Functions and Structures of Animal Skin
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Integumentary system
Includes skin, hair, nails, and glands.
Skin
Largest organ, 12% to 24% body weight.
Vitamin D production
Skin synthesizes vitamin D via sunlight.
Homeostasis
Maintains stable body conditions.
Barrier function
Protects from dehydration and harmful substances.
Protective function
Waterproof shield against UV and injuries.
Immune defense
Contains immune cells to fight infections.
Sensory function
Detects touch, pain, temperature, and pressure.
Exocrine function
Glands secrete sweat, sebum, and wax.
Epidermis
Outer skin layer, no blood vessels.
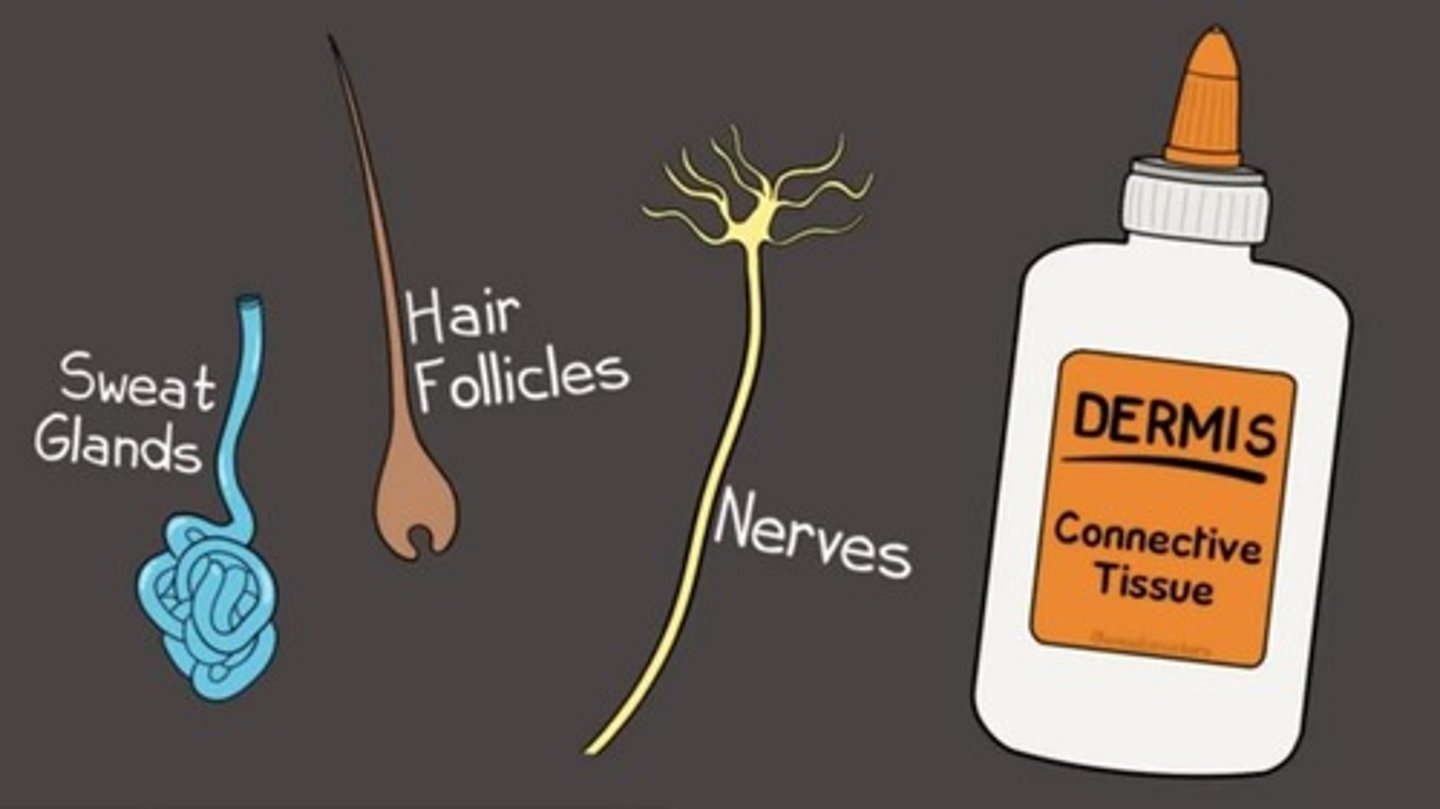
Dermis
Inner skin layer with connective tissue.
Subcutaneous tissue
Fat layer providing insulation and cushioning.
Stratum corneum
Outermost epidermis layer, dead keratinized cells.
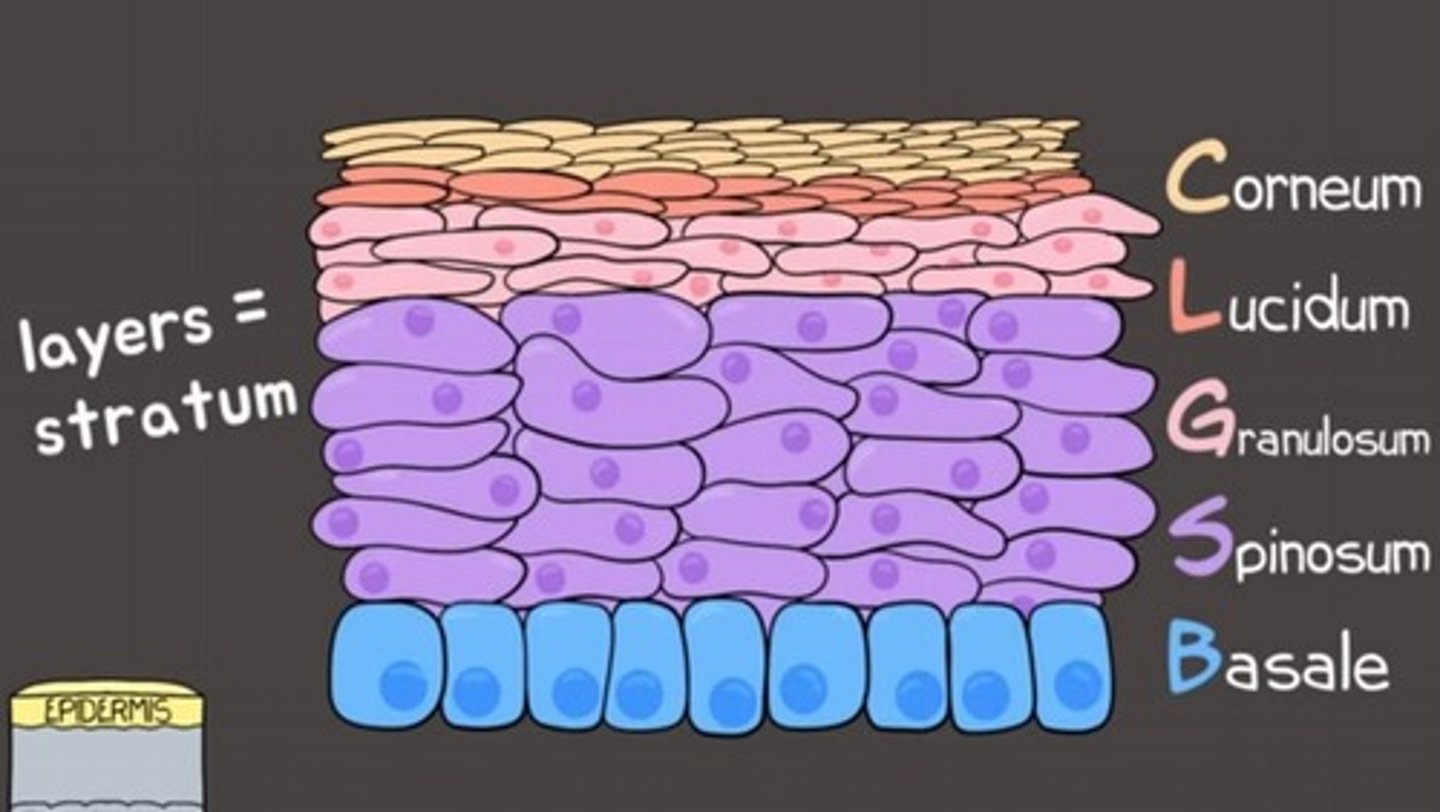
Stratum lucidum
Thin layer, found in thick skin areas.
Stratum granulosum
Contains keratin and waterproofing lipids.
Stratum spinosum
Upper dermis layer with visible tonofilaments.
Stratum basale
Deepest epidermis layer, mitotically active.
Hair
Keratin structure growing from hair follicles.
Sweat glands
Secrete water and salts for cooling.
Sebaceous glands
Produce sebum to lubricate skin and hair.
Ceruminous glands
Produce earwax to protect eardrum.
Mammary glands
Produce milk for newborn nutrition.
Preen gland
Secretes oil for feather waterproofing.
True horns
Permanent, keratin-covered bone structures.
Antlers
Branching bone structures, shed yearly.
Economic importance
Animal skins used for leather and products.
Rabbit fur
Used for coat linings and accessories.
Kangaroo hide
Commonly used for bullwhips.
Feathers
Used for insulation and ceremonial items.