Toxic Release and Dispersion
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Toxic release models
These are used to estimate the effects of a release on the plant and community environments.
Dispersion models
These describe the airborne transport of toxic materials away from the accident site and into the plant and community.
Plume, puff
After a release, the airborne toxic material is carried away by the wind in a characteristic ___ or a ___.
At the release point
Where does the maximum concentration of toxic material occur?
True
TRUE OR FALSE. Concentrations downwind are less, because of turbulent mixing and dispersion of the toxic substance with air.
To provide a tool for performing release mitigation
What is the purpose of a toxic release model?
Wind speed
Atmospheric stability
Ground conditions (buildings, water, trees)
Height of the release above ground level
Momentum and buoyancy of the initial material released
Enumerate the five (5) parameters affecting atmospheric dispersion of toxic materials.
Neutrally buoyant dispersion models
These are used to estimate the concentrations downwind of a release in which the gas is mixed with fresh air to the point that the resulting mixture is neutrally buoyant.
Neutrally buoyant dispersion models
These models apply to gases at low concentrations, typically in the parts per million range.
Plume models
Puff models
Enumerate the two (2) types of neutrally buoyant vapor cloud dispersion models.
Plume model
TYPES OF NEUTRALLY BUOYANT VAPOR CLOUD DISPERSION MODELS. Determine what is being asked below.
It describes the steady-state concentration of material released from a continuous source.
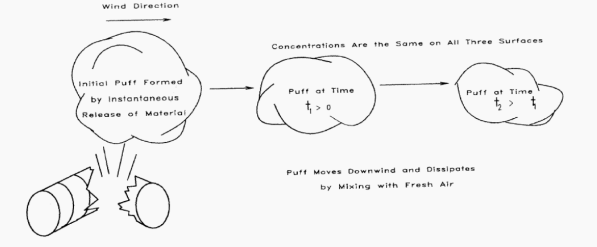
Puff model
TYPES OF NEUTRALLY BUOYANT VAPOR CLOUD DISPERSION MODELS. Determine what is being asked below.
It describes the temporal concentration of material from a single release of a fixed amount of material.
Puff model
TYPES OF NEUTRALLY BUOYANT VAPOR CLOUD DISPERSION MODELS. Determine what is being asked below.
This model is used when you have essentially an instantaneous release and the cloud is swept downwind.
Plume
TYPES OF NEUTRALLY BUOYANT VAPOR CLOUD DISPERSION MODELS. Determine what is being asked below.
It is the release of continuous puffs.
True
TYPES OF NEUTRALLY BUOYANT VAPOR CLOUD DISPERSION MODELS. Determine what is being asked below.
TRUE OR FALSE. Puff model can be used to describe a plume.
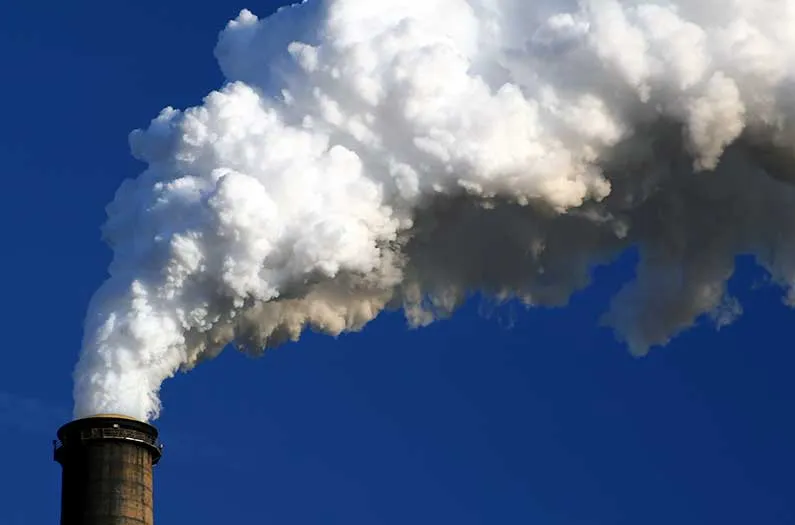

Plume model
(ADDITIONAL: A smokestack looks like this.)
TYPES OF NEUTRALLY BUOYANT VAPOR CLOUD DISPERSION MODELS. Determine what is being asked below.
The model was originally developed for dispersion from a smokestack.
True
TRUE OR FALSE. A plume can develop if there is a leak in a large tank.

FAMILIARIZE (Plume model).
FAMILIARIZE (Plume model).

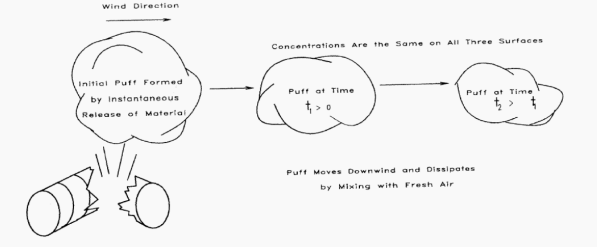
FAMILIARIZE (Puff model).
FAMILIARIZE (Puff model).
Pasquill-Gifford or Gaussian Dispersion models
This model assumes that the materials spread out in a normal Gaussian-type distribution.
Pasquill-Gifford or Gaussian Dispersion models
This dispersion model applies only to neutrally buoyant dispersion of gases in which the turbulent mixing is the dominant feature of the dispersion.
0.1 to 1 km
Pasquill-Gifford or Gaussian Dispersion models are typically valid only for a distance of ___ to ___ km from the release point.
Dense gas dispersion (Britter and McQuaid Model)
This model is best suited for instantaneous or continuous ground-level releases of dense gases where the release is assumed to occur at ambient temperature and without aerosol or liquid droplet formation.
Dense gas
It is defined as any gas whose density is greater than the density of the ambient air through which it is being dispersed.
Initial cloud volume
Initial plume volume flux
Duration of release
Initial gas density
Wind speed at the height of 10 m
Distance downwind
Ambient gas density
Britter and McQuaid model requires (7):
Dense gas
This result can be due to a gas with a molecular weight greater than that of air or a gas with low temperature resulting from auto refrigeration during release or other processes.
Release mitigation
It is defined as “lessening the risk of a release incident by acting on the source (at the point of release) either (1) in a preventive way by reducing the likelihood of an event that could generate a hazardous vapor cloud or (2) in a protective way by reducing the magnitude of the release and/or the exposure of local persons or property".”
Inherent safety
Engineering design
Management
Early vapor detection
Countermeasures
Emergency response
Release mitigation can be divided into six (6) aspects:
READ.
Under inherent safety,
Inventory reduction
Chemical substitution
Process attenuation
READ.
Under inherent safety,
Inventory reduction
Chemical substitution
Process attenuation
READ.
Under engineering design,
Physical integrity of seals and construction
Process integrity
Emergency control
Spill containment
READ.
Under engineering design,
Physical integrity of seals and construction
Process integrity
Emergency control
Spill containment
READ.
Under management,
Policies and procedures
Training for vapor release
Audits and inspections
Equipment testing
Routine maintenance
Management of change
Security
READ.
Under management,
Policies and procedures
Training for vapor release
Audits and inspections
Equipment testing
Routine maintenance
Management of change
Security
READ.
Under early vapor detection,
Sensors
Personnel
READ.
Under early vapor detection,
Sensors
Personnel
READ.
Under countermeasures,
Water sprays and curtains
Steam or air curtains
Deliberate ignition
Foams
READ.
Under countermeasures,
Water sprays and curtains
Steam or air curtains
Deliberate ignition
Foams
READ.
Under emergency response,
On-site communications
Emergency shutdown
Site evacuation
Safe havens
PPE
Medical treatment
On-site emergency plans, procedures, training, and drills
READ.
Under emergency response,
On-site communications
Emergency shutdown
Site evacuation
Safe havens
PPE
Medical treatment
On-site emergency plans, procedures, training, and drills