
water, oxyge, and carbon dioxide diffuse across membrane
impermeable to most ions
impermeable to most water soluble molecules
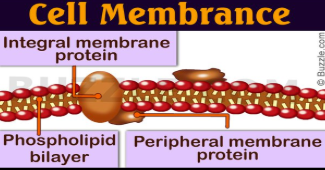
What are the types of membrane proteins?
Integral proteins
Peripheral proteins
Cholesterol
Glycolipids
Lipid-anchored protei
Characteristics of integral proteins
embedded in bilayer
cannot be released
hydrophobic on part of the surface
many are trans-membrane (transmembrane proteins)
some are partially embedded
Types of integral proteins
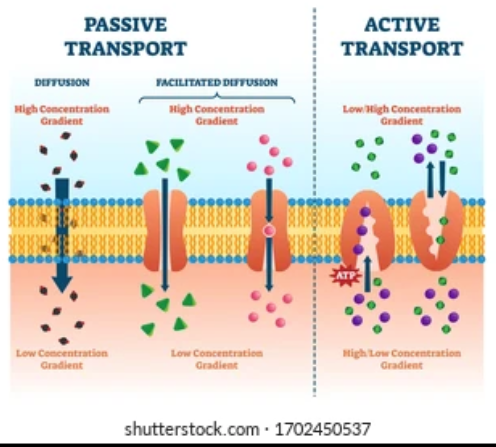
Channel proteins - for passive transport. This allows hydrophilic substances through by facilitated diffusion
Protein pumps - active transport. These proteins us ATP to move particles against the concentration gradients
Carrier proteins - They change shape to move ions with the concentration gradient
Receptor proteins - Bind extracellular substances like enzymes or hormones that trigger cell activity to change. More than one protein can work together to make a metabolic pathway.
Adhesion proteins - help cells of the same type to stick together and form tissues
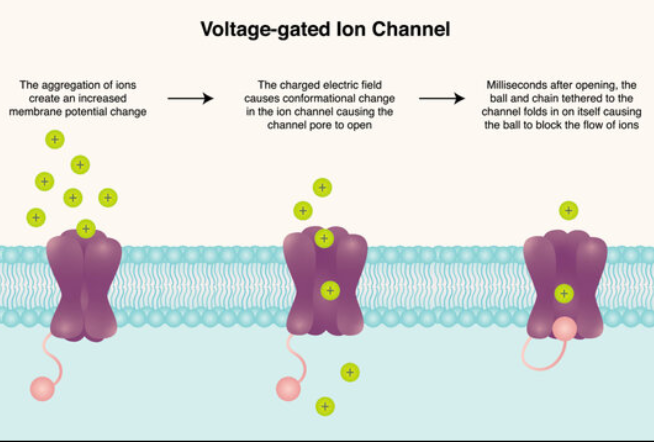
Voltage-gated ion channel
passive vs active transport
Characteristics of peripheral proteins
proteins that are attached to the inner or outer surface of membrane
they can be attached to proteins or lipids
they are hydrophilic
Types of peripheral proteins
Glycoproteins - act as communication and identification tags.
Support proteins - help hold the cytoskeleton in place and provide structural support for the cell
Adhesion proteins - help cells of same type to stick together and form tissues
Six major functions of membrane proteins
Transport channels
Receptors (hormones)
Anchorage
Enzymetic activity
Signal induction
Cell recognition
Inter cellular connection
attachment to cytoskeleton and extracellular matric
Characteristics of cholesterol
steroid
mainly hydrophobic
amounts vary cell to cell
Function of cholesterol
increase fluidity at low temp
reduces fluidity at high temps
holds phospholipids together
prevents crystallization
reduces permeability to Na and H
Assists in formation of vesicles during endocytosis
What are glycolipids and what do they do
molecules which are carbohydrates linked to lipids
help the immune system to distinguish between self and non self
glycoproteins form the glycocalyx